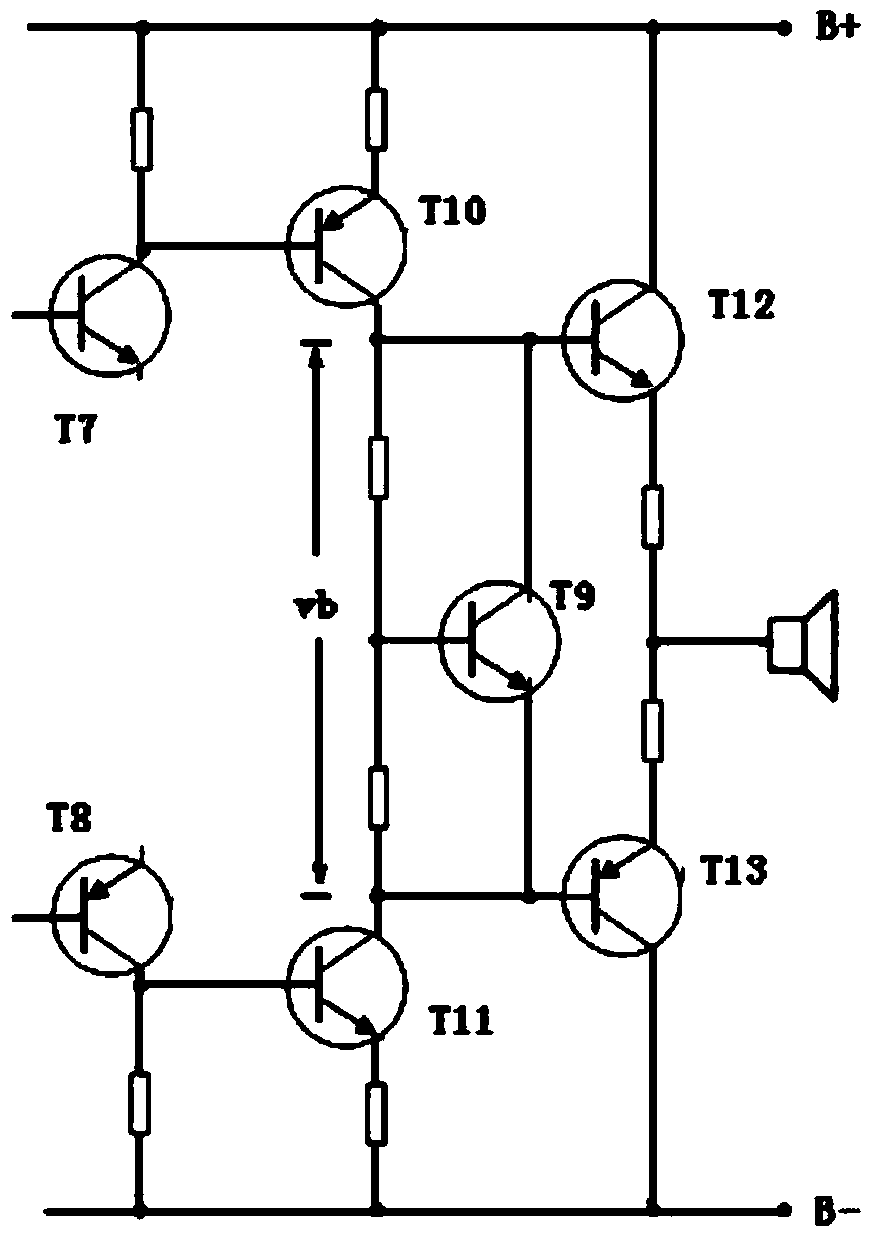
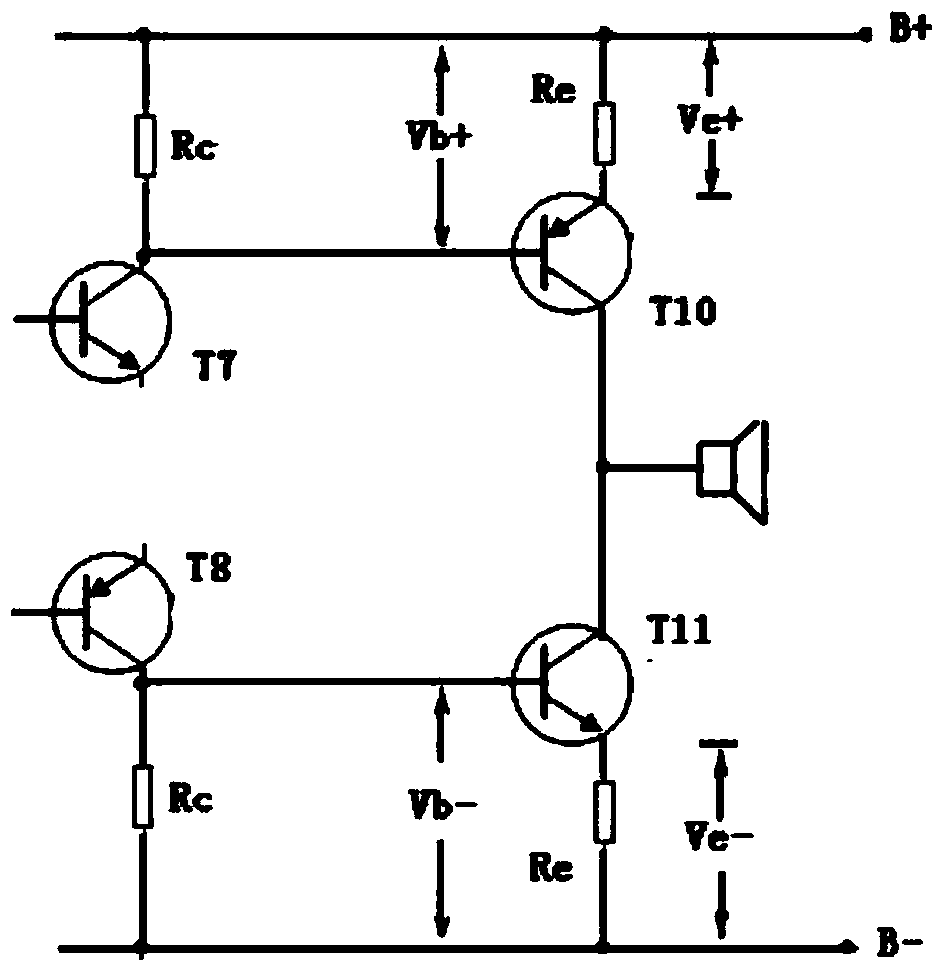
Audio frequency amplifier adjunct circuit used for eliminating emitter output stage
A technology of audio amplifiers and additional circuits, applied in the direction of transducer circuits, sensors, electrical components, etc., can solve the problems of unstable working status of T10 and T11, and achieve the effect of eliminating interference
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0043] Such as Figure 4 and Figure 5 As shown, the detection circuit includes a pair of diodes D1, D2 and a group of symmetrical detection PNP transistor T1 and detection NPN transistor T2, the cathode of the diode D1 is connected to the base of the PNP transistor T1, and the diode D2 The anode of the NPN transistor T2 is connected to the base.
[0044]The amplifying circuit then includes a pair of amplifying NPN transistor T3 and amplifying PNP transistor T4 with the function of amplifying the current. In addition, resistors R3 and R4 are connected in series between the emitters of the amplifying transistors T3 and T4 in the amplifying circuit, and the R7, T3, R3, R4, T4 and R8 are sequentially connected in series, and the resistance values of R7 and R8 are equal.
[0045] The adjustable constant current source circuit is composed of a group of symmetrical constant current source PNP transistors T5 and constant current source NPN transistors T6.
[0046] The collector ...
Embodiment 2
[0051] Such as Figure 6 and Figure 7 As shown, the difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that: the detection circuit includes a diode D and a detection transistor T1 for detection, and the diode D is connected to the base of the detection transistor T1; The amplifying