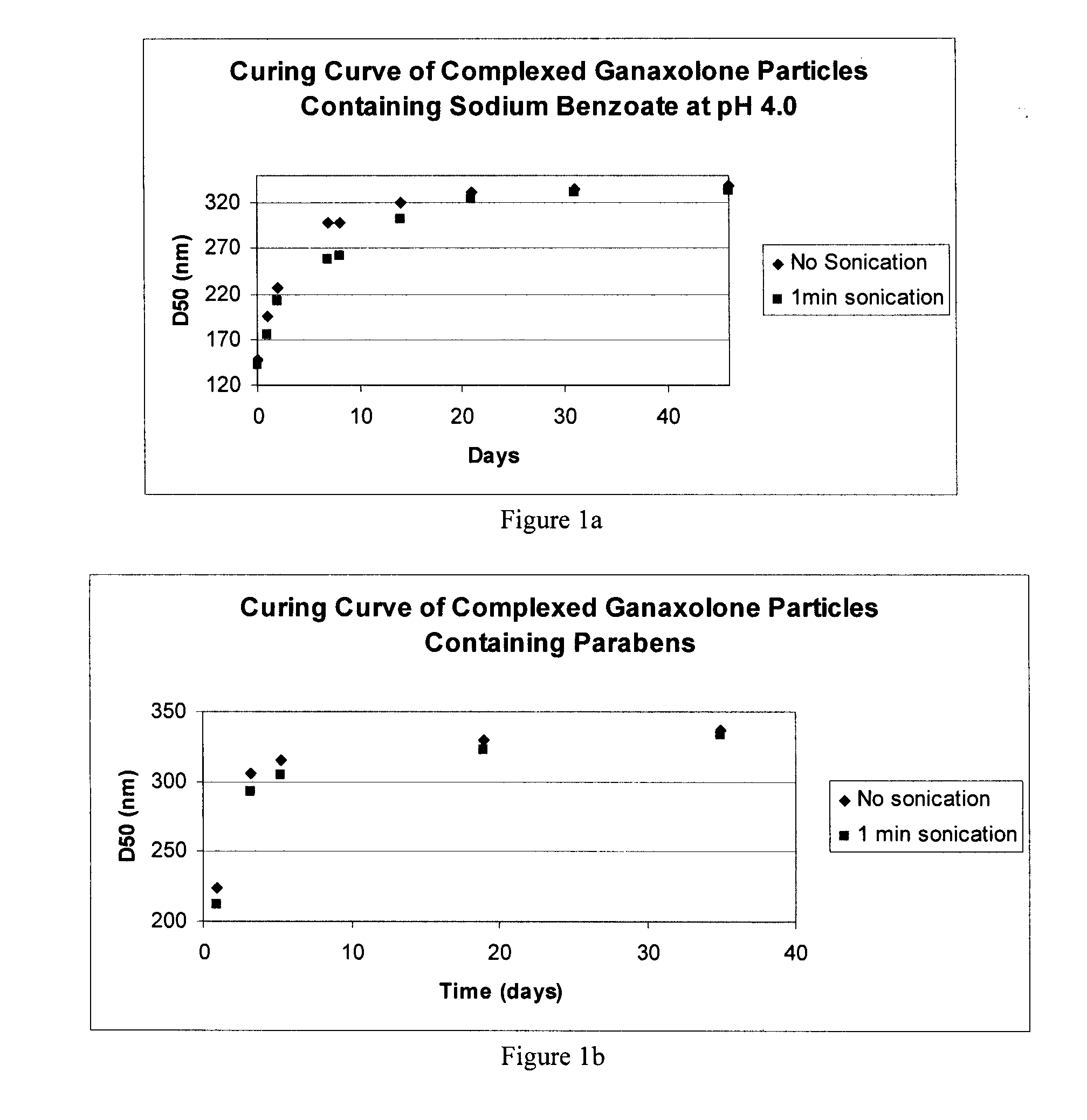
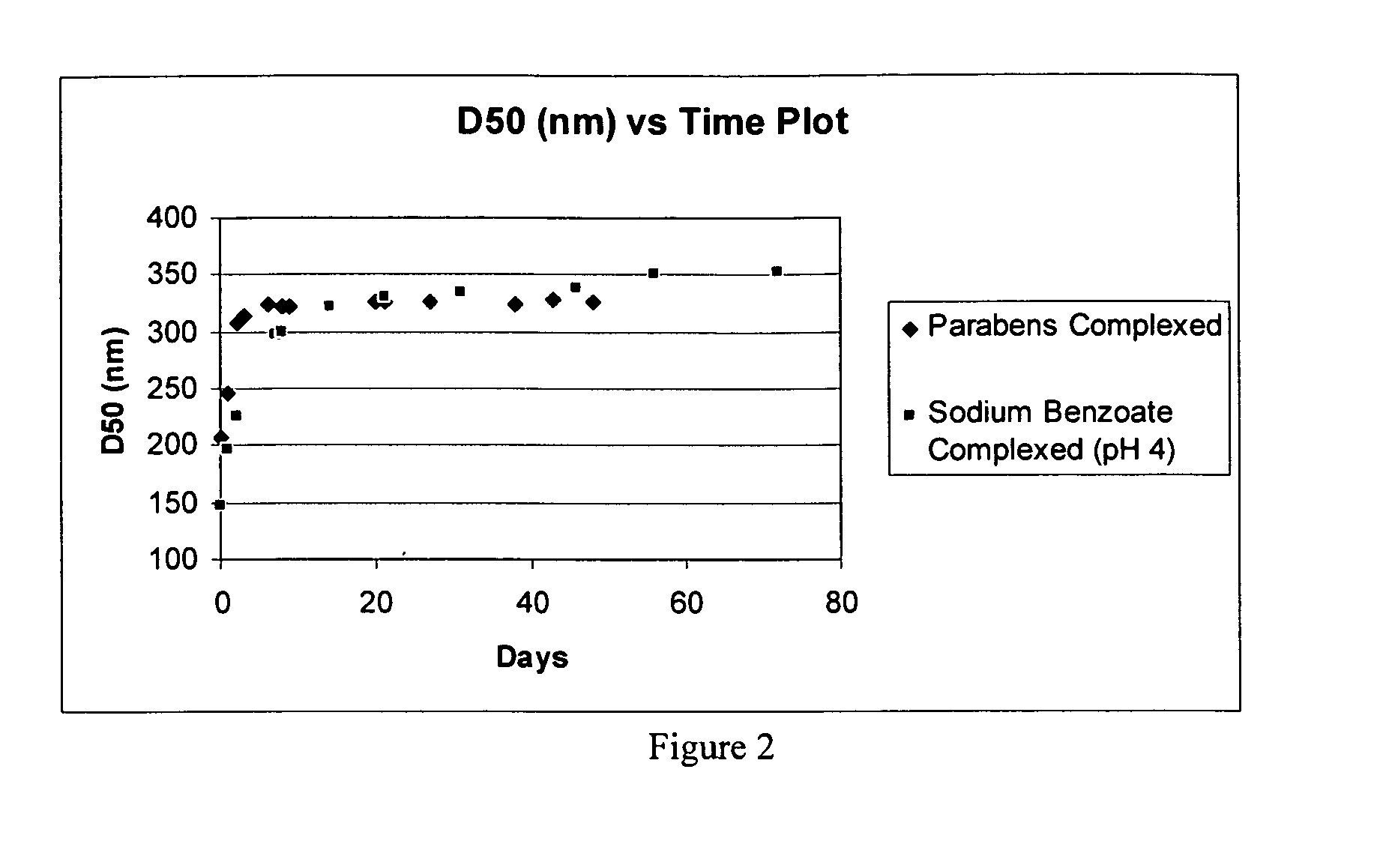
