Method for reducing coal consumption by comprehensively and circularly utilizing waste heat of Webster furnace
A Webster furnace and waste heat technology, applied in the field of non-ferrous metal smelting, to reduce consumption, realize energy saving and emission reduction, and reduce production costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0045] Example 1: The Method of Reducing Coal Consumption by Carrying Out Comprehensive Recycling of Wechsler Furnace Waste Heat under Spring Climate Conditions
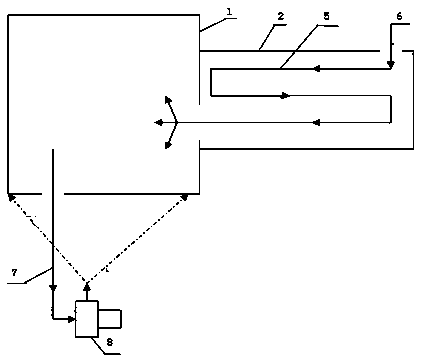
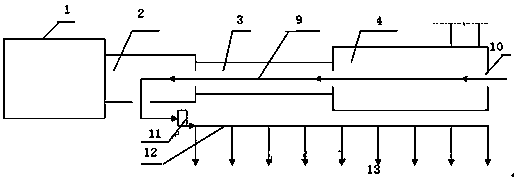
[0046] Step a: Install thermometers: install one at five meters away from production (thermometer 1), at the air inlet of the oxidation chamber top (thermometer 2), at the inlet of the furnace bottom fan (thermometer 3), and at the outlet of the furnace bottom fan (thermometer 4) Thermometer: Install a thermometer at the air inlet (thermometer 5) of the dust collection chamber, the air inlet of the blower (thermometer 6), and the air outlet of the blower (thermometer 7).
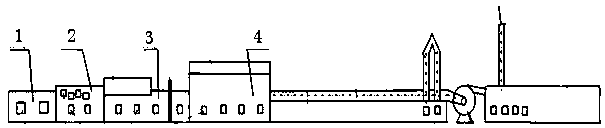
[0047] Step b: According to the ratio of zinc and carbon in the briquette of 1.6:1, the batching is carried out, and a comprehensive sample of the briquette is taken. After testing, the indicators of the briquette are: 28.59% zinc, 17.27% fixed carbon, and 15.6% moisture. The lump ore is stacked in the nearby image 3 The stacking site shown is ...
Embodiment 2
[0055] Example 2: Method of reducing coal consumption by comprehensive recycling of waste heat from Webster furnace under summer climate conditions
[0056] Step a: Install thermometers: install one at five meters away from production (thermometer 1), at the air inlet of the oxidation chamber top (thermometer 2), at the inlet of the furnace bottom fan (thermometer 3), and at the outlet of the furnace bottom fan (thermometer 4) Thermometer: Install a thermometer at the air inlet (thermometer 5) of the dust collection chamber, the air inlet of the blower (thermometer 6), and the air outlet of the blower (thermometer 7).
[0057] Step b: Dosing according to the ratio of zinc and carbon in the briquette 1.6:1, take a comprehensive sample of the briquette, and after testing, the indicators of the briquette are: 29.14% zinc, 18.27% fixed carbon, and 14.3% moisture. The lump ore is stacked in the nearby image 3 The stacking site shown is dried, and the blower is started, and the ...
Embodiment 3
[0065] Example 3: The Method of Reducing Coal Consumption by Comprehensive Recycling of Waste Heat from Webster Furnace in Winter Climate Conditions
[0066] Step a: Install thermometers: install one at five meters away from production (thermometer 1), at the air inlet of the oxidation chamber top (thermometer 2), at the inlet of the furnace bottom fan (thermometer 3), and at the outlet of the furnace bottom fan (thermometer 4) Thermometer: Install a thermometer at the air inlet (thermometer 5) of the dust collection chamber, the air inlet of the blower (thermometer 6), and the air outlet of the blower (thermometer 7).
[0067] Step b: According to the ratio of zinc and carbon in the briquette of 1.6:1, the batching is carried out, and a comprehensive sample of the briquette is taken. After testing, the indicators of the briquette are: 27.29% zinc, 17.02% fixed carbon, and 12.4% moisture. The lump ore is stacked in the nearby image 3 The stacking site shown is dried, and t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com