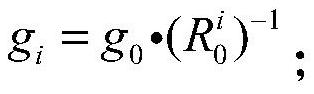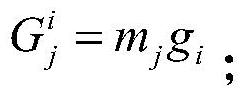Patents
Literature
376 results about "Orthopedics surgery" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Profession
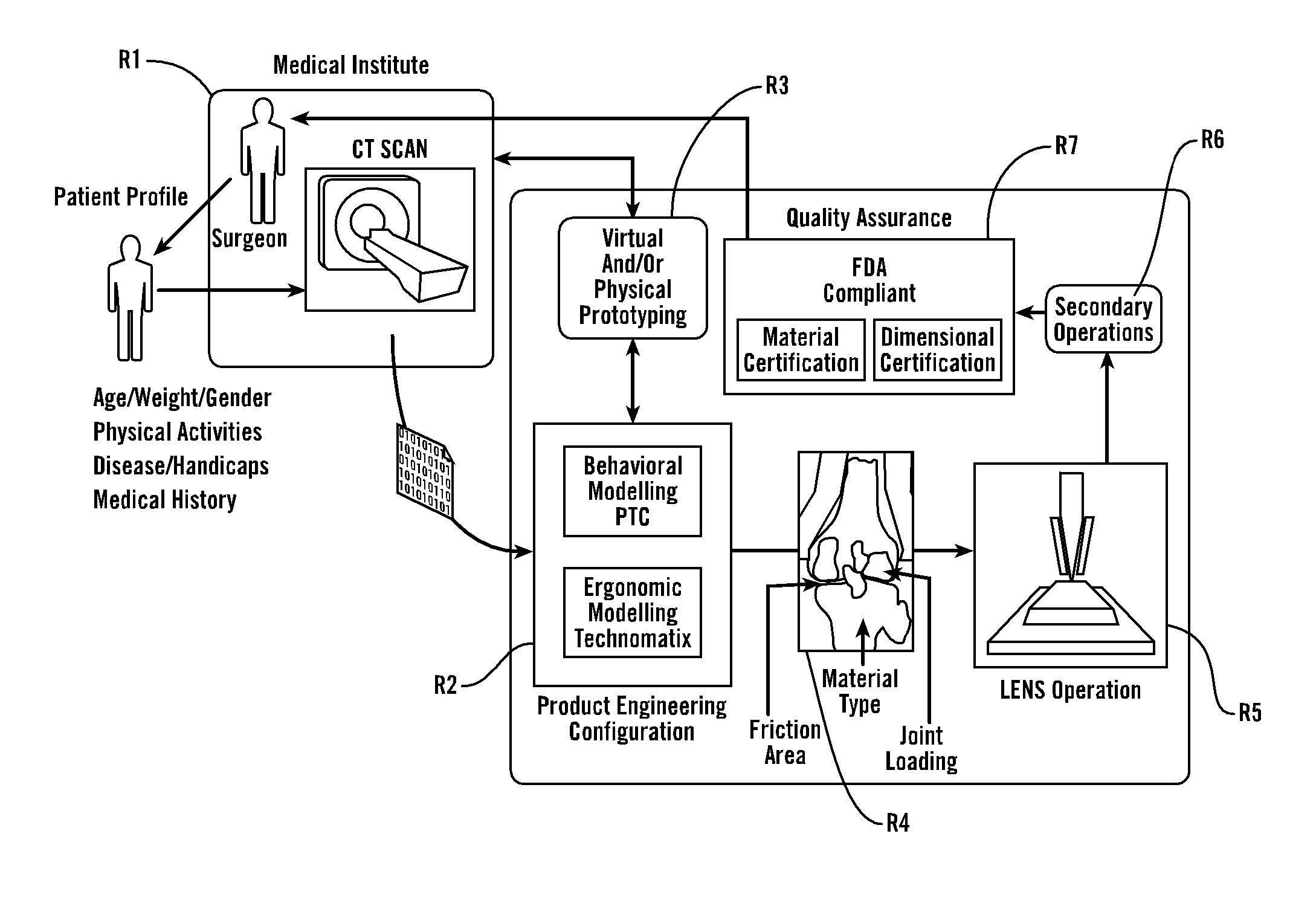
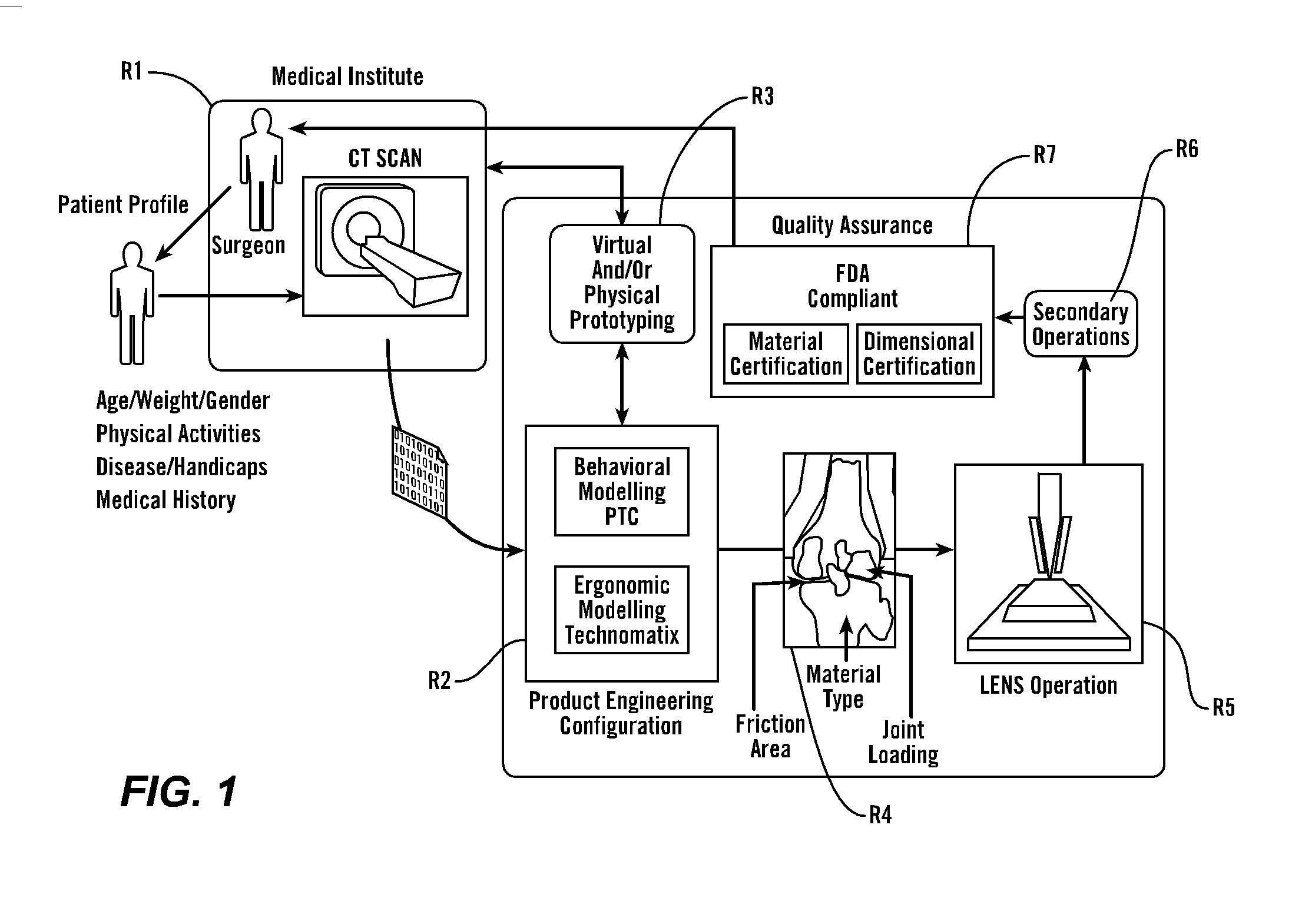
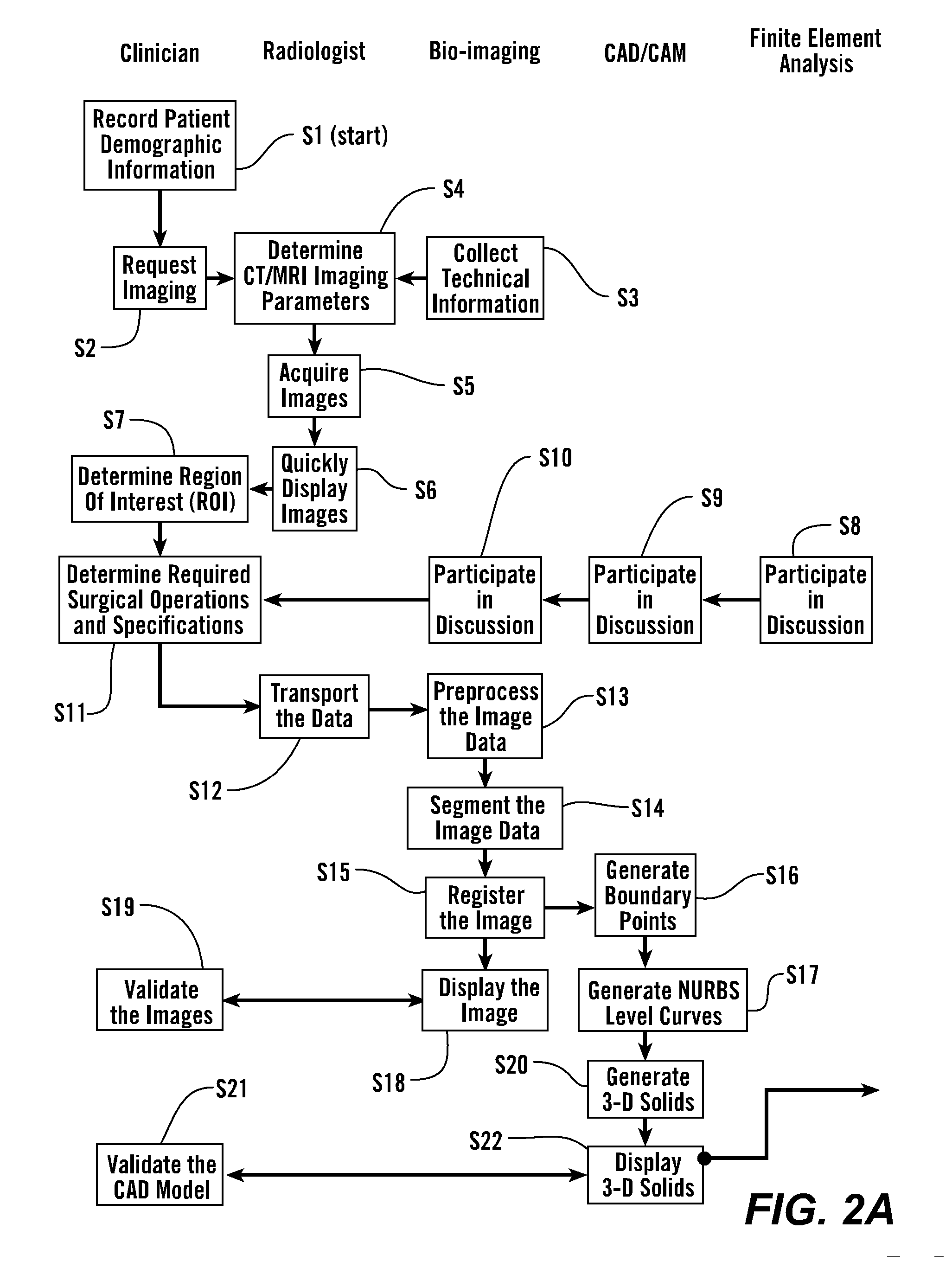
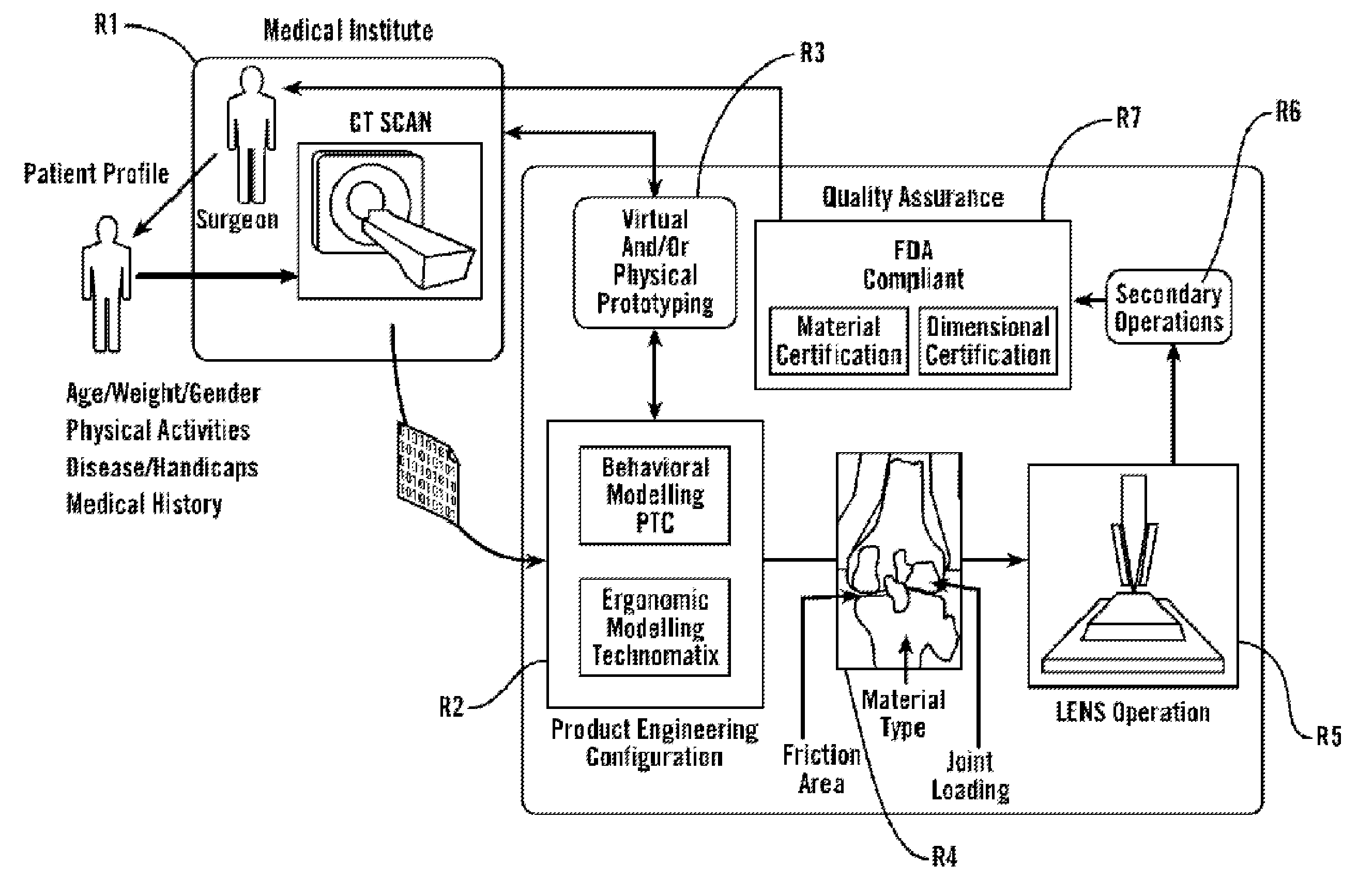
Personal fit medical implants and orthopedic surgical instruments and methods for making
InactiveUS20070118243A1Minimizing Ni toxicityImprove visualizationElectrotherapyMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesPersonalizationManufacturing technology
The present invention provides methods, techniques, materials and devices and uses thereof for custom-fitting biocompatible implants, prosthetics and interventional tools for use on medical and veterinary applications. The devices produced according to the invention are created using additive manufacturing techniques based on a computer generated model such that every prosthesis or interventional device is personalized for the user having the appropriate metallic alloy composition and virtual validation of functional design for each use.
Owner:VANTUS TECH CORP
Personal fit medical implants and orthopedic surgical instruments and methods for making
ActiveUS20100292963A1Avoids useSimple designMedical simulationAdditive manufacturing apparatusImage analysisMedical imaging
The present invention provides methods, devices, systems, and instruments related to medical implants and surgical instruments produced to precisely fit individual subjects. In particular, the present invention utilizes a combination of medical imaging, quantitative image analysis, CAD, CAM, and additive manufacturing processes to personalized biocompatible devices.