circuit includes an amplifying transistor T3, the adjustable constant current source circuit is composed of a group of symmetrical constant current source PNP transistor T5 and constant current source NPN transistor T6, the constant current source PNP transistor T5 and constant current source NPN The bases of the transistor T6 are respectively connected to two sets of equal-value voltage dividers R7 and R8.
[0052] The amplifying circuit is connected with the adjustable constant current source circuit through an optocoupler OC.
[0053] The specific connection relationship of each circuit is: the collector of the detection transistor T1 is connected to the base of the amplifier transistor T3...
Embodiment 3
[0057] Such as Figure 8 and Figure 9 As shown, this embodiment is a combination and extension of Embodiment 1 and Embodiment 2, wherein the detection circuit uses a pair of diodes D1, D2 and a group of symmetrical detection PNP transistor T1 and detection NPN transistor T2, the diode D1 The negative pole of the diode D2 is connected to the base of the detection PNP transistor T1, and the anode of the diode D2 is connected to the base of the detection NPN transistor T2.
[0058] Correspondingly, the amplifying circuit includes an amplifying NPN transistor T3 and an amplifying PNP transistor T4, and the adjustable constant current source is composed of a constant current source PNP transistor T5 and a constant current source NPN transistor T6, and the constant current source The bases of the PNP transistor T5 and the constant current source NPN transistor T6 are respectively connected to two sets of equal voltage dividers R7, R5 and R6, R8.
[0059] The connection relationsh...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com