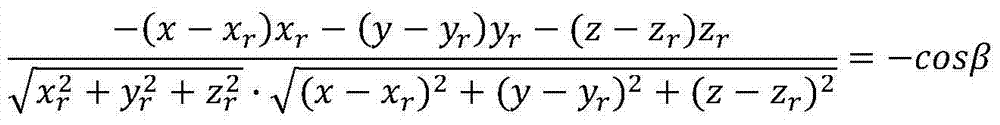Satellite-borne passive radar location method based on GNSS-R (global navigation satellite system-reflection) signal geometrical relationship
A passive radar, positioning method technology, applied in satellite radio beacon positioning system, radio wave measurement system, radio wave reflection/re-radiation and other directions, can solve the problems of increasing the complexity of the positioning algorithm, too many parameters, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
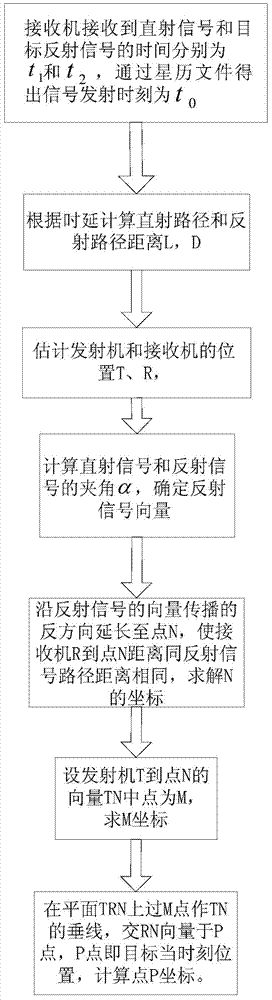
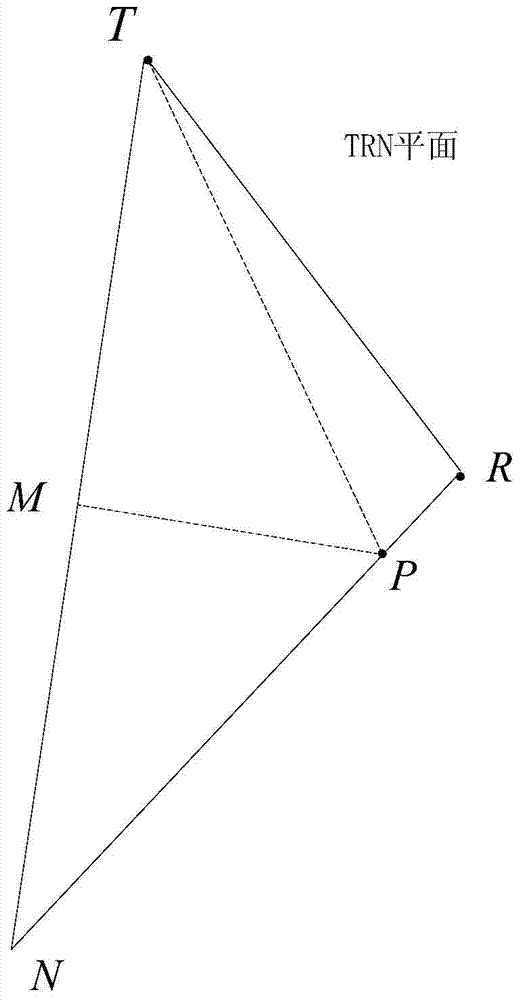
[0087] See figure 1 , 2 , in the WGS-84 coordinate system, in meters, let the R coordinate of the receiver be (-4069896, -3583236, 4527639), and the T coordinate of the transmitter be (-11178791, -13160191, 20341528), the measured reflected signal and The angle between the direct signal and the velocity direction of the receiver is arccos(-0.1394), the angle between the reflected signal and the normal vector of the moving plane is arccos(0.5881), and the normal vector of the moving plane is arccos(0.5881). The vector is (-4069896, -3583236, 4527639), the receiver velocity vector is (-4738, -1796, -5654), and the direct signal vector is (7108895, 9576955, -15813889)
[0088] A kind of target positioning method based on GNSS-R geometric relation of the present invention concrete steps are as follows:
[0089] Step 1: The moment when the receiver receives the direct signal from the GPS satellite is t 1 , the ephemeris file in the GPS signal contains the launch time t 0 , in ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com