Owner:SCHROEDER JAMES
Novel bone surgery fixing system and method of use thereof and polyurethane applied therein
InactiveCN101279110ALearn about recoveryLow costSurgeryPlaster of paris bandagesPolyether polyurethaneMedicine
The invention provides a novel fixing system applied to orthopedic surgery. The novel fixing system comprises a cotton cavity with a dual-layer structure and an opening at one side and polymer foaming material; the polymer foaming material is filled in a sandwich layer of the cavity; the cotton cavity is provided with a zip or a nylon fastener belt to connect the cotton cavity; the cotton cavity closely covers and is attached to the part to be fixed. The invention also provides an application method of the system and polyether polyurethane used for the system.
Owner:上海优创医疗器械技术股份有限公司 +1
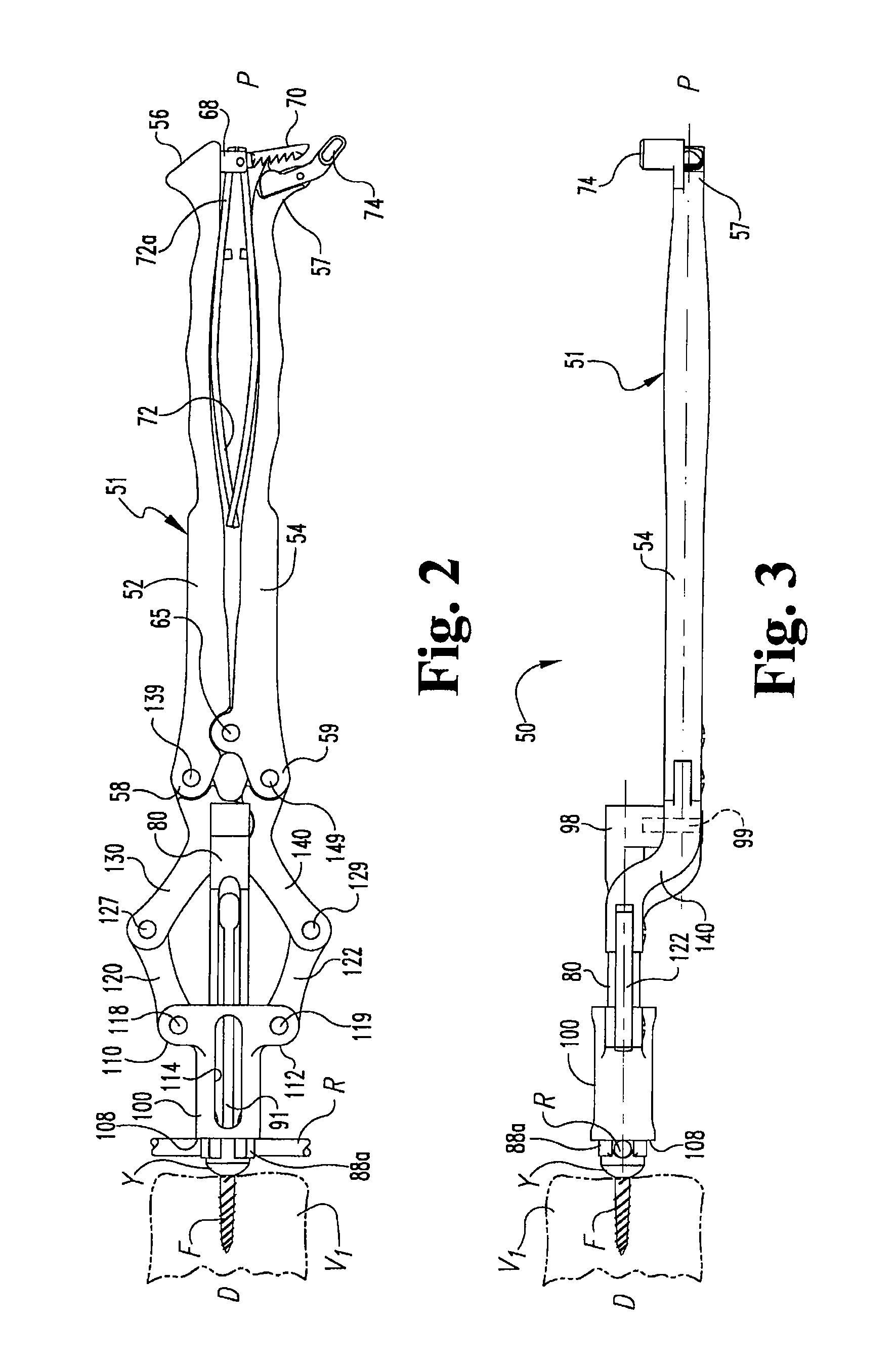
Rod reducer instruments and methods
InactiveUSRE44813E1Efficient and convenient to useGood adhesionInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsEngineeringReducer
Rod reducers for use in orthopedic surgery are disclosed that include a fastener engaging member and a reducing member coupled together by an actuator assembly. The fastener engaging member can be secured to a fastener engaged to bone or tissue of the patient. The actuator assembly moves the reducing member such that its distal end contacts a rod and moves it toward the fastener.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
Collagen/hydroxyapatite composite artificial bone and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN106620869AImprove toughnessNothing producedTissue regenerationProsthesisOrthopedics surgeryFreeze-drying
The invention relates to a collagen / hydroxyapatite composite artificial bone and a preparation method thereof. The artificial bone comprises type I collagen, hydroxyapatite and poly-p-dioxanone. The preparation method disclosed by the invention comprises the following steps: adding the type I collagen in a solvent to prepare a collagen solution, adding an appropriate amount of the hydroxyapatite and performing uniform stirring; placing the mixed slurry in a mold, performing pre-freezing, performing freeze-dried forming, and crushing the freeze-dried forming porous material to obtain blended powder; dissolving the poly-p-dioxanone in tetrafluoroacetic acid to prepare a solution, adding the blended powder in proportion, performing uniform stirring and performing cold press forming; and washing the formed pre-product with water, and drying the washed pre-product to obtain collagen / hydroxyapatite composite artificial bone. The preparation method disclosed by the invention is simple and low in the production cost. The collagen / hydroxyapatite composite artificial bone has compressive strength of 75-90MPa and favorable toughness, so that the collagen / hydroxyapatite composite artificial bone can meet requirements for bone filling and partial replacement in orthopedic surgery.
Owner:WUHAN YIJIABAO BIOMATERIAL CO LTD
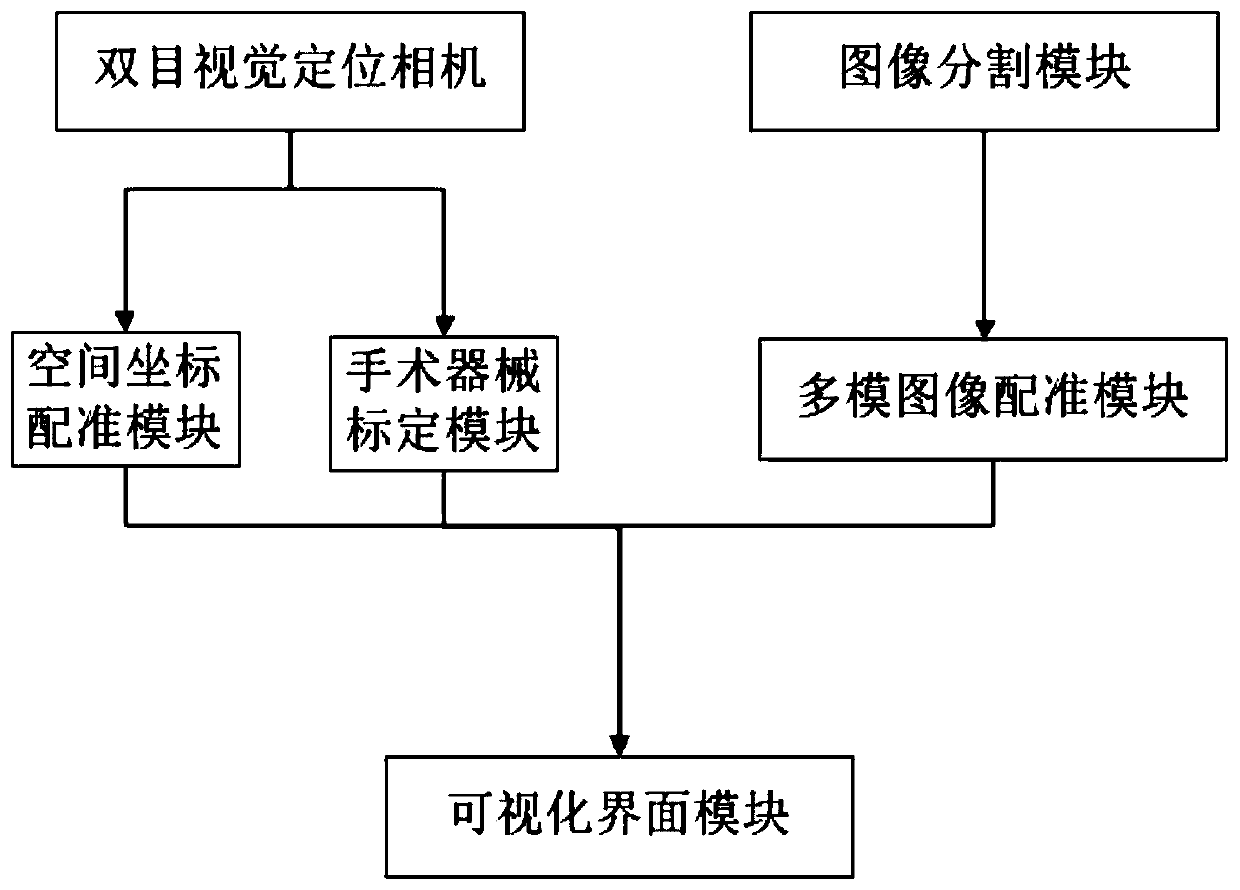
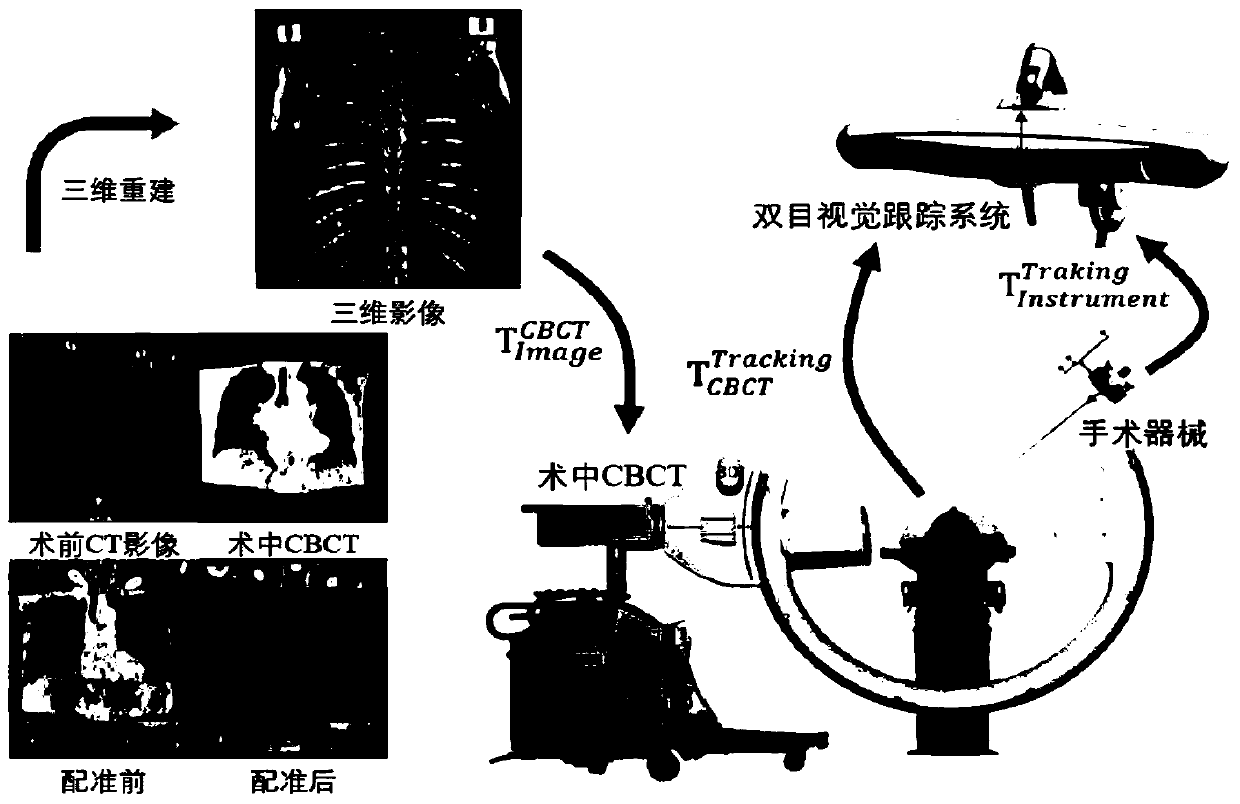
Orthopedic surgery navigation system based on multimode image fusion
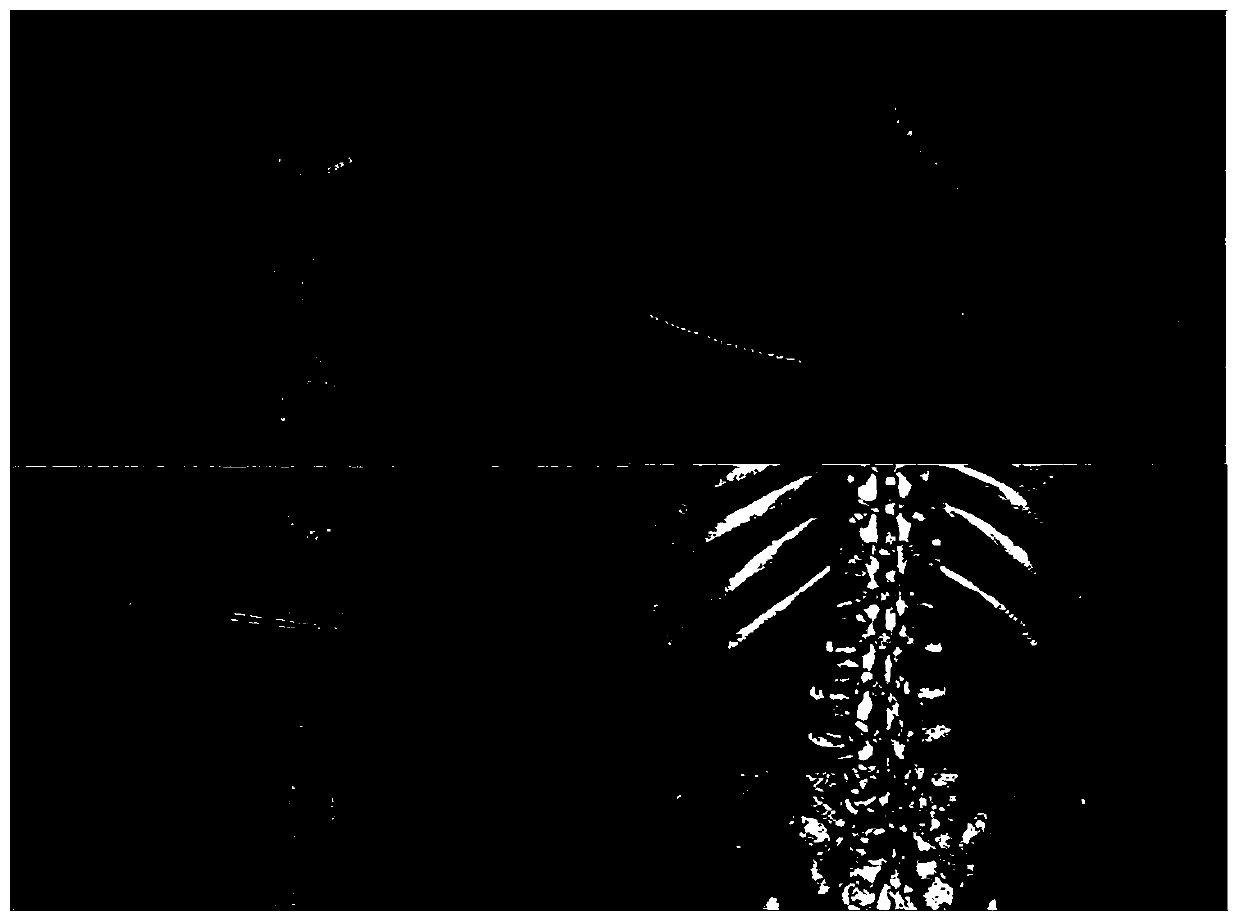
ActiveCN110946654AAccurate real-time locationPrecise and Reliable NavigationSurgical navigation systemsOrthopedics surgery3d image
The invention provides an orthopedic surgery navigation system based on multimode image fusion, which comprises a binocular vision positioning camera used for acquiring space coordinates of a passiveinfrared reflection marking ball placed on a surgical instrument and the skin surface of a subject in real time; an image segmentation module used for accurately segmenting a spine part in an initialimage; a space coordinate registration module used for registering the space coordinates and the image coordinates; a surgical instrument calibration module used for establishing a conversion relationship between surgical instrument tip coordinates and passive infrared reflection marking ball coordinates placed at the tail end; a multimode image registration module used for registering an intraoperative cone beam CT image to a preoperative CT image; and a visual interface module used for establishing a three-dimensional image and displaying the position of the surgical instrument in the subject image in real time during a surgery. According to the invention, the real-time position of the surgical instrument in the body of the subject during the surgery can be accurately positioned, accurate and reliable navigation is provided for the orthopedic surgery, the surgical risk is effectively reduced, the surgical time is reduced, and the system is simple and convenient to operate and high inapplicability.
Owner:HEFEI INSTITUTES OF PHYSICAL SCIENCE - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
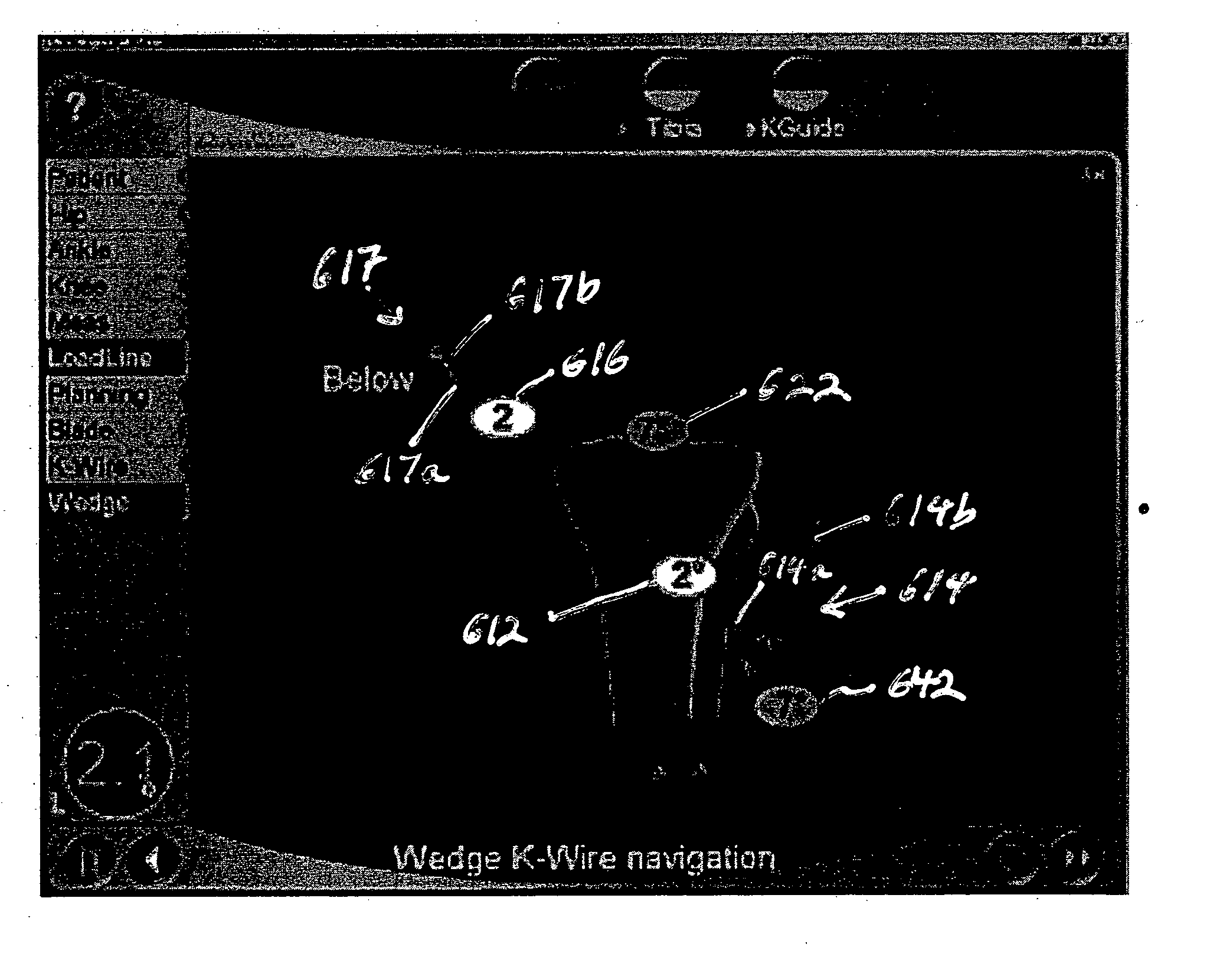
Method and apparatus for navigating a cutting tool during orthopedic surgery using a localization system
InactiveUS20070118140A1Precise cuttingImprove accuracyDiagnosticsSurgical navigation systemsTibiaLocalization system
The invention provides methods and apparatus for accurately cutting bones with a surgical cutting device, such as a sagittal saw, using a surgical navigation system without use of a complex cutting jig. A surgical navigation system is used to navigate a guide tube to be used to drill a k-wire into the bone. The k-wire will act as a guide to control at least one degree of freedom of a saw blade for making a cut in the bone. In an exemplary high tibial osteotomy procedure, in which two intersecting planar cuts must be made in the tibia in order to remove a wedge of bone, a surgical navigation marker is mounted on the guide tube. The surgeon uses the surgical navigation system to navigate the guide tube to the desired varus-valgus angle and height of the first cut and then drills a k-wire into the tibia at that varus-valgus angle using the guide tube. The process is repeated for the second cut. The surgeon then uses the two k-wires as guides for controlling the varus-valgus angle of a sagittal saw for the two planar cuts. The surgeon rests the saw blade flat on the respective k-wire to define the varus-valgus angle of the cut. The saw itself also is navigated, with the surgical navigation system providing a display showing the surgeon at least (1) the varus-valgus angle, (2) the cut depth, and (3) the anterior-posterior slope. The anterior-posterior slope and the depth of the cut is controlled freehand by the surgeon.
Owner:AESCULAP AG
Joint replacement surgical robot navigation and positioning system and method
ActiveCN112641510AReduce bleedingTraumaSurgical navigation systemsJoint implantsOrthopedics surgeryOrthopedic department
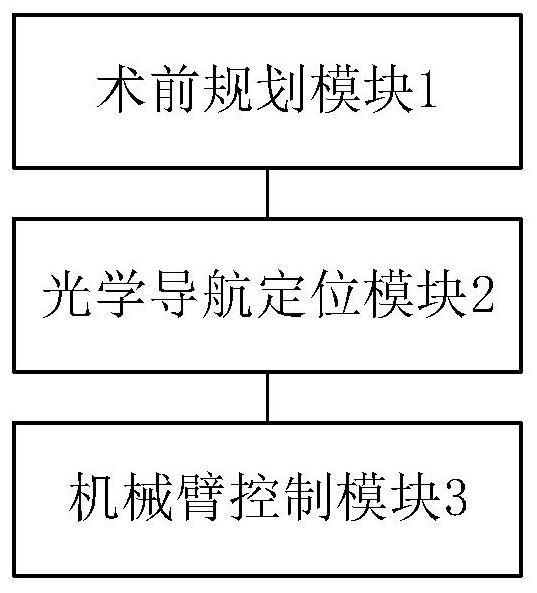
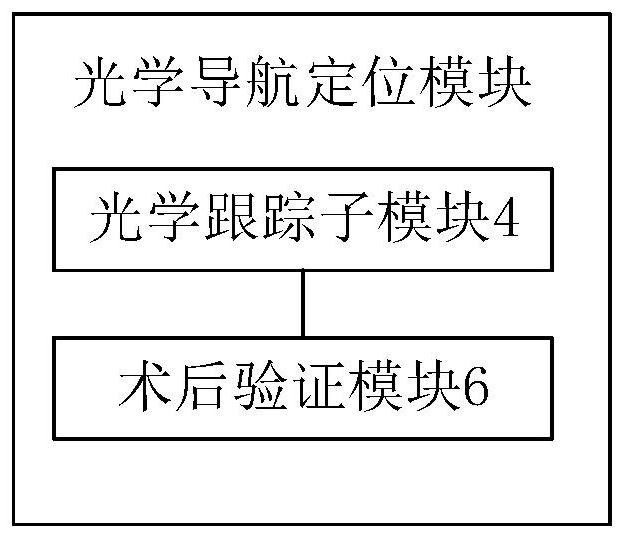
The embodiment of the invention discloses a joint replacement surgical robot navigation and positioning system and method. The system comprises a preoperative planning module which is used for carrying out segmentation and reconstruction of a hip joint according to the obtained medical image data of the hip joint, obtaining a three-dimensional model of the hip joint, carrying out the preoperative planning, and determining a surgical scheme; an optical navigation positioning module which is used for generating a navigation instruction according to the surgical scheme, registering the hip joint three-dimensional model according to the spatial position relationship between the hip joint of a patient and an operation probe to obtain a hip joint solid model, and determining the bone operation position of the patient according to the hip joint solid model; and a mechanical arm control module which is used for moving an end effector to the bone surgery position of the patient and controlling the end effector to perform osteotomy, filing and press-fit operation on the hip joint according to the navigation instruction. Preoperative planning is executed through the orthopedic surgery robot, surgery operation is completed at a high level, the operation intensity of doctors can be greatly reduced, the operation time is saved, and the operation precision is improved.
Owner:LONGWOOD VALLEY MEDICAL TECH CO LTD +1
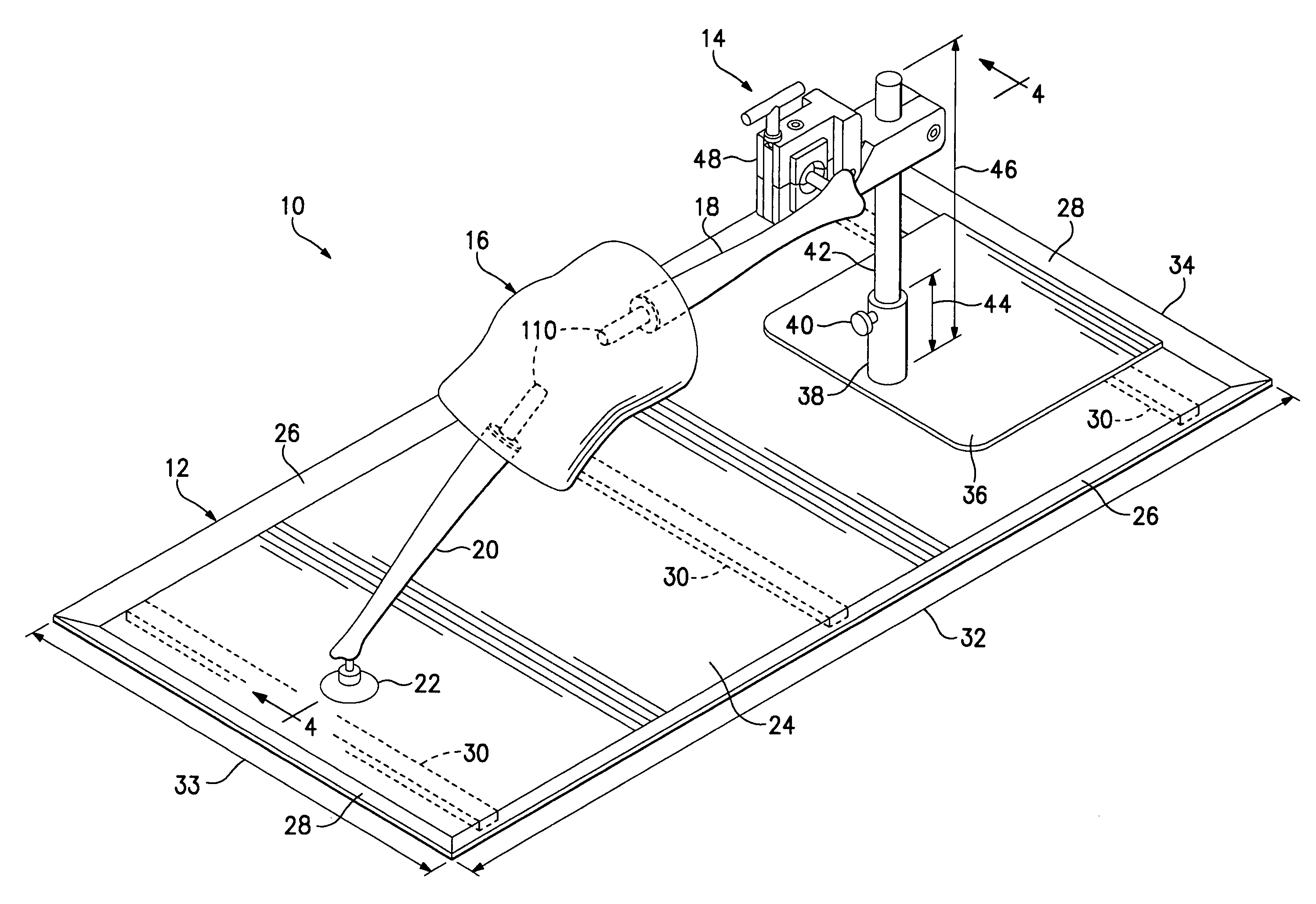
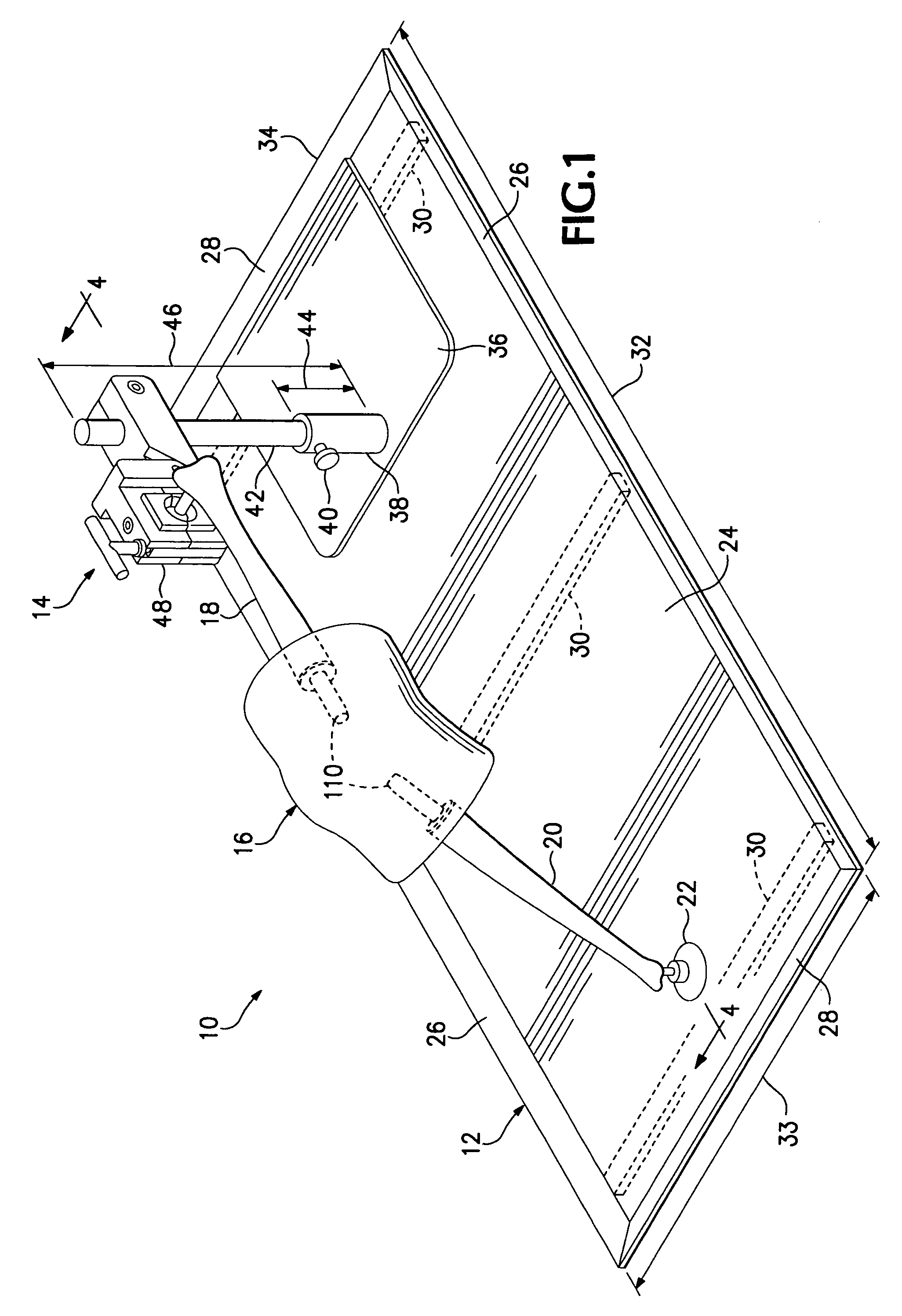
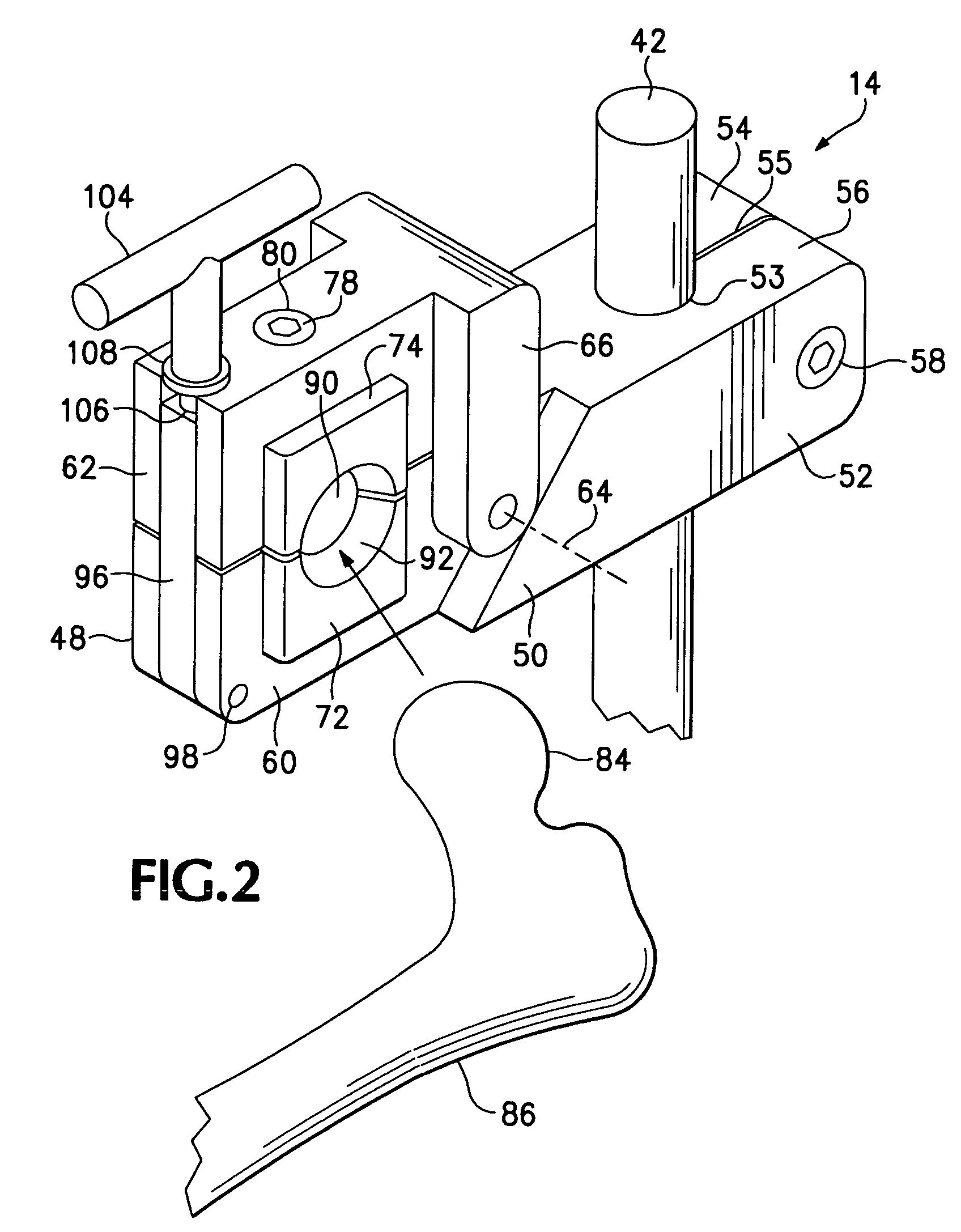
Apparatus and method for instruction in orthopedic surgery
A tray and a clamp mounted adjustably on the tray and supporting a leg or other limb or simulated limb including an articulated animal joint or a joint from a cadaver, for use in instruction of and practice by surgeons in joint replacement or other orthopedic surgery. A bone mounting device for fastening a joint to an artificial bone includes an expandable engagement member that fits within a cavity formed within a bone to hold the bone securely so that a surgical procedure can be performed on the joint.
Owner:EVERGREEN ORTHOPEDIC RES LAB LLC
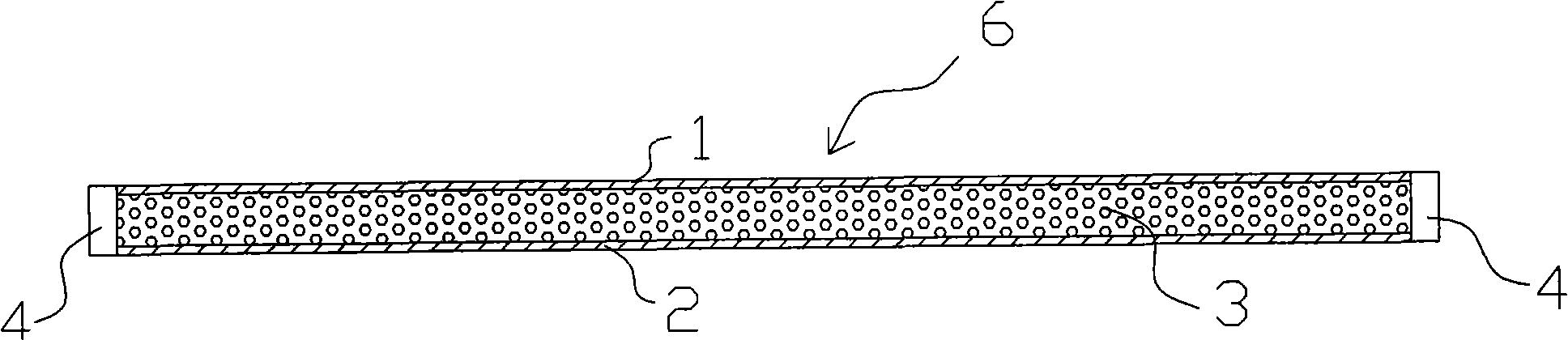
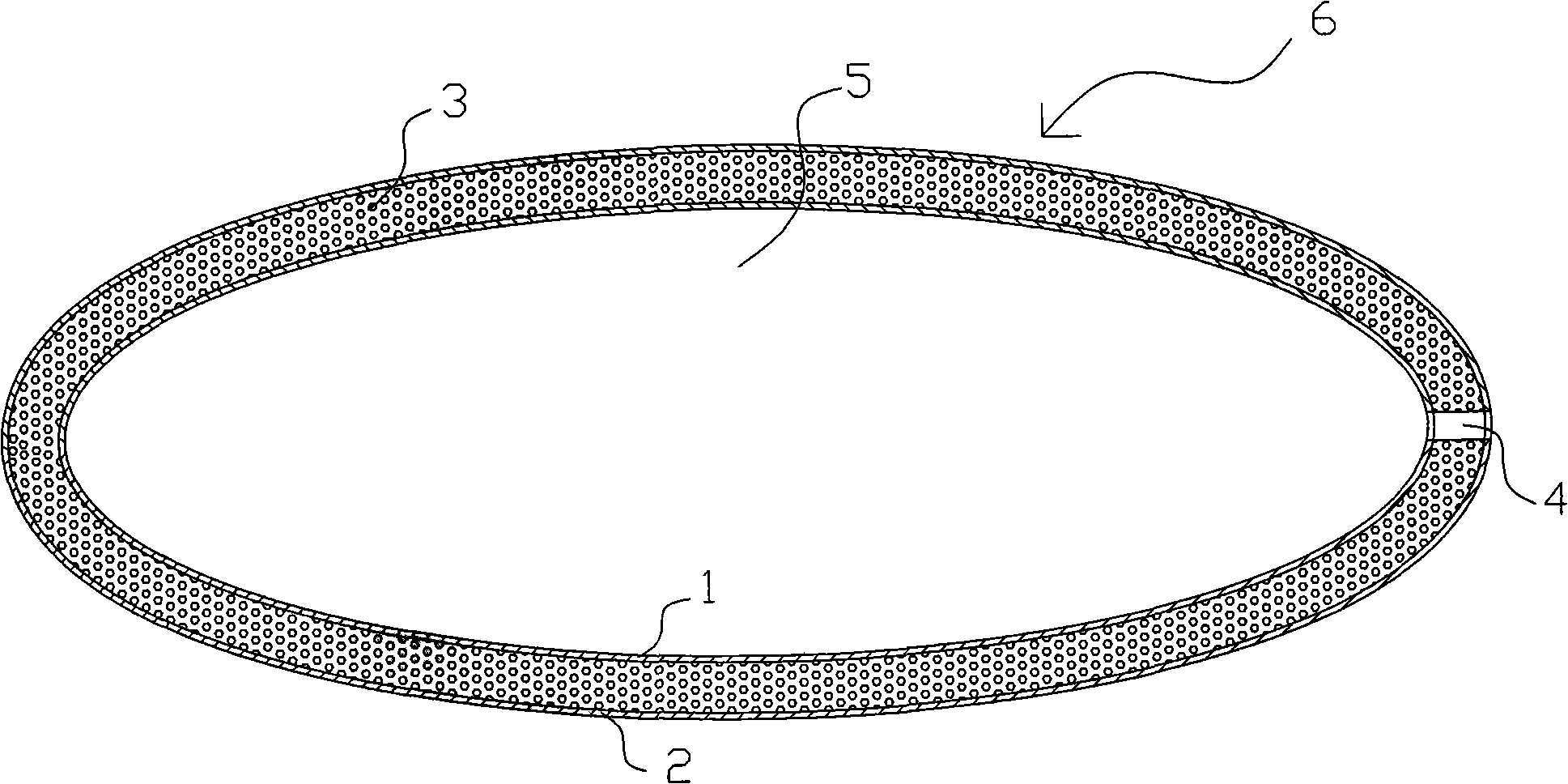
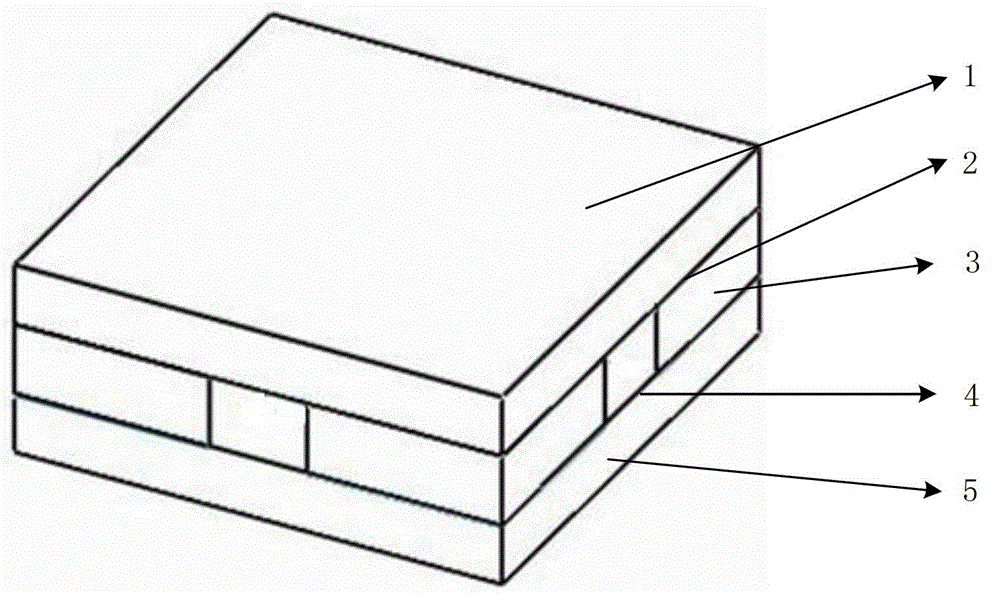
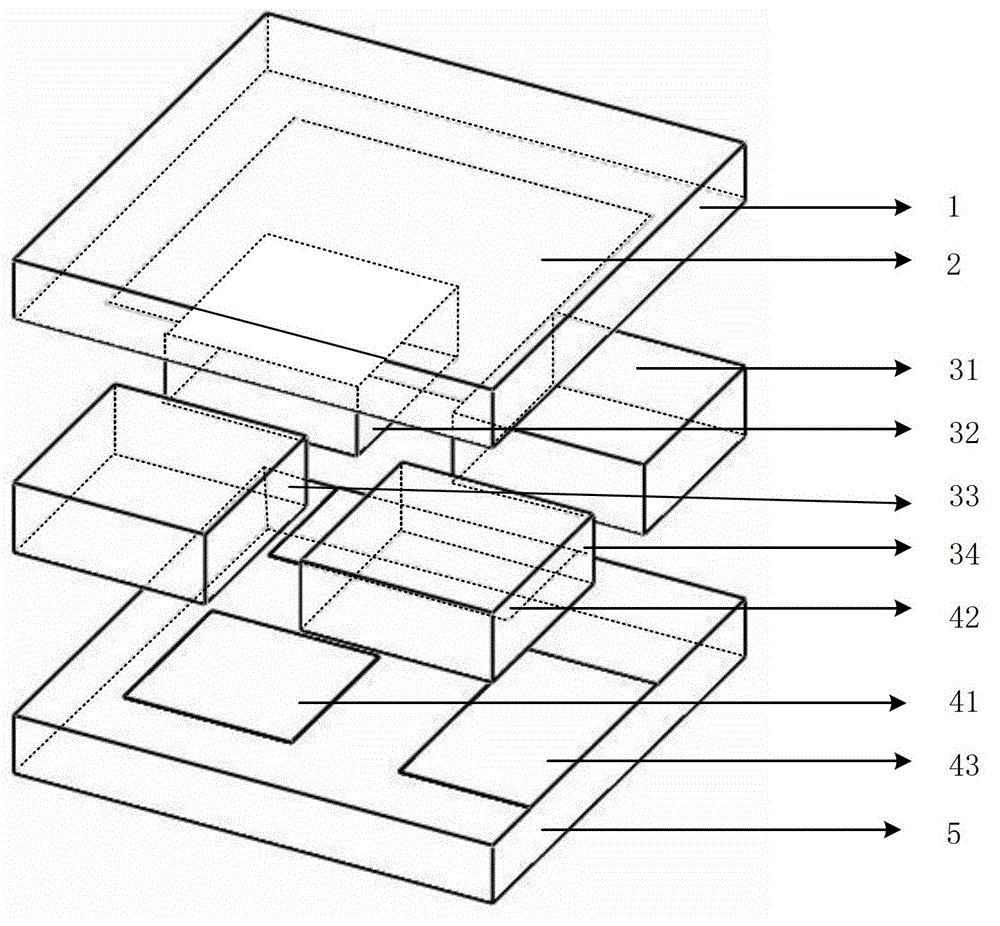
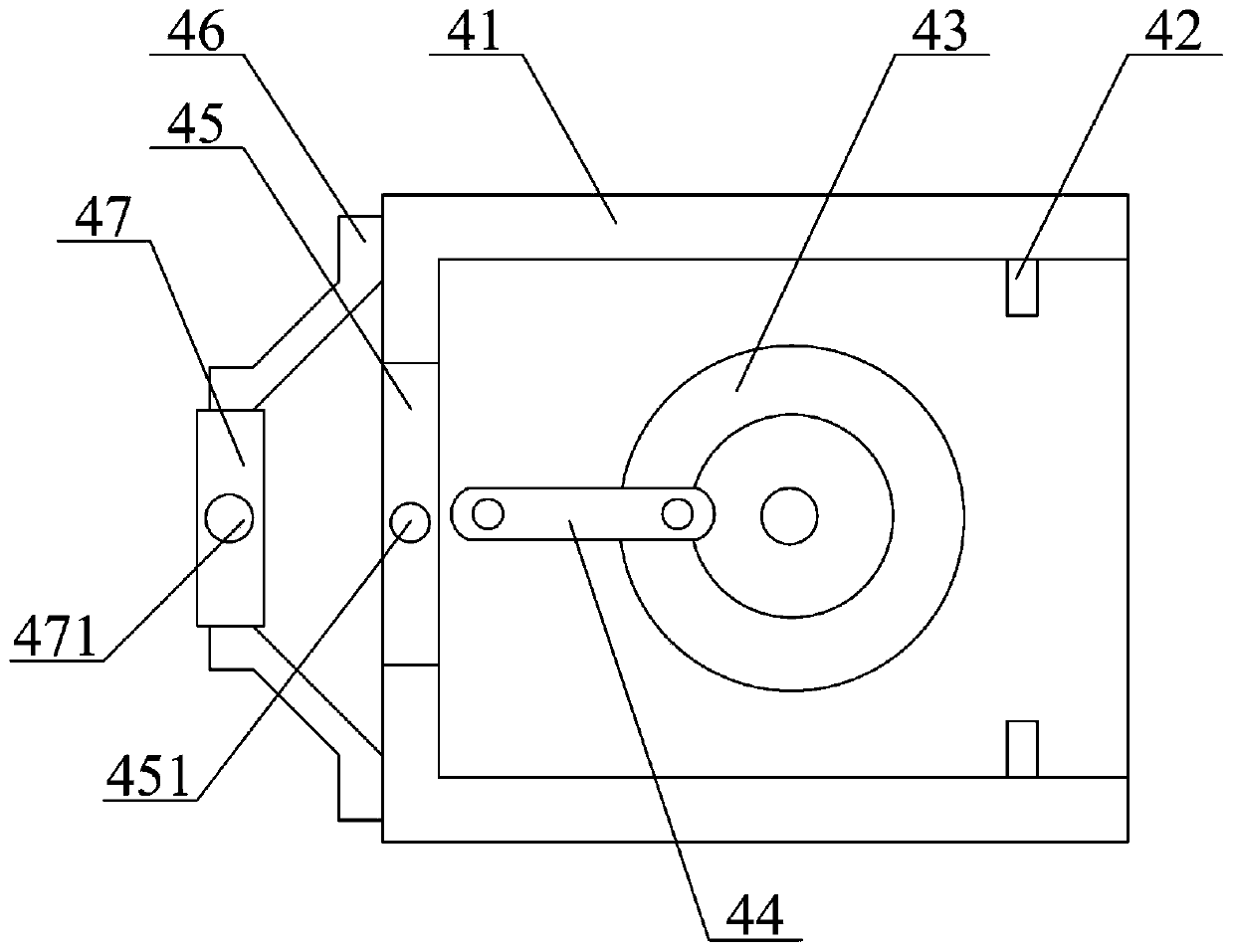
Three-dimensional interface stress sensor
ActiveCN102980691ASmall geometryEasy to integrateForce measurementOrthopedics surgeryAthletic training
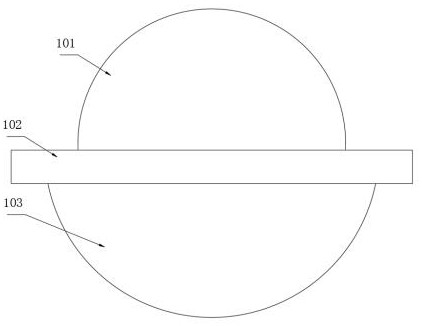
The invention discloses a three-dimensional interface stress sensor which mainly solves the problem of the prior art that the three-dimensional interface stress cannot be measured in the real time. The three-dimensional interface stress sensor comprises a top layer (1), a driving electrode (2), a middle layer (3), a sensing electrode (4) and a bottom layer (5), wherein the driving electrode (2) is coupled on the bottom surface of the top layer (1); the middle layer (3) consists of four separating pillars (31, 32, 33 and 34) which are fixed between the top layer (1) and the bottom layer (5); the sensing electrode (4) consists of a Z-direction sensing electrode (41), an X-direction sensing electrode (42) and a Y-direction sensing electrode (43); the Z-direction sensing electrode (41) is coupled in the middle of the upper surface of the bottom layer (5); and the X-direction sensing electrode (42) and Y-direction sensing electrode (43) are respectively coupled on two adjacent sides of the upper surface and are vertical to each other. The three-dimensional interface stress sensor has the advantages of small geometric dimension, large measurement range, high sensitivity and easy integration, can realize real-time measurement of the three-dimensional interface stress and can be used for rehabilitation medicine, orthopedic surgery, athletic training and shoemaking industry.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Rod reducer instruments and methods
InactiveUSRE44296E1Efficient and convenient to useGood adhesionInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsOrthopedics surgeryPlastic surgery
Rod reducers for use in orthopedic surgery are disclosed that include a fastener engaging member and a reducing member coupled together by an actuator assembly. The fastener engaging member can be secured to a fastener engaged to bone or tissue of the patient. The actuator assembly moves the reducing member such that its distal end contacts a rod and moves it toward the fastener.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
Process for producing tools used in orthopedic surgeries
InactiveUS20100262149A1Ceramic shaping apparatusNon-surgical orthopedic devicesCobalt chromium alloyPlastic surgery
An orthopedic tool being made from an alloy in the group comprising stainless steel alloys, cobalt-chrome alloys, titanium alloys and alumina and zirconia ceramic alloys, and having a density less than 98% of a theoretical possible density for the alloy, the orthopedic tool being made by a metal injection moulding process.
Owner:MAETTA SCI
Distal automatic cutting bone core extraction device
The invention relates to a distal automatic cutting bone core extraction device which belongs to the technical field of orthopedic surgical equipment, and is used for complete extraction of a bone core with the length being multiple times of diameter length of the bone core, and the technical scheme is as follows: the device comprises a positioning needle, a soft tissue separator, a positioning sleeve, a path-opening trephine, a cutting trephine and a drillstock, wherein the path-opening trephine and the cutting trephine are cylinders, cutting teeth are circumferentially arranged on the upper edge of the end surface of the wall of the distal cylinder, two pin holes are arranged on the wall of the proximal cylinder, the path-opening trephine cylinder and the cutting trephine cylinder have the same inner diameter and the same outer diameter, cutting-off teeth which are arranged obliquely are fixedly arranged on the inner wall at the lower end of the cutting trephine, and scales along the direction of a long shaft are arranged on the surface of the outer wall of each cylinder. By utilizing the device, the difficult problem that the bone core with the length being a plurality of times or even more than ten times larger than the diameter can not be extracted completely at the distal end in an orthopedic surgery is solved, thereby having the ground-breaking significance; and the device is mainly used for extracting the bone core with complete shape from a thick bone block through a blind hole, and especially applicable to extracting the bone cones with femur proximal or distal expansion parts and tibia proximal expansion parts.
Owner:孙涛
Robot for minimally invasive orthopedic surgery
InactiveCN103654960AReduce work intensityHigh positioning accuracyDiagnosticsSurgeryOrthopedics surgeryOrthopedic department
The invention provides a robot for minimally invasive orthopedic surgery. The robot is characterized in that the robot for the minimally invasive orthopedic surgery is composed of a robot body, X-ray perspective equipment, a master control system, a ray registration device, a cross-shaped registration device, a double-implantation mechanical hand and a single-implantation mechanical hand, the master control system is composed of a control table, a computer, a manual controller, an external scene display system and a motor driver, a liquid crystal displayer is adopted as the displayer of the external scene display system, registration is carried out on virtual labels arranged in the human vertebrae and same virtual labels on an extracorporal registration device through X-rays, and transpedicular implantation or puncturing is guided.
Owner:SUZHOU IDEAL MEDICAL APPLIANCE
Method and device for assisting a surgeon fit a prosthesis, in particular a hip prosthesis, following different surgical protocols
PendingUS20200000527A1Freedom of movementImage enhancementImage analysisOrthopedics surgeryVirtual space
A method and a device for helping a surgeon during the application of a determined and known orthopedic surgery protocol, comprising steps of overlaying determined and recorded virtual data, based on 3D markers, so as to allow the surgeon to continuously overlay the virtual spatial information with the actual data of the limbs of the patient.
Owner:CAZAL LAURENT
Bone holder for minimally invasive orthopedic surgery
The invention discloses a bone holder for minimally invasive orthopedic surgery.The bone holder comprises two annular fixing devices and further comprises traction devices and clamping devices.The traction devices are used for adjusting the distance between the two annular fixing devices.The clamping devices are arranged on the annular fixing devices.Each annular fixing device comprises a snap ring composed of a first arc part and a second arc part.Each clamping device comprises a clamping seat arranged on the corresponding snap ring, a hollow beak which is arranged on the clamping seat and can reciprocate in the radial direction of the corresponding snap ring, and a steel needle which is arranged in the hollow beak and can reciprocate in the radial direction of the corresponding snap ring.The annular fixing devices, the traction device and the clamping device are matched and are independent, precise clamping, traction and reset functions on broken bones during the surgery can be effectively achieved, the problems existing in clamping, traction and the like of closed reset and small-incision reset in the minimally invasive orthopedic surgery, especially long bone fracture minimally invasive surgery can be well solved, the requirements for long bone fracture surgery reset under the minimally invasive condition are met, and the defects of existing instruments are overcome.
Owner:HUBEI ENG UNIV
Orthopedic department reset positioning robot
ActiveCN112716603AAchieve positioningRealize resetInternal osteosythesisSurgical navigation systemsOrthopedics surgeryPhysical medicine and rehabilitation
The invention relates to an orthopedics department reset positioning robot, which solves the technical problem that an existing orthopedics department operation robot is low in reset precision during an operation and comprises a reset robot body, a navigation robot and a positioning robot body, the reset robot body comprises a reset platform, a far-end fixator and a far-end reference frame, and the far-end reference frame is fixed to the far-end fixator; the far-end fixator comprises a connecting base plate, a movable connecting plate, a first locking device, a reference frame, a first connecting side plate, a second connecting side plate, a first fixed sleeve, a second fixed sleeve, a fixing plate, a first fixed needle, a second fixed needle, a third fixed sleeve, a fourth fixed sleeve, a third fixed needle and a fourth fixed needle. The invention is widely applied to orthopedic surgery.
Owner:WEIHAI WEIGAO ORTHOPEDIC SURGICAL ROBOT CO LTD
Porous biological activity glass bone restoration material, preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN109248342AHigh osteoinductive activityGood osteoinductive activityPeptide/protein ingredientsTissue regenerationBiocompatibility TestingCytotoxicity
The invention belongs to the technical field of glass bone restoration, and discloses a porous biological activity glass bone restoration material, a preparation method and application thereof. Aftera prepared porous biological activity glass bone restoration material being implanted into an organism, the biocompatibility is good; the prepared bone restoration material is composed of natural macromolecular materials and inorganic materials being bone-like components, the surface of the prepared bone restoration material is capable of forming a good interface relation with cells, any parts ofany bone defect can be implanted in a orthopedic surgery, application parts are not limited, good biocompatibility, no cytotoxicity and no immune rejection are achieved. According to the prepared bonerestoration material adopted by the preparation method, good degradation performance is achieved, materials are gradually degraded with growth of new bone, and thus no occupation and no interfere tobone reconstruction are achieved; and the restoration cycle is shortened.
Owner:HUBEI SHUANGXING PHARMA CO LTD
Three-dimensional reconstruction method for CT image of bone joint replacement surgical robotand system
PendingCN114041878ARealize 3D reconstructionImage analysisComputer-aided planning/modellingOrthopedics surgeryOrthopedic department
The invention relates to the field of bone joint replacement surgical robots, and discloses a three-dimensional reconstruction method for a CT image of a bone joint replacement surgical robot and a computer-assisted orthopedic surgery system based on augmented reality. The method comprises the steps of firstly, acquiring bone segmentation data of a CT image; then generating a three-dimensional skeleton model according to the obtained skeleton segmentation data of the CT image; a video image matching algorithm based on improved SURF feature points is adopted, matching tracking is carried out on a target of a video image, then the spatial attitude of the target is solved, corresponding spatial transformation is carried out on a virtual three-dimensional object, and therefore the effect of augmented reality is achieved. The main purpose of the invention is to provide a technology capable of establishing a sufficiently complex and accurate three-dimensional image for three-dimensional reconstruction of a CT image of a patient before an operation, so that a surgical robot can autonomously complete hip joint, knee joint and shoulder joint replacement orthopedic operations by means of the technology.
Owner:SHANDONG JIANZHU UNIV
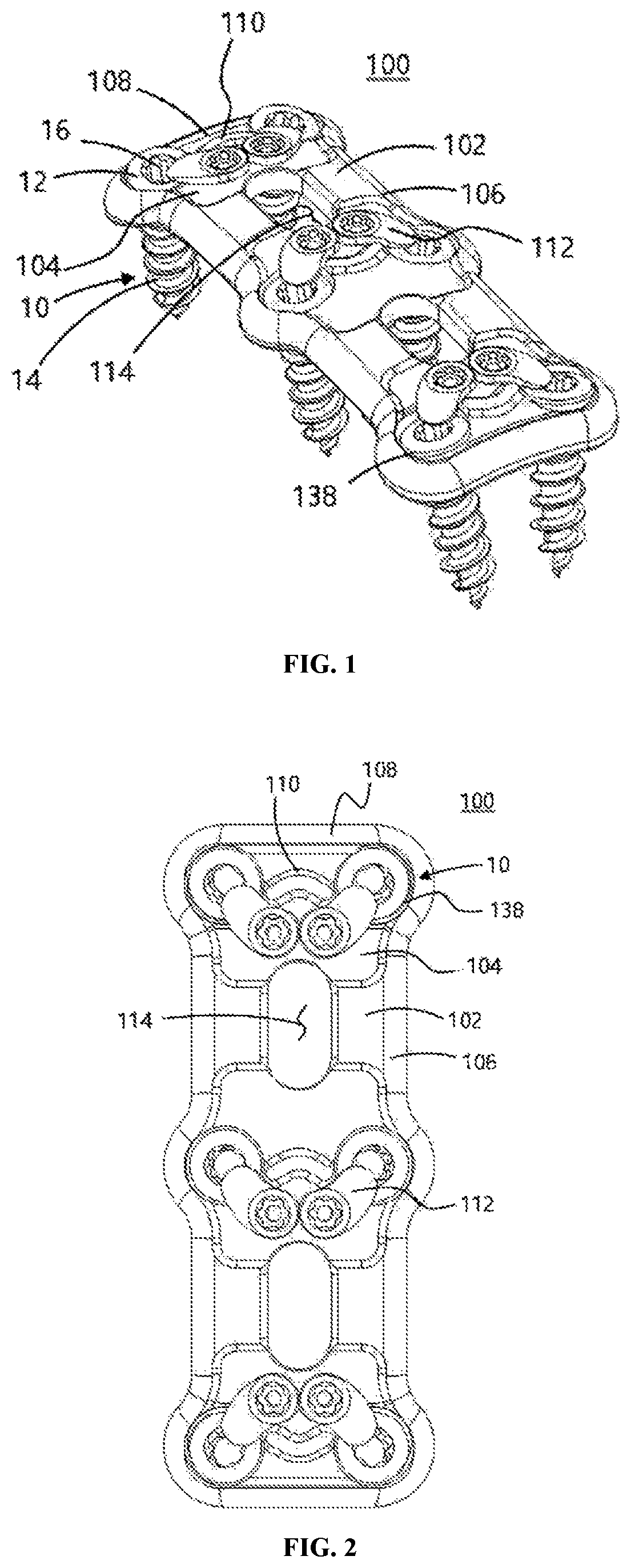
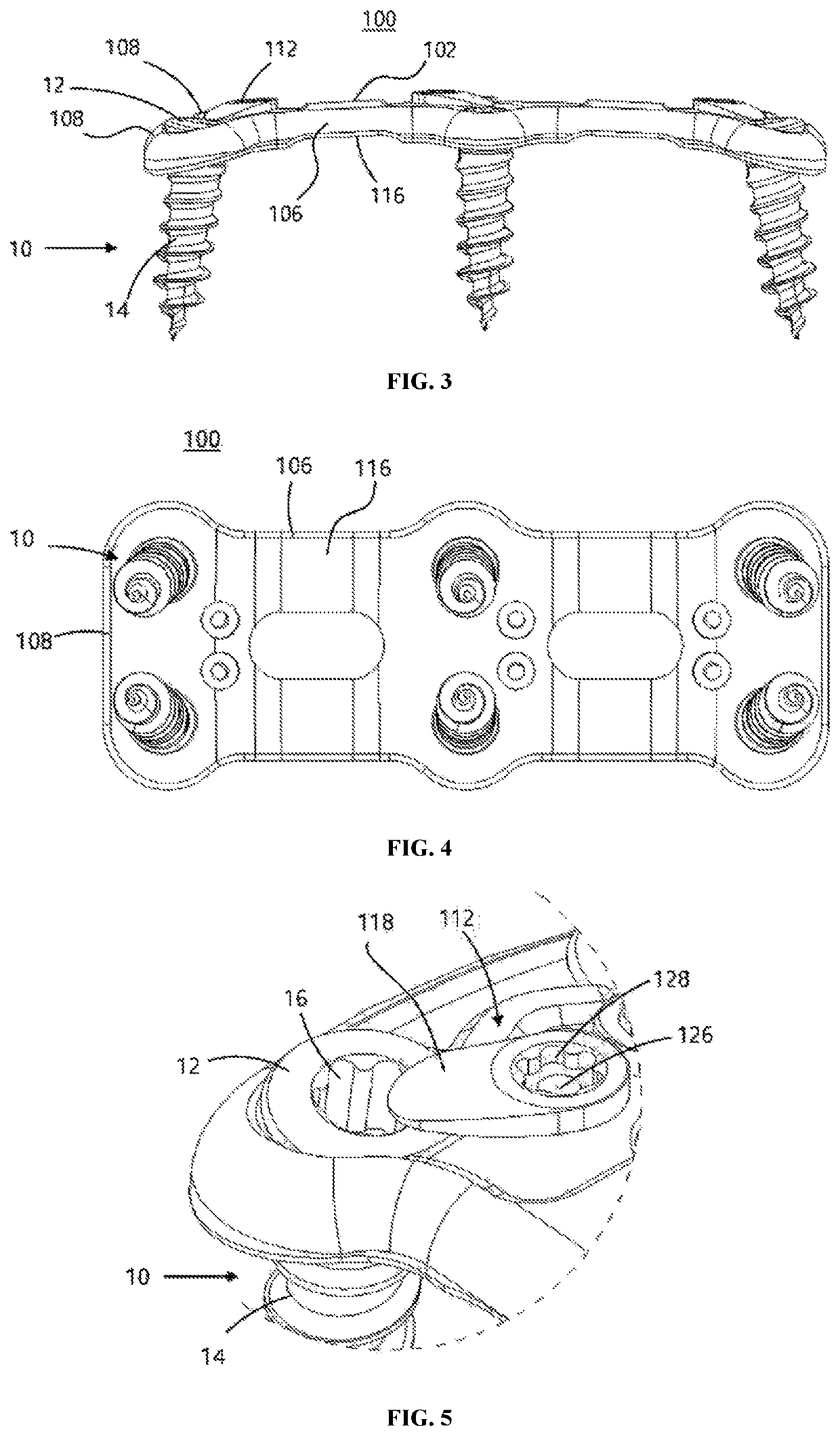
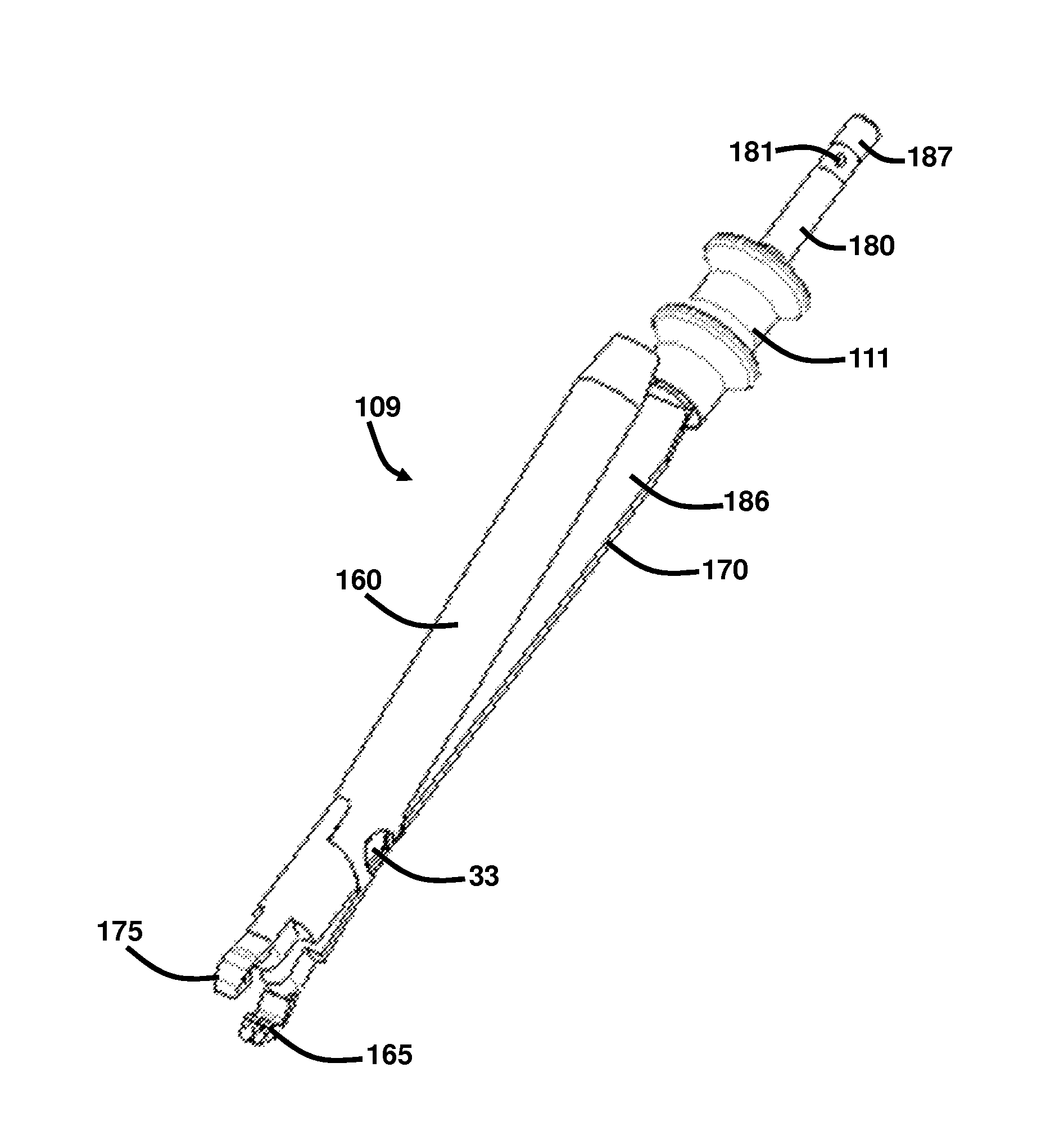
Anterior cervical spine plate
ActiveUS11065043B2Avoid foreign body sensationAvoid separationInternal osteosythesisFastenersOrthopedics surgeryOrthopedic department
The present invention relates to an anterior cervical spine plate which is used to perform anterior fixation surgery on a cervical spine in orthopedic surgery and neurosurgery, which includes: a plate body formed to extend in a longitudinal direction thereof; two or more bone screw holes formed in the plate body to support head parts of bone screws; and a locking element configured to maintain the bone screws while being inserted into the bone screw holes, respectively. The locking element is rotatably coupled to the plate body, and the plate body has reinforcing parts formed at outer circumferences thereof.
Owner:L&K BIOMED CO LTD
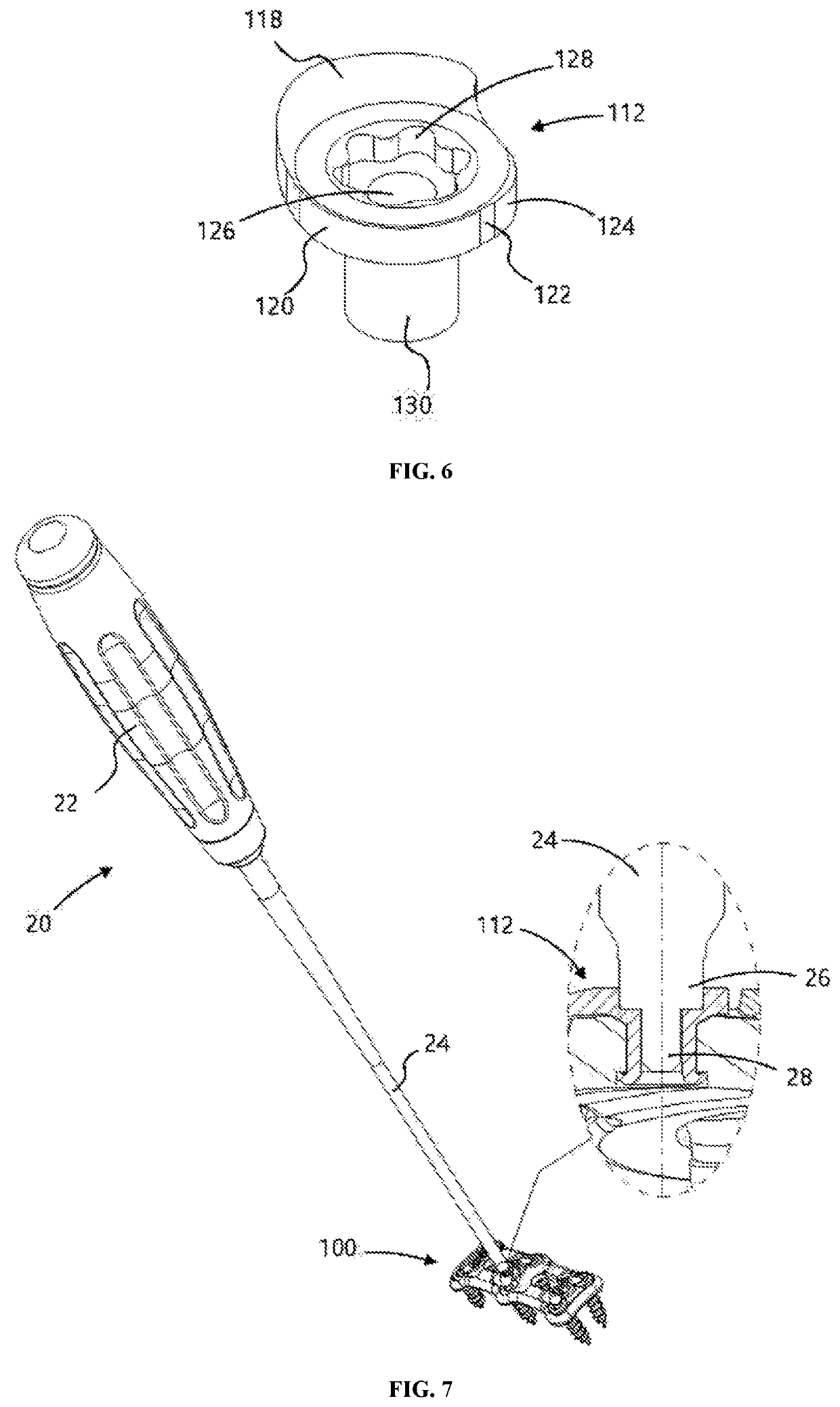
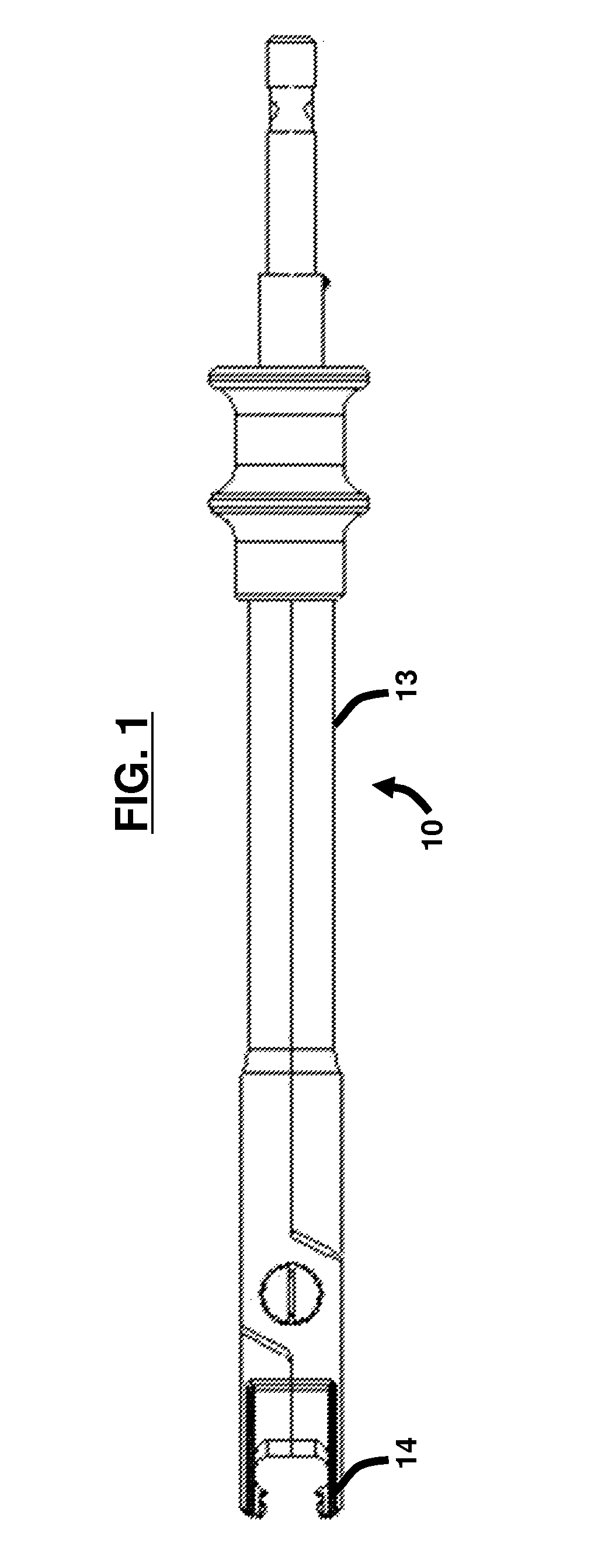
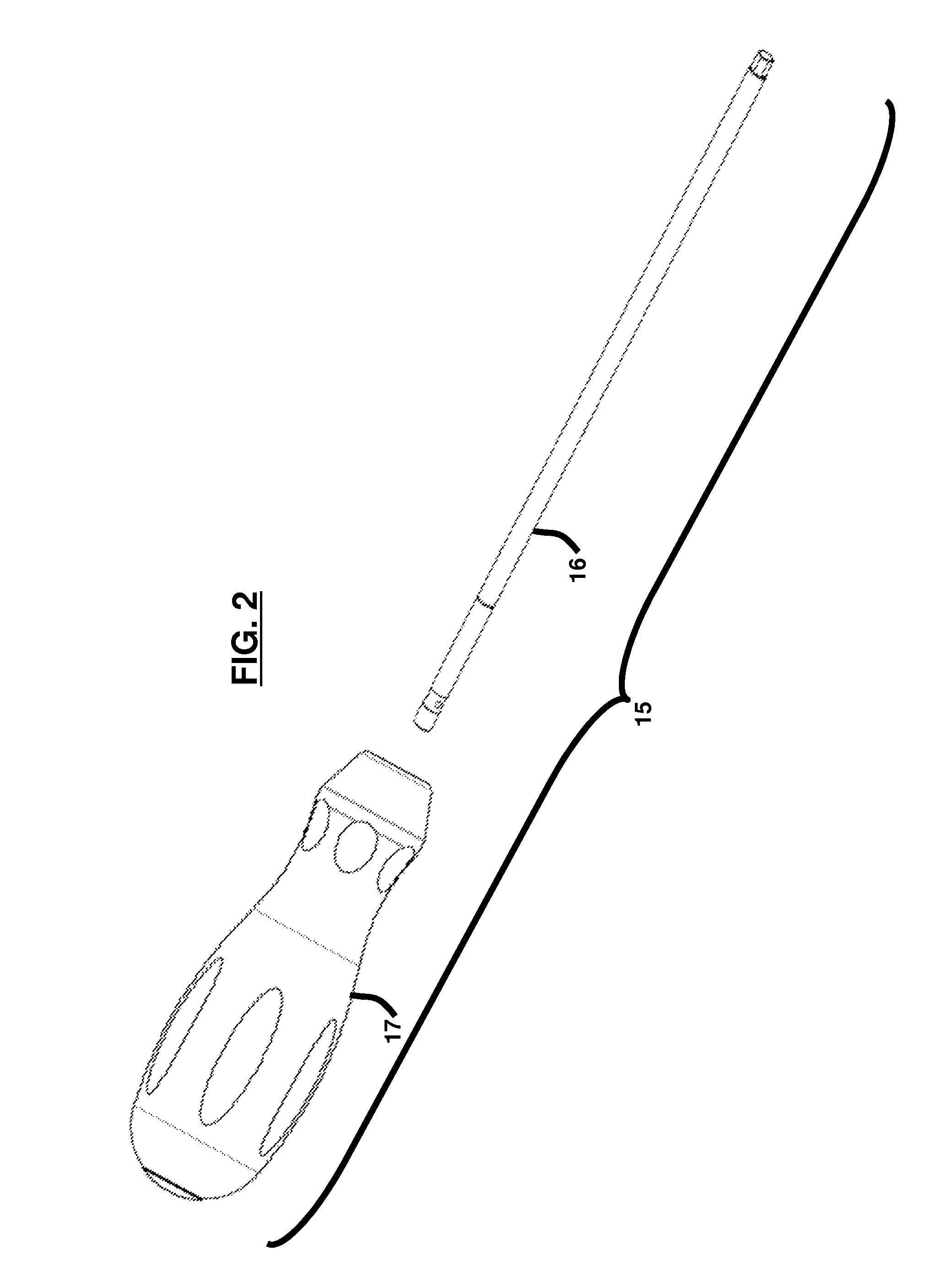
Radiolucent screwdriver for orthopedic surgery
A surgical tool for inserting a surgical implant in a body and a method of performing a surgical procedure, wherein the tool is composed of materials consisting essentially of radiolucent materials. In one embodiment the radiolucent materials comprise plastic. In another embodiment the radiolucent materials comprise carbon fibers. In still another embodiment the radiolucent materials comprise thin aluminum. The tool has a torque capacity of at least 6 Nm.
Owner:CUSTOM SPINE INC
Color-doppler-ultrasound dual-guiding control system for orthopedic-department puncturing
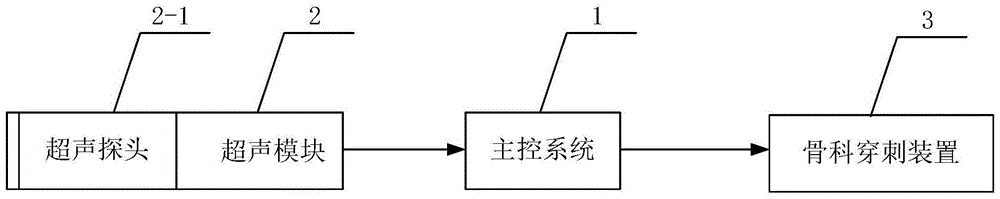
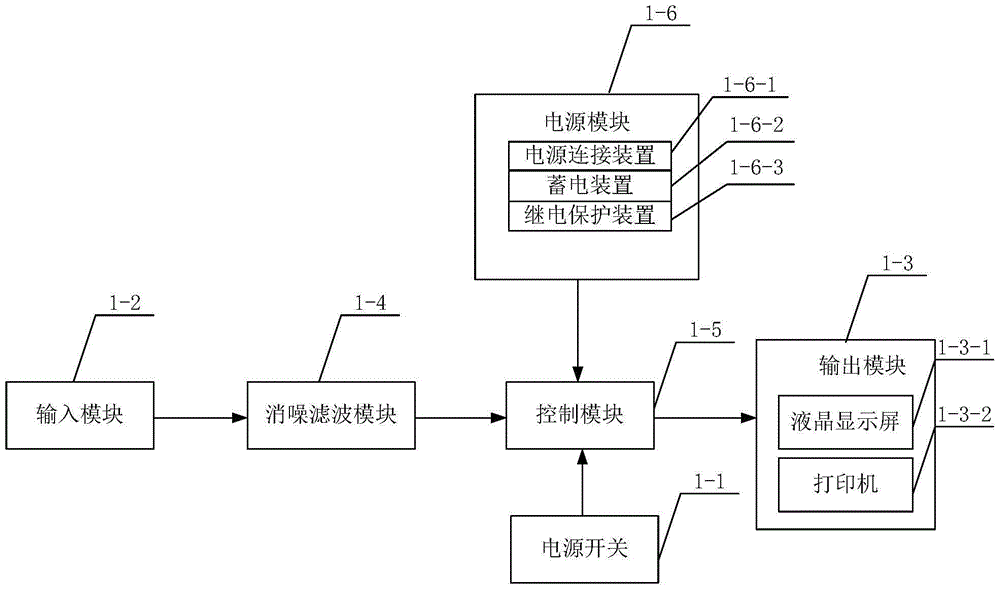
InactiveCN105662546ARelieve painAccurate puncture positioningSurgical needlesTrocarSedationControl system
The invention discloses a color ultrasound orthopedic puncture dual-guidance control system. The main control system is respectively connected with an ultrasonic module and an orthopedic puncture device; the ultrasonic module is connected with an ultrasonic probe, and the main control system receives color ultrasound data information from the ultrasonic module and guides the control after processing. The orthopedic puncture device performs orthopedic puncture work. The present invention is a color ultrasound orthopedic puncture dual-guidance control system that is easy to use and has a reasonable structural design. The position and shape of the orthopedic puncture can be controlled by using the double-guidance method of color ultrasound images and physical functions at the same time, which can effectively perform puncture in orthopedic surgery and facilitate surgery. Instrument operation improves surgical efficiency. The present invention can also implement effective nerve block and puncture under sedation or basic anesthesia. It is suitable for patients with anatomical variation, children and patients who cannot cooperate well, improving medical level, reducing medical risks, Reduce the suffering of patients and reduce medical expenses.
Owner:THE MILITARY GENERAL HOSPITAL OF BEIJING PLA
Recovery assisting device for use after orthopedic surgery
ActiveCN111317631AAvoid pain injuryAvoid causing painDiagnosticsChiropractic devicesOrthopedics surgeryOrthopedic department
The invention relates to a recovery assisting device for use after an orthopedic surgery. According to the recovery assisting device, the problems that existing devices cannot be operated and controlled by a patient and are narrow in application ranges are effectively solved. The technical scheme for solving the problems comprises a main plate and four support pillars fixed at the lower end of themain plate, wherein a left plate is cooperatively and rotatably arranged at the left end of the main plate, and a right plate is cooperatively and rotatably arranged at the right end of the main plate; two lower limb plates are cooperatively and rotatably arranged on the left plate, and two upper limb plates are cooperatively and rotatably arranged on the right plate; when the main plate, the left plate and the right plate are in a horizontal state, the device is of a bed plate form, the two upper limb plates can be respectively driven to rotate by two groups of first driving devices when thetwo lower limb plates rotate, and the lower limb plates do not rotate when the upper limb plates rotate; and when the main plate, the left plate and the right plate are in a vertical state, the device is of a chair form, the two lower limb plates can be respectively driven to rotate by two groups of second driving devices when the two upper limb plates rotate, and the upper limb plates do not rotate when the lower limb plates rotate. The recovery assisting device is wide in applicability and has a very good recovery assisting effect.
Owner:HENAN PROVINCE HOSPITAL OF TCM THE SECOND AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF HENAN UNIV OF TCM
Auxiliary arm for orthopedic surgery robot
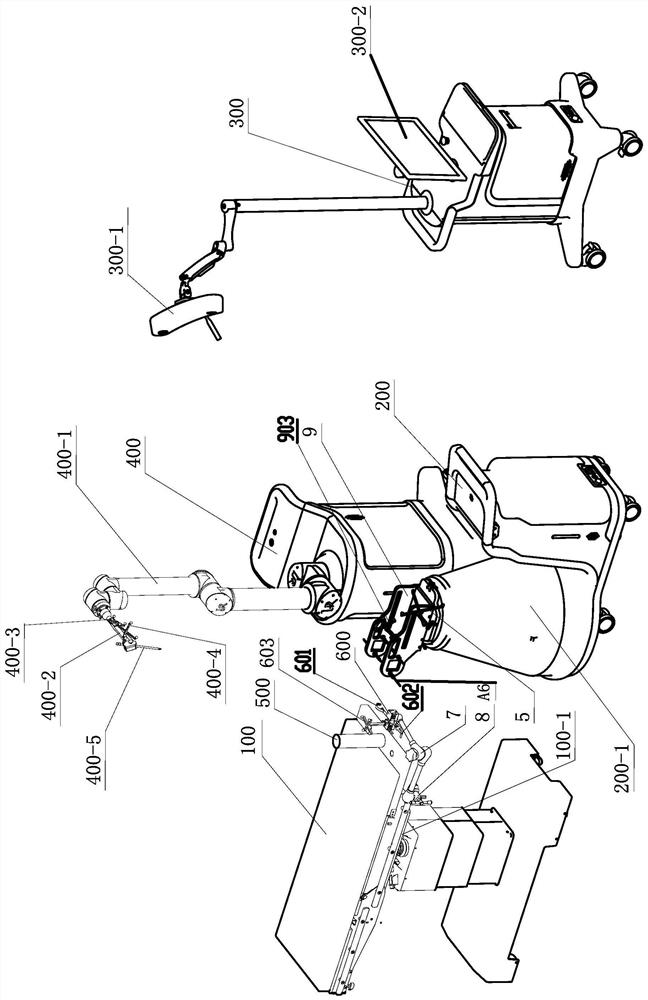
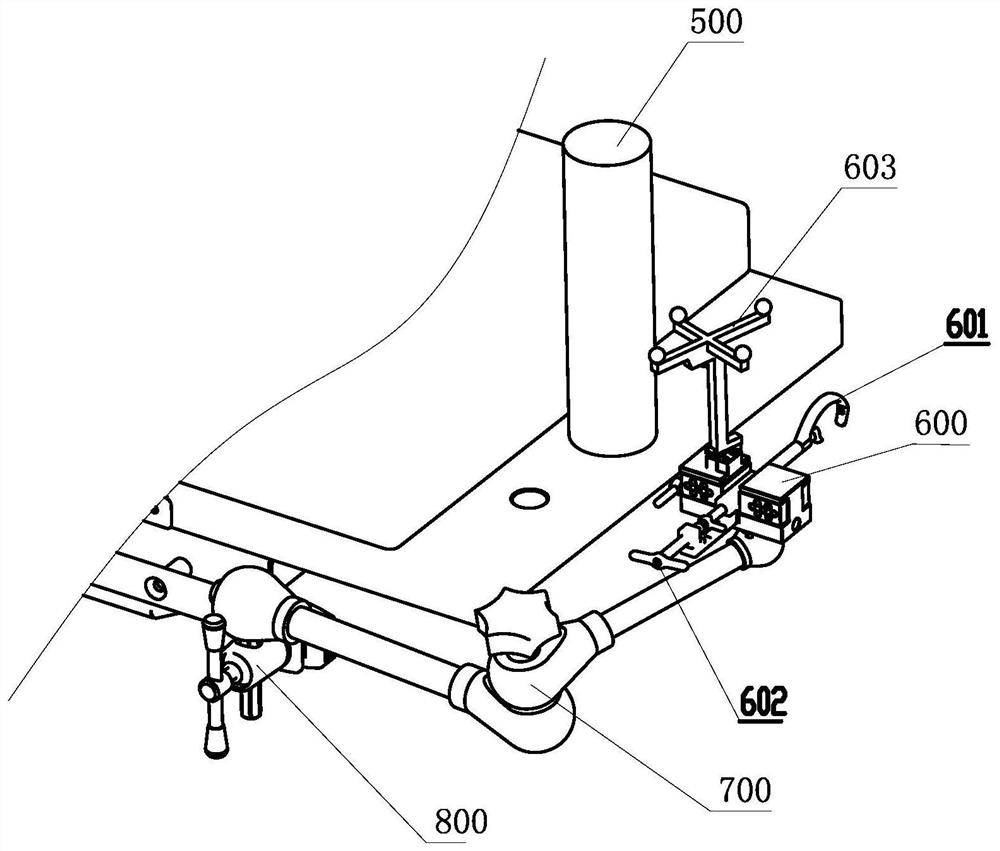
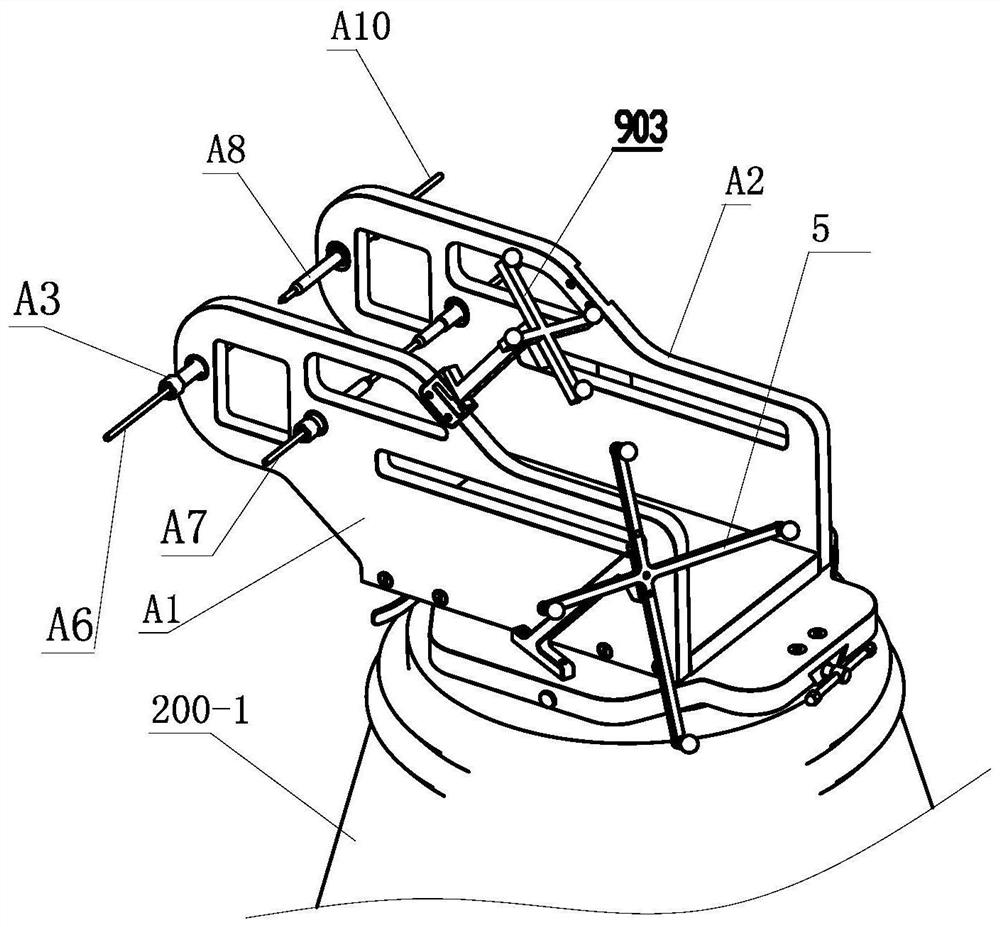
ActiveCN111920523AQuick switchImprove space utilization spaceDiagnosticsSurgical instrument supportOrthopedics surgeryPhysical medicine and rehabilitation
The invention discloses an auxiliary arm for an orthopedic surgery robot, and belongs to the field of orthopedic surgery mechanical arms. The auxiliary arm for the orthopedic surgery robot comprises amechanical arm body, a movable arm stretcher is connected on the mechanical arm body; a turntable is rotationally connected to the movable arm support; a first electric push rod is fixedly connectedin the movable arm support; a center rod is fixedly connected to the telescopic end of the first electric push rod. A through hole matched with the telescopic end of the first electric push rod is formed in the turntable; a plurality of uniformly distributed movable claws are hinged to one end, far away from the movable arm, of the turntable; a plurality of small motors matched with the movable claws are mounted in the turntable; a steering gear set is fixedly connected to the power output end of the small motors, multiple operation auxiliary tools can be used for assisting the operation by using multiple movable claws in an orthopaedic remote operation, multiple tool assistance is provided for the remote operation through one mechanical arm, and the space utilization rate is greatly increased.
Owner:江苏逸动医疗设备有限公司
Calibration device at tail end of orthopedic surgery robot
ActiveCN111631818AQuick installationImprove stabilitySurgical manipulatorsSurgical robotsOrthopedics surgeryEngineering
The invention discloses a calibration device at tail end of an orthopedic surgery robot, and relates to the technical field of orthopaedic medical instruments. A calibration reflective ball base component comprises a calibration reflective ball base main body, the interior of the calibration reflective ball base main body is provided with a calibration reflective ball base sphere limiting groove located in the circle center of a calibration reflective ball base upper sinking groove, the interior of the calibration reflective ball base main body is provided with a calibration reflective ball base quick-mounting hemisphere part located at the bottom of the circle center of the calibration reflective ball base sphere limiting groove, the maximum diameter of the calibration reflective ball base fast-mounting hemisphere part is smaller than the diameter of the calibration reflective ball base sphere limiting groove, and a calibration reflective ball base fixing block is installed at the bottom of the calibration reflective ball base body. Existing calibration devices only need to perform calibration once, so that interference caused by matrix fixation in the operation process of an operator can be avoided, and the time of the whole operation can be fully saved.
Owner:HANGZHOU JOINTECH LTD
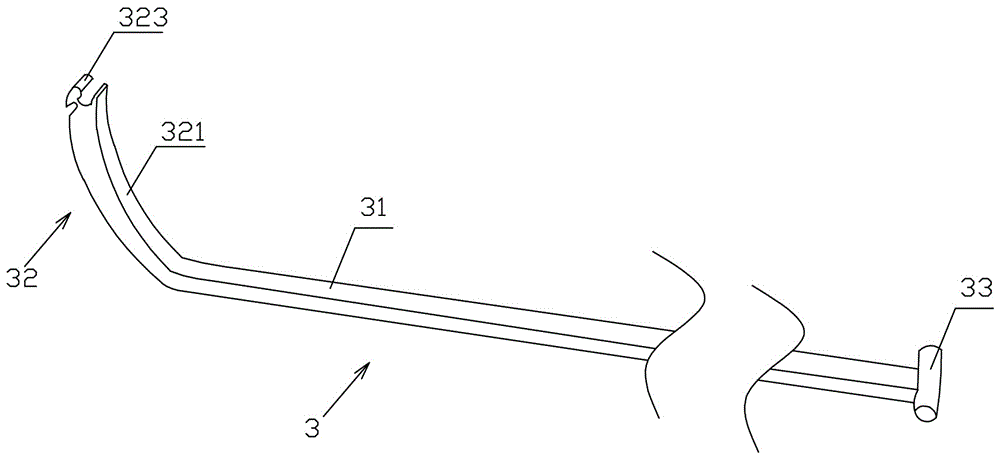
Tibial tunnel pass thread dragging, pushing and pulling device special for orthopedic surgery
The invention discloses a tibial tunnel pass thread dragging, pushing and pulling device special for orthopedic surgery. The device comprises a stretching-in pipe capable of penetrating through a tibial tunnel in adaptive mode. A movable push-pull rod is arranged in the pipe in a matched mode. The bending radian of the front working end of the movable push-pull rod can deform after force is borne and be automatically and elastically restored. When the device penetrates through the tunnel, the front end of the device can be sent to a position of which the height is 1-2 cm higher than the tunnel plane, a dragged thread is convenient to grasp or push out, the front end of the movable push-pull rod can be customized according to different thread pushing and dragging functions, and the bending radian of the movable push-pull rod can be customized to meet different strength requirements. Medical staff can more conveniently drag, push and eject the pass thread passing through the tibial tunnel, the push-pull rod can be rapidly replaced according to different surgical requirements, a doctor can conveniently perform surgical operation, pain of a patient is relieved, and the success rate of the surgery is increased.
Owner:吕宏升
Orthopedic surgery robot control method based on kinetic model
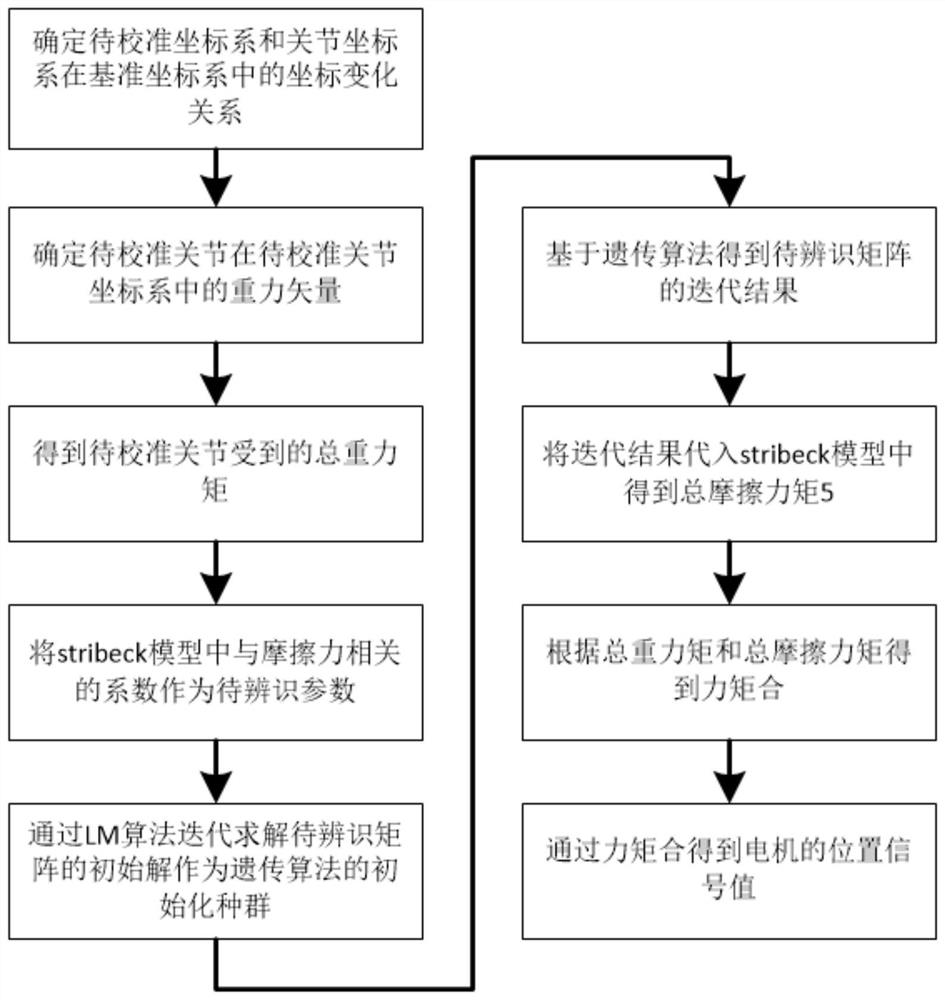
ActiveCN112975987AAvoid the impact of positioning accuracyFew parametersProgramme-controlled manipulatorOrthopedics surgeryOrthopedic department
The invention discloses an orthopedic surgery robot control method based on a kinetic model, and relates to the field of robots. The method comprises the steps: determining the total gravitational moment borne by a to-be-calibrated joint through a coordinate change relation and a gravity vector; taking a coefficient related to the friction force in a stribeck model as a parameter to be identified, and constructing a matrix to be identified; performing iterative solution through an LM algorithm to obtain an initial solution of the matrix to be identified, and taking the initial solution as an initial population of a genetic algorithm; obtaining an iteration result of the matrix to be identified based on the genetic algorithm; substituting the iteration result into the stribeck model to obtain the total friction moment of the to-be-calibrated joint; obtaining the resultant moment of the to-be-calibrated joint; and obtaining a position signal value of a corresponding motor of the to-be-calibrated joint through the resultant moment, and driving the to-be-calibrated joint according to the position signal value. The influence of external force on the positioning accuracy of an orthopedic surgery robot is avoided by calculating the resultant moment, and the stability and the safety are effectively improved.
Owner:江苏集萃复合材料装备研究所有限公司
Method for setting up a control and technical orthopedic device
The invention relates to a method for setting up a control, and to a control for a technical orthopedic device, and a technical orthopedic device as such. Actuations of the technical orthopedic device (1) are provided by means of an output device (2, 3), biometric signals are received by sensors (12), and said signals are associated with the respective actuations.
Owner:OTTO BOCK HEALTHCARE PROD GMBH
Automatic vertebral body puncture forming device and orthopedic surgery robot system
PendingCN113425414ARealize fully automatic operationReduce labor intensitySurgical needlesSurgical manipulatorsOrthopedics surgeryPuncture procedure
The invention discloses an automatic vertebral body puncture forming device and an orthopedic surgery robot system. The automatic vertebral body puncture forming device comprises a bottom plate, a puncture unit and a bone cement filling unit, wherein the puncture unit and the bone cement filling unit are arranged on the bottom plate; the automatic vertebral body puncture forming device further comprises a linear feeding unit and a tool replacement unit which are installed on the bottom plate; the linear feeding unit carries the puncture unit or the bone cement filling unit to move forwards to conduct puncture operation or injection molding operation of bone cement or moves backwards to return to the tool replacement unit; and the puncture unit or the bone cement filling unit conducts position replacement on the tool replacement unit so as to leave or enter the linear feeding unit. The automatic vertebral body puncture forming device is used in cooperation with an orthopedic surgery robot, and intelligent automatic orthopedic surgery puncture and bone cement injection are achieved.
Owner:SHENZHEN XINJUNTE SMART MEDICAL EQUIP CO LTD
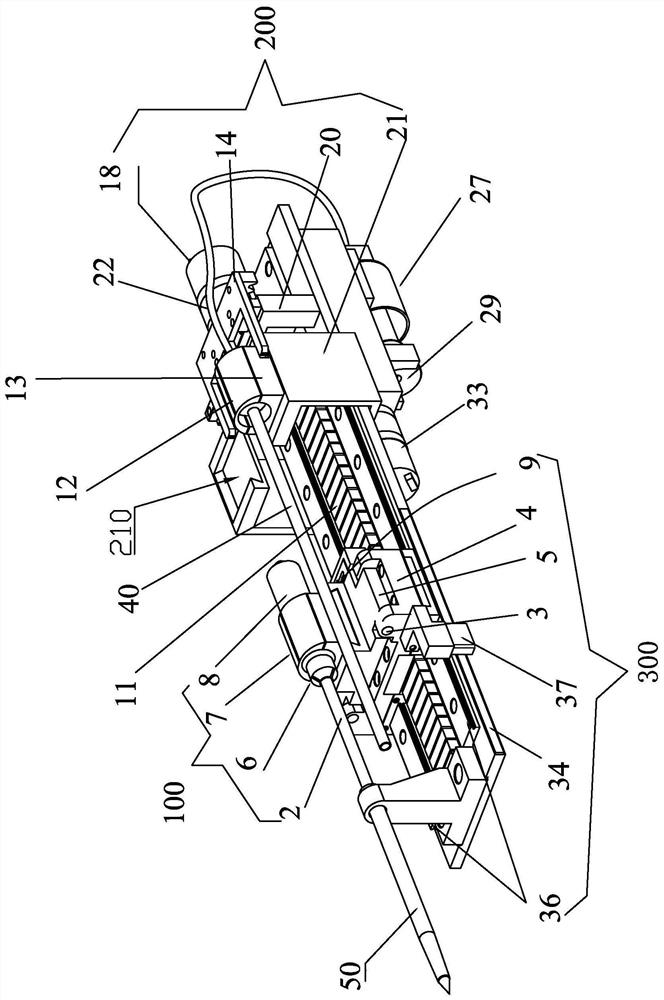
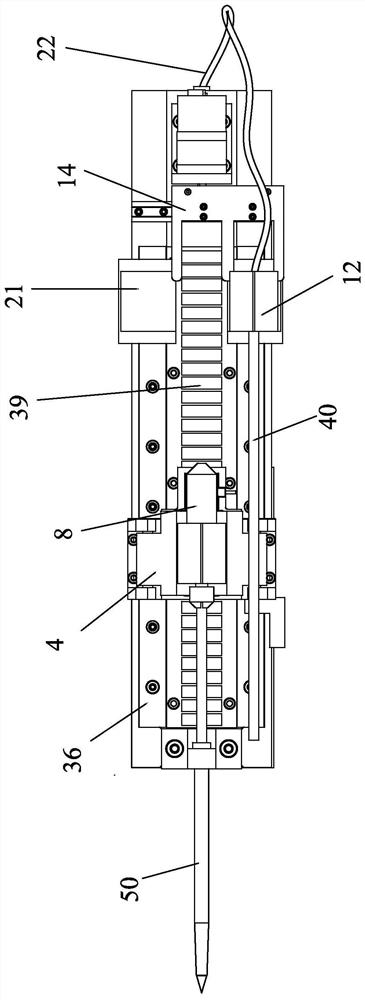
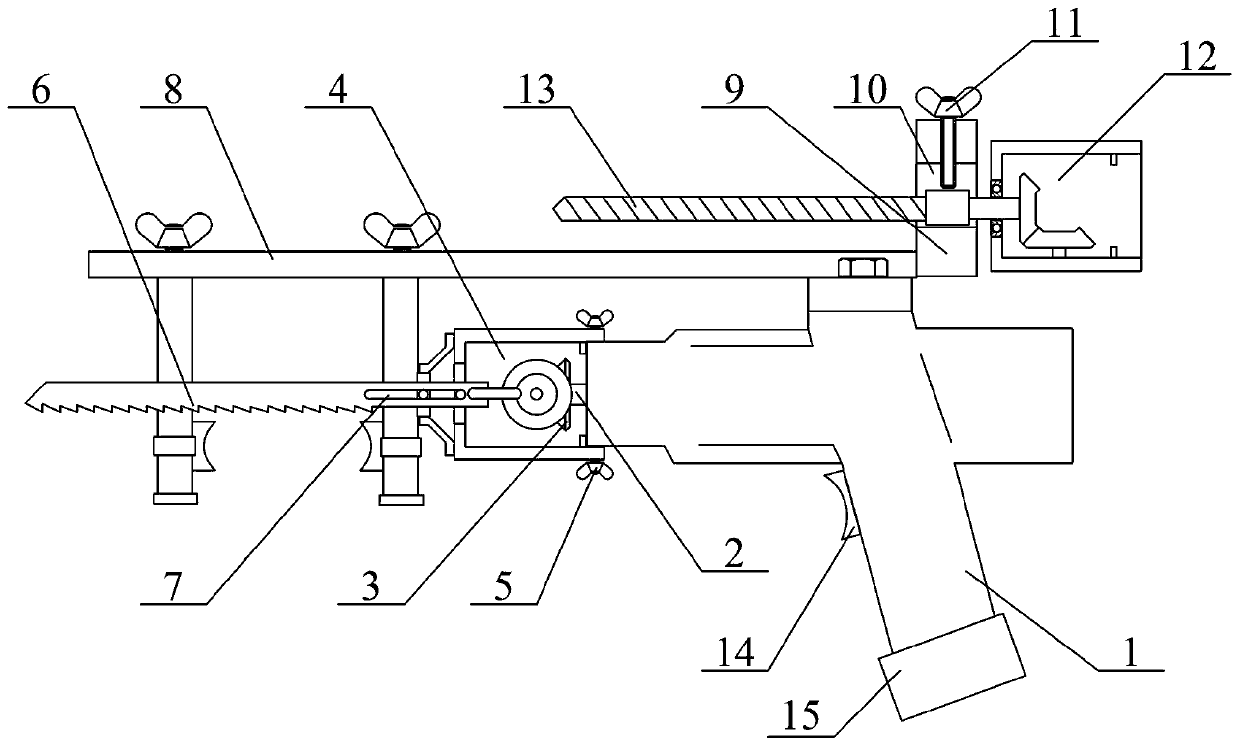
Multifunctional special orthopedic saw for orthopedic surgery
The invention provides a multifunctional special orthopedic saw for orthopedic surgery. The orthopedic saw comprises a motor shell, a starting motor, a driving bevel gear, a saw blade mounting frame structure, a fixing bolt, a medical saw blade, a sliding groove, a supporting frame structure, a containing frame, a containing hole, a wing-shaped bolt, a drill bit mounting frame structure, a medicaldrill bit, a switch and a rechargeable lithium battery, and the starting motor is mounted on the left portion of the inner side of the motor shell through bolts; the driving bevel gear is in bolted connection with an output shaft of the starting motor; the saw blade mounting frame structure is connected to the left portion of the motor shell in a sleeving mode; and the fixing bolt penetrates through the saw blade mounting frame structure and is connected to the motor shell. The orthopedic saw has the beneficial effects that: through the arrangement of a saw blade mounting shell, a rotary bevel gear and a connecting rod, rotary motion is conveniently converted into linear motion, the saw blade mounting frame structure can be detached to replace other medical tools, the application range iswidened, and the functions of the equipment are perfected.
Owner:LUOYANG ORTHOPEDIC TRAUMATOLOGICAL HOSPITAL
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com