Polypeptide and nucleic acid drug nanoparticles containing same
A nucleic acid drug and nanoparticle technology, applied in the field of nucleic acid drug nanoparticles and peptides, can solve the problems of inability to enter specific tissues in a targeted manner, lack of targeting of RNA, poor stability of RNA, etc. Improve targeting and good stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
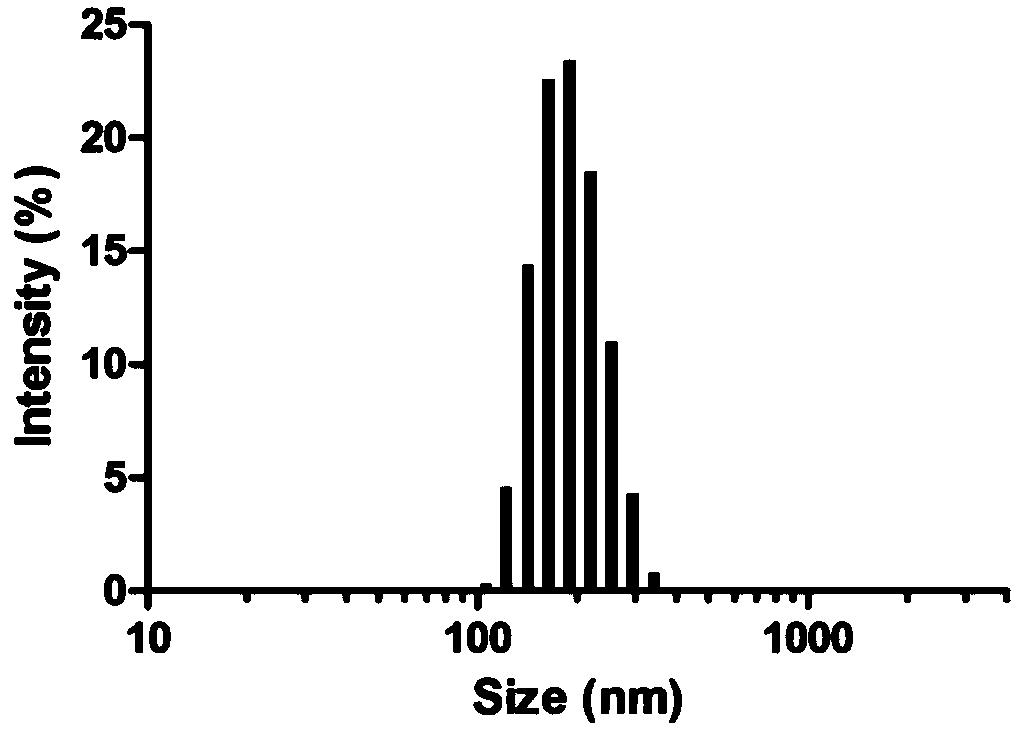
[0035] The preparation of embodiment 1 polypeptide-nucleic acid nanoparticles
[0036]Design and solid-phase synthesize a polypeptide with the following sequence:
[0037] SFSIIHTPILPLGGGGRRRRRRRRR (R is D-arginine, hereinafter referred to as SP94-dR);
[0038] Small interfering RNA (hereinafter referred to as siFOX) was designed with Foxo3a, which is highly expressed in liver cancer cells, as the targeting gene. The sense strand of siFOX is: 5’-GCACAGAGUUGGAUGAAGUTT-3’; the antisense strand is: 5’-ACUUCAUCCAACUCUGUGCTT-3’;
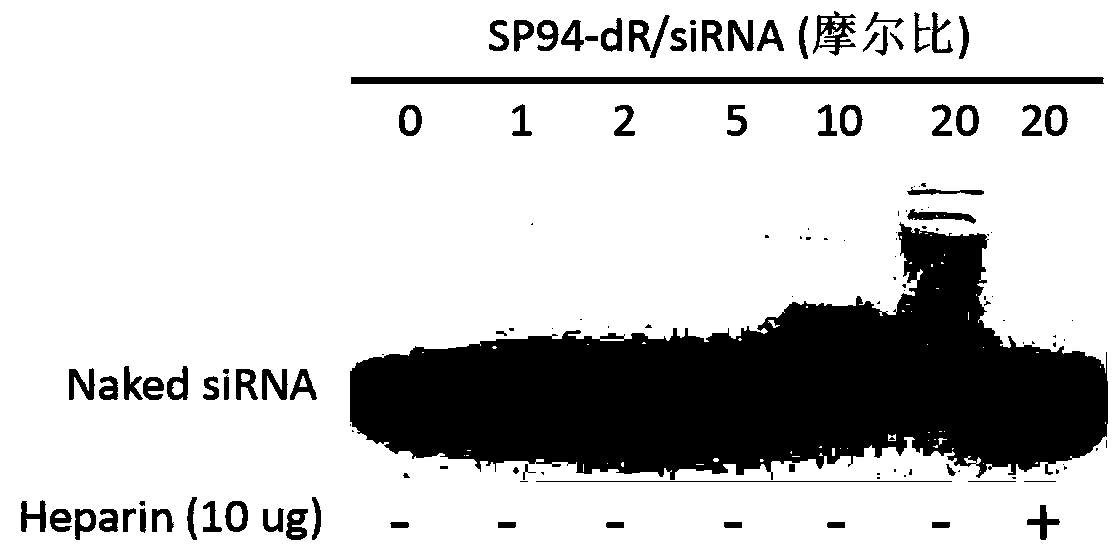
[0039] After mixing siFOX and SP94-dR in DEPC water at different molar ratios (1:1-1:20), let stand at room temperature for 15 minutes, and use 2% agarose electrophoresis to analyze the degree of recombination between the two. The result shows that when the molar ratio of the two is 1:20, the band of siRNA disappears, indicating that siRNA has formed a complex with the polypeptide ( figure 1 ). The complex reappeared after adding heparin, which has a ...
Embodiment 2
[0041] Example 2: Interference of nanoparticles on target gene Foxo3a in liver cancer cells Huh7
[0042] (1) Add the SP94-dR / siFOX nanoparticles prepared in Example 1 to the Opti-MEM culture medium grown with Huh7 cells, and the final concentration of the SP94-dR / siFOX nanoparticles in the culture medium is 12.5-100nM;