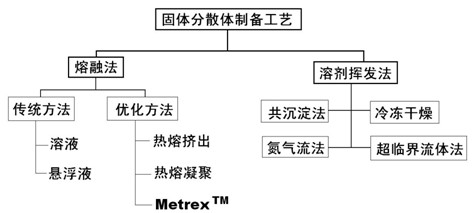
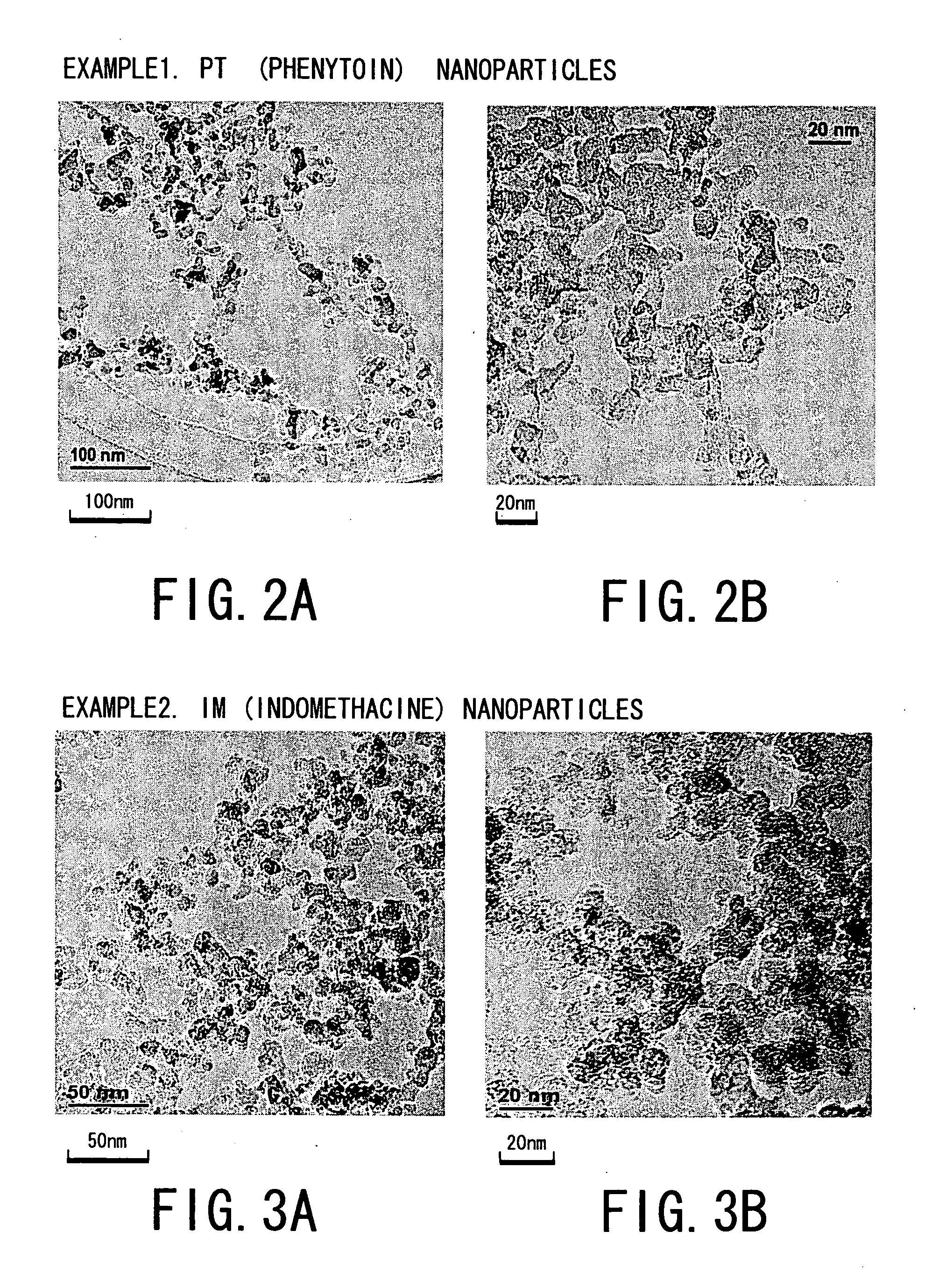
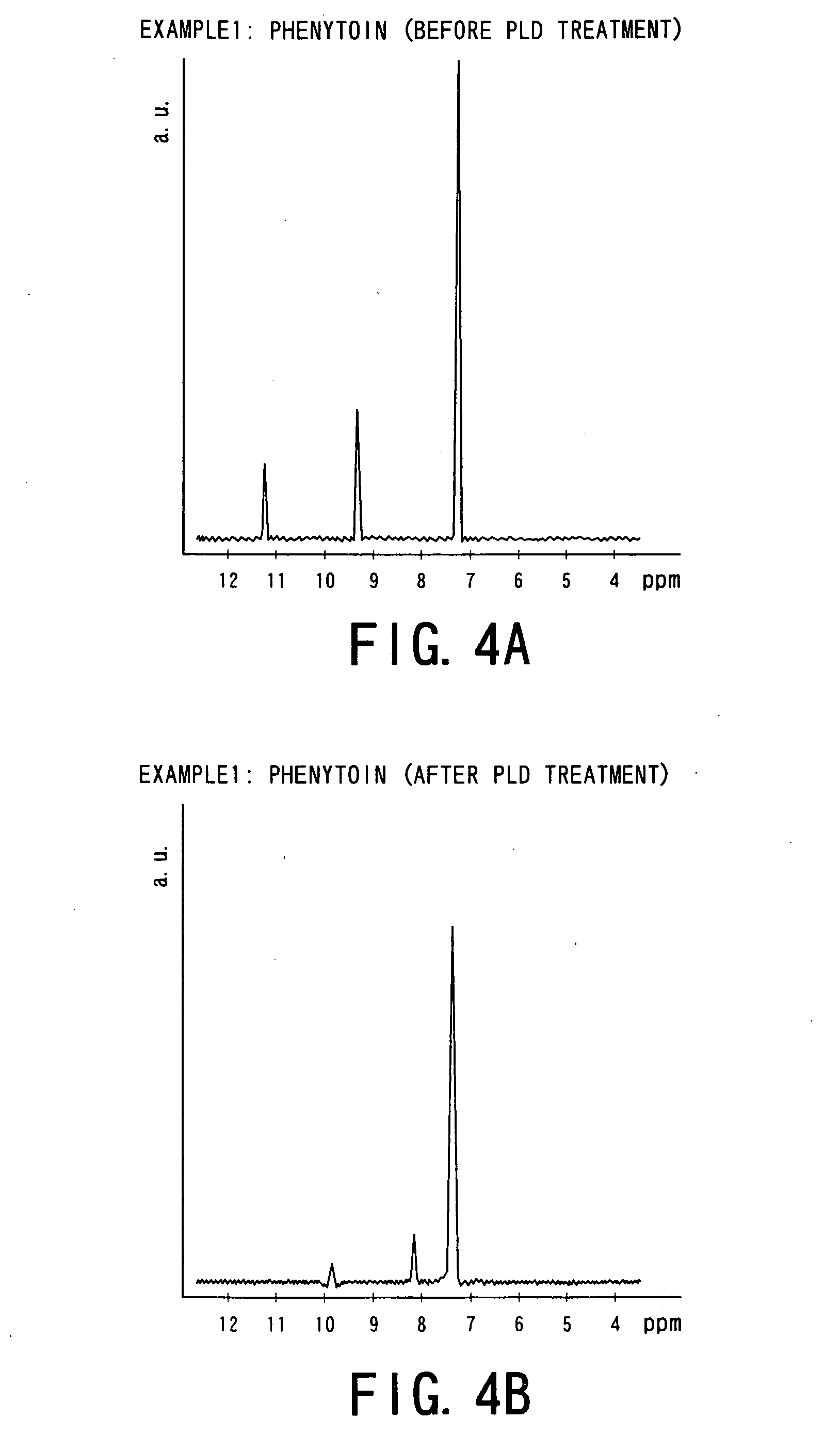
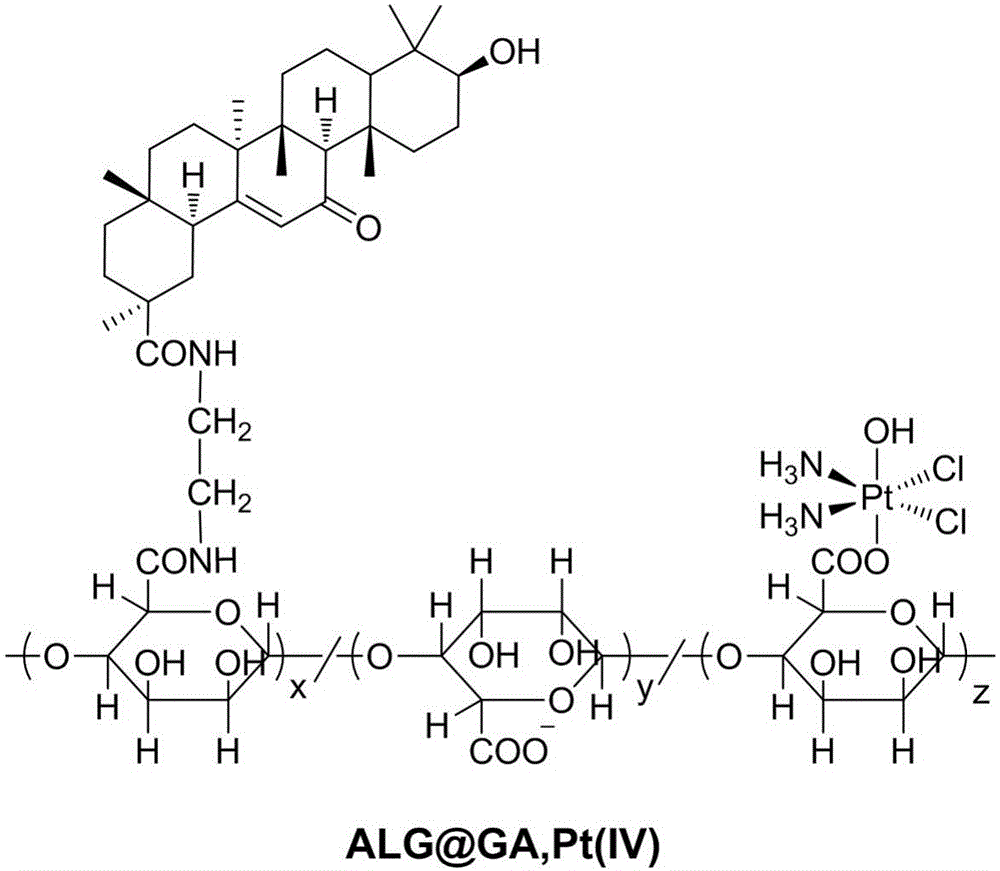
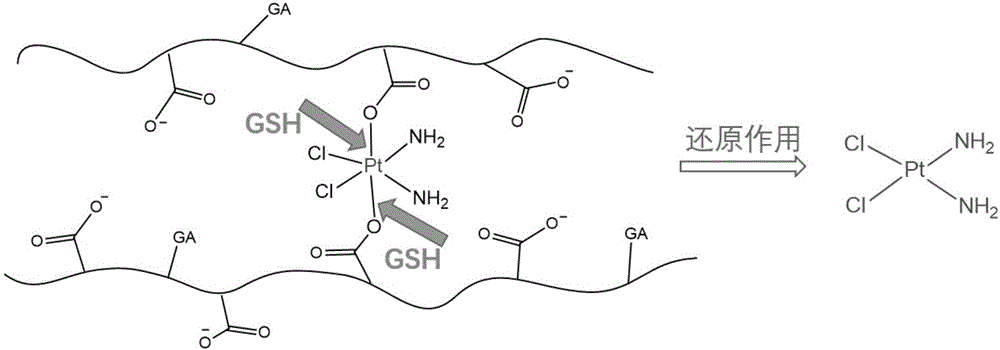
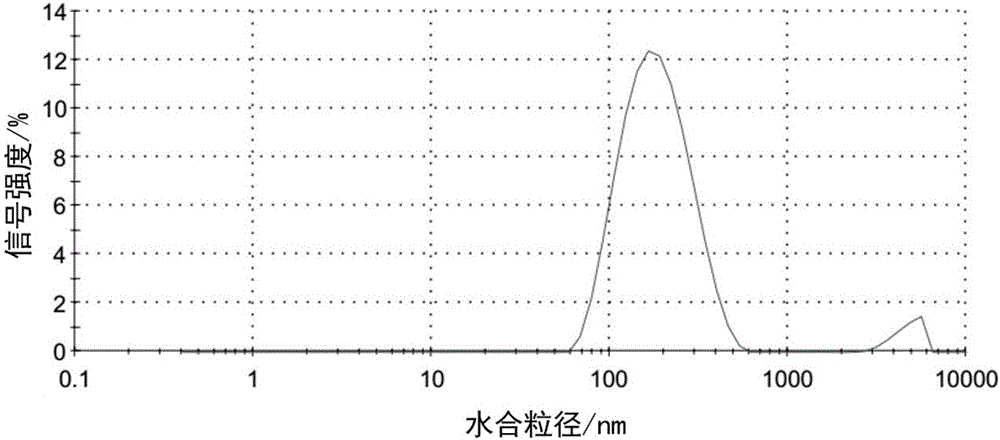
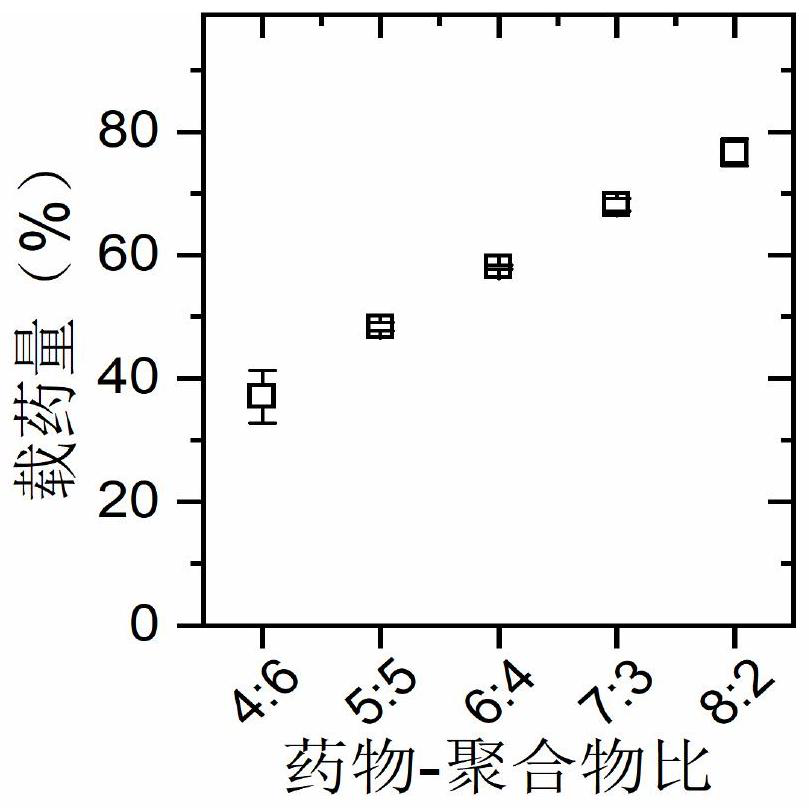
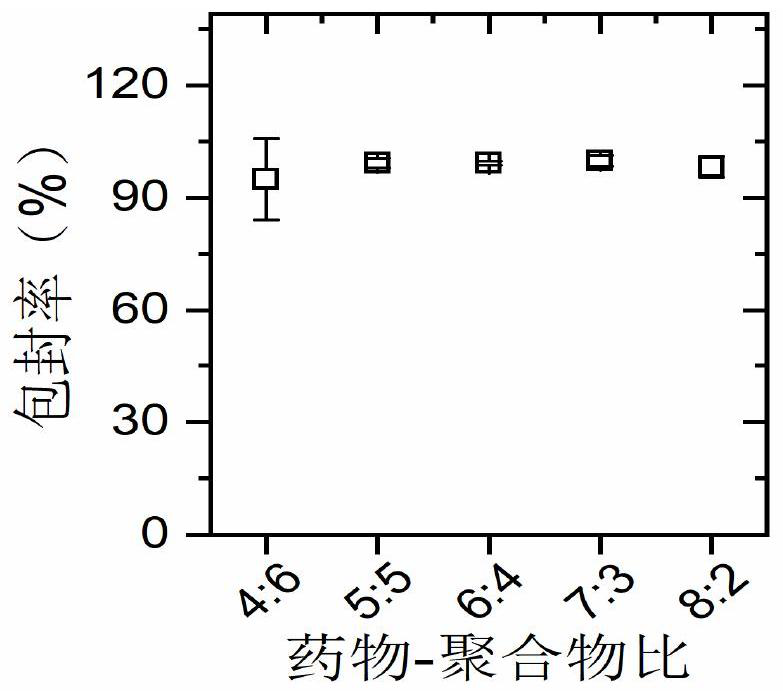
