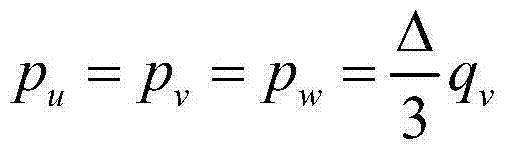Method for determining carrying capacity and temperature field of submarine cable
A submarine cable and determination method technology, applied in the field of power cables, can solve the problems of error in calculation results, inability to accurately represent the temperature field of the cable, the heat conduction between the cable and the soil, and the complex heat exchange between the soil and seawater or air.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0061] In order to describe the present invention more specifically, the technical solution and related principles of the present invention will be described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
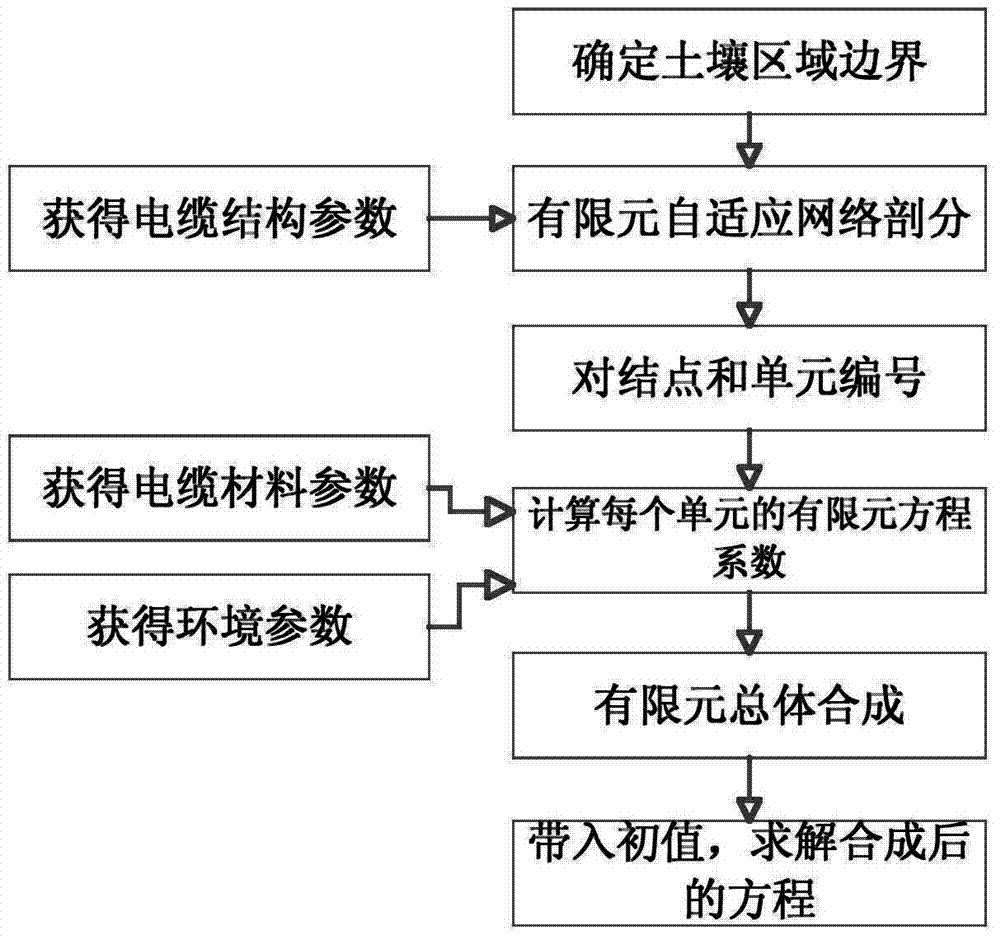
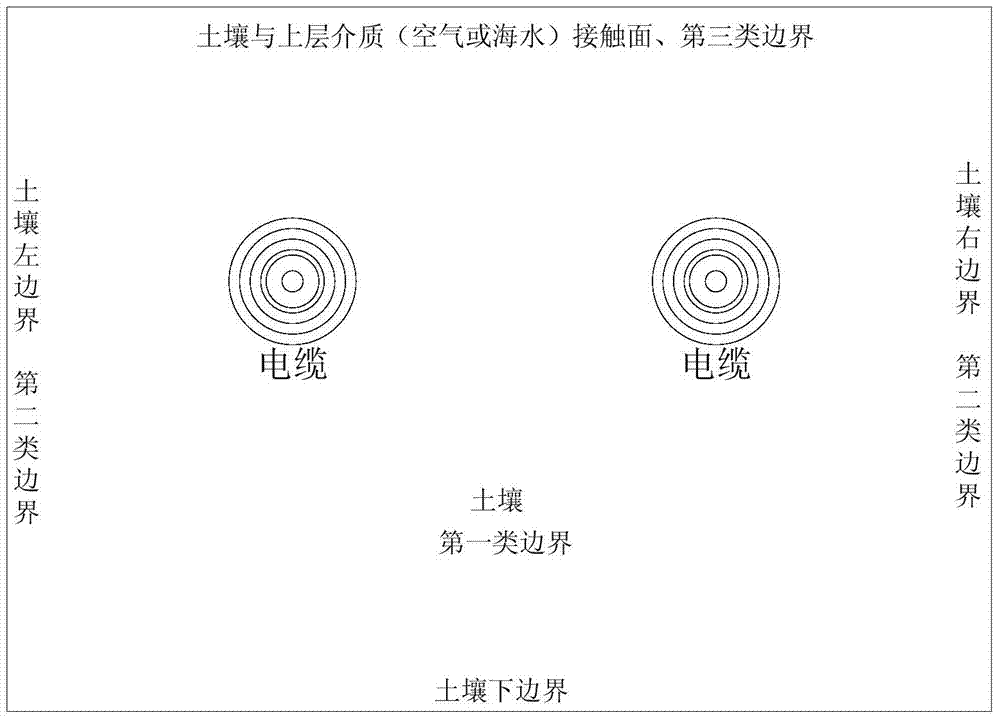
[0062] Such as figure 1 As shown, a method for determining the ampacity and temperature field of a submarine cable includes the following steps:
[0063] (1) The structural parameters and material parameters of the cable are found in the product manual from the cable selection; the cable can be divided into: core conductor, conductor shielding layer, insulation layer, insulation shielding layer, inner lining layer, armoring layer, outer sheath layer, the structural parameters of the cable are mainly obtained by obtaining the inner diameter and outer diameter of each layer of the cable, and the material parameters of the cable are mainly obtained by obtaining the density, resistivity, thermal conductivity, and constant pressure of the materials used in each l...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com