[0043] (2) Place the Petri dish in 5% CO 2 , After culturing in a 37°C incubator for 6 hours, replace it with fresh DMEM culture medium that does not contain SP94-dR / siFOX nanoparticles and continue culturing for 24 hours;
[0044] (3) Huh7 cells were recovered, lysed with RIPA lysate for 30 minutes, and Western blot was used to detect the interference of SP94-dR / siFOX nanoparticles on the expression of Foxo3a protein. The test results were as follows: Figure 4 shown.
[0045] The results showed that SP94-dR / siFOX nanoparticles could target siFOX to liver cancer cells and efficiently down-regulate the expression level of the target gene Foxo3a.
Embodiment 3
[0046] Example 3: Interference of nanoparticles on target gene Foxo3a in lung cancer cell H1299
[0047] (1) Add the SP94-dR / siFOX nanoparticles prepared in Example 1 to the Opti-MEM culture medium grown with H1299 cells, and the final concentration of the SP94-dR / siFOX nanoparticles in the culture medium is 12.5-200nM;
[0048] (2) Place the Petri dish in 5% CO 2 , After culturing in a 37°C incubator for 6 hours, replace it with fresh RPMI1640 culture medium that does not contain SP94-dR / siFOX nanoparticles and continue culturing for 24 hours;
[0049] (3) Recover H1299 cells, lyse them with RIPA lysate for 30 minutes, and use Western blot to detect the interference of SP94-dR / siFOX nanoparticles on Foxo3a protein expression. The test results are as follows: Figure 5 shown.
[0050] The results showed that SP94-dR / siFOX nanoparticles could not down-regulate the expression of the target gene Foxo3a in lung cancer H1299 cells, indicating that the nanoparticles had selectivit...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| polydispersity index | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com