Method for simultaneously measuring distributed type temperatures and strain
A measurement method and distributed technology, applied in the field of measurement, can solve the problems such as the inability to use communication optical cables or optoelectronic composite cables, the difficulty of applying single-mode optical fibers, and the complex system structure, so as to reduce complexity, expand the scope of application, reduce The effect of manufacturing cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
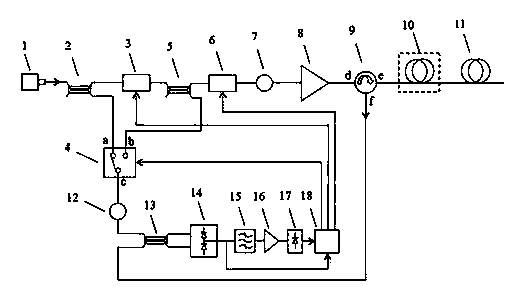
[0037] The optical path system of the present invention works alternately in BOTDR and COTDR modes.
[0038] 1) BOTDR working mode.
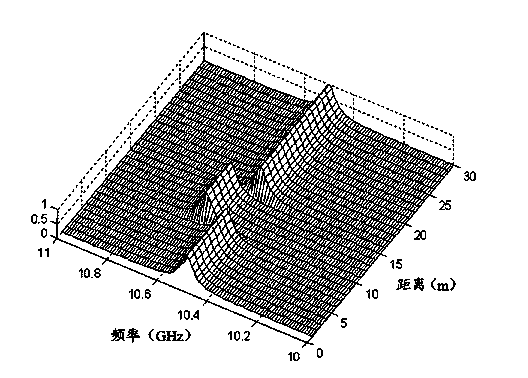
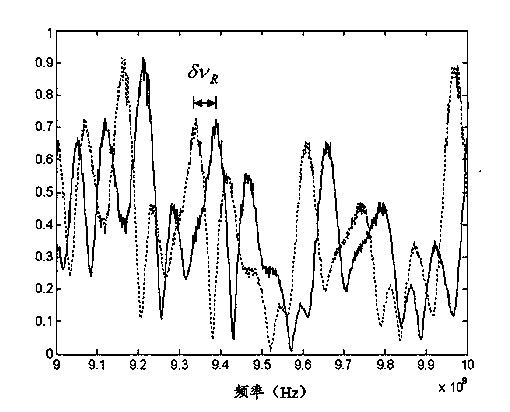
[0039] The signal processing and control unit 18 controls the a-end and c-end of the optical switch 4 to be connected, so that the measurement system works in the BOTDR mode, assuming that the center frequency of the Brillouin scattering spectrum is (When the incident light wavelength is 1550nm, Typical values are around 10.5 GHz).
[0040] The narrow-linewidth tunable laser 1 emits continuous light with a wavelength of C-band (for example, 1550nm), which is divided into two paths by the first fiber coupler 2, and the first path passes through the optical frequency shifter 3, so that the frequency of the incident light is generated ( GHz)~( GHz) upper offset (for example, 9~10 GHz, when GHz), that is, the optical frequency increases ( GHz)~( GHz), and at ( GHz)~( GHz) range is a discrete frequency point with a fixed...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com