Patents
Literature
85 results about "Minimally invasive spine surgery" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
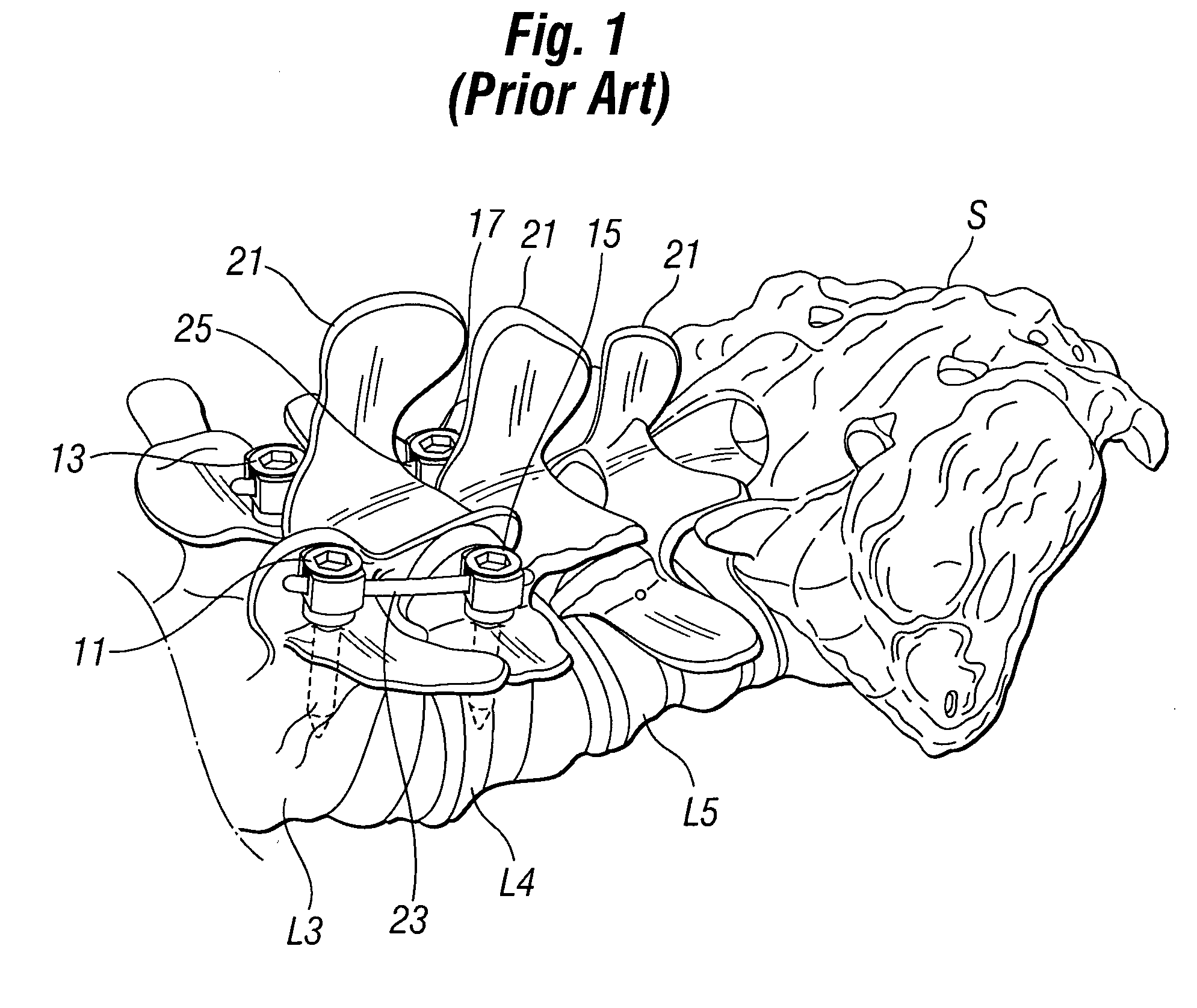
Minimally invasive spine surgery, also known as MISS, has no specific meaning or definition. Basically, it is marketing language that implies a lack of severe invasion, that may or may not be the case. The old style open-spine surgery for a simple disc problem used to require a 5-6 inch incision and a month in the hospital, 60 years ago. Miss techniques utilize more modern technology, advanced imaging techniques and special medical equipment to reduce tissue trauma, bleeding, radiation exposure, hospital stays and recovery by minimizing the size of the incision. Modern endoscopic procedures (see below) can be done through a 2 to 5 mm skin opening, with no internal cutting (truly minimally invasive). By contrast, procedures done with a microscope require skin openings of approximately one inch, or more. Since the one inch cut goes all the way down, it can only be called relatively MISS.
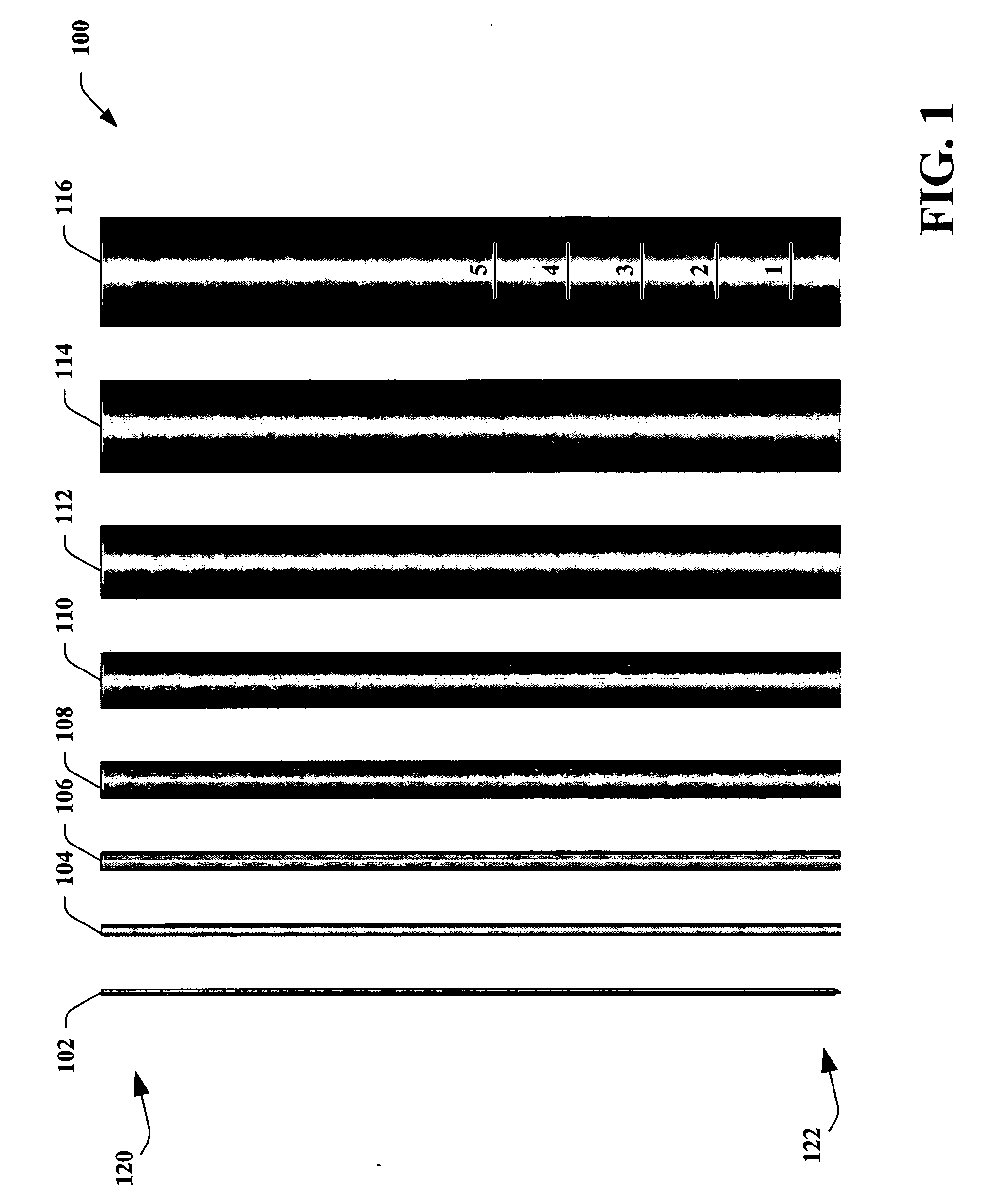
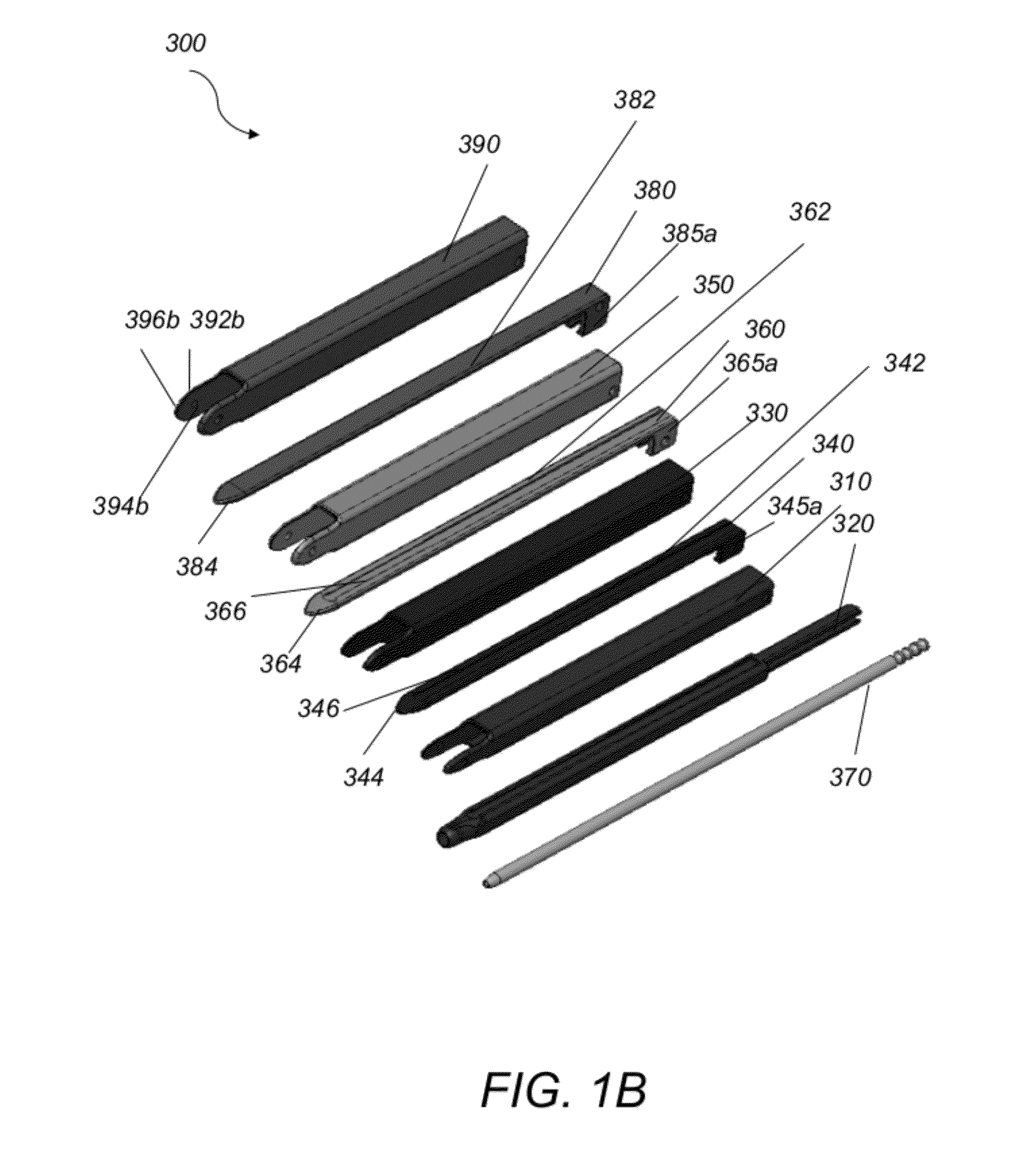
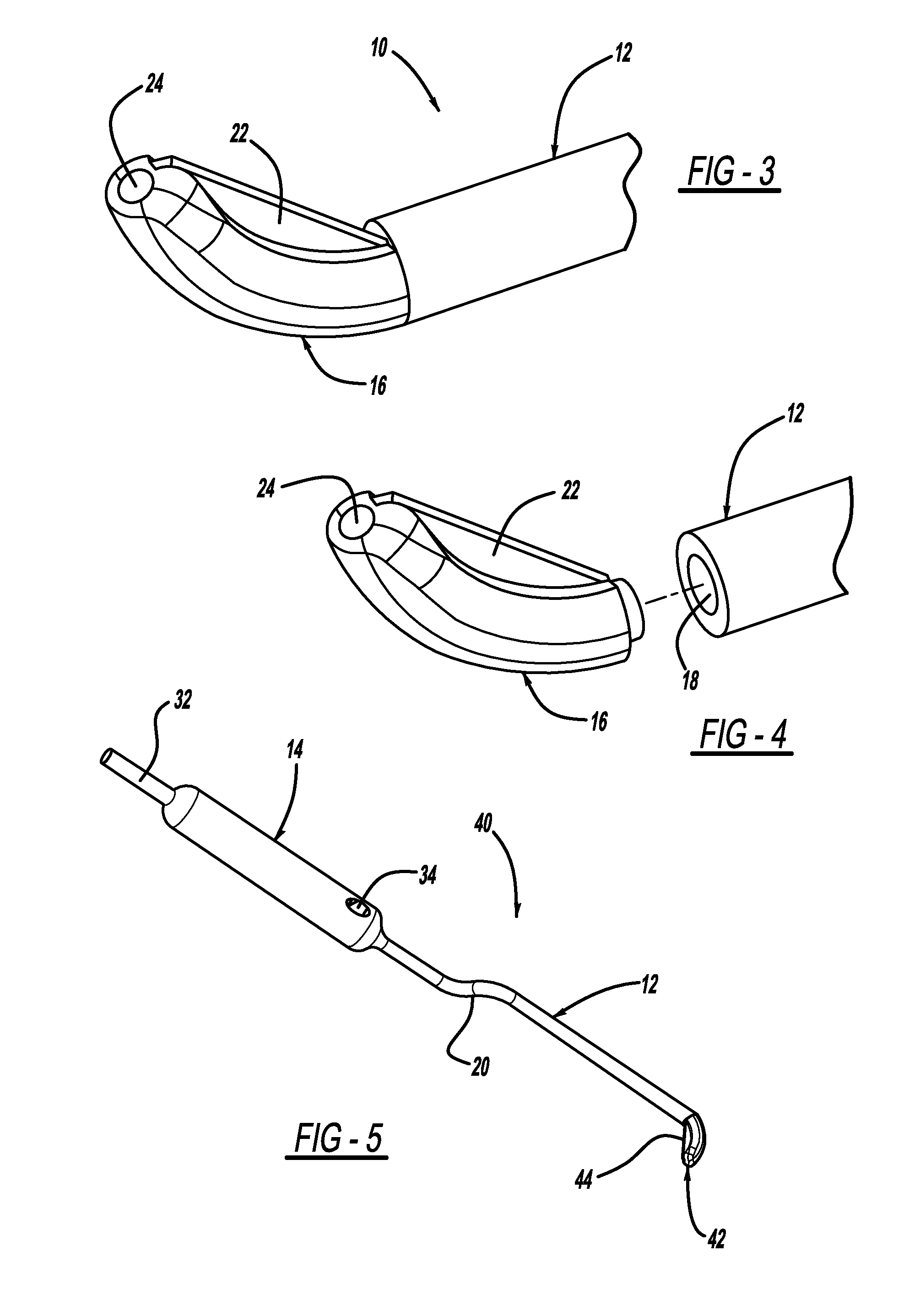
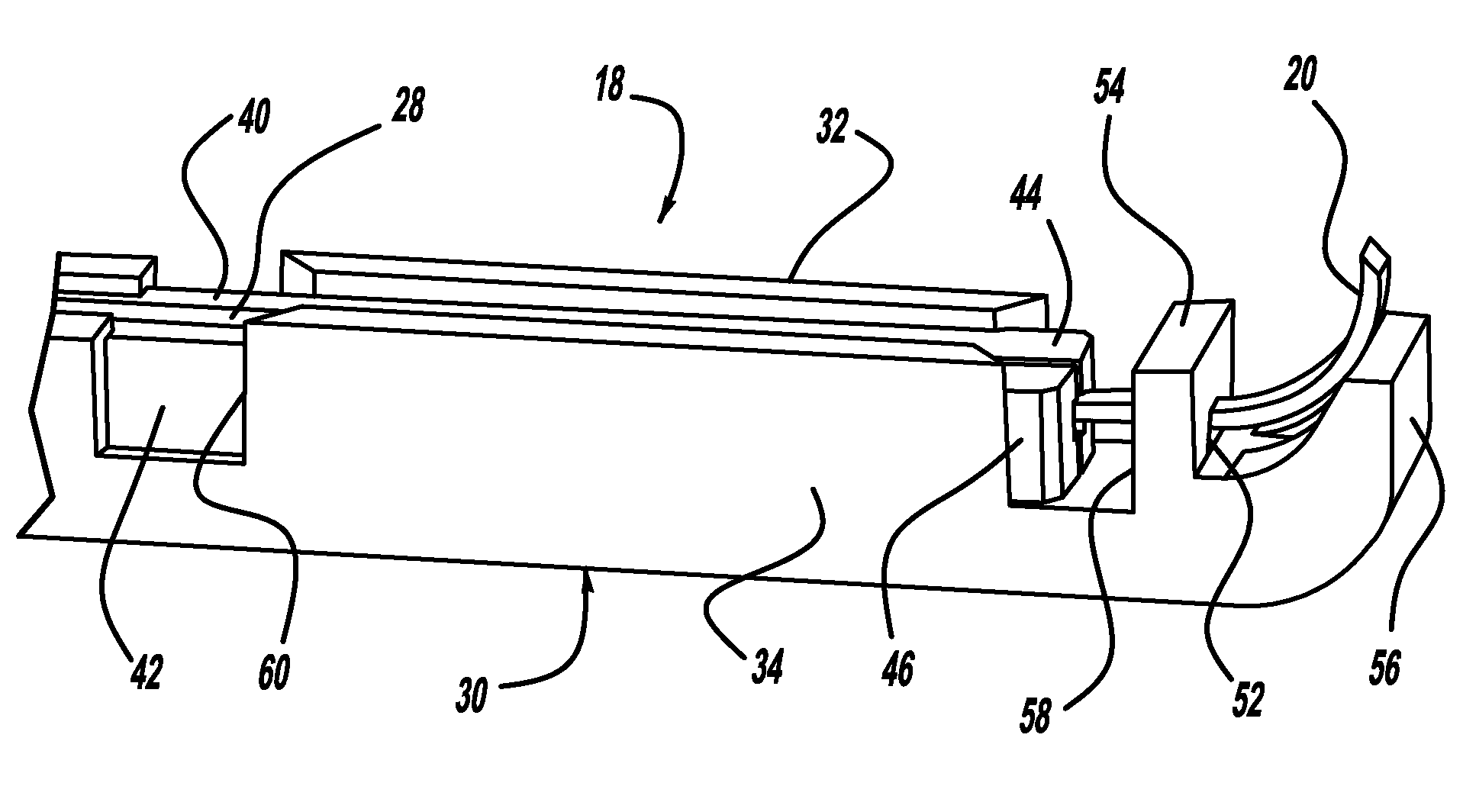
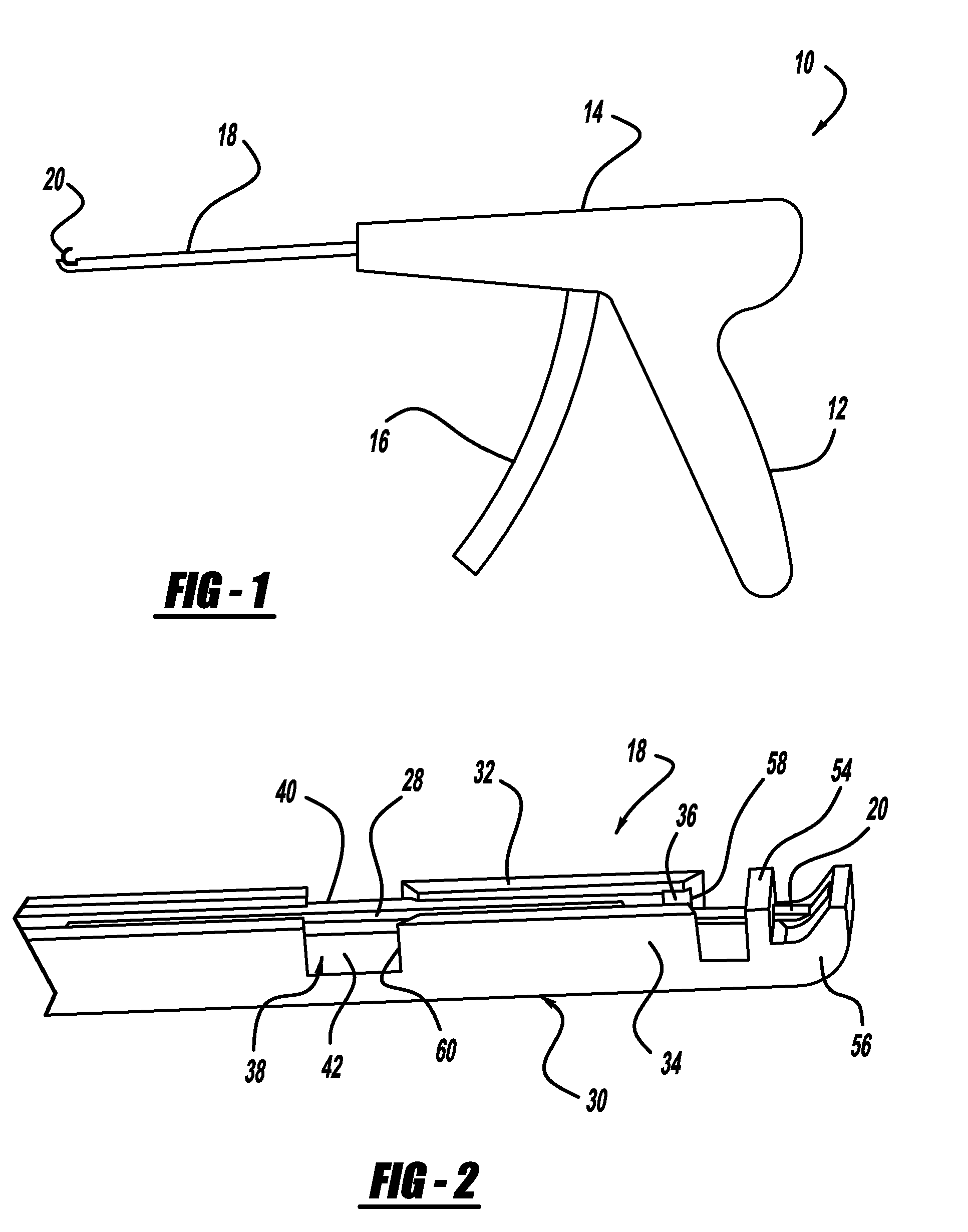
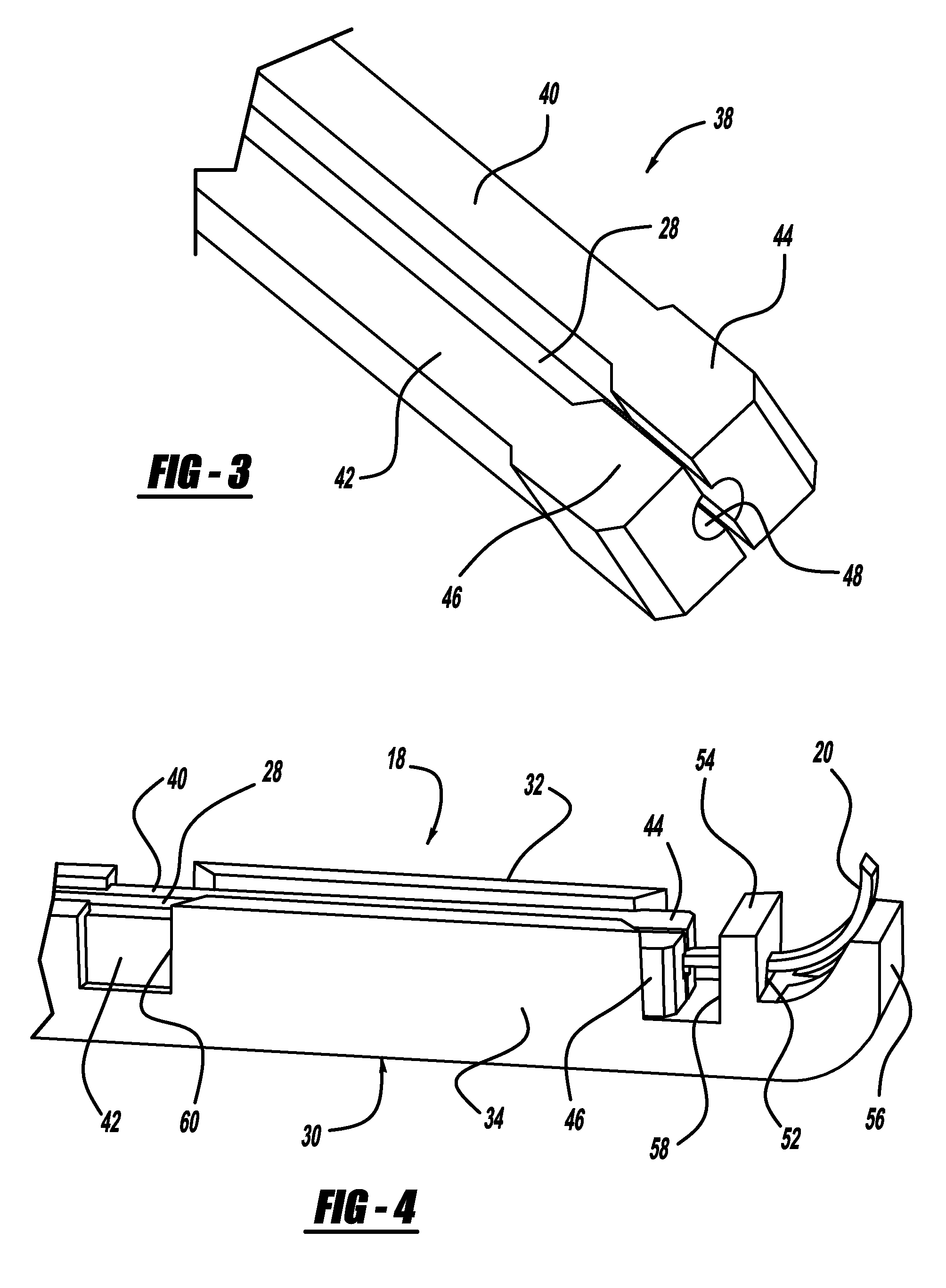
Systems and methods that facilitate minimally invasive spine surgery
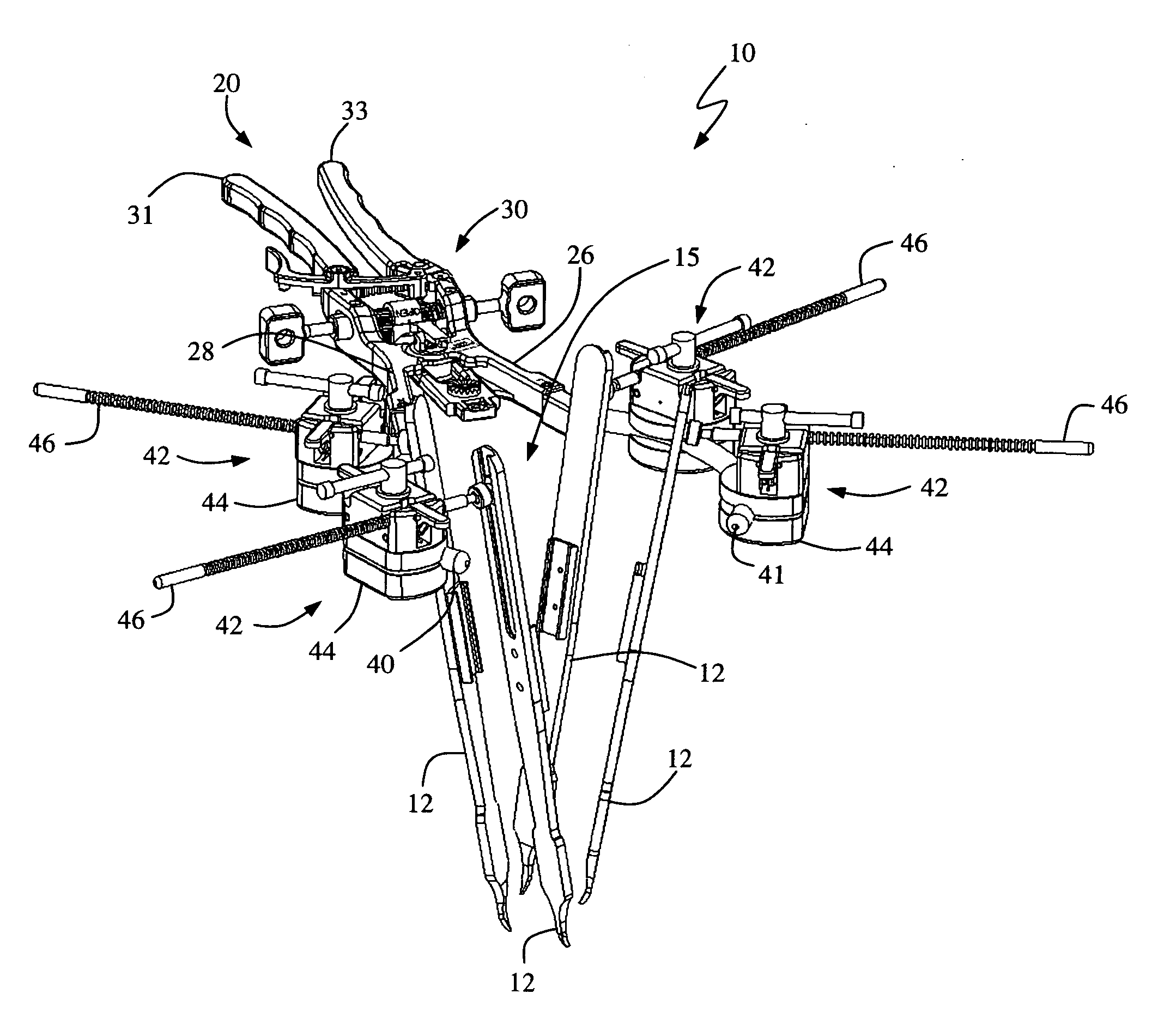
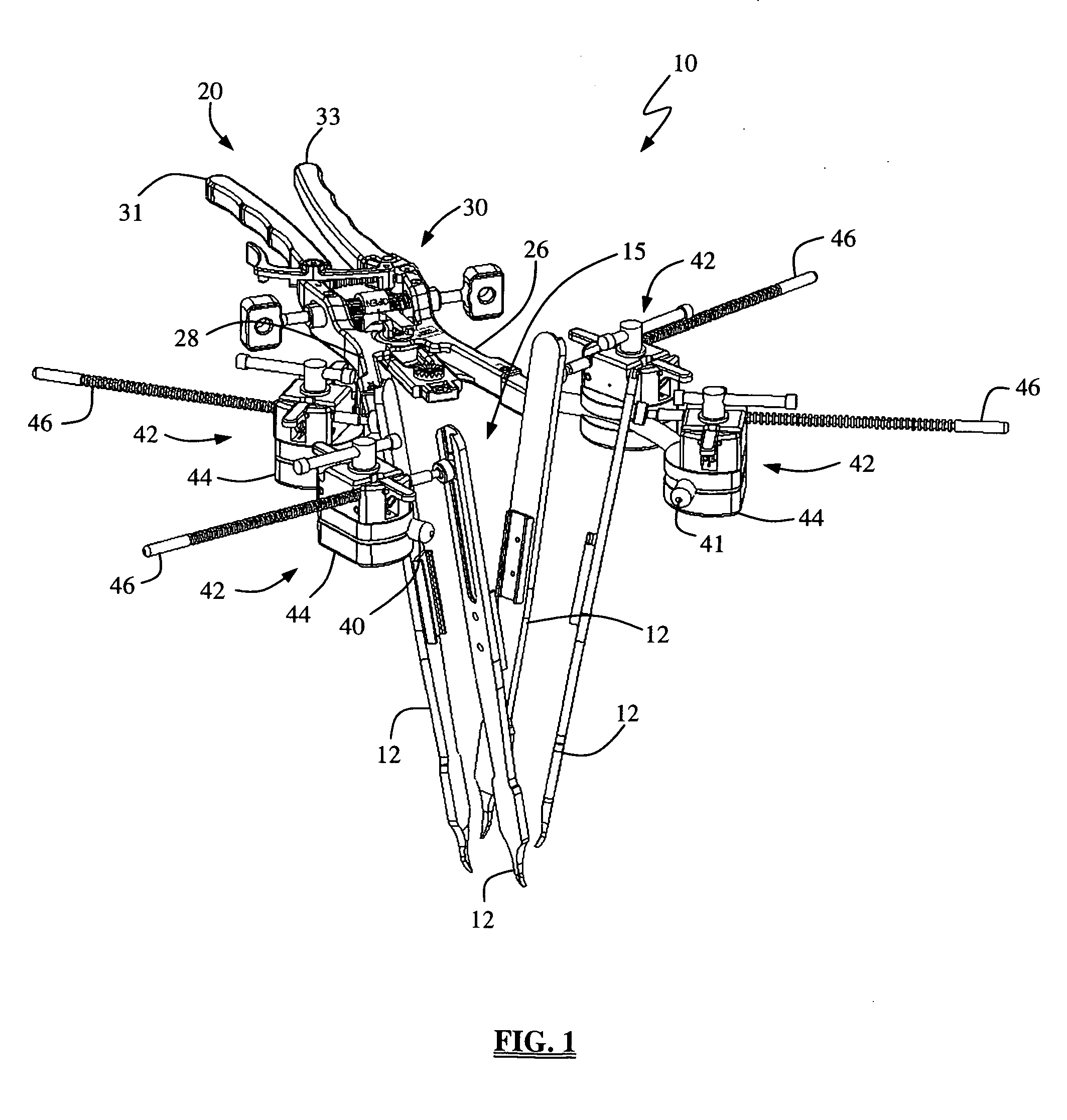
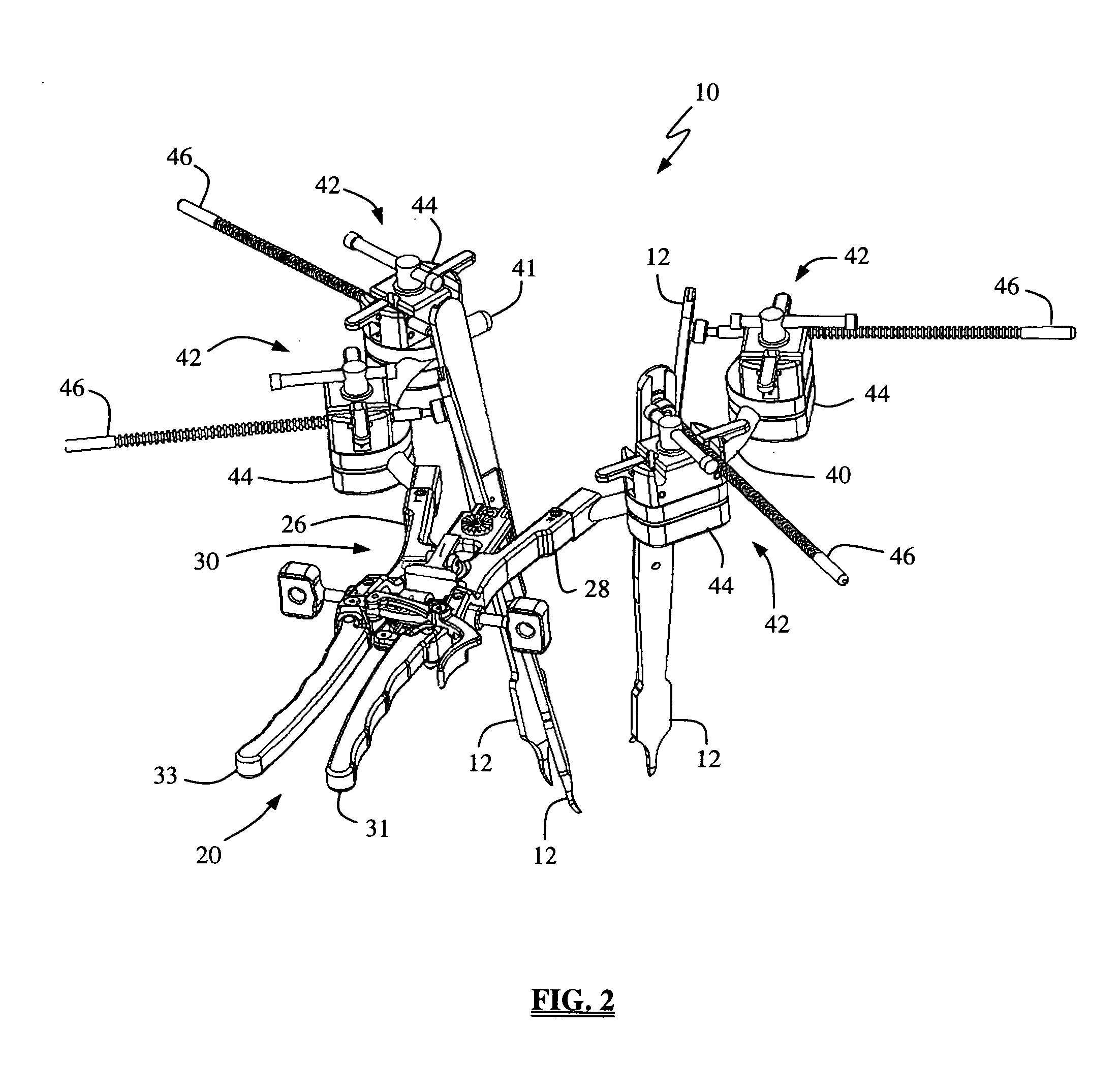
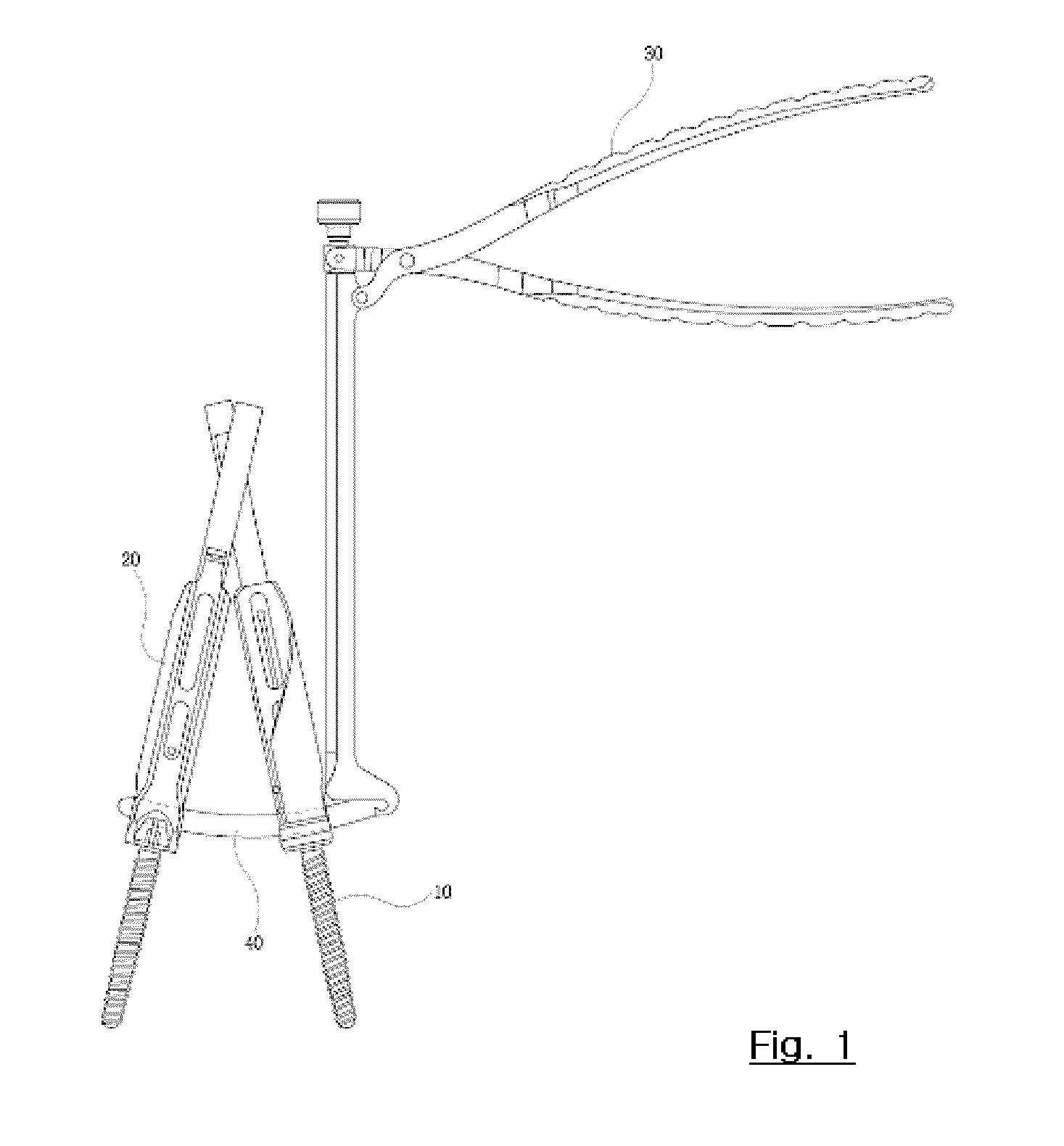
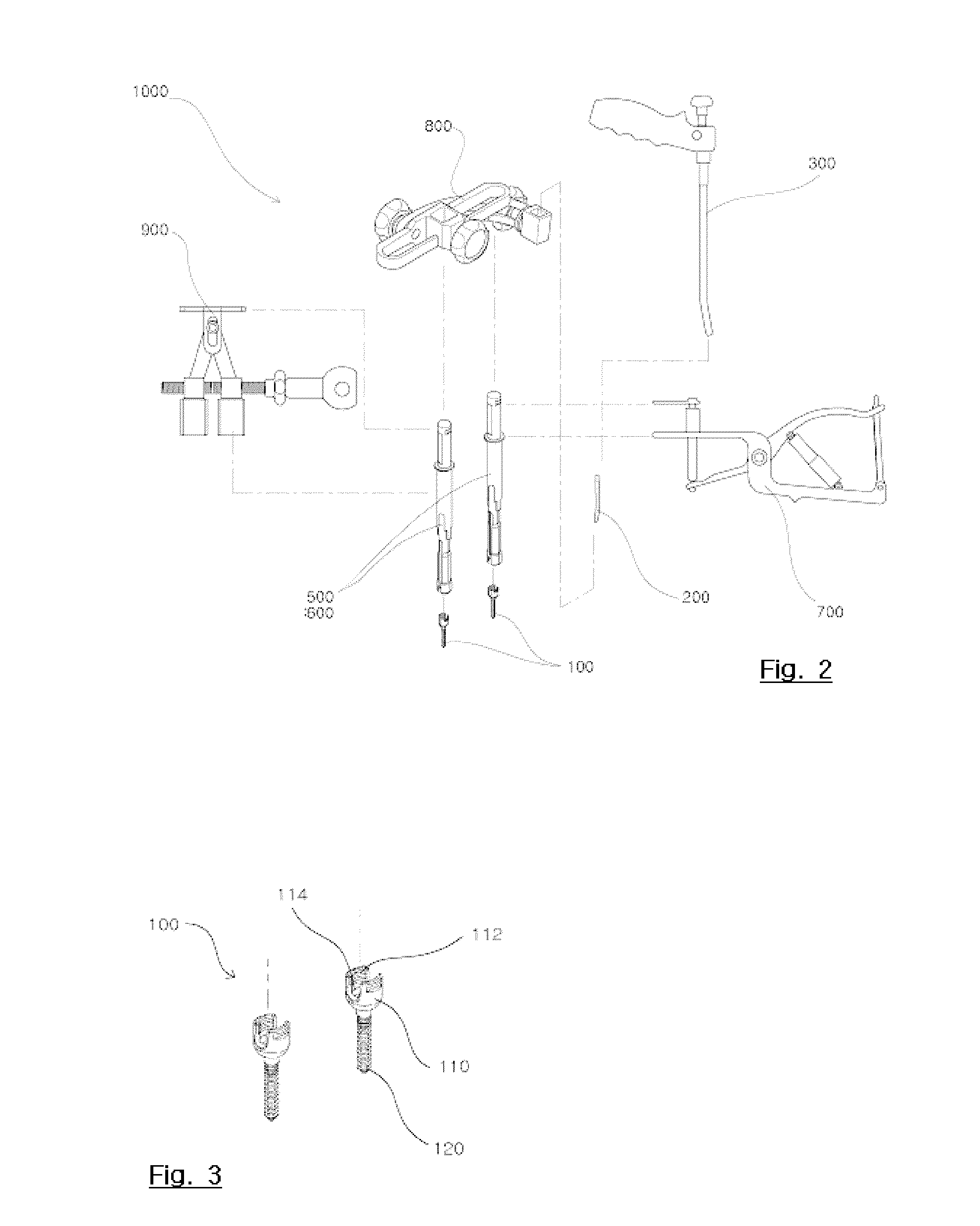
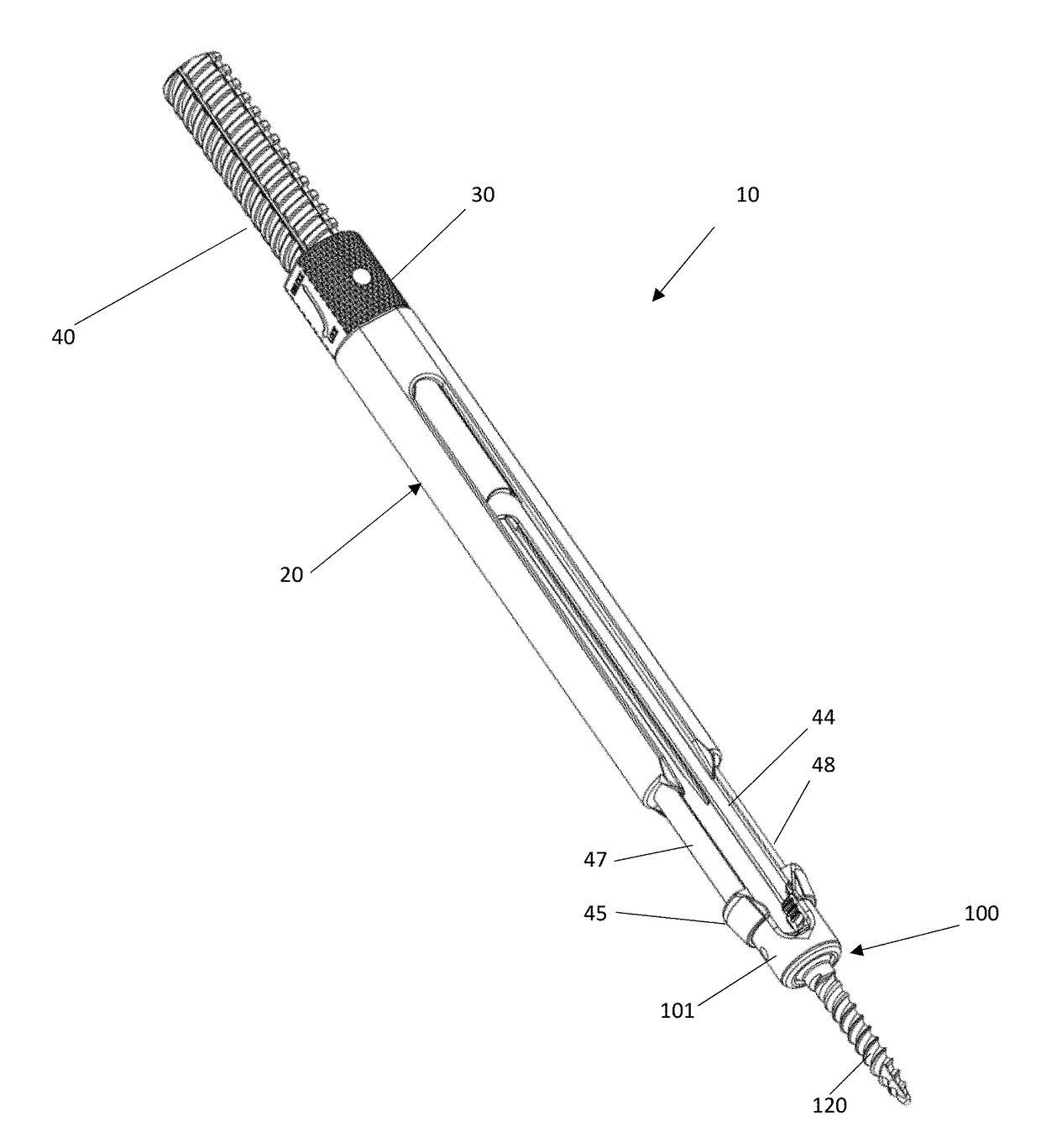
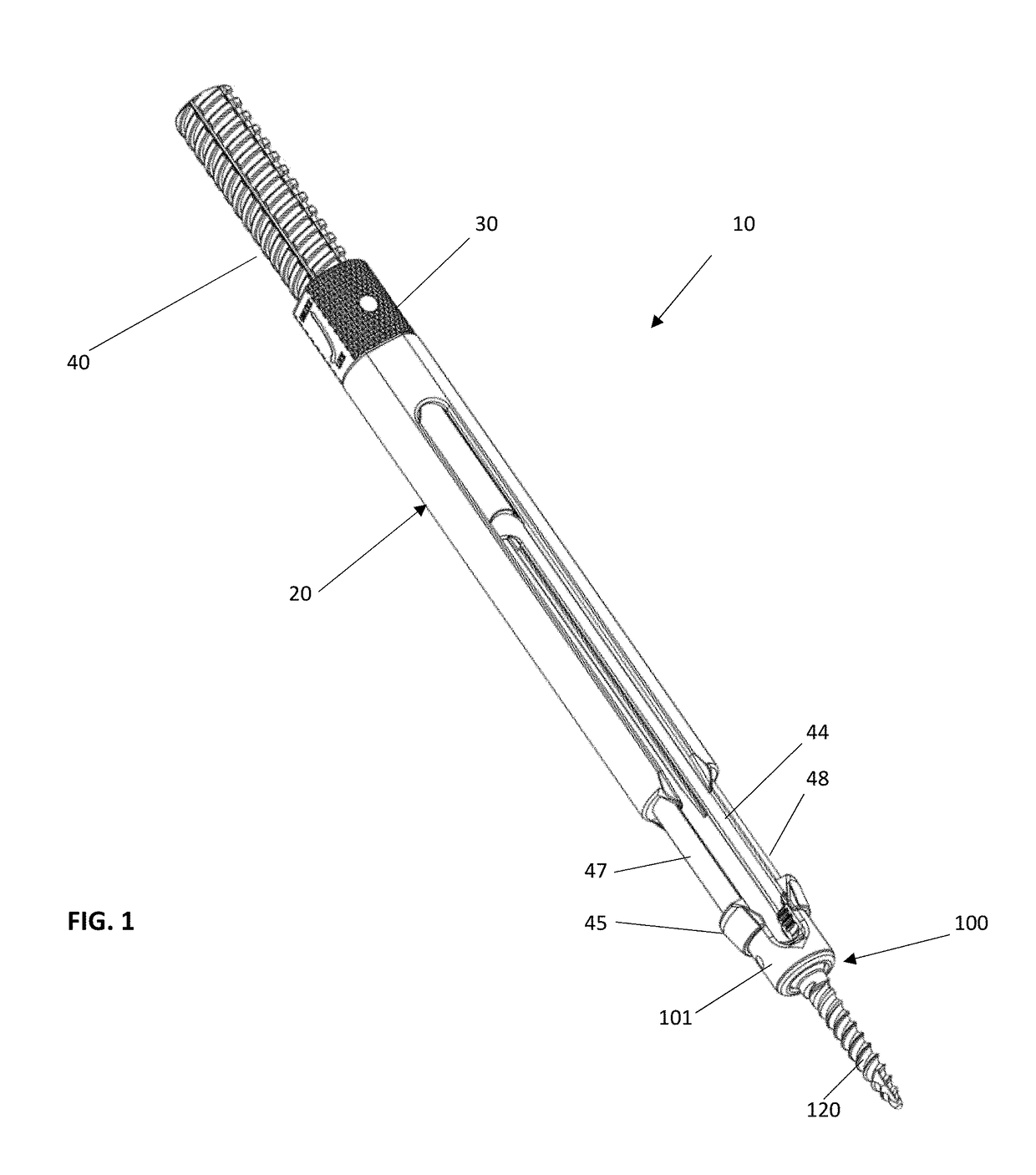
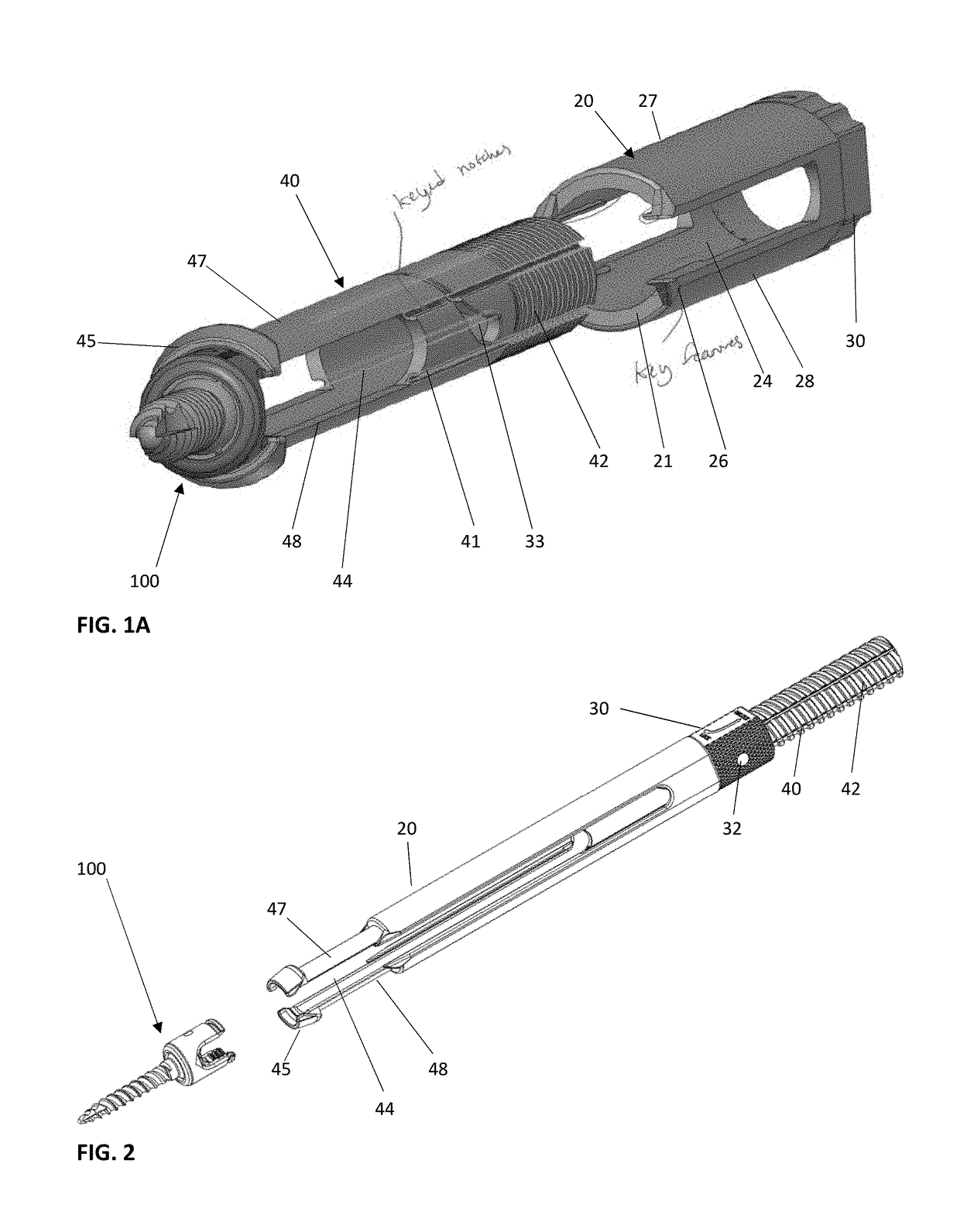
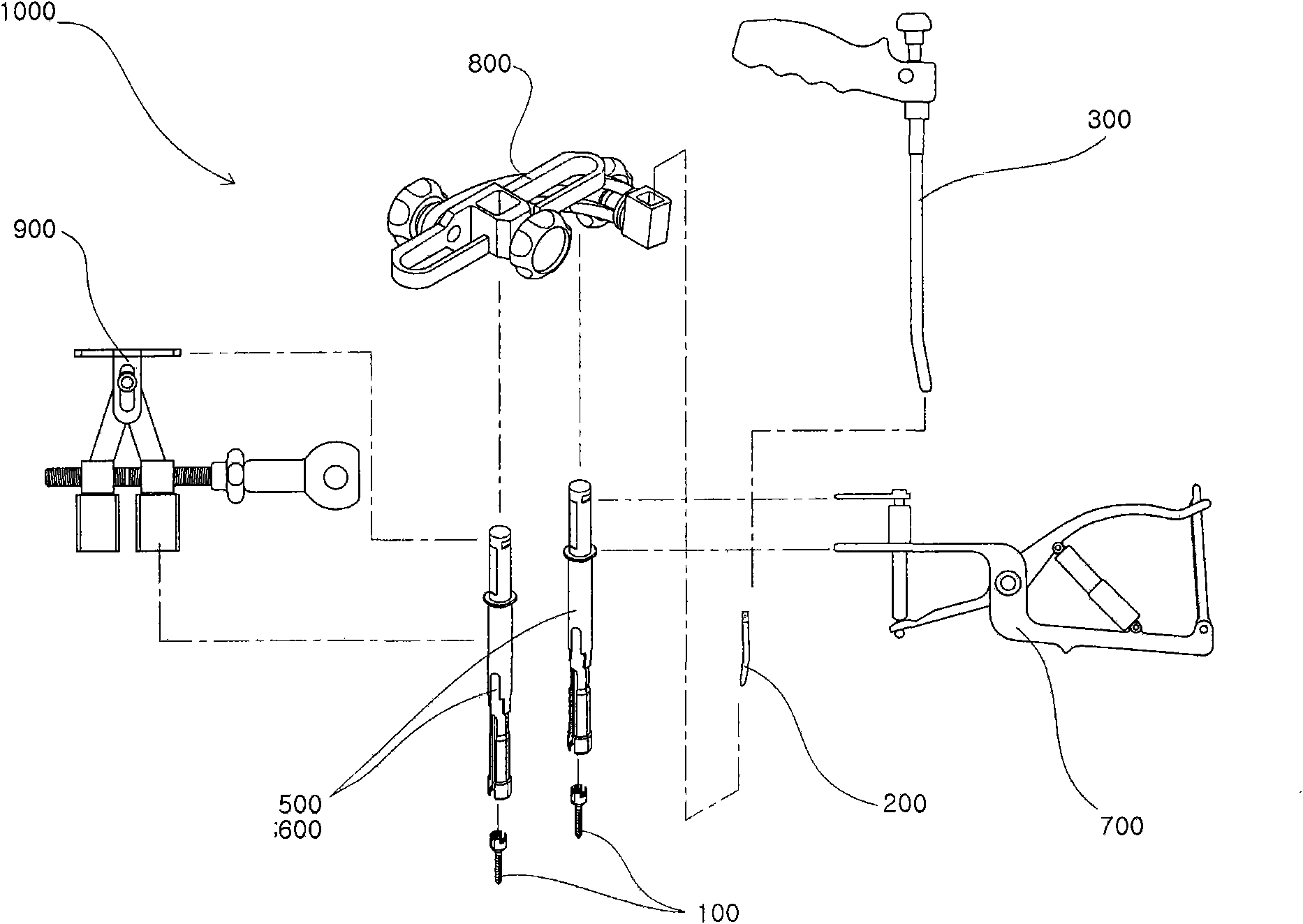
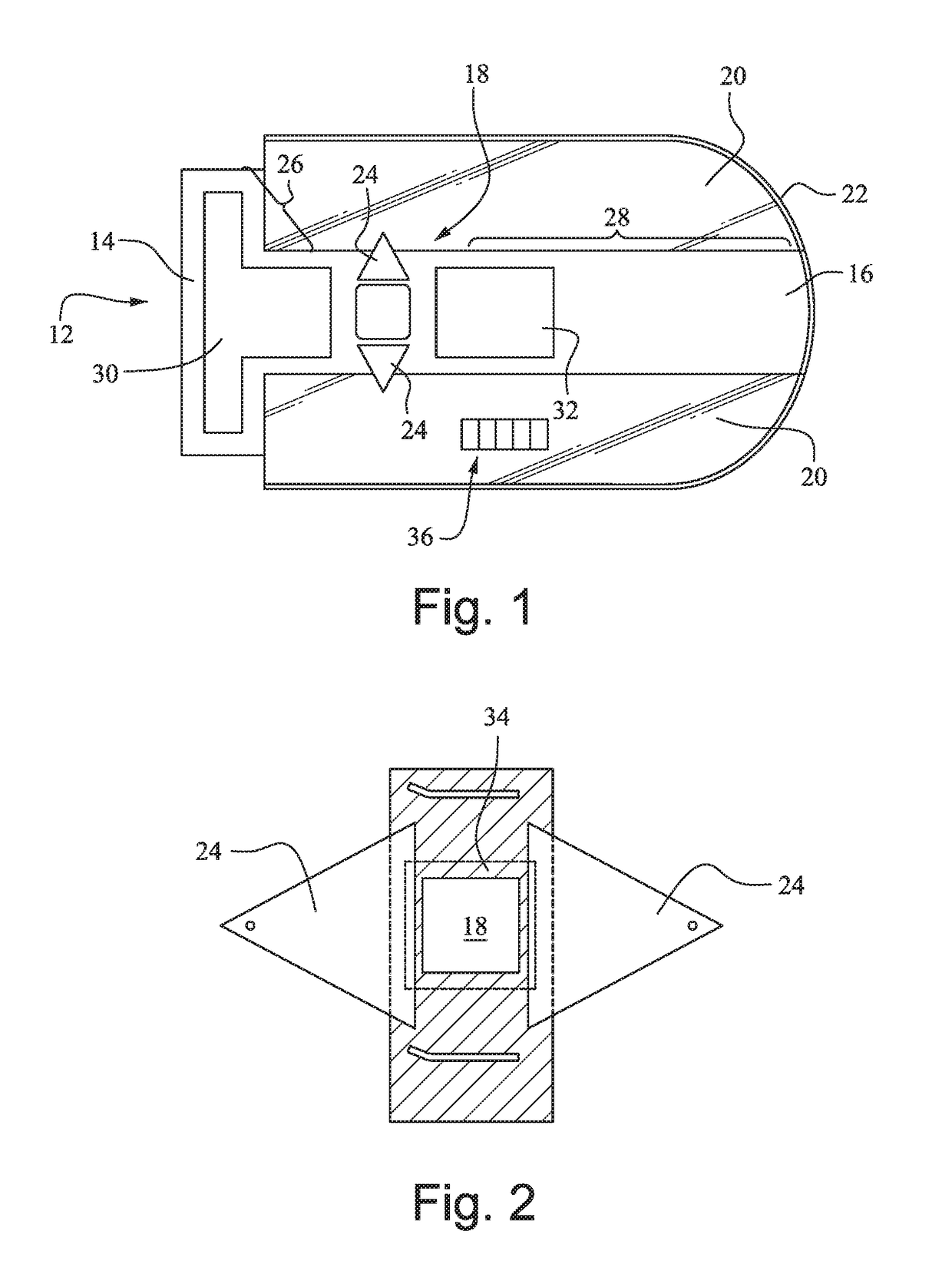
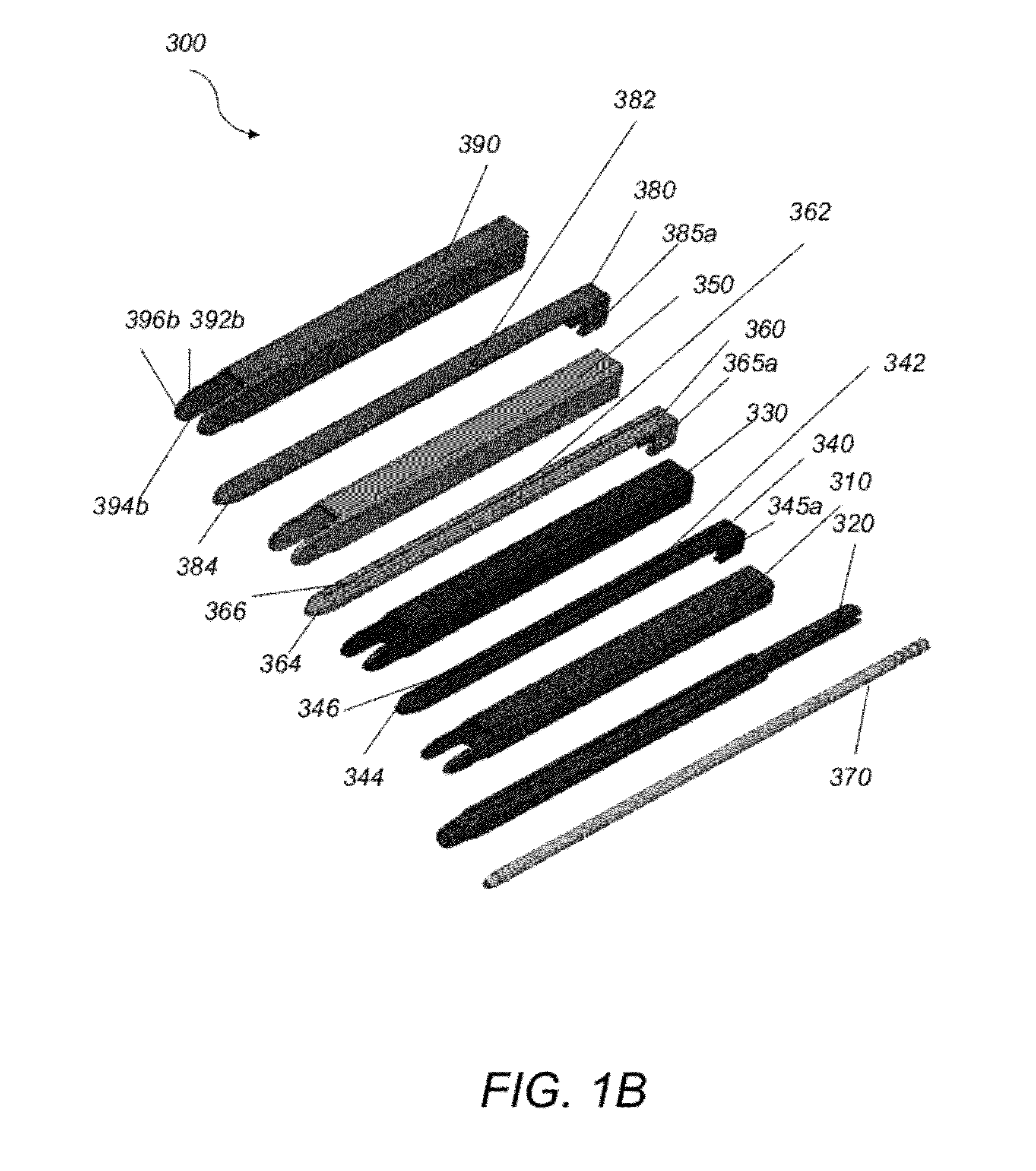
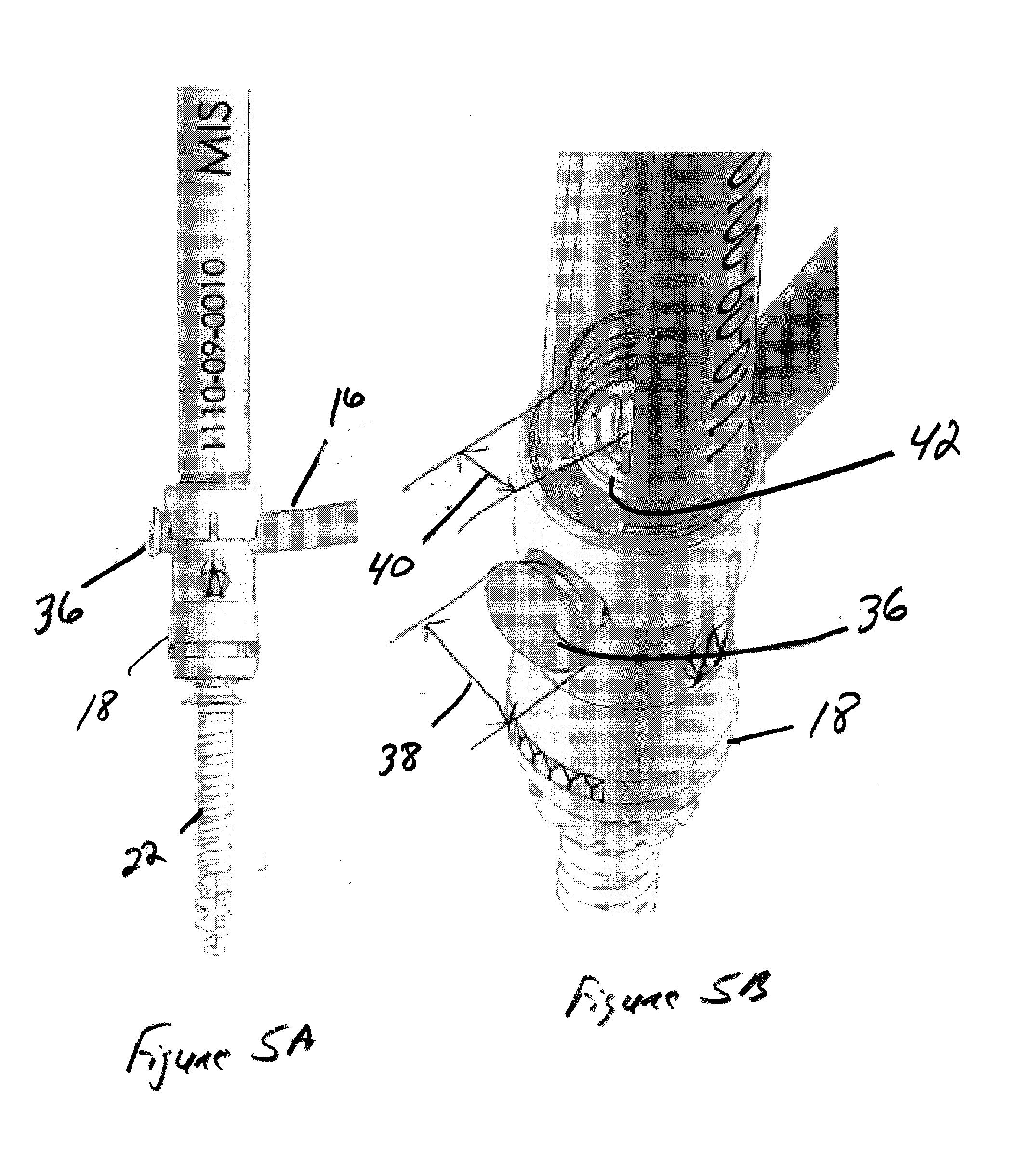
A system and method that facilitates minimally invasive spine surgery. The system includes screw preparation instruments that include a targeted guide with a laser attached to a fluoroscope, at least one polyaxial screw and rod guidance instruments that selectively insert the at least one polyaxial screw within the spine. The screw preparation instruments include an awl, a hand-held drill or tap, a ball-tipped probe, a cannulated depth gauge ruler, and a hexagonal screwdriver. Each screw preparation instrument have respective handles marked with a targeting guide oriented along respective central axes of the instruments. The rod guidance instruments include a rod with a tapered tip, a T-handle rod holder, a T-handle alignment guide, an alignment marker sleeve, a flexible alignment marker with a polyaxial head, and a template rod.
Owner:STRYKER EURO OPERATIONS HLDG LLC
Spinal surgery system and method
InactiveUS20060036241A1Small sizeEasy to fixInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsSpinal columnSpinal cord
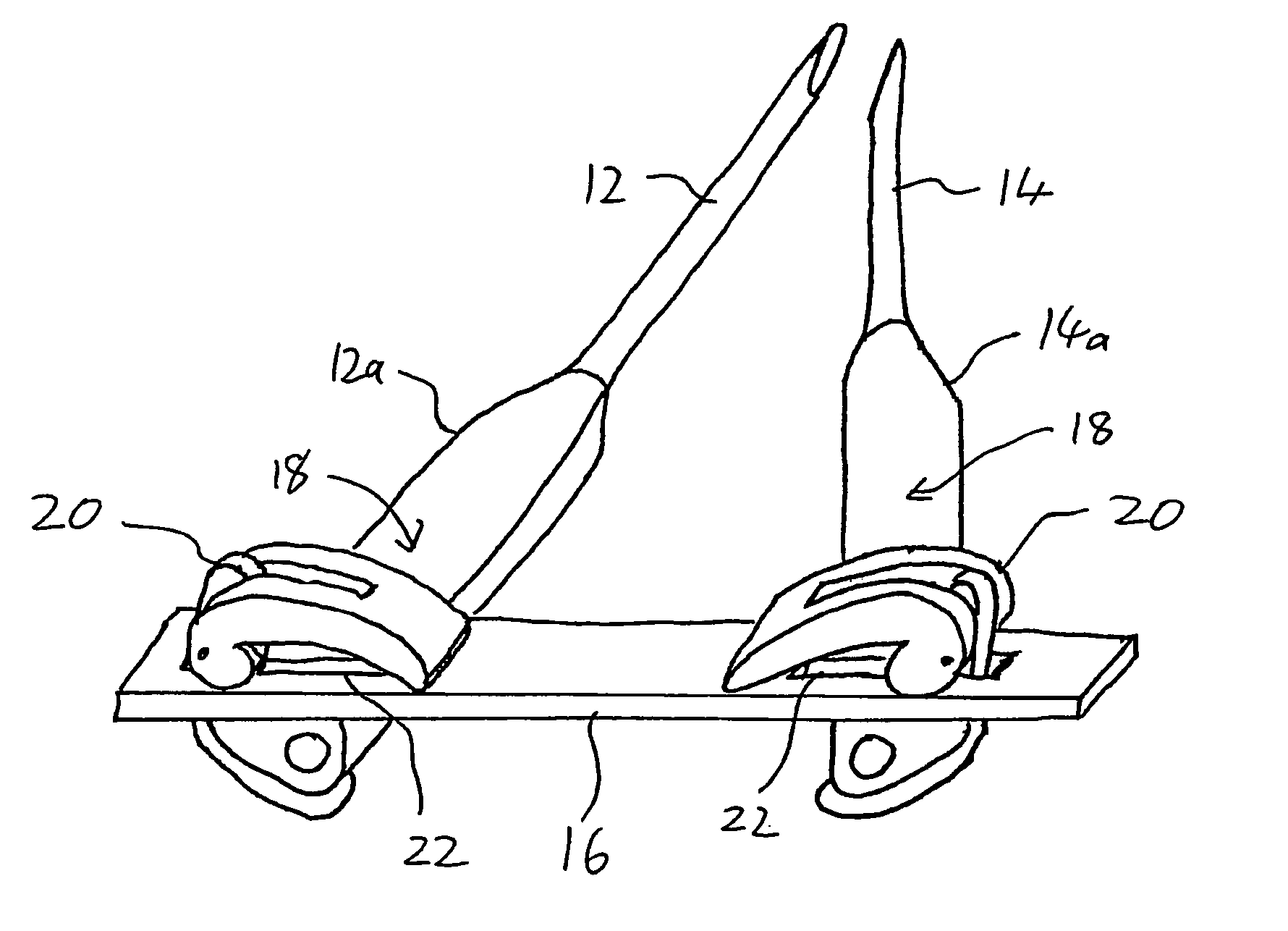
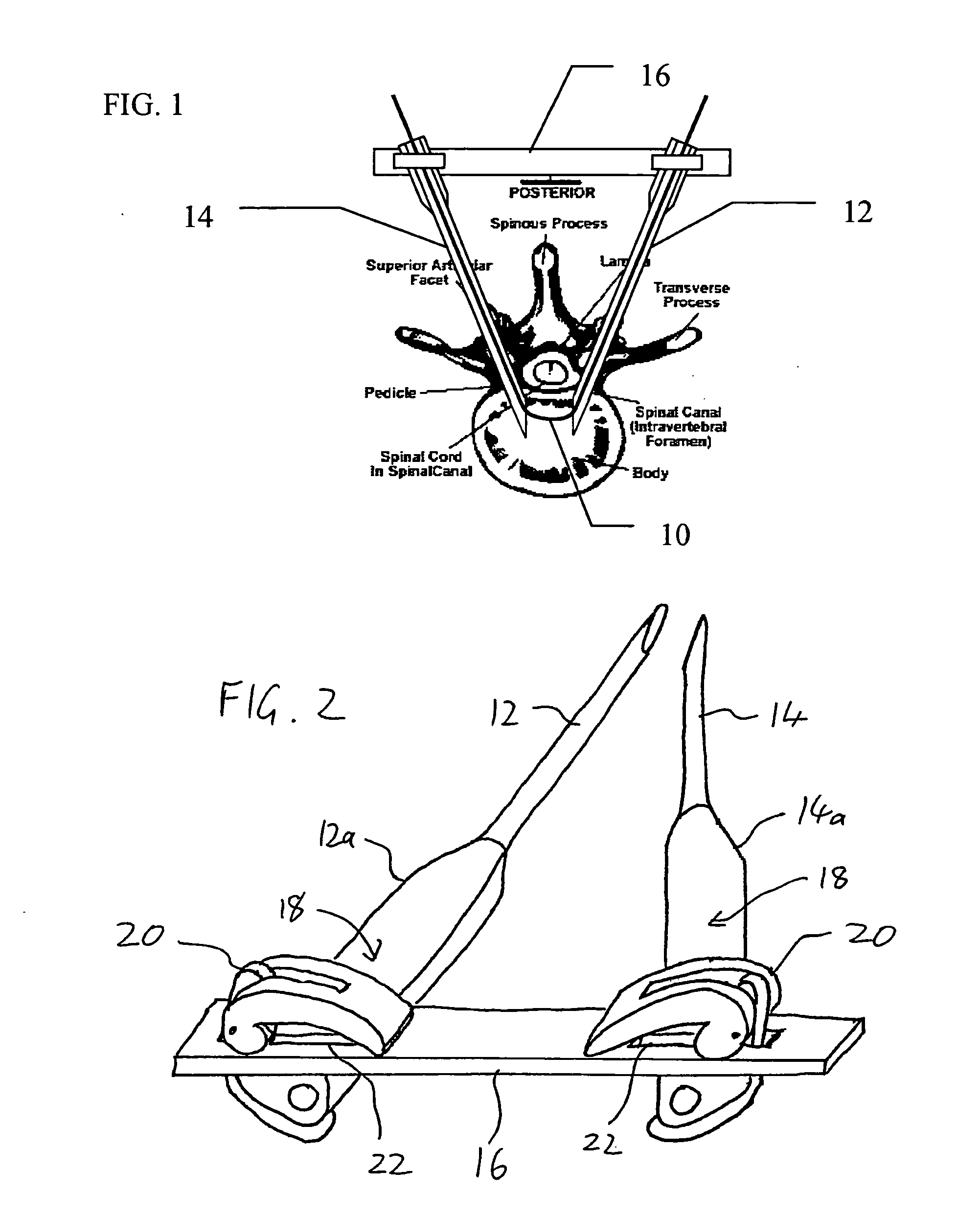
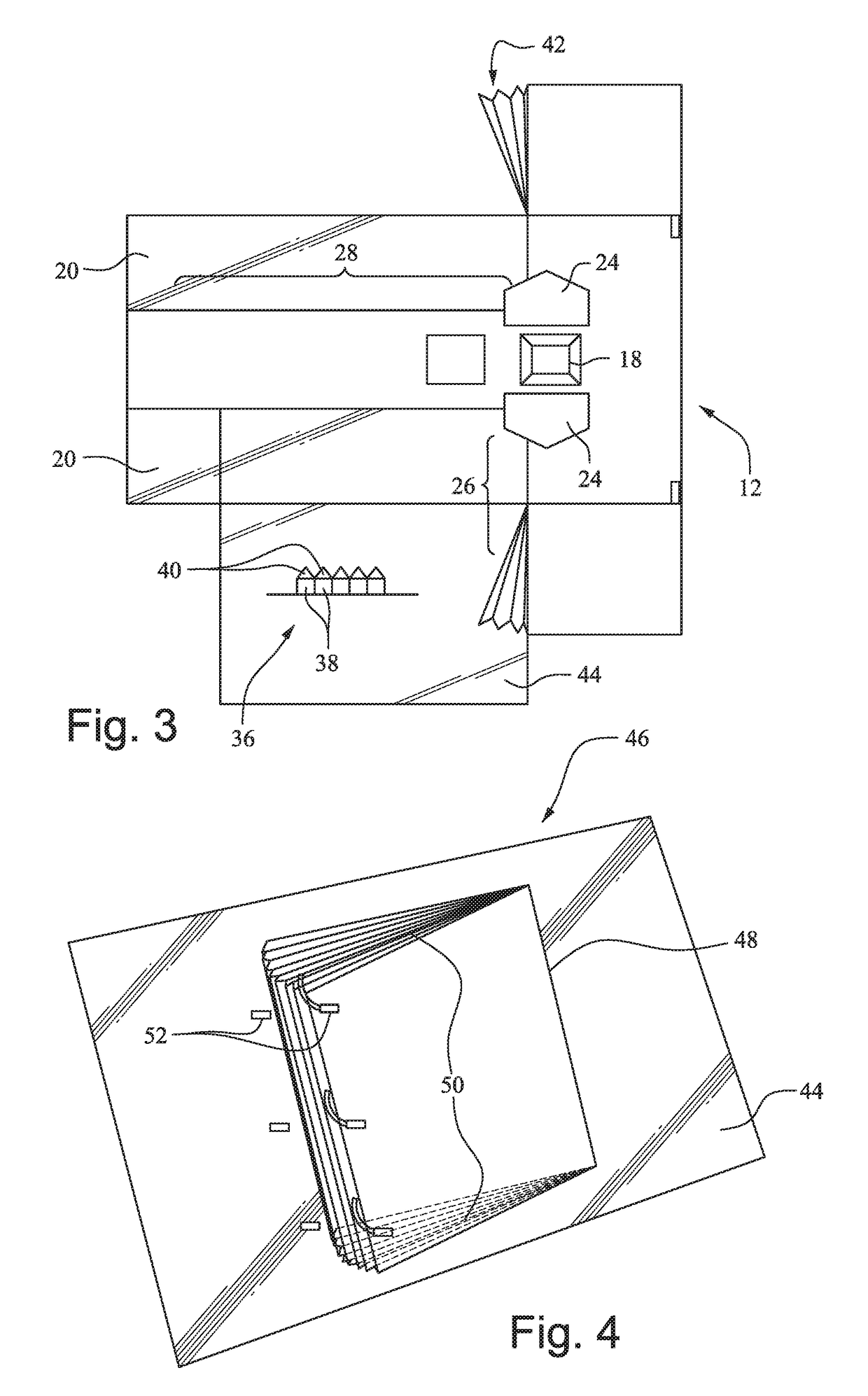
Apparatus and method for minimally invasive spinal surgery employs an elongated flexible guide element inserted so as to pass in through a first lateral posterior incision, through the spinal column anterior to the spinal cord, and out through a second lateral posterior incision contralateral to said first incision. The guide element is used to guide various elements to a desired position within the spinal column as part of the surgical procedure. Preferably, two hollow rigid tubes rigidly coupled outside the body in converging relation are used to define a working gap within the spinal column through which the guide element passes. This provides a platform for manipulation of tissues and introduction of implants anterior to the spinal cord. Procedures described include reinforcement of a degenerative intervertebral disc and restoration of a damaged vertebral body.
Owner:SIEGAL TZONY
Directional soft tissue dilator and docking pin with integrated light source for optimization of retractor placement in minimally invasive spine surgery
InactiveUS20100114147A1Facilitate preferentially dilatePreferential dilationSurgeryEndoscopesDilatorSurgical procedures
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF TOLEDO
Surgical access system and related methods
A retractor-based access system for performing minimally invasive spine surgery via an anterior approach. The anterior access system and related methods of the present invention involve a plurality of retractor blades under the control of a single retractor handle apparatus.
Owner:NUVASIVE
One step entry pedicular preparation device and disc access system
ActiveUS8236006B2Limit distanceQuicker procedureSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisBone structureIntervertebral disc
A one step entry pedicular preparation device works well with Minimal Invasive Spine Surgery (MISS) to facilitating such approach. A related intervertebral disc access system and pedicle screw compatible with the systems is also illustrated. The systems include a manipulator having a bar handle and main body with main barrel bore a pedicle dart having a proximal tip end and a second distal open end selectably attachable to the manipulator using a variety of interconnect configurations, both of which work in conjunction with a guide pin. The pedicle darts can be made of any material, disposable or re-usable and can be utilized for a variety of purposes, including bone structure formation for faster conventional pedicle screw insertion with precision and vertebra fixation.
Owner:LIFE SPINE INC
Instruments and Method of Use for Minimally Invasive Spine Surgery in Interspine Space Through Only One Side
InactiveUS20100010548A1Reduce pressureSimple technologyInternal osteosythesisSurgical needlesSpinal columnIntervertebral disc
The present disclosure provides a save and single method, as well as a new instrumentation to improve the technique of the minimally invasive spine surgery in only one side with the use of hooks and a new interspinal device of improved stabilization which is placed to decrease the pressure on the affected disk, fastening the intervertebral space and achieving the segmentary stability.
Owner:HERMIDA OCHOA ELIAS HUMBERTO
Method and apparatus for minimally invasive spine surgery
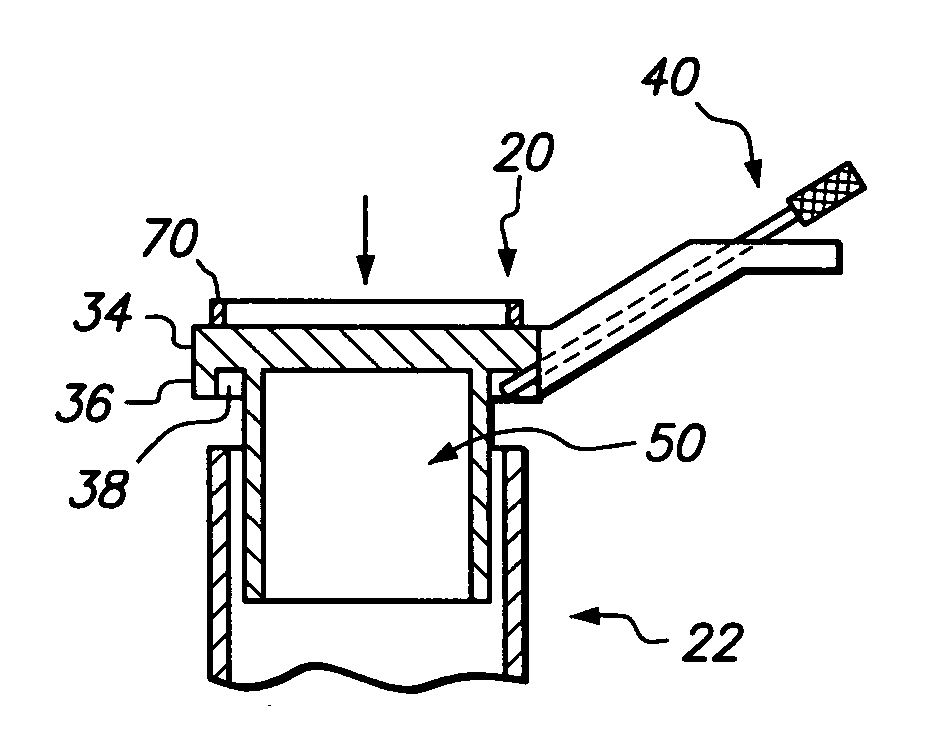
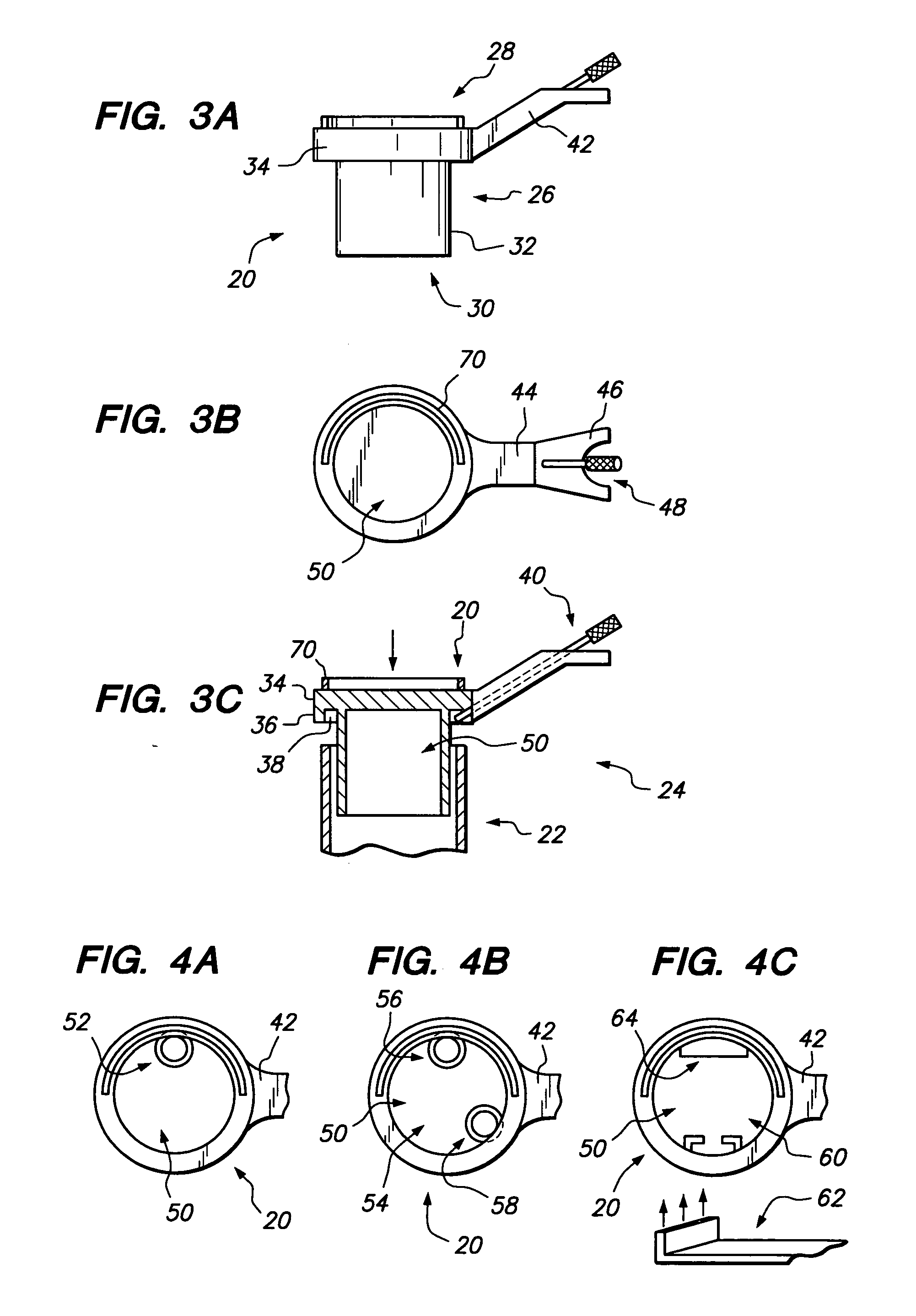
An access port provides access through tissue to a surgical site or field, such as at the spine, in a minimally invasive manner. In one configuration, the access port is defined by a cannula-style retractor having a passage therethrough, a first end for insertion through tissue to the surgical site and a second end for positioning external therefrom. An access controller is associated with the second end of the retractor, the access controller selectively lockable to the retractor and including a passage leading to the retractor passage. The access controller may be used to selectively move the retractor and thus change the access path defined by the access port to the surgical site. The access controller may include features such as mirrors, light sources and retractor holders. The access port permits a user to clearly view and access the surgical field, including areas medial thereto, in a minimally invasive manner.
Owner:PRUSMACK CHAD J
Rod holder and minimally invasive spine surgery system using the same
InactiveUS20110077690A1Easy to operateEasy to insertInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsSurgical operationSpinal column
A rod holder configured to operate in a two-stage loading manner allows a rod to be easily received. A minimally invasive system for spinal surgical operation allows a rod to be more accurately and stably received to a pedicle screw inserted into a vertebra by using the rod holder, a rod guide and a rod guide holder. The rod holder may control a rod with three stages: a first loading stage for moving back and fixing a loading unit to fixedly grip the rod; a second loading stage for rotatably gripping the rod; and a rod mounting stage for separating the rod from the rod holder. The spine surgery system includes a pair of rod guides connected to upper ends of a pair of pedicle screws to form a moving path of the rod; a rod holder; and a rod guide holder for defining an insertion path.
Owner:GS MEDICAL CO LTD
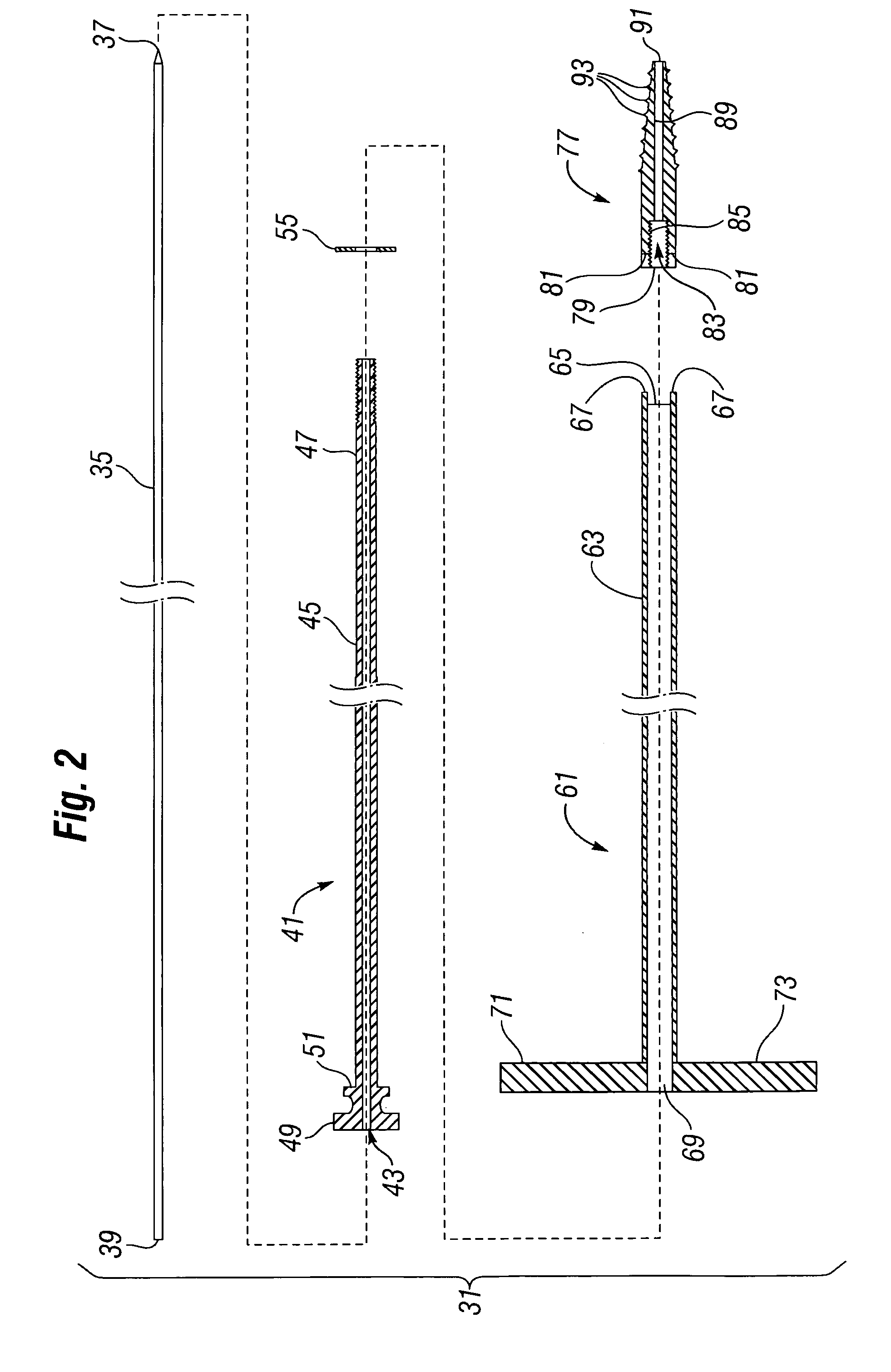
Methods, tools and devices for percutaneous access in minimally invasive spinal surgeries
A cannula assembly for providing percutaneous access in minimally invasive spinal surgeries, includes an outer cannula, a nerve probe dilator and a multistage dilator system comprising a first dilator, a second dilator, a third dilator and a fourth dilator. The outer cannula and the dilators are slidable relative to each other and are arranged sequentially so that the fourth dilator surrounds the nerve probe dilator, the third dilator slides over a surface of the fourth dilator, the second dilator slides over a surface of the third dilator, the first dilator slides over a surface of the second dilator, and the outer cannula surrounds the first dilator.
Owner:KIC VENTURES LLC
Systems and methods that facilitate minimally invasive spine surgery
A system and method that facilitates minimally invasive spine surgery. The system includes screw preparation instruments that include a targeted guide with a laser attached to a fluoroscope, at least one polyaxial screw and rod guidance instruments that selectively insert the at least one polyaxial screw within the spine. The screw preparation instruments include an awl, a hand-held drill or tap, a ball-tipped probe, a cannulated depth gauge ruler, and a hexagonal screwdriver. Each screw preparation instrument have respective handles marked with a targeting guide oriented along respective central axes of the instruments. The rod guidance instruments include a rod with a tapered tip, a T-handle rod holder, a T-handle alignment guide, an alignment marker sleeve, a flexible alignment marker with a polyaxial head, and a template rod.
Owner:STRYKER EURO OPERATIONS HLDG LLC
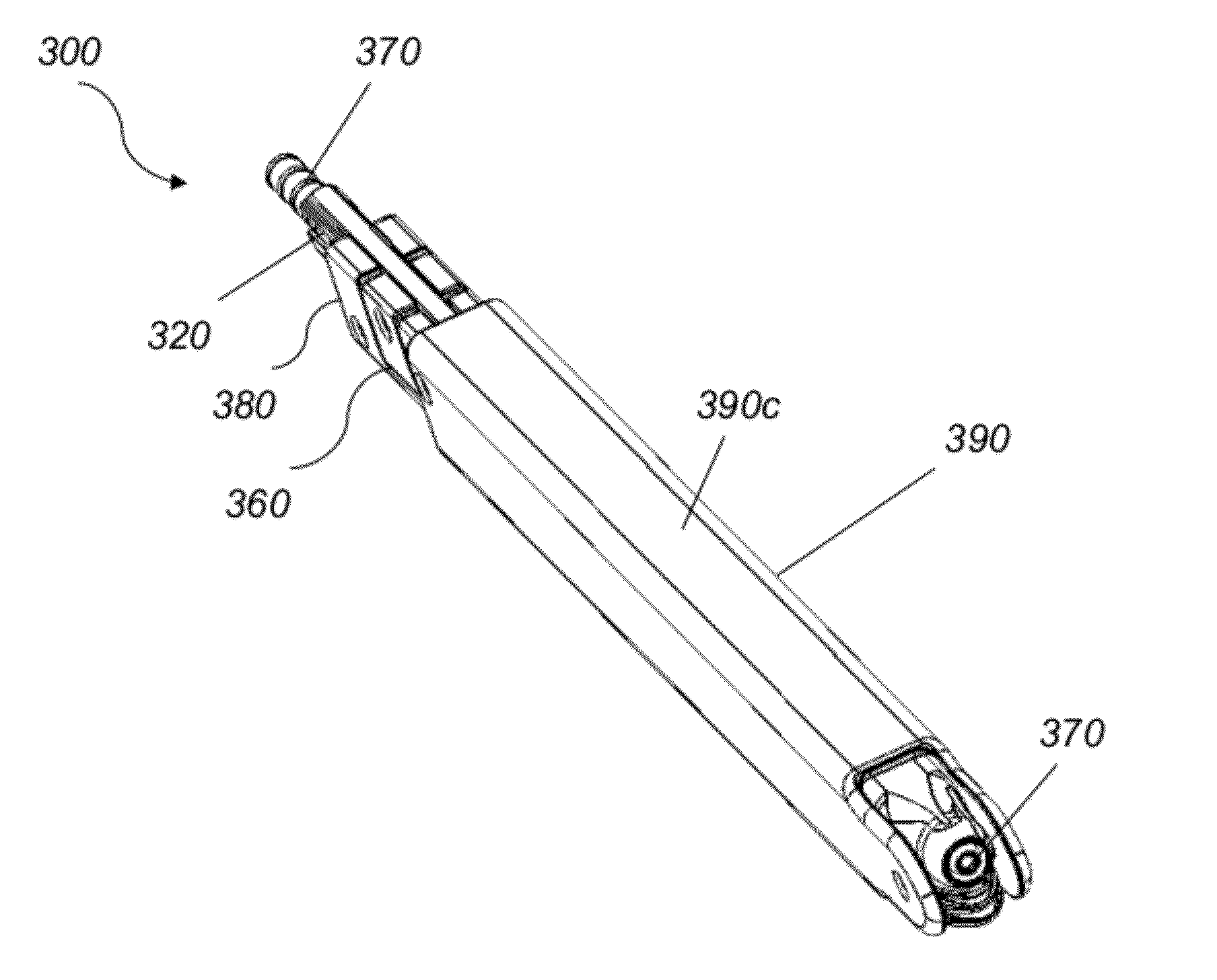
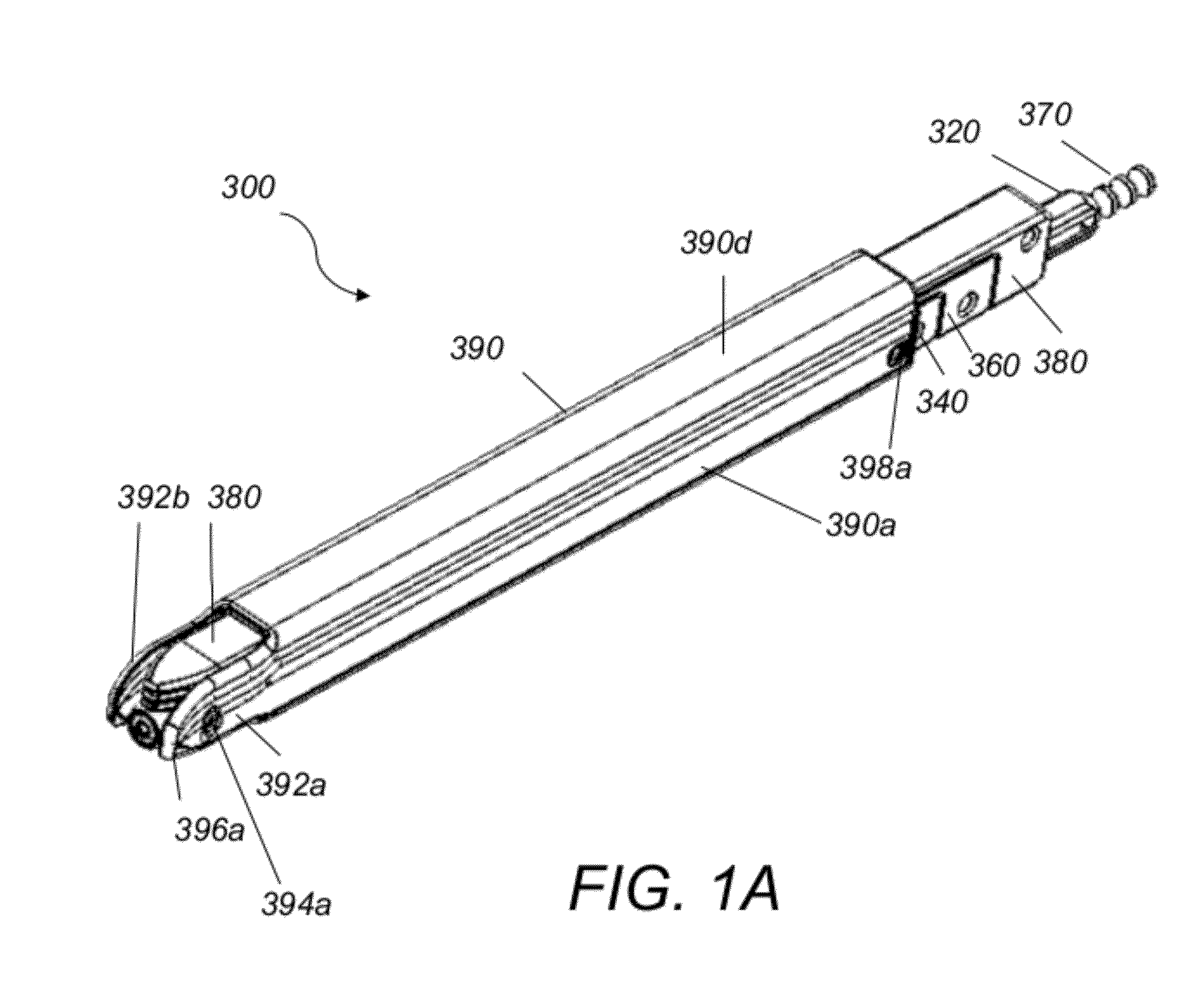
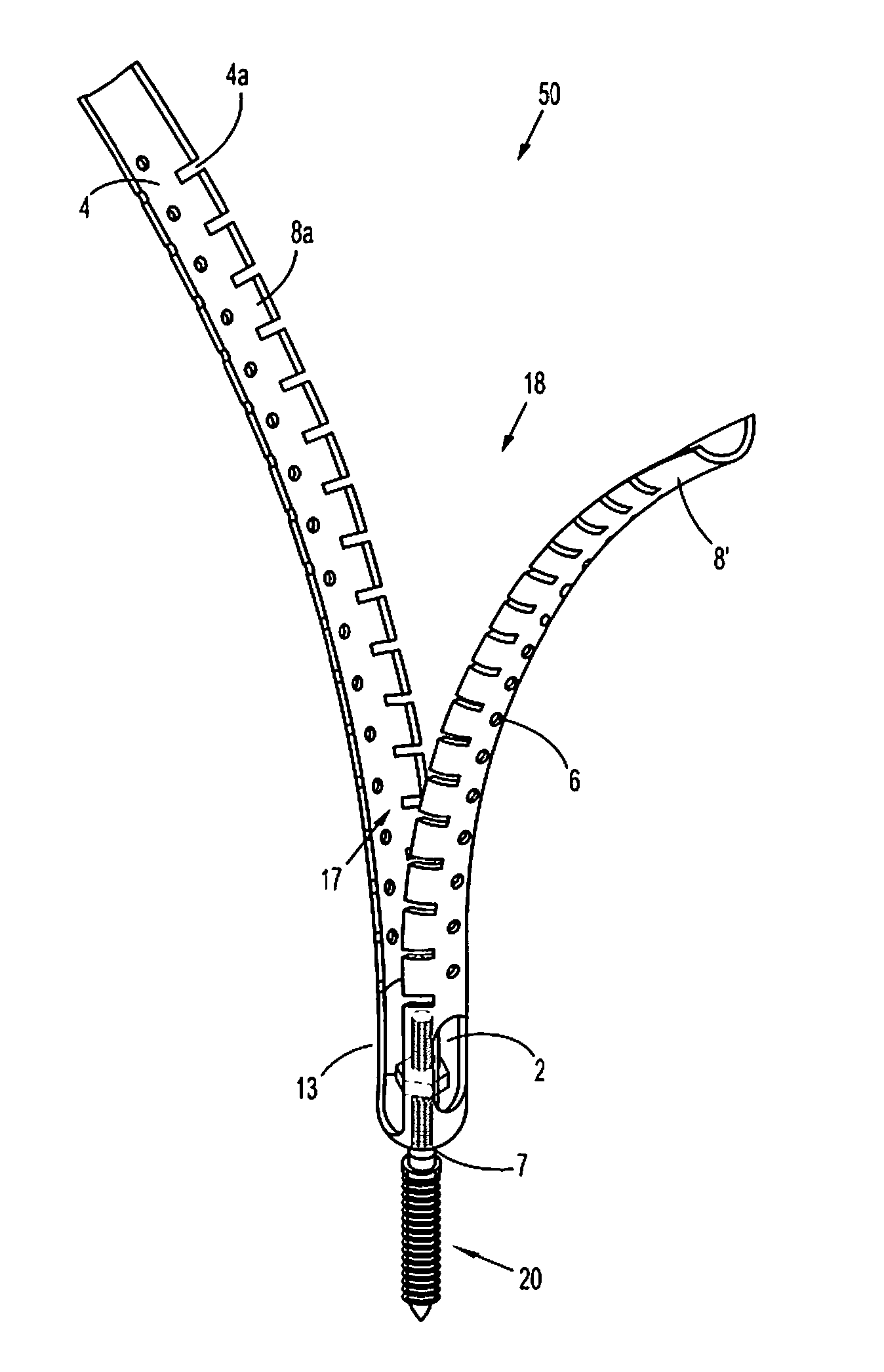
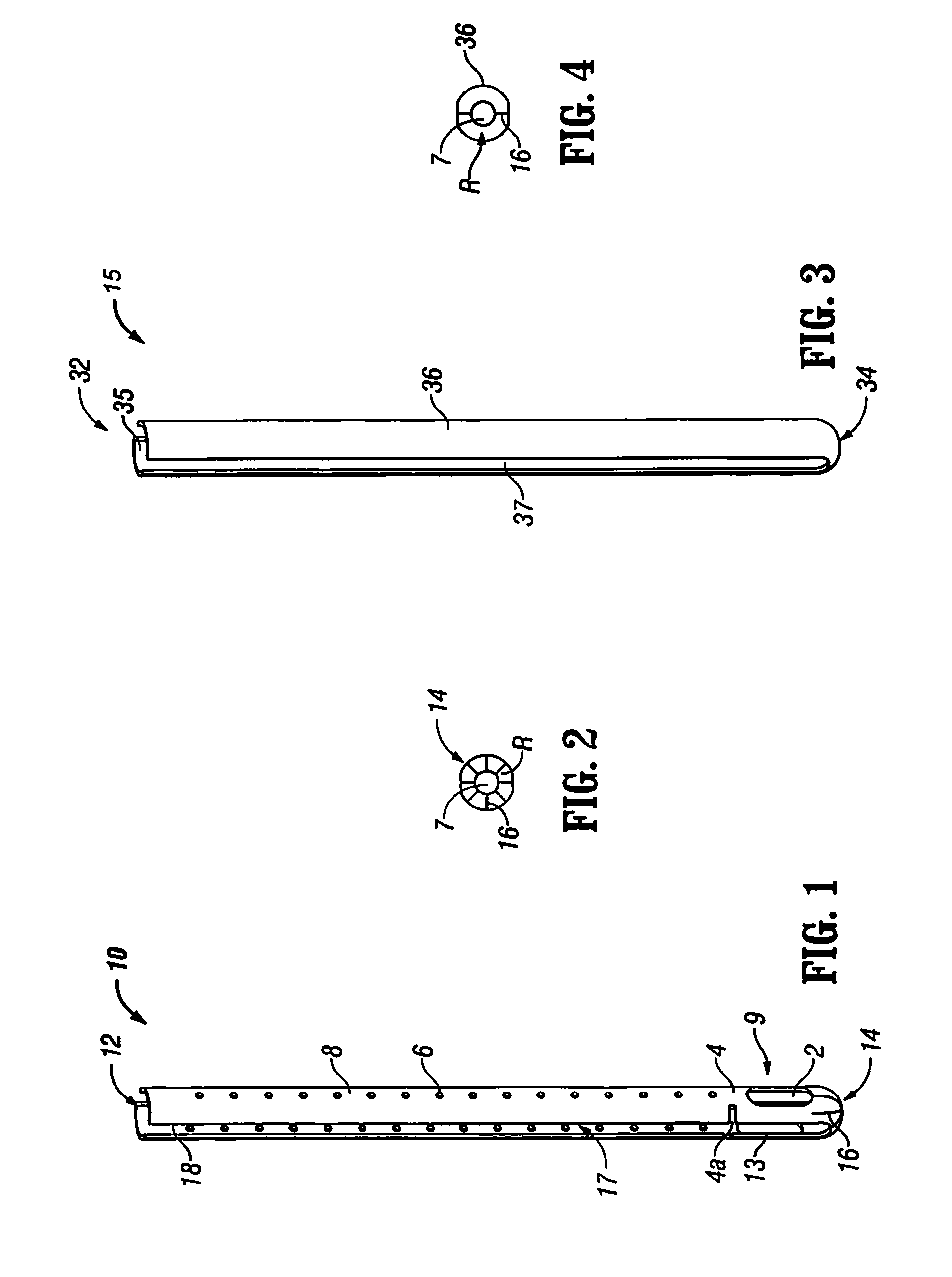
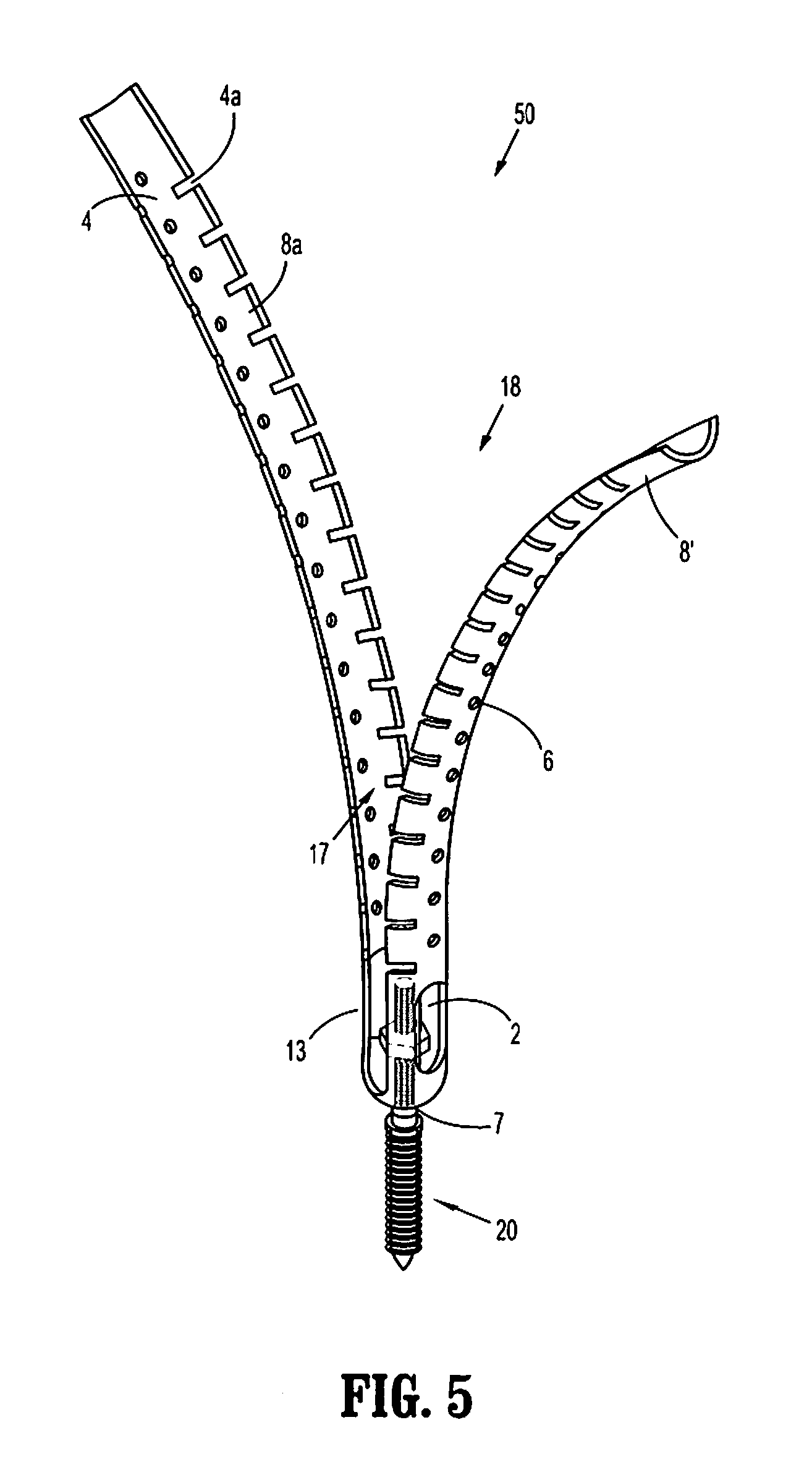
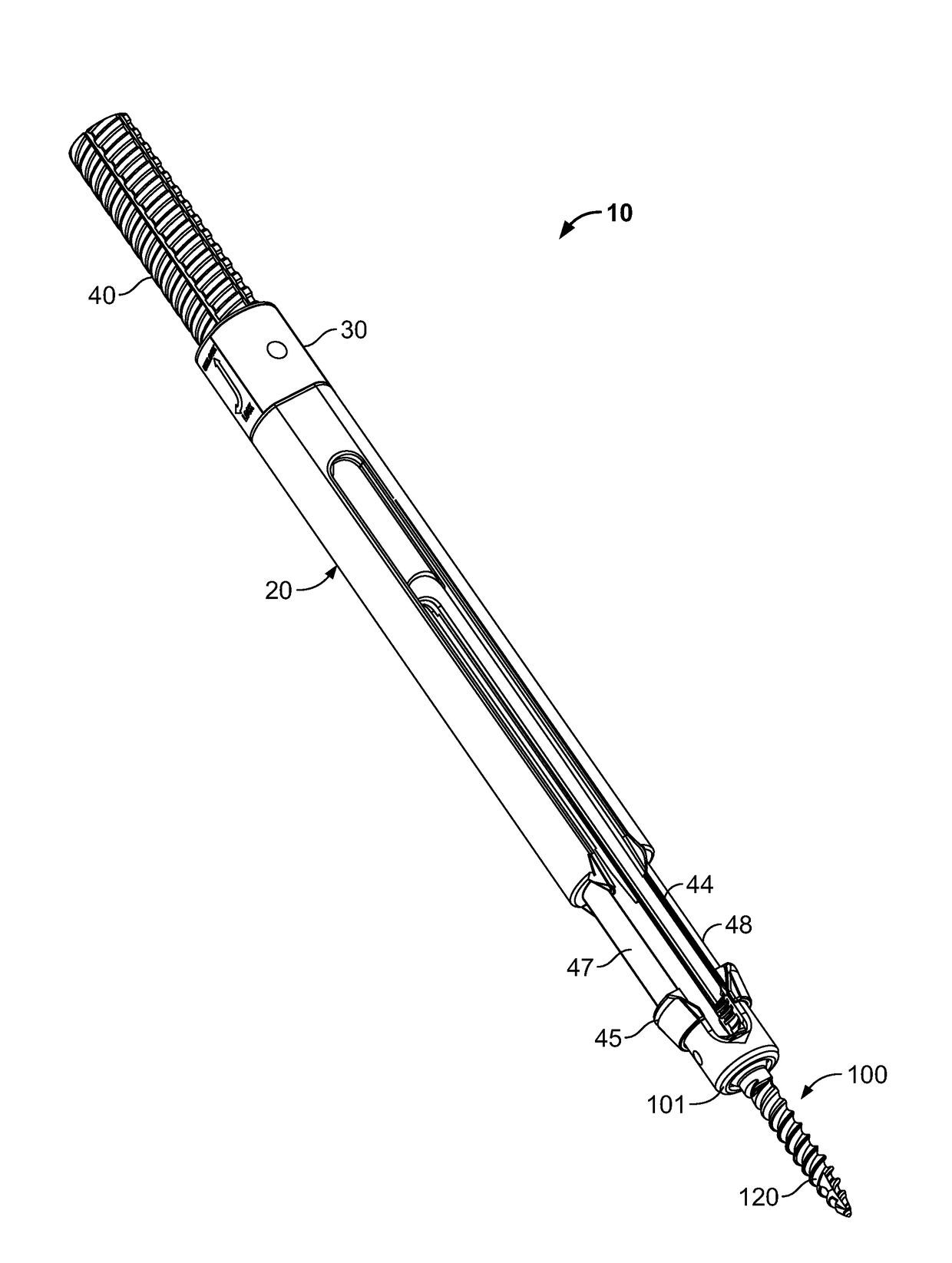
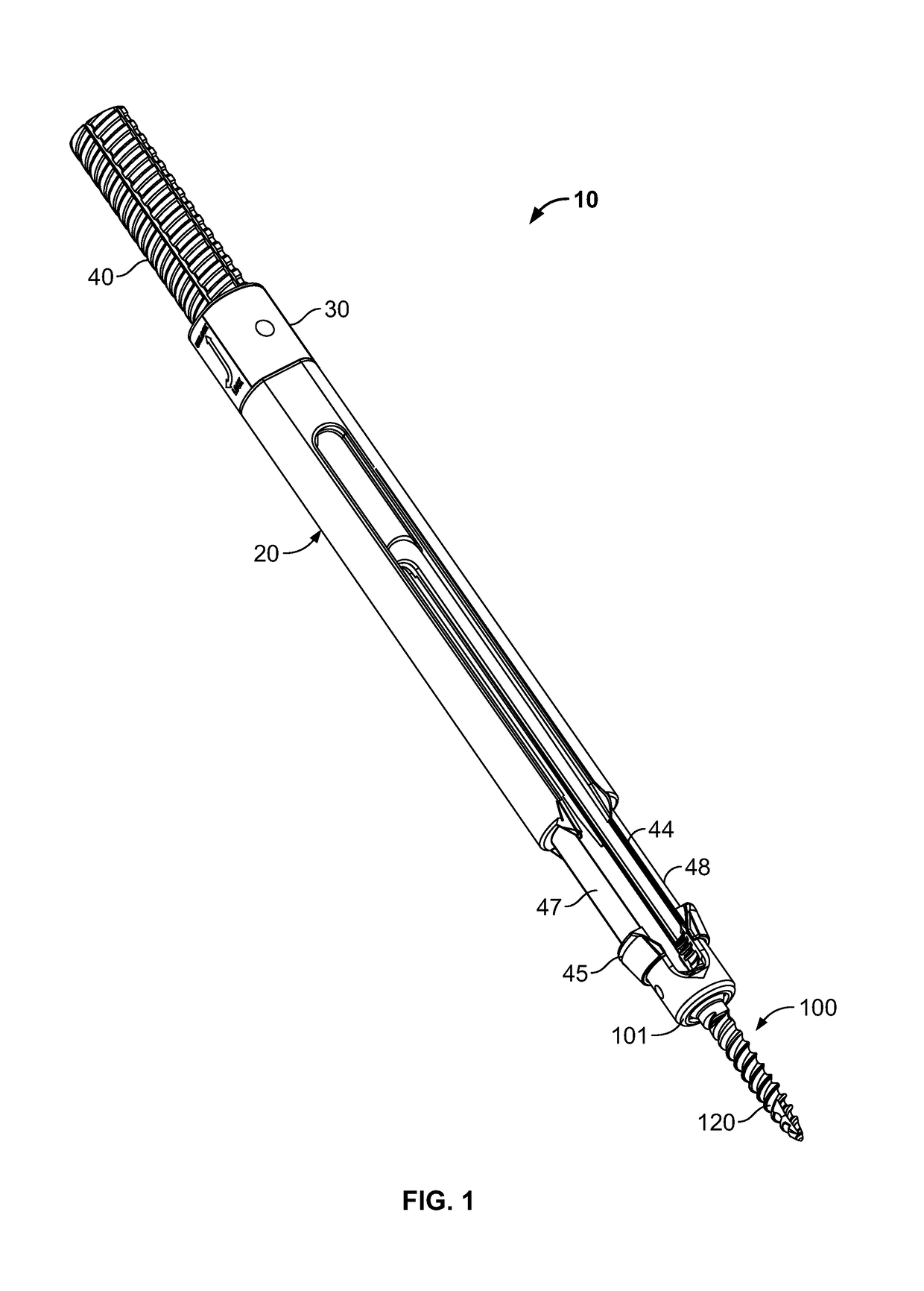
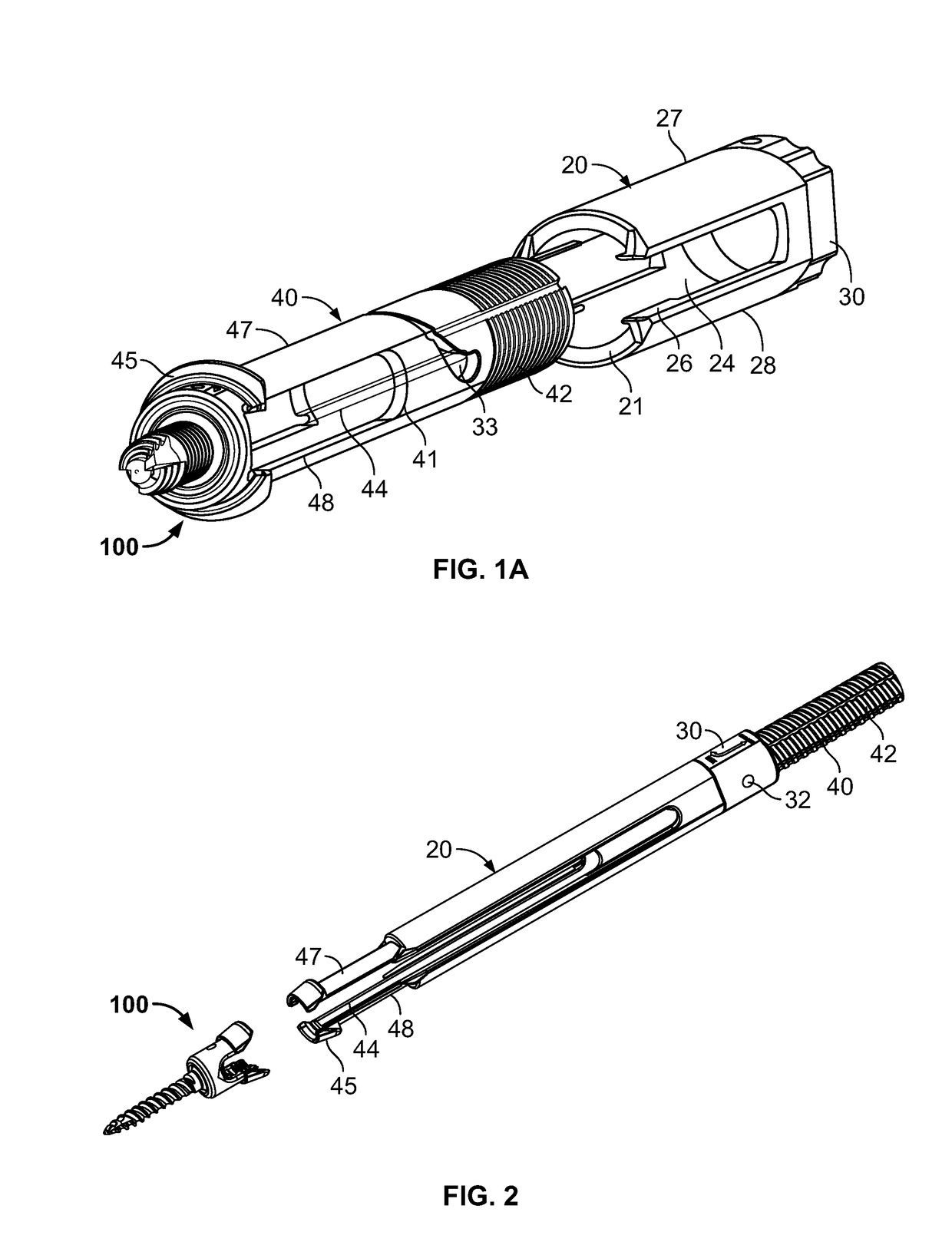
Minimally invasive screw extension assembly
A screw extension assembly for use in minimally invasive spinal surgery, the assembly has an inner slotted shaft and an outer shaft, a rod reducer and a removable nut. The combination when assembled is configured to move a spinal fixation rod into a slotted rod receiving spinal implant where it is seated and affixed thereto. The screw extension assembly further has a locking knob rotationally coupled to a proximal end of the outer shaft, wherein the inner shaft has one or more cam grooves and the locking knob has a pin extending into and guided by said cam groove causing the outer shaft to translate longitudinally upon rotation of the locking knob relative to the inner shaft toward an engaged position locking the deflectable legs in the coupled position to the slotted rod receiving implant.
Owner:SPINAL ELEMENTS INC
Rod holder and minimally invasive spine surgery system using the same
Owner:GS MEDICAL CO LTD
Digital location minimally invasive spine surgery 3D printing guide plate and manufacturing method
ActiveCN107157580AGuaranteed parallelReduce the impactAdditive manufacturing apparatusDiagnostic markersCoronal planeSagittal plane
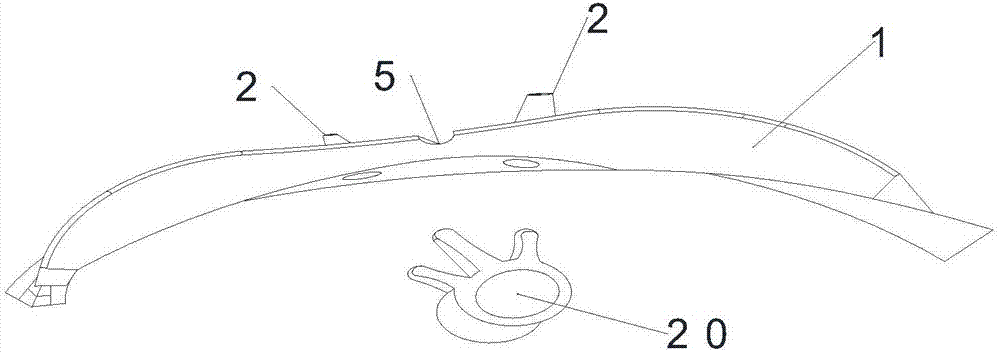
The invention discloses a digital location minimally invasive spine surgery 3D printing guide plate. A locating block cavity and a spinous process locating line are arranged in the middle of the guide plate; guide holes are formed in two sides of the guide plate; a locating block is arranged in the locating block cavity; a T-shaped groove is formed in the bottom of one side of a central axis of the locating block; a T-shaped fixed groove is formed in the bottom side of the guide plate; a locating scale plate is arranged in the T-shaped fixed groove; and scales are arranged on the surface of the locating scale plate. The guide plate provided by the invention, in combination with digital measurement, can optimize and facilitate a locating process; secondary location can be directly implemented in accordance with marks made on the surface of a tested object, so that such inconvenience as an operating area of the tested object cannot be completely disinfected and the like can be avoided; puncture points can be also rapidly and accurately determined by doctors in an operation, and puncture directions can be guaranteed to be accurate simultaneously in both coronal plane and sagittal plane; and the guide plate, in comparison with a conventional operating mode, can shorten an operating time, reduce radiation amounts on both the doctors and a patient in the operation and enhance safety and accuracy of the operation; therefore, the guide plate has broad applicability in the field of minimally invasive spine surgeries.
Owner:刘大鹏 +2
Minimally Invasive Instruments and Methods for the Micro Endoscopic Application of Spine Stabilizers in the Interspinous Space
InactiveUS20100010546A1Relieve pressureFast securityInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsSpinal nerveIntervertebral disk
The present disclosure provides a safe and simple method, as well as a new instrumentation to improve the technique of the minimally invasive spine surgery through micro endoscopy with the use of hooks and a new improved stabilization interspinous device or implant which is placed as an auxiliary in the function of the affected intervertebral disk, by relieving the pressure on spinal nerves.
Owner:HERMIDA OCHOA ELIAS HUMBERTO
Minimally invasive spine surgery drape
InactiveUS20170258544A1Preventing and minimizing entanglementUpper partSurgical drapesTherapeutic coolingX-rayEngineering
A surgical drape includes a center section having an operating window and extending longitudinally from a head end to a foot end, and a side section positioned on each longitudinal side of the center section. The side sections may be at least partially transparent. An elastic band extends through outermost ends of the side sections and across the foot end of the center section, and at least one surgical fluid collection pocket is disposed adjacent the operating window. Additional features of the drape may include a warming bladder and / or an extension section that is expandable to cover a machine adjacent the drape, such as an x-ray fluoroscope machine.
Owner:OSMAN SAID G
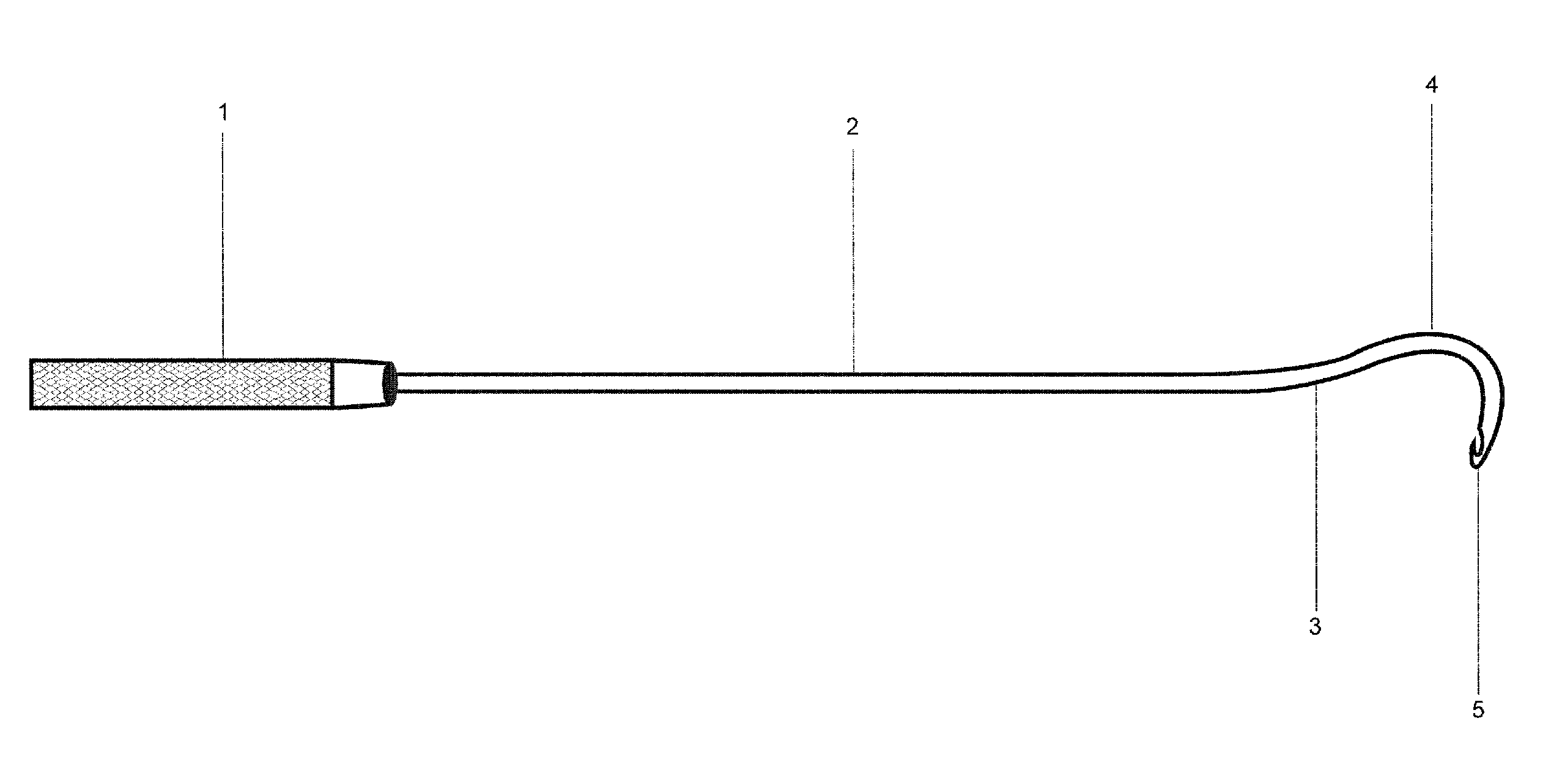
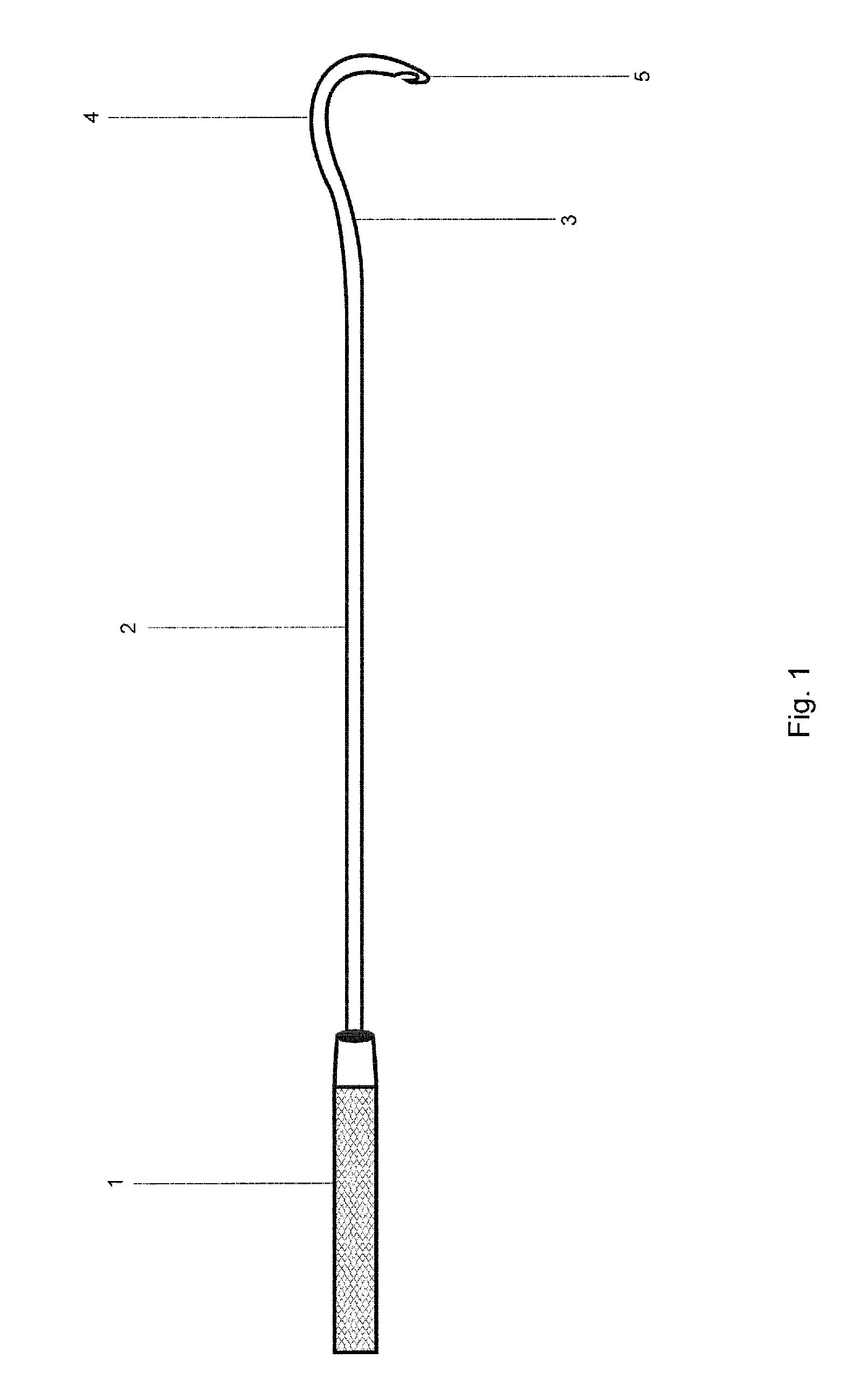
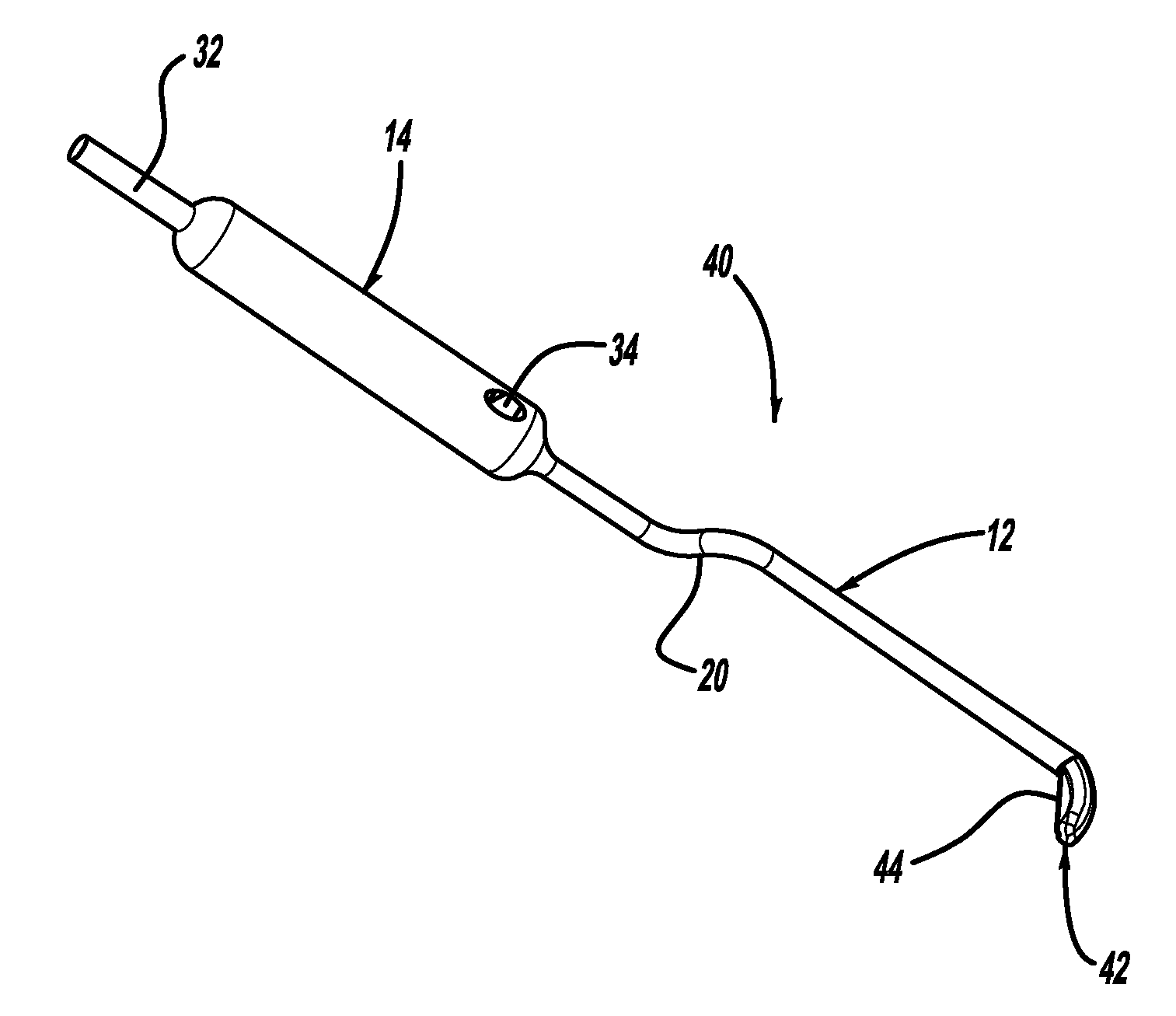
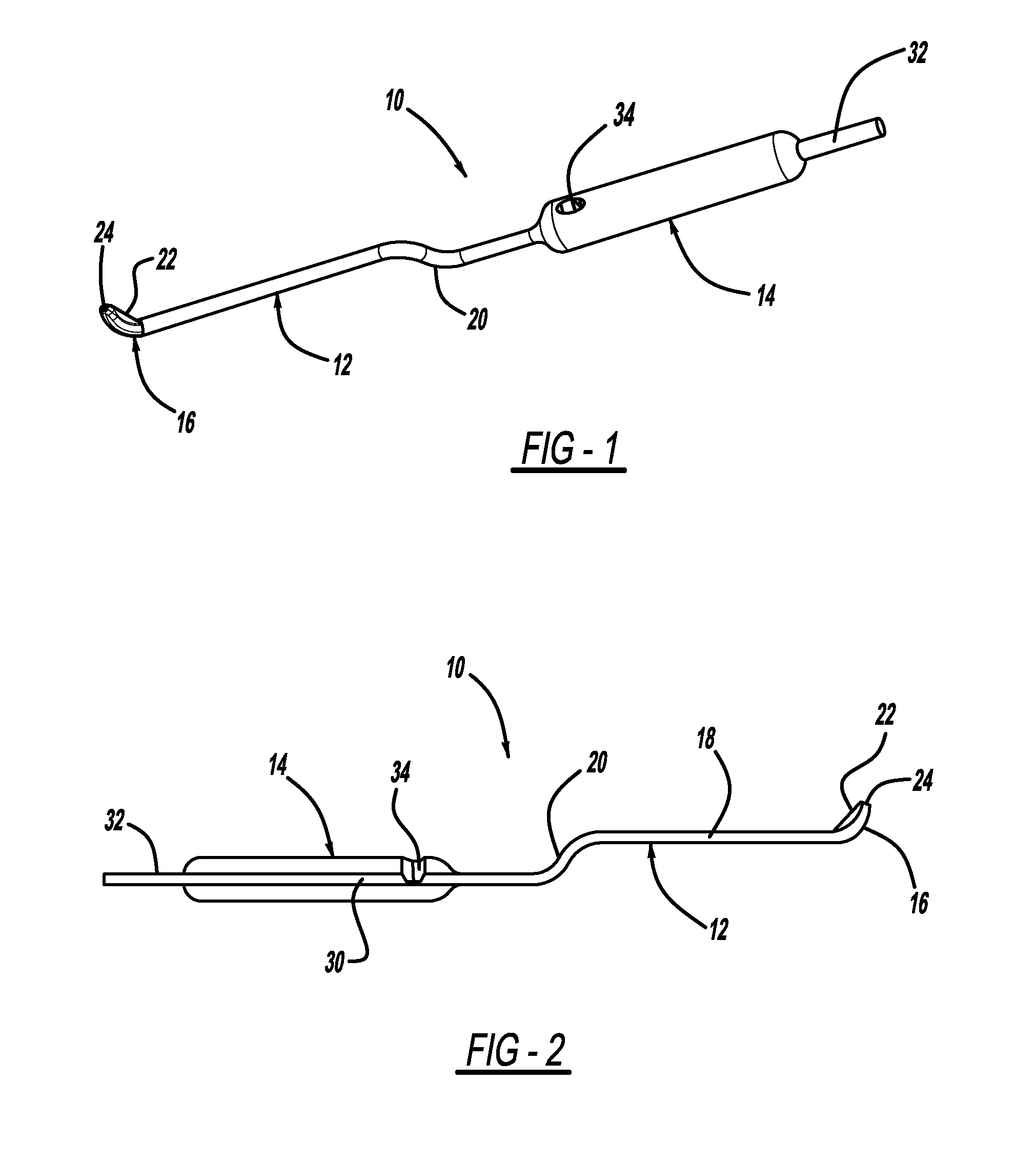
Up cutting knife with suction
An up-cutting knife that has particular application for minimally invasive spinal surgical procedures. The knife includes an elongated tube that is operable to be inserted through a tubular retractor used in minimally invasive surgical procedures. One end of the elongated tube includes a curved head portion having a cutting blade formed on a top surface thereof and a suction port, and an opposite end of the tube is coupled to a handle having a chamber. A suction device can be coupled to an outlet port in the handle that causes blood and other surgical material to be drawn through the tube and out of the handle.
Owner:MI4SPINE
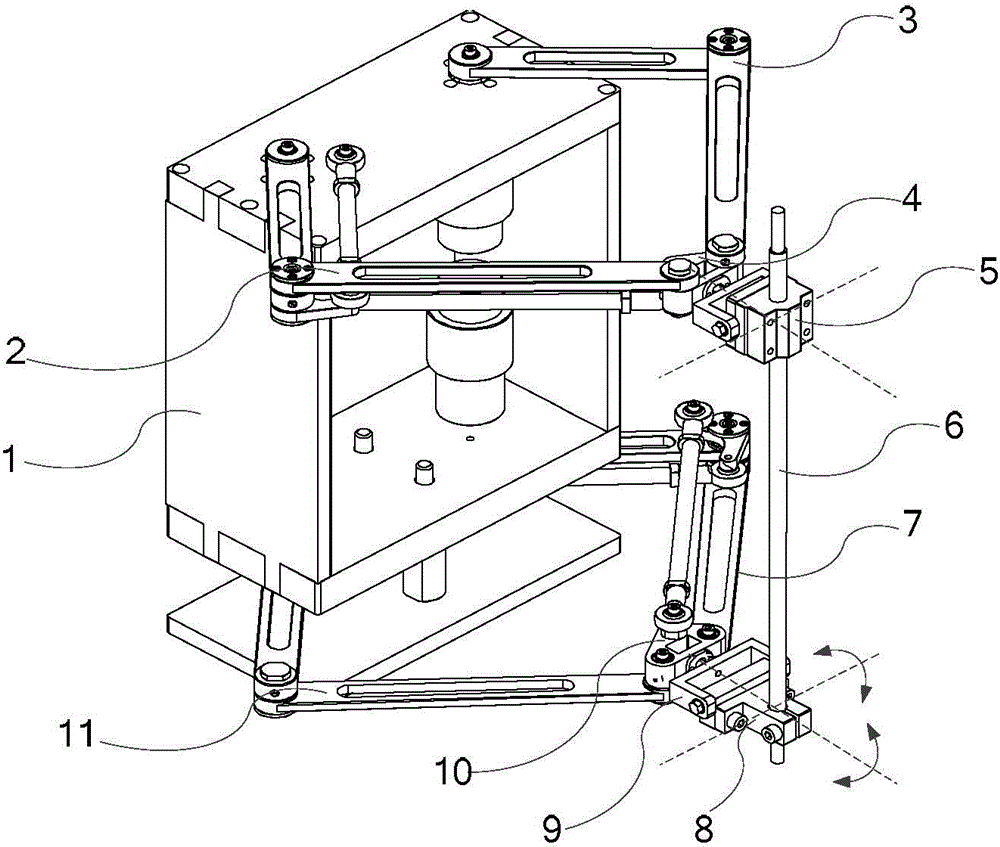
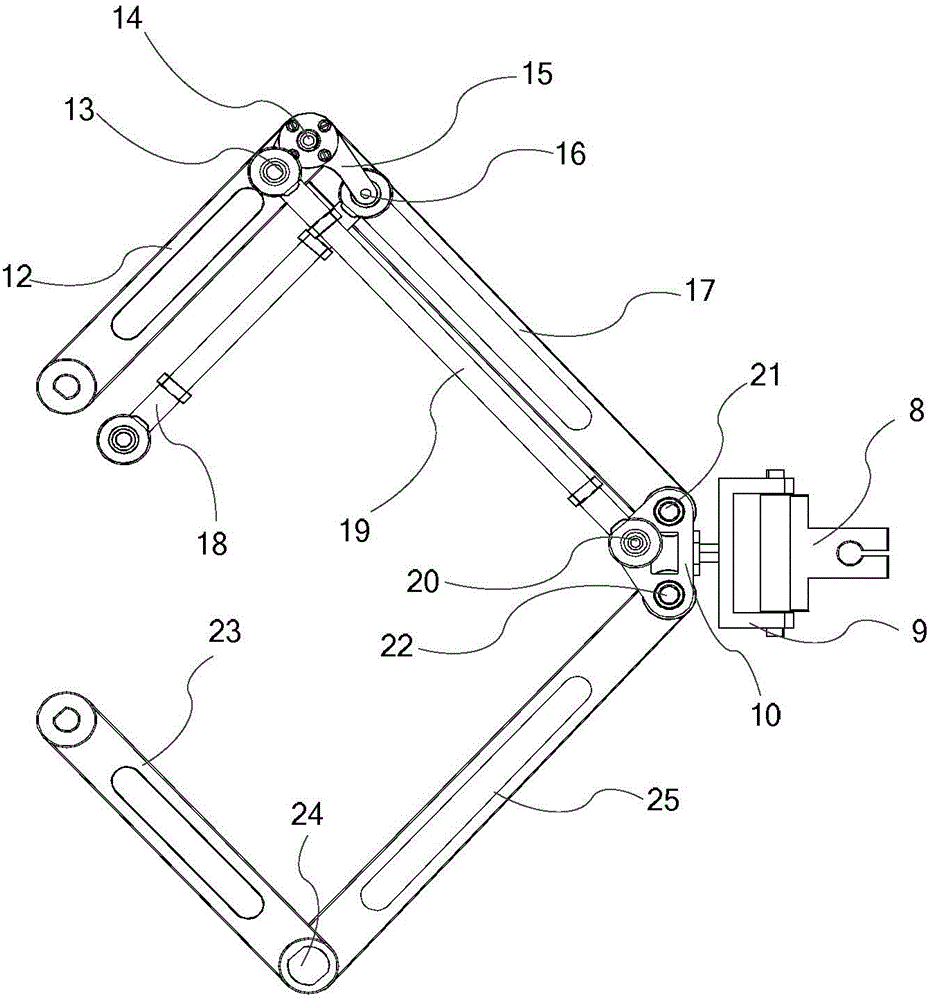
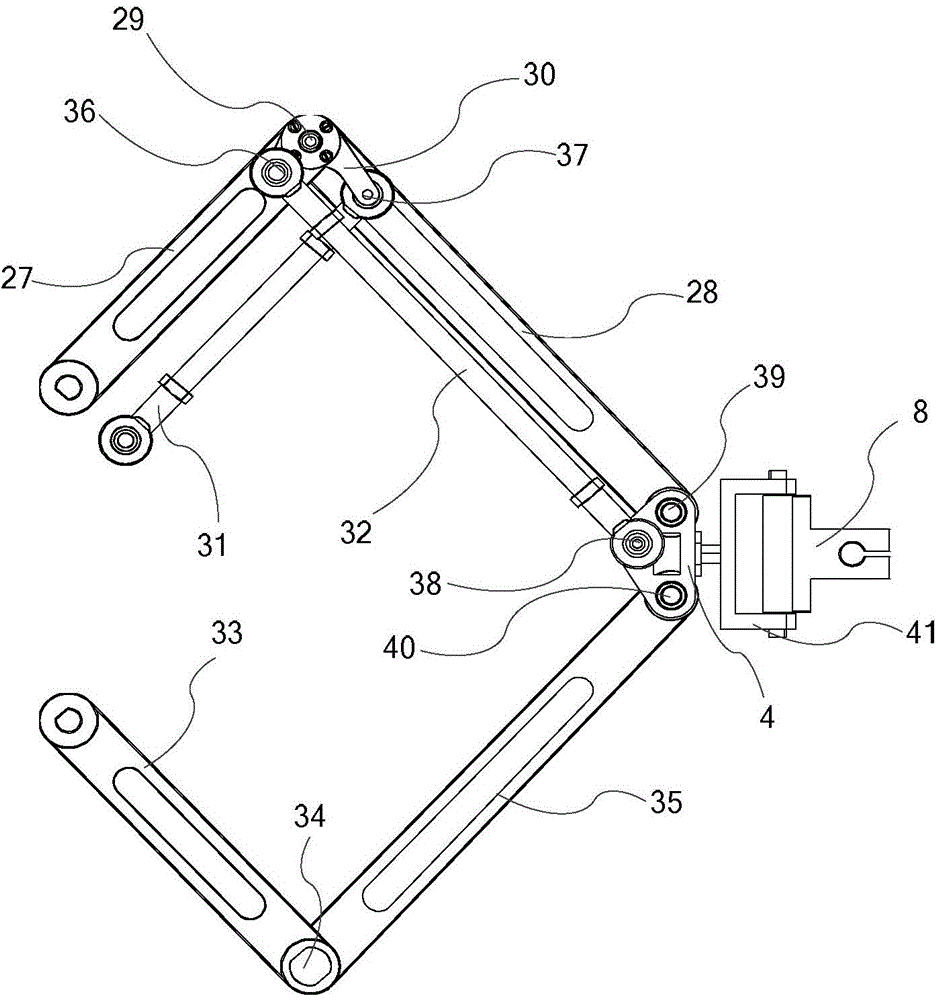
Bi-plane parallel mechanism capable of achieving plane two-dimensional positioning and spatial two-dimensional orientation
ActiveCN104972456AHigh positioning accuracyHigh orientation accuracyProgramme-controlled manipulatorMedical robotEngineering
The invention relates to the technical field of parallel robots, in particular to a bi-plane parallel mechanism capable of achieving plane two-dimensional positioning and spatial two-dimensional orientation. The bi-plane parallel mechanism aims to solve the problems that an existing medical robot for minimally-invasive spine surgery is low in precision, poor in reliability and low in surgical safety due to the complex structure, the large size and high operating difficulty, and is used for completing positioning and orientation of a tail-end instrument of a medical robot for minimally-invasive spine surgery. The bi-plane parallel mechanism is composed of an upper plane driving mechanism, a lower plane driving mechanism and the tail-end instrument. The two plane mechanisms are connected with the tail-end instrument through U pairs, and the upper plane U pair can slide along the axis of the instrument. Each plane driving mechanism is formed by sequentially connecting four rods through connecting shafts or fixing shafts. The bi-plane parallel mechanism is also suitable for completing plane two-dimensional positioning and spatial two-dimensional orientation for other tools.
Owner:HARBIN SIZHERUI INTELLIGENT MEDICAL EQUIP CO LTD
Minimally invasive retractor and posted screw
ActiveUS20120190934A1Facilitates the reliable securing of the screw within the retractorFacilitate further securing of the screw and the retractor bladesSurgeryIliac screwRetractor blade
A minimally invasive retractor assembly includes a posted screw and one or more retractor blades. Each retractor blade is releasably coupled to the posted screw. The retractor blade or blades are manipulated or flexed relative to the posted screw allowing retraction of tissue surrounding the incision. The retractor is made of a biocompatible material, sterile packaged and disposable after one use. A system and method for using the retractor and performing a minimally invasive spine surgical procedure are also disclosed.
Owner:K2M
End-of-arm tooling quick replacing mechanism for minimally-invasive spine surgery robot
The invention relates to an end-of-arm tooling for a minimally-invasive spine surgery robot, in particular to an end-of-arm tooling quick replacing mechanism for a minimally-invasive spine surgery robot. The problems that an end-of-arm tooling for the minimally-invasive spine surgery robot is replaced frequently, a quick replacing device used in the industrial environment is either unsuitable for a minimally-invasive spine surgery or is low in location accuracy and long in quick replacing time are solved. The end-of-arm tooling quick replacing mechanism comprises an installing base, a quick replacing connector and a locking assembly, wherein the quick replacing connector is inserted in the installing base and connected with the installing base through the locking assembly, an inserting groove is machined in the installing base, an inserting part arranged to be matched with the inserting groove and inserted into the inserting groove is arranged on the quick replacing connector, a single slope is machined on the side face, opposite to the inserting groove, of the installing base, and a butt-joint part making contact with the single slope in a matched mode is arranged on the quick replacing connector. The end-of-arm tooling quick replacing mechanism is used for the minimally-invasive spine surgery.
Owner:HARBIN SIZHERUI INTELLIGENT MEDICAL EQUIP CO LTD
Methods, tools and devices for percutaneous access in minimally invasive spinal surgeries
A cannula assembly for providing percutaneous access in minimally invasive spinal surgeries, includes an outer cannula, a nerve probe dilator and a multistage dilator system comprising a first dilator, a second dilator, a third dilator and a fourth dilator. The outer cannula and the dilators are slidable relative to each other and are arranged sequentially so that the fourth dilator surrounds the nerve probe dilator, the third dilator slides over a surface of the fourth dilator, the second dilator slides over a surface of the third dilator, the first dilator slides over a surface of the second dilator, and the outer cannula surrounds the first dilator.
Owner:KIC VENTURES LLC
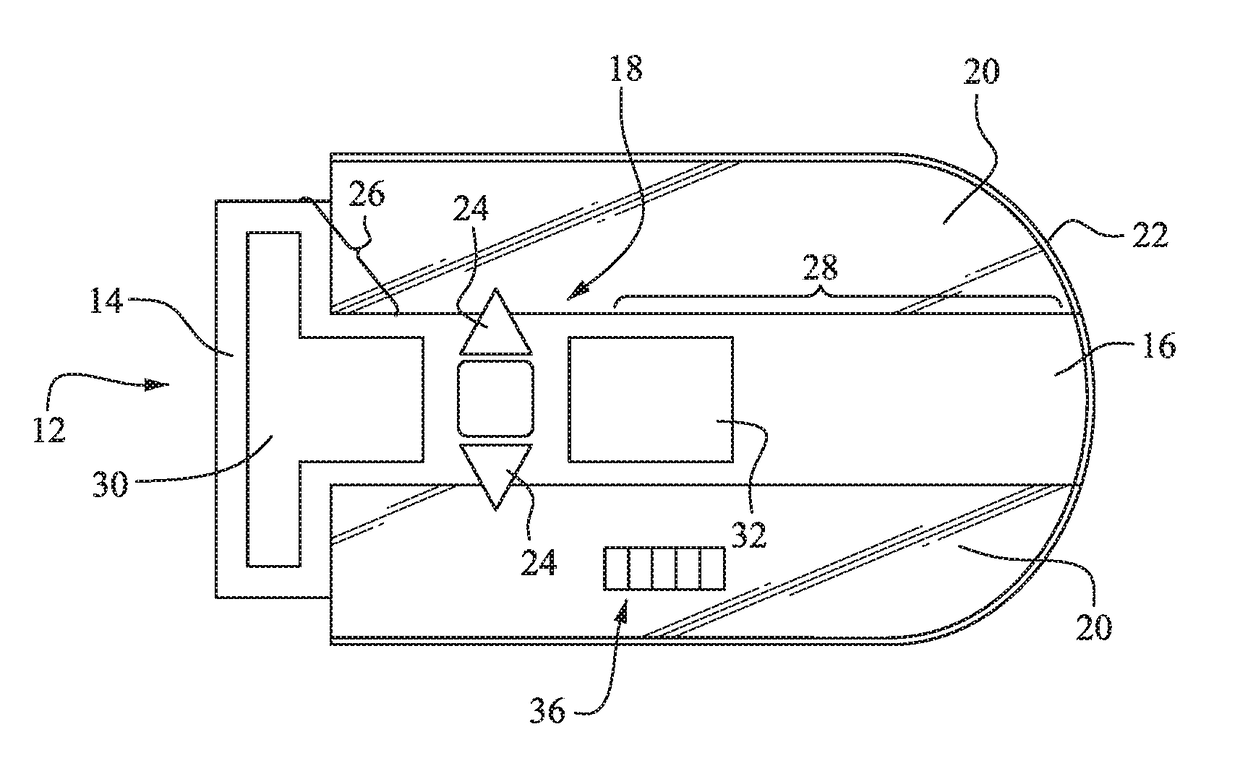
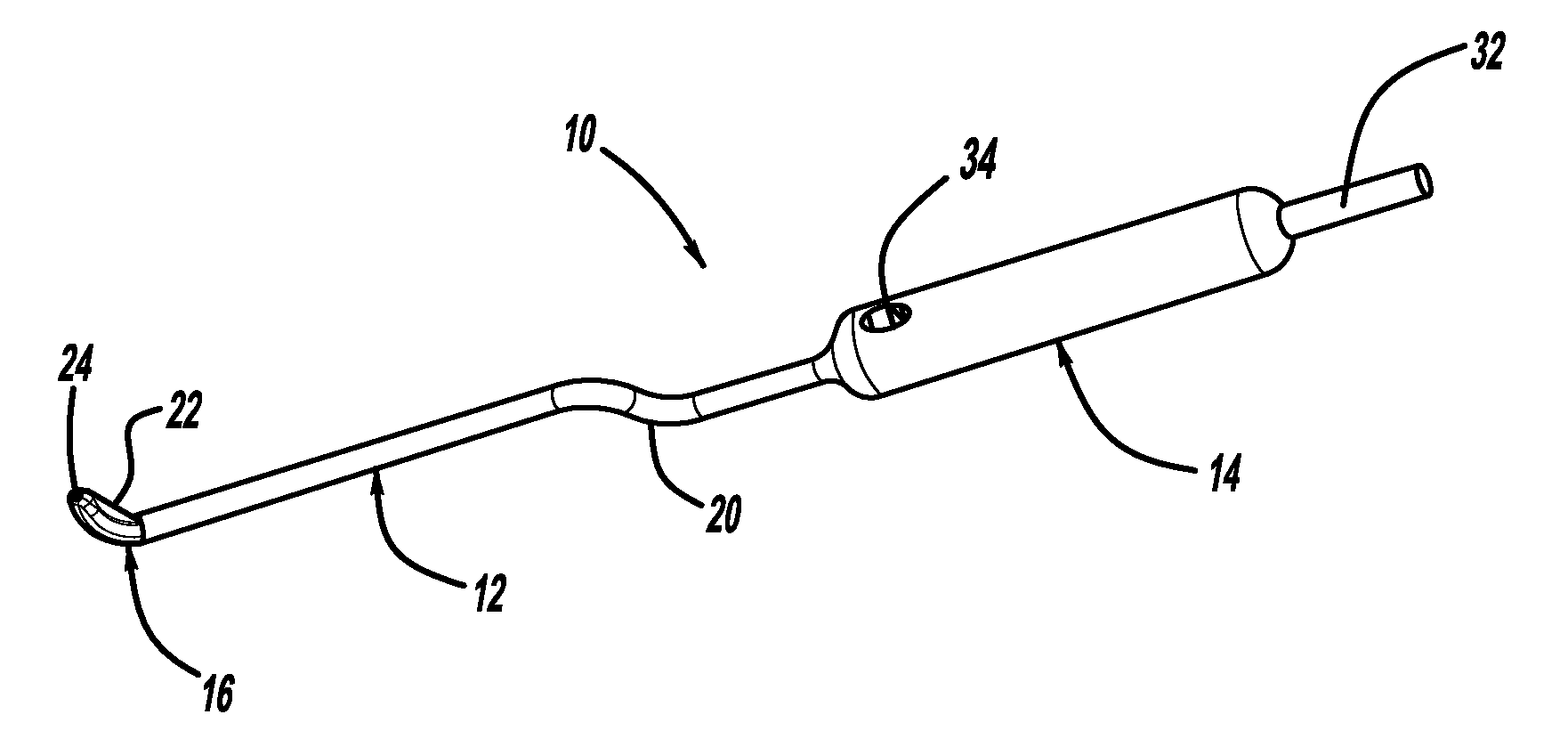
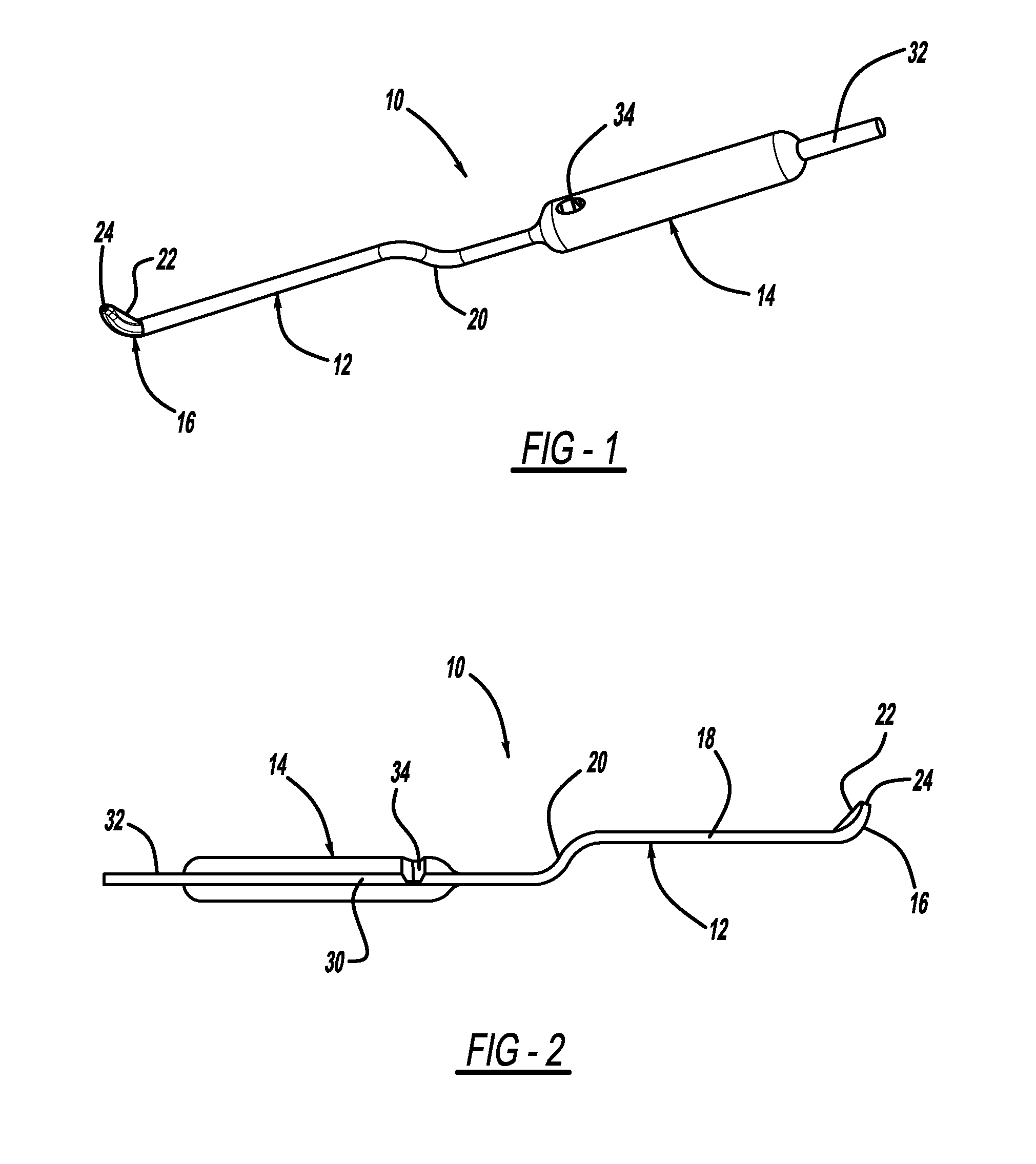
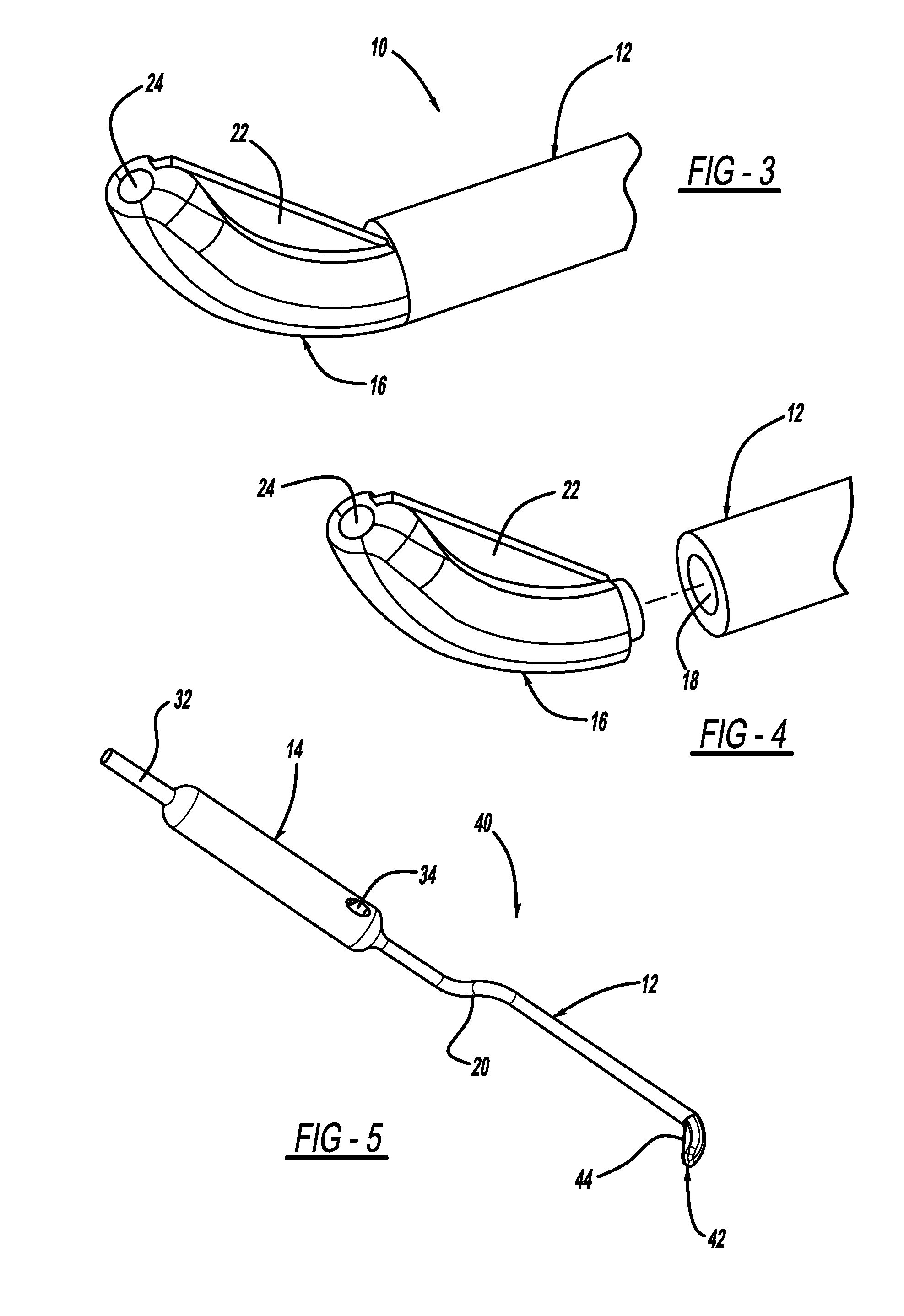
Fabric Retraction Device and Method for Minimally Invasive Surgery
The present invention is directed to methods and instruments for performing tissue retraction in minimally invasive spinal surgery. Another specific application includes surgical methods performed through the percutaneously retracted tissue at any location in a patient's body. The tissue retraction is provided by an elongated sleeve formed from fabric materials, which may include the ability to stretch beyond their original length along at least one axis, for passage of instruments or implants.
Owner:RODRIGUEZ CARLOS ANDRES
Positioning system for minimally invasive spine surgery and application of same in minimally invasive spine surgery positioning
InactiveCN106264702AAvoid damageAvoid fixationSurgical needlesTrocarLess invasive surgeryPositioning system
The invention discloses a positioning system for a minimally invasive spine surgery and application of the same. The system comprises a base, a z-axis guide rod disposed on the base, a z-axis scale, a first graduated scale and a first vernier extending in the x-axis direction, a second graduated scale and a second vernier extending in the y-axis direction, a first angle scale connected to the second vernier, a first rotation part, a second angle scale, a second rotation part, an indication pointer and a needle clamping device used to hold a puncture needle, wherein the first angle scale extends in the x-z plane and has scales; the first rotation part is connected to the second vernier and can be rotated along a center axis parallel to the y-axis; the second angle scale extends in the plane perpendicular to the first angle scale and has scales; the second rotation part is rotated along a second rotation axis perpendicular to the second angle scale; and the indication pointer can be rotated with the second rotation part and is used to mark a rotation angle. The positioning system for the minimally invasive spine surgery has the advantages that damage of important tissues caused by puncture position inaccuracy in the minimally invasive surgery can be avoided; risks in a patient's surgery can be reduced; and thus, positioning of the minimally invasive spine surgery becomes more accurate.
Owner:XUANWU HOSPITAL OF CAPITAL UNIV OF MEDICAL SCI
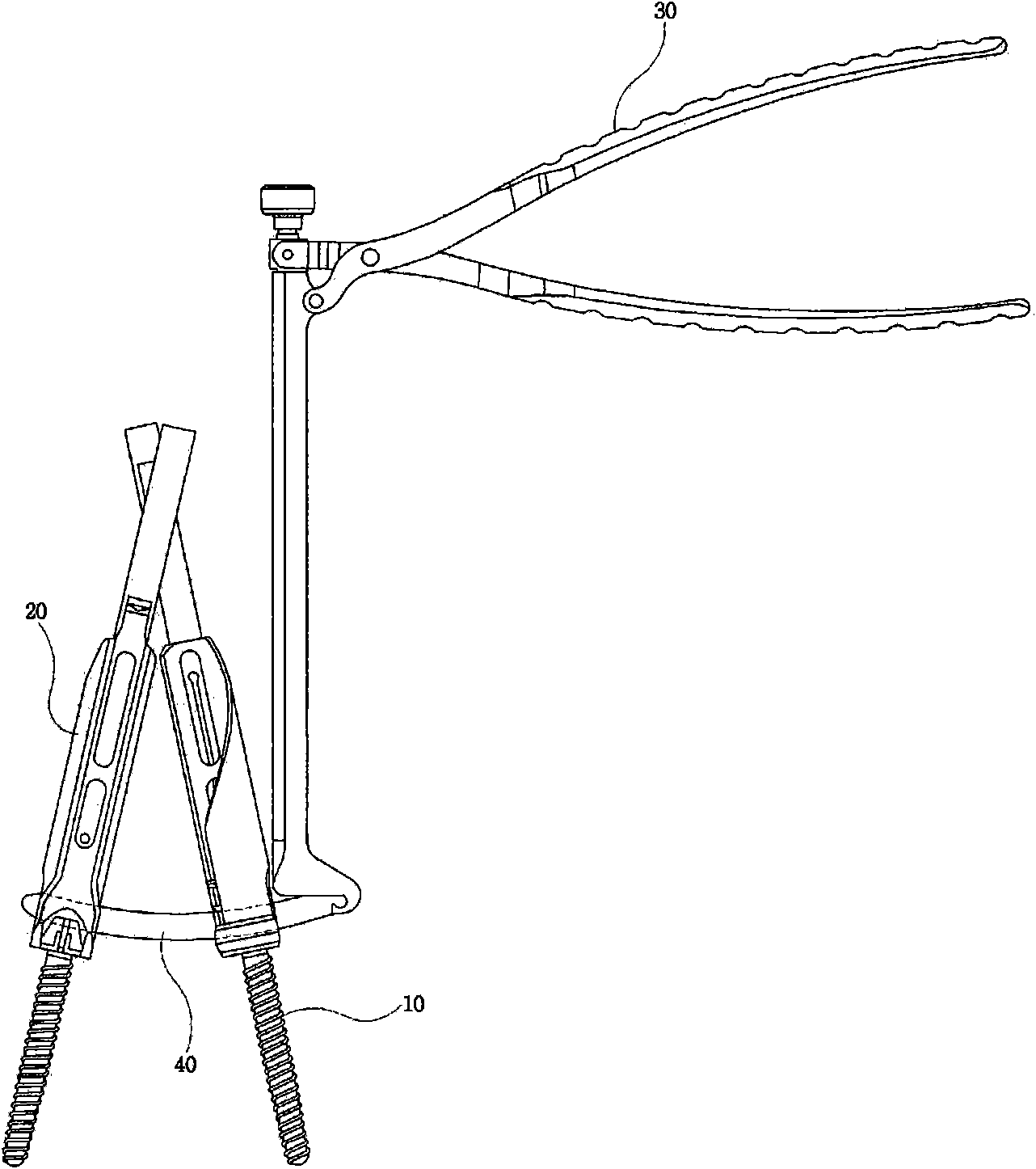
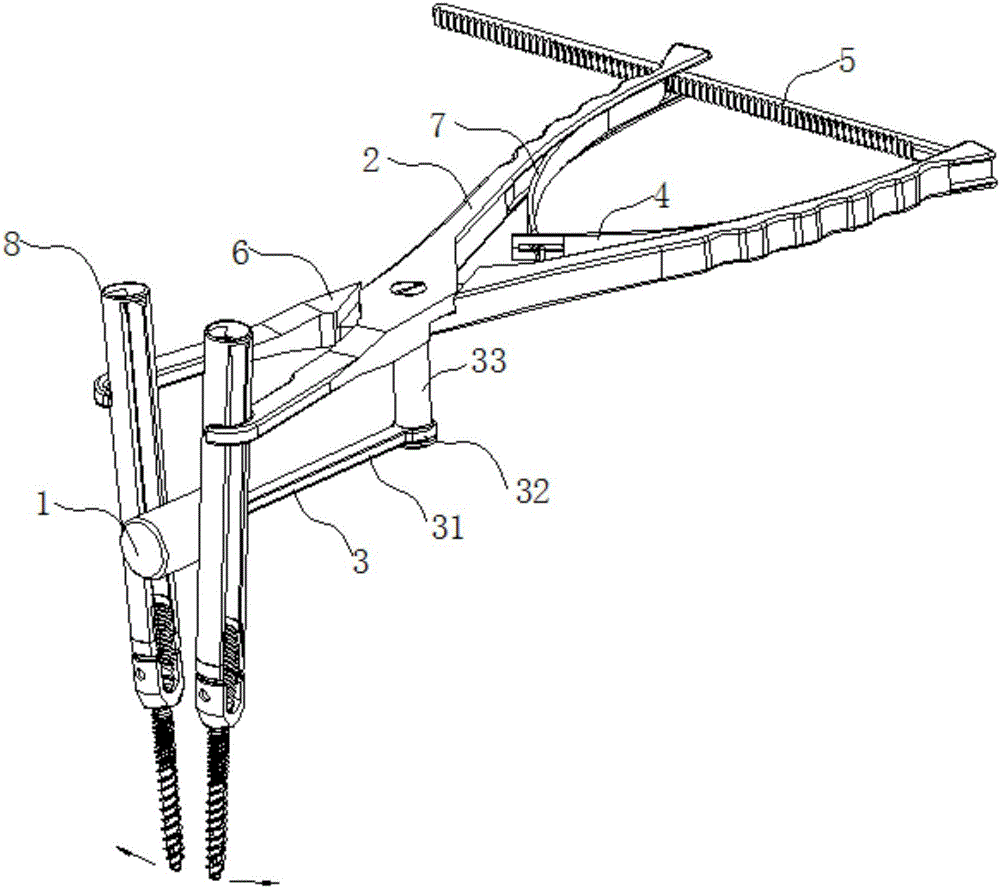
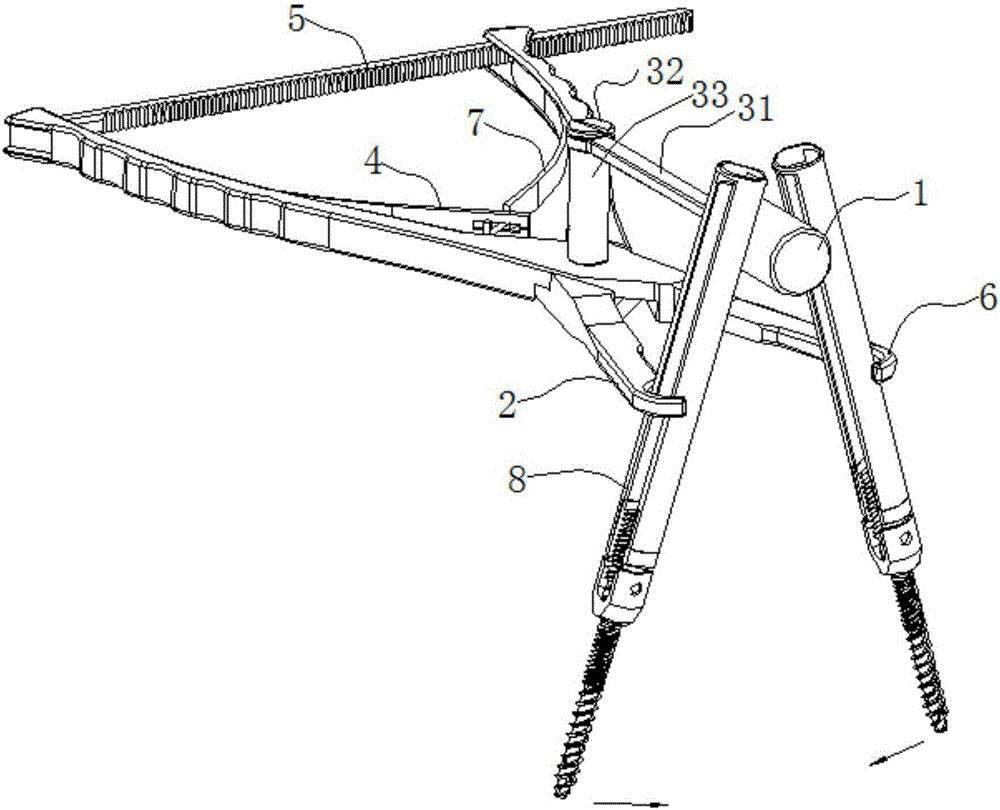
Distraction compression clamp for minimally invasive spine surgery
The invention relates to a distraction compression clamp for minimally invasive spine surgery. The compression clamp comprises a left clamping handle, a right clamping handle, a fulcrum, a connecting device and a fixing device, wherein the left clamping handle and the right clamping handle are connected in an X-shape by virtue of the connecting device, and can rotate around the connecting device; a holding part is respectively arranged at the front end of the left clamping handle and the front end of the right clamping handle, and a grasp part is respectively arranged at the rear end of the left clamping handle and the rear end of the right clamping handle; one end of the fixing device is fixedly connected with the rear end part of the left clamping handle, and the other end of the fixing device is blocked to the rear end part of the right clamping handle. The distraction compression clamp can perform angular distraction and compression operations on the vertebral body with a minimally invasive pedicle screw under the condition of not enlarging an existing cut.
Owner:CHUANGHUI MEDICAL EQUIP JIANGSU
Minimally invasive spine surgery instruments: spinal rod with flange
InactiveUS20140088647A1Sufficient engagementOvercomes shortcomingInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsSurgical instrumentationMedicine
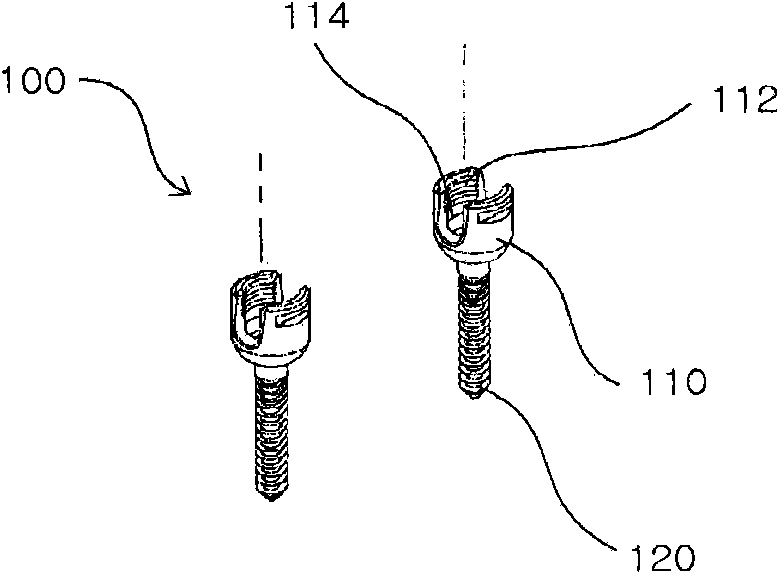
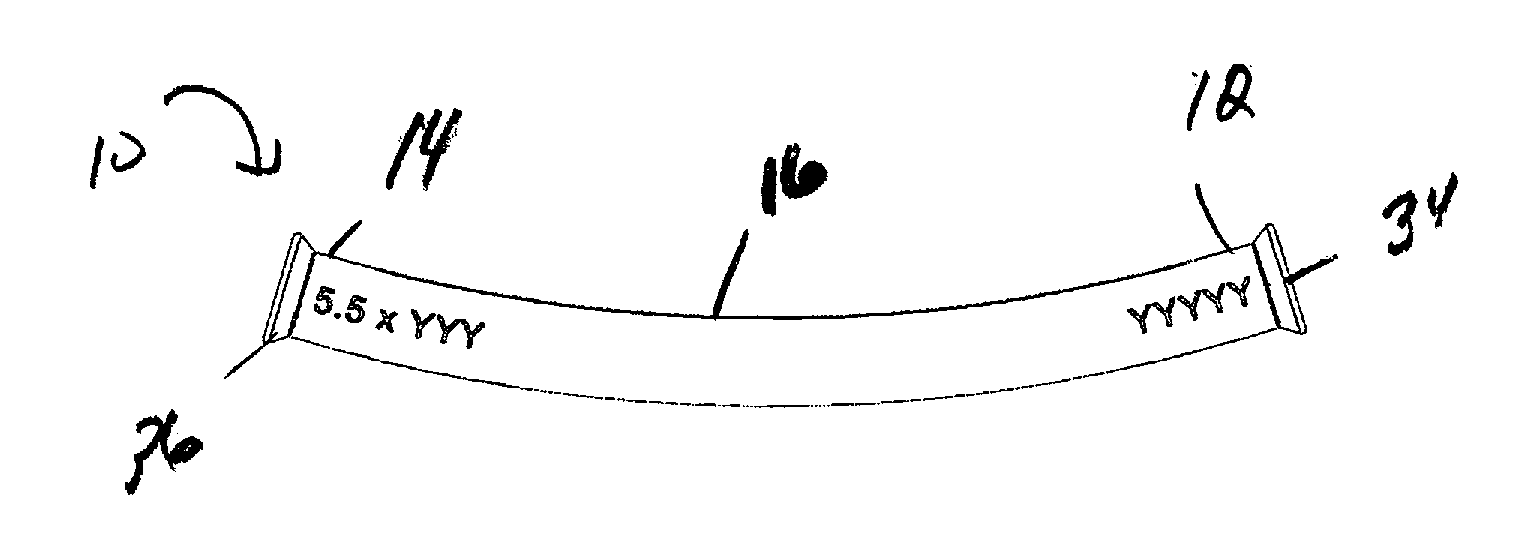
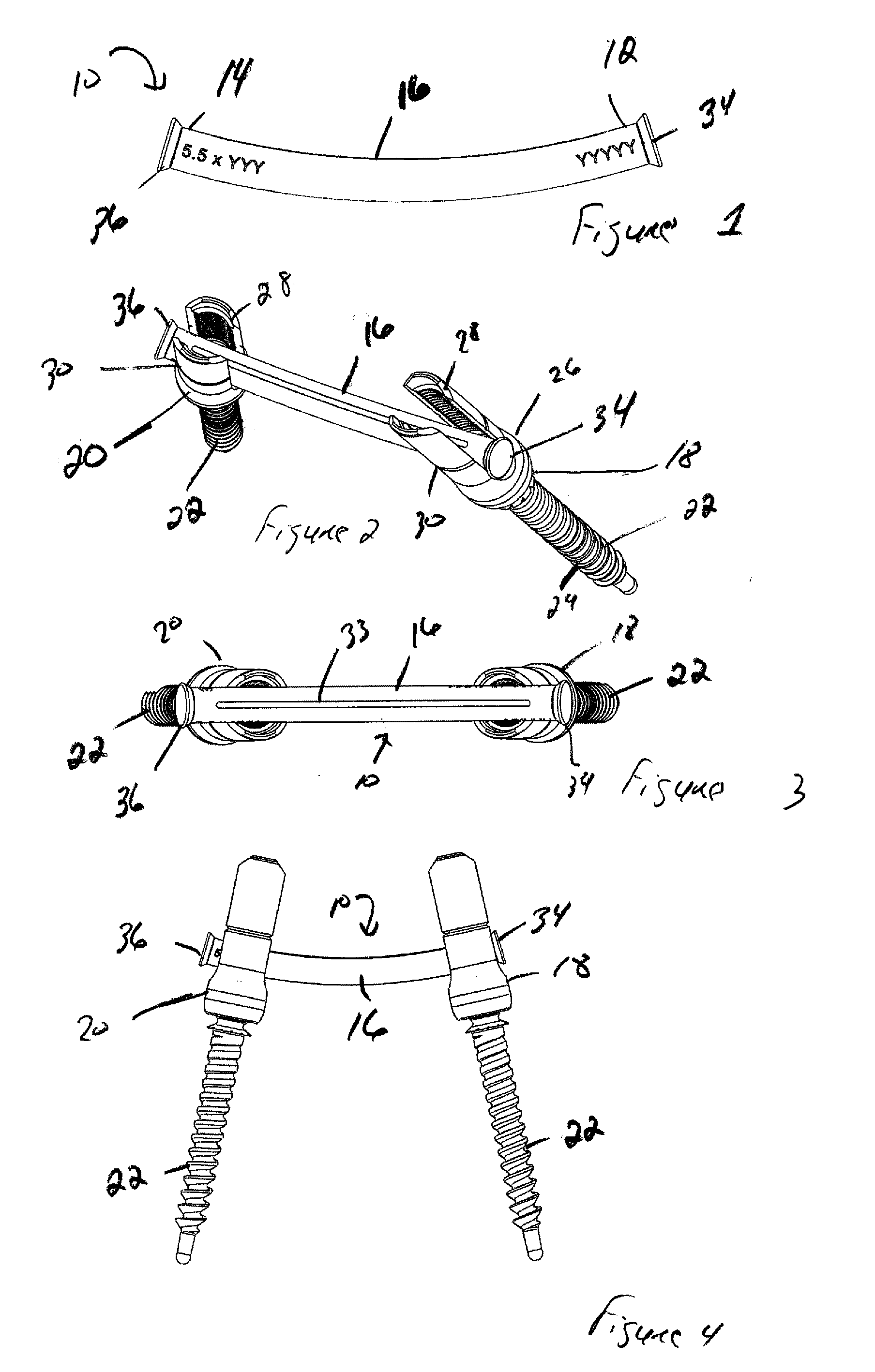
The present invention provides for a bone fixation device, illustrated as a spinal rod, for use in bone fixation surgeries. The bone spinal rod of the present invention is constructed and arranged to allow a surgeon to control proper placement while prohibiting the rod from passing out of a receiving component. In an illustrative embodiment, the spinal rod includes comprises a first end, a second opposing end, and a main body there between. At least one end contains a flange.
Owner:ATLAS SPINE
Minimally invasive screw extension assembly
A screw extension assembly for use in minimally invasive spinal surgery, the assembly has an inner slotted shaft and an outer shaft, a rod reducer and a removable nut. The combination when assembled is configured to move a spinal fixation rod into a slotted rod receiving spinal implant where it is seated and affixed thereto. The screw extension assembly further has a locking knob rotationally coupled to a proximal end of the outer shaft, wherein the inner shaft has one or more cam grooves and the locking knob has a pin extending into and guided by said cam groove causing the outer shaft to translate longitudinally upon rotation of the locking knob relative to the inner shaft toward an engaged position locking the deflectable legs in the coupled position to the slotted rod receiving implant.
Owner:SPINAL ELEMENTS INC
Axial needle and suture delivery device and method
Owner:MI4SPINE
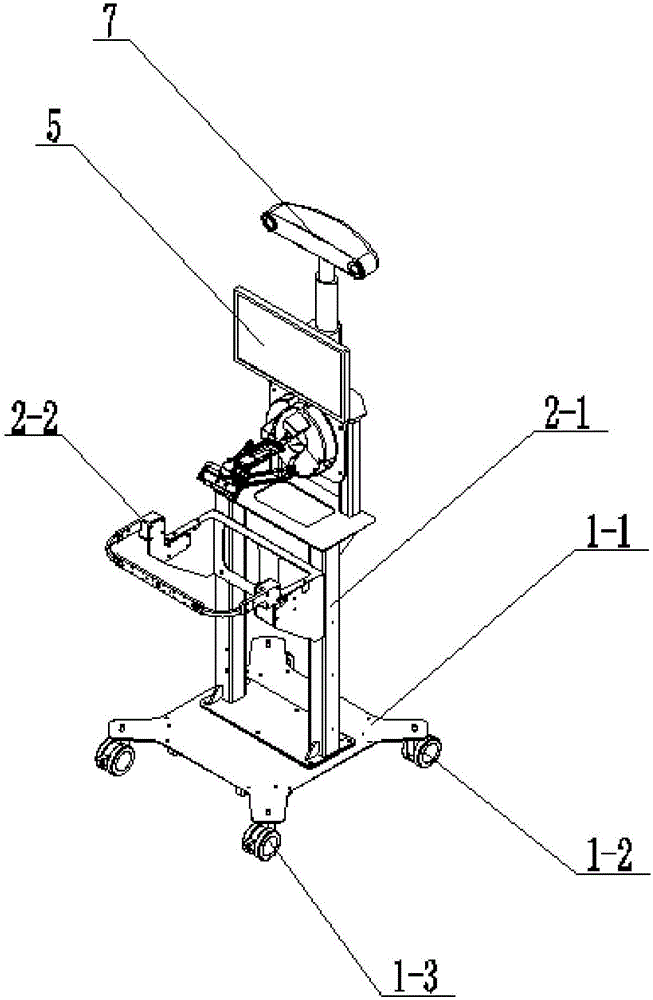
Minimally invasive spine surgery robot main terminal work station
ActiveCN106510847AEnsure safetyGuaranteed real-timeSurgical navigation systemsSurgical robotsSurgical robotDisplay device
Provided is a minimally invasive spine surgery robot main terminal work station, and the work station relates to a main terminal work station. The invention solves the problems of multiple placement requirements by the existing surgery robot at an initial placement, and no favorable placement function provided by the main operation terminal and lengthy time spent in preparing surgeries. The main body of the work station is installed on a base seat, the master manipulator and the keyboard and the mouse are all installed on the main body, the displaying device is installed on the upper part of the main body through a holder, an optical measuring system is installed on the upper end of the main body, the optical measuring system provides the information of locations and poses on the patient and the robot in surgery on a real time basis for a robot navigation system. The work station achieves an integration of the master manipulator, the optical measuring system and the main operation terminal, satisfies the surgery demands in the most simple and fast manner, speeds up the transmission speed of the measuring data, and saves the occupied space in a surgery room. The work station is applied in the field of surgery robot.
Owner:HARBIN SIZHERUI INTELLIGENT MEDICAL EQUIP CO LTD
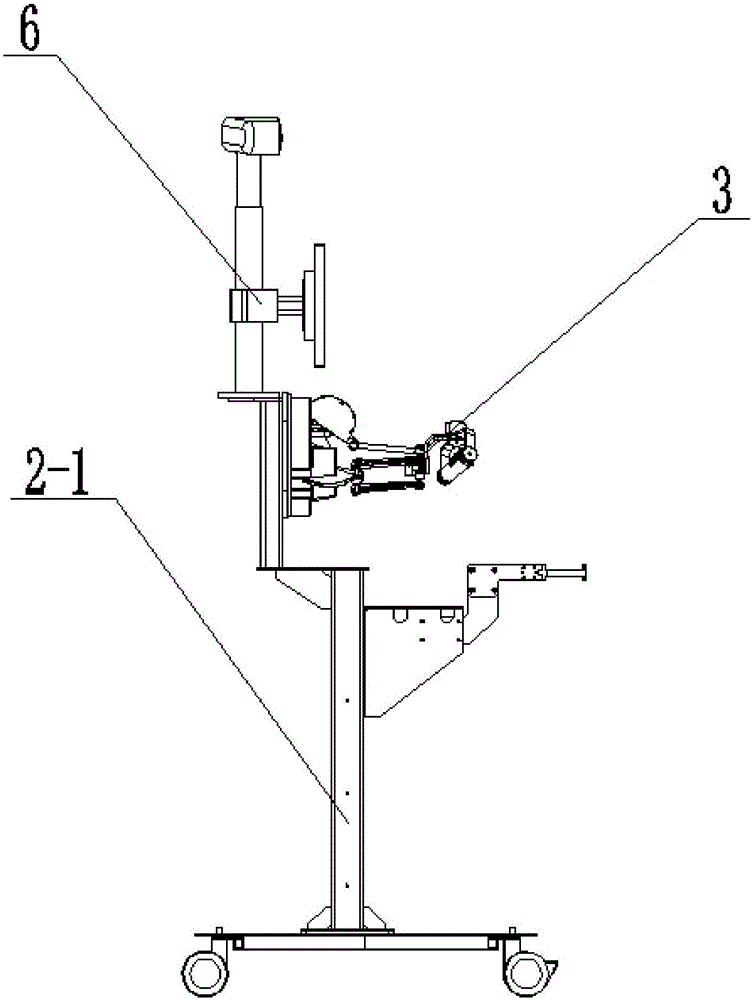
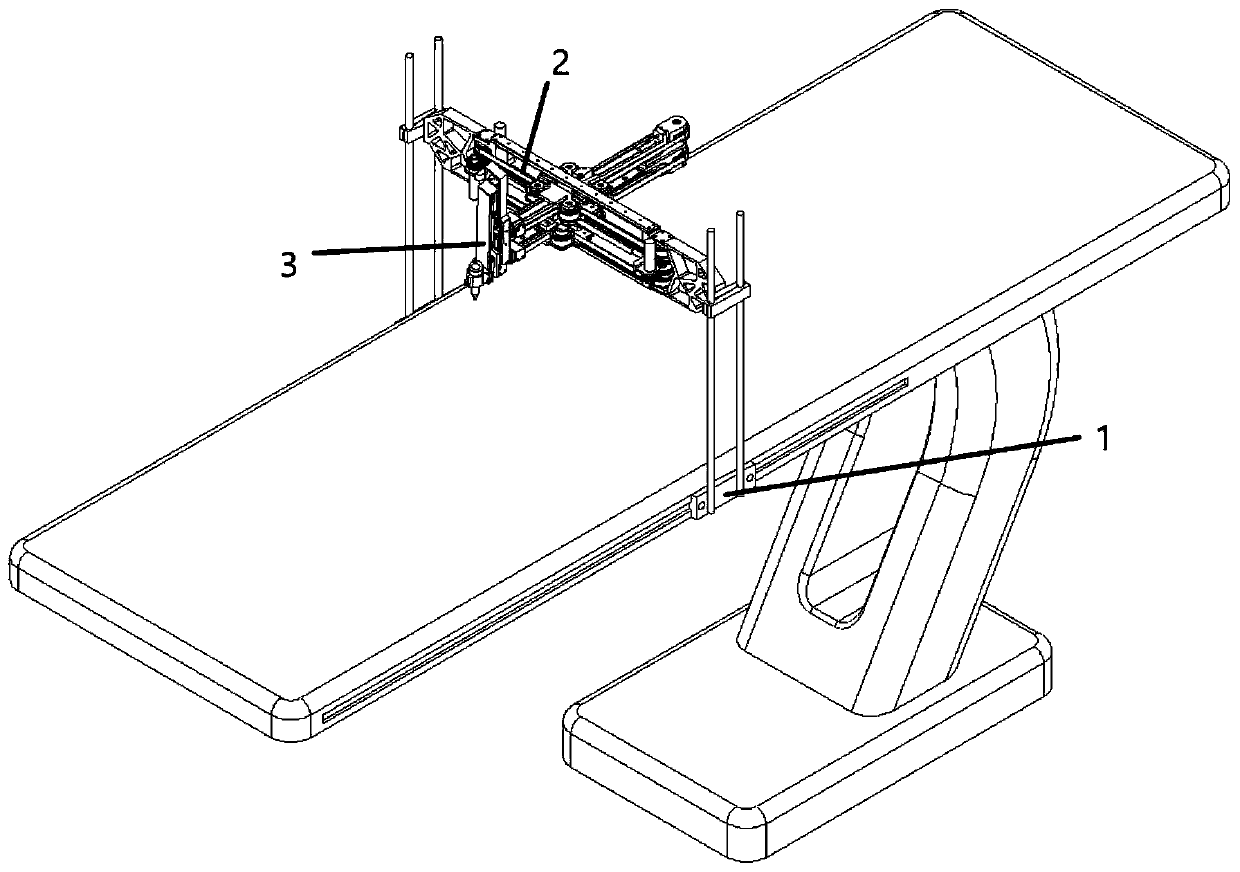
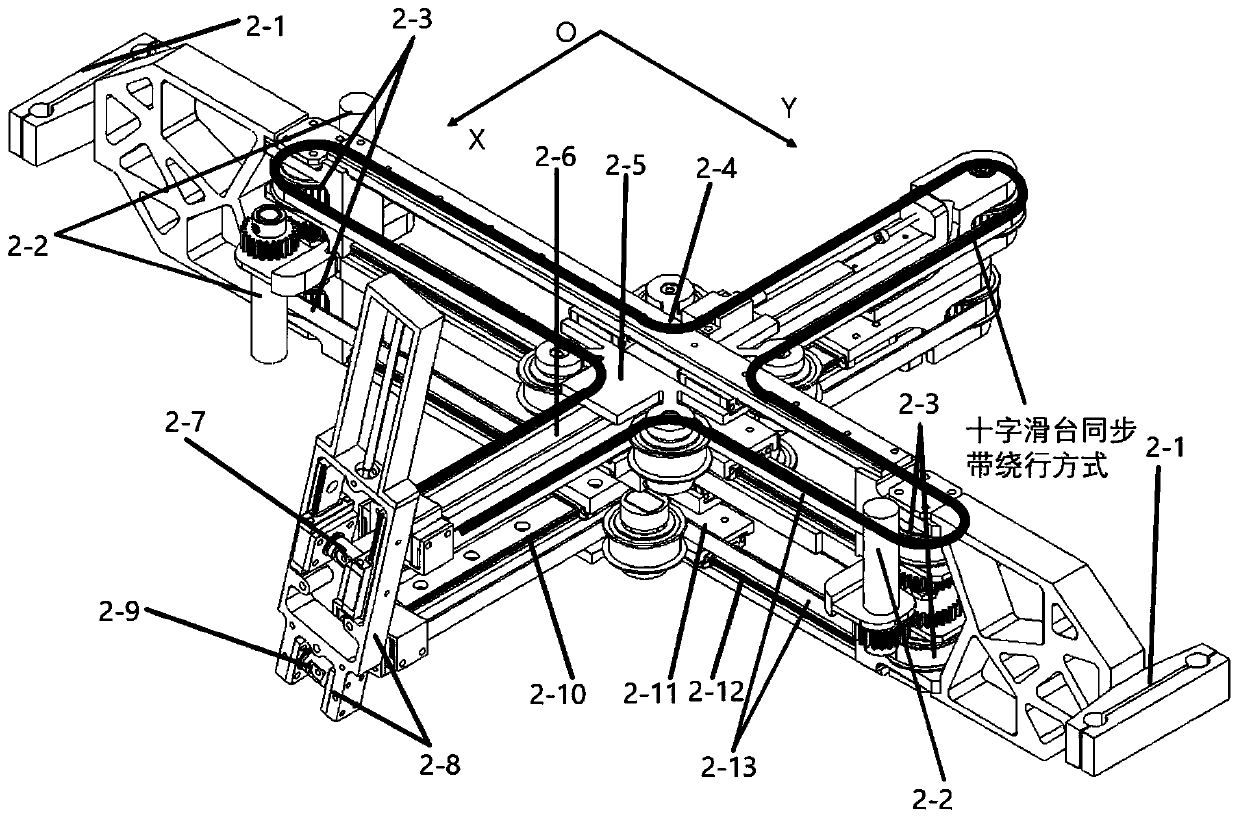
Cross-shaped sliding table driving-type series-parallel spinal surgery robot
ActiveCN111467035AIn line with the physiological structure characteristicsOperating tablesSurgical navigation systemsSpinal columnEngineering
The invention discloses a cross-shaped sliding table driving-type series-parallel spinal surgery robot, and belongs to the technical field of surgical robots. The invention aims to solve the problem that existing spine minimally invasive surgery robots cannot achieve active grinding and drilling functions. The spinal surgery robot comprises sliding bases, a four-degree-of-freedom parallel structure and an axial feeding structure, and the four-degree-of-freedom parallel structure is arranged between the two sliding bases in a connection mode; the four-degree-of-freedom parallel structure comprises an upper group and a lower group of cross-shaped sliding tables which are driven by synchronous belts, and the two cross-shaped sliding tables can achieve feeding in the X direction and the Y direction in a coordinate system XYZ; tail end movable platforms of longitudinal branches of the two sets of cross-shaped sliding tables are connected to the axial feeding structure, and the axial feedingstructure can be driven by the two sets of cross-shaped sliding tables to achieve pitching yawing motion; and the axial feeding structure is connected to surgical instruments and can provide feedingof the surgical instruments in the Z direction in the coordinate system XYZ. The spinal surgery robot is used for minimally invasive spine surgery.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Up cutting knife with suction
An up-cutting knife that has particular application for minimally invasive spinal surgical procedures. The knife includes an elongated tube that is operable to be inserted through a tubular retractor used in minimally invasive surgical procedures. One end of the elongated tube includes a curved head portion having a cutting blade formed on a top surface thereof and a suction port, and an opposite end of the tube is coupled to a handle having a chamber. A suction device can be coupled to an outlet port in the handle that causes blood and other surgical material to be drawn through the tube and out of the handle.
Owner:MI4SPINE
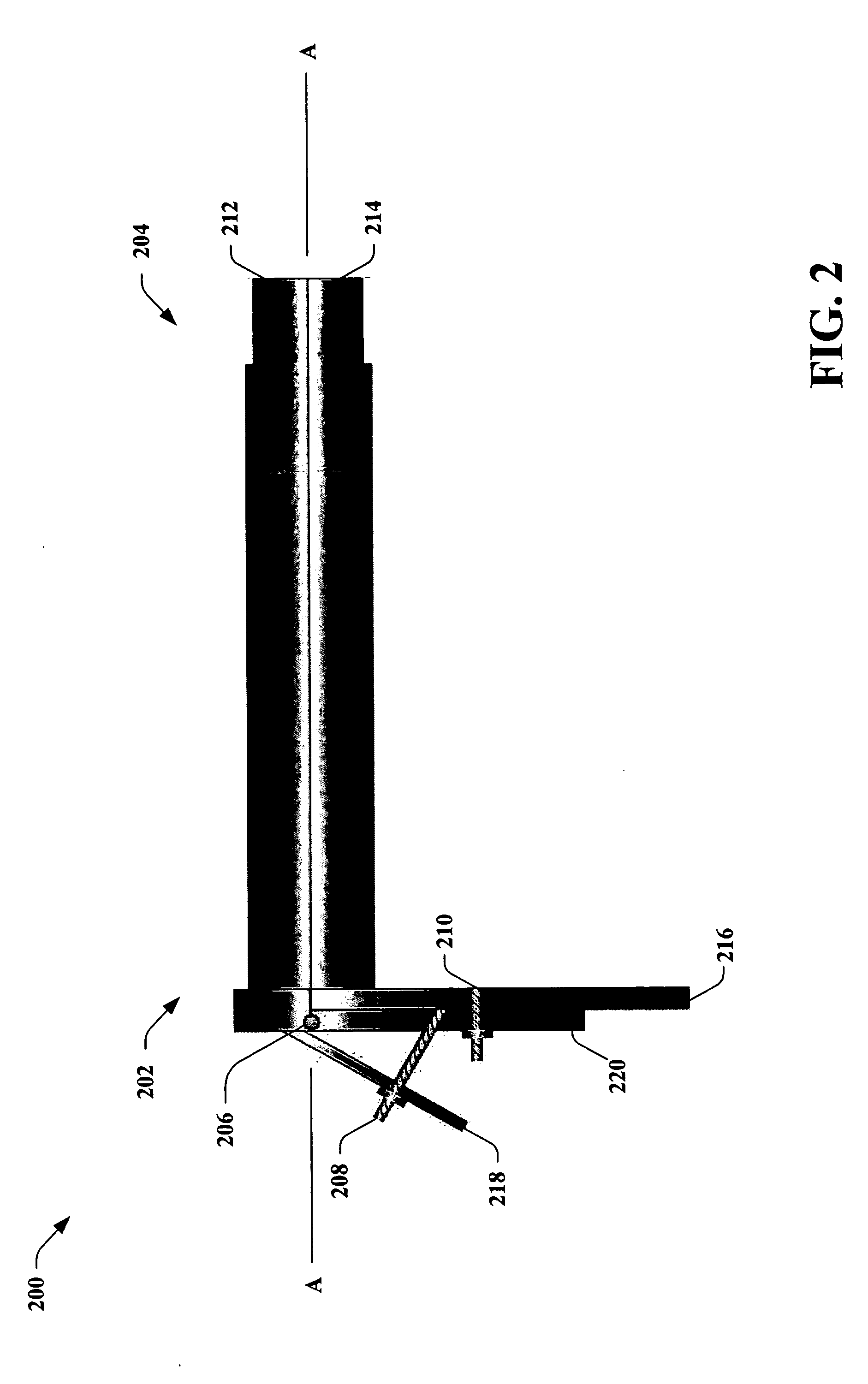
Working channel for minimally invasive spine surgery
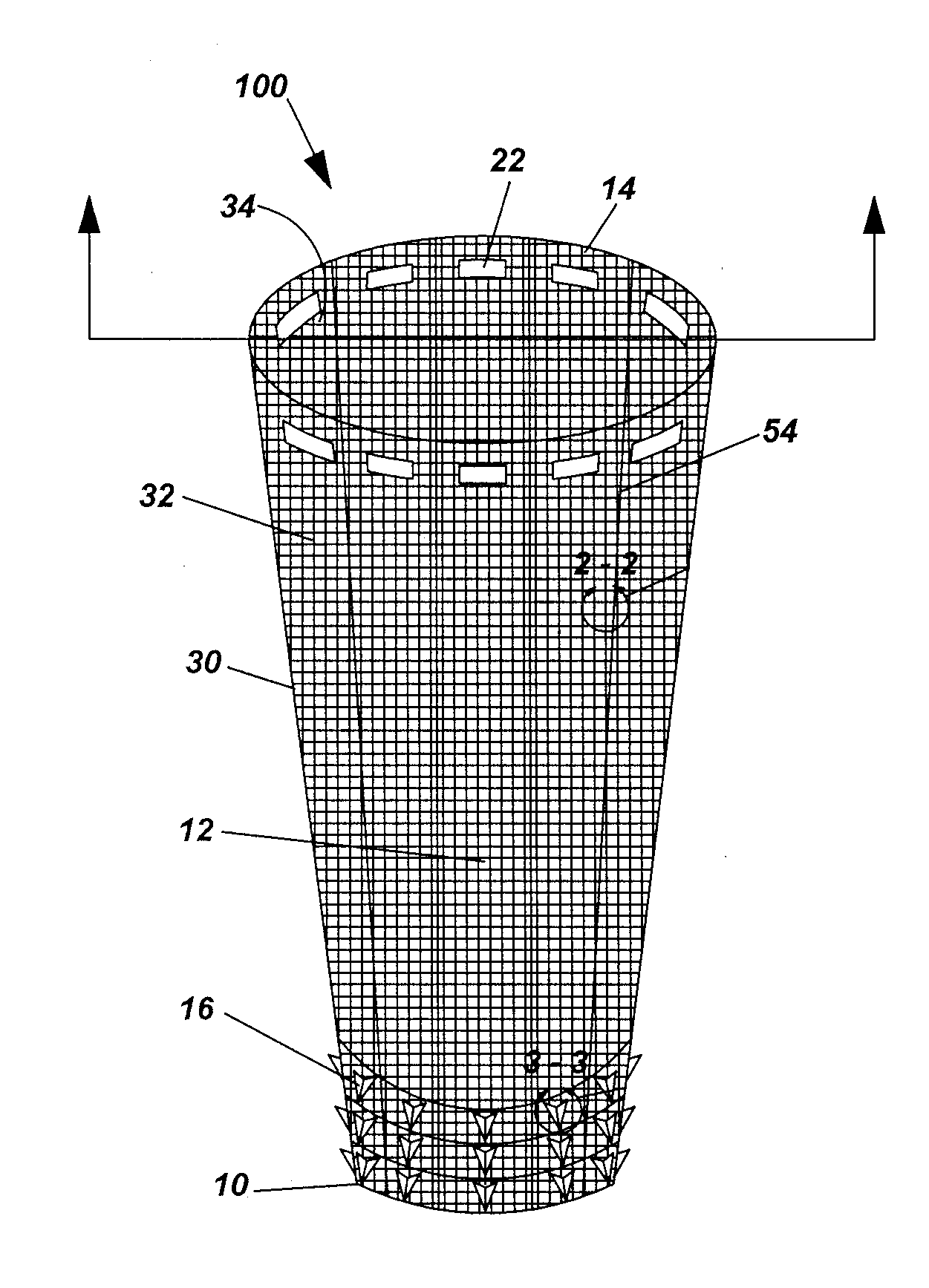
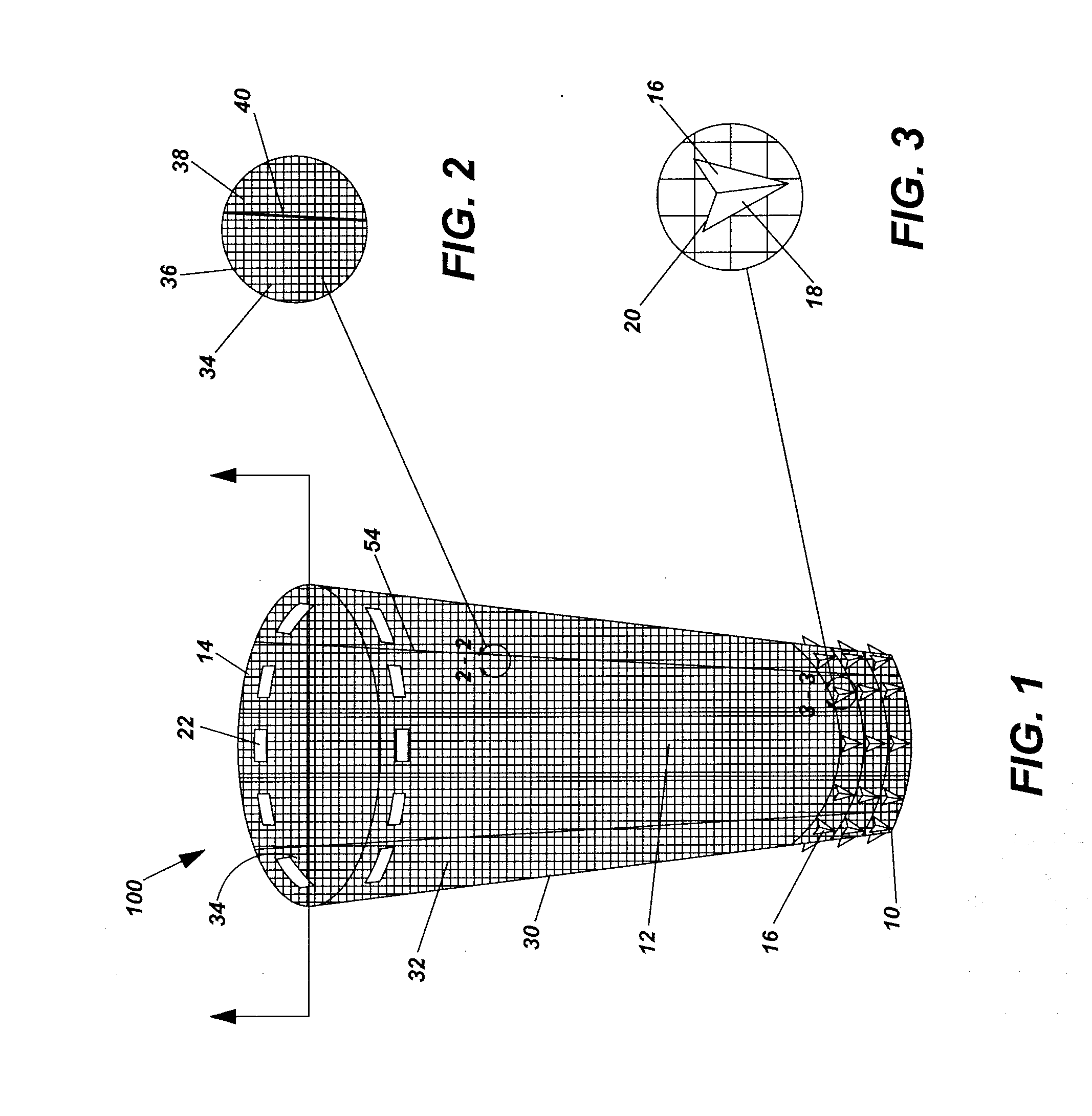
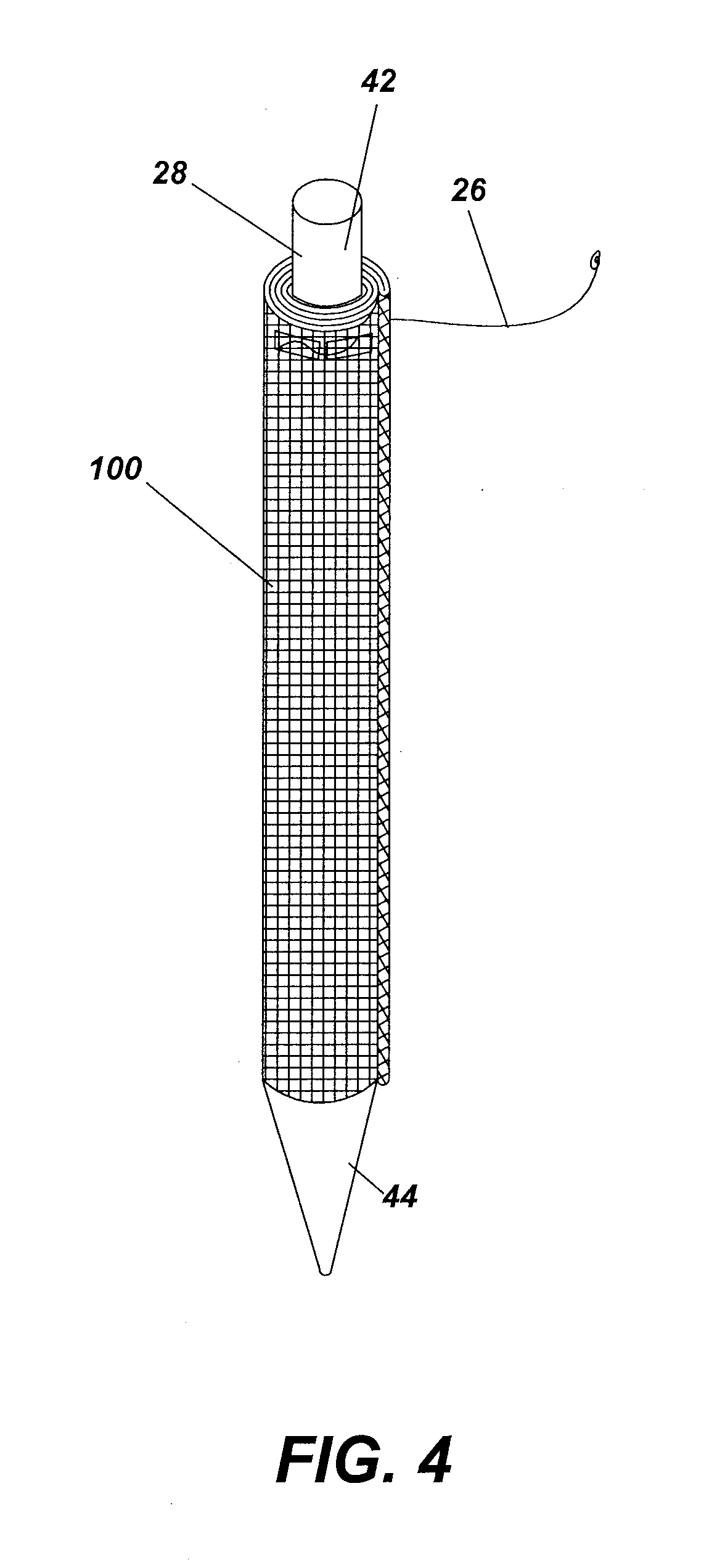
A working channel for spinal surgery includes a body having a distal end, a proximal end and an interior lumen traversing through the elongate body. The elongate body generally has a parallelogram-shaped cross-section. Another working channel for spinal surgery includes a flared upper section having a distal end, a proximal end and an interior lumen traversing through the flared upper section. The proximal end of the flared upper section is wider than the distal end of the flared upper section. The working channel also includes a lower section extending from the distal end of the flared upper section. The lower section has a distal end, a proximal end and an interior lumen traversing through the lower section. The lower section generally has a parallelogram-shaped cross-section.
Owner:SPINAL ELEMENTS INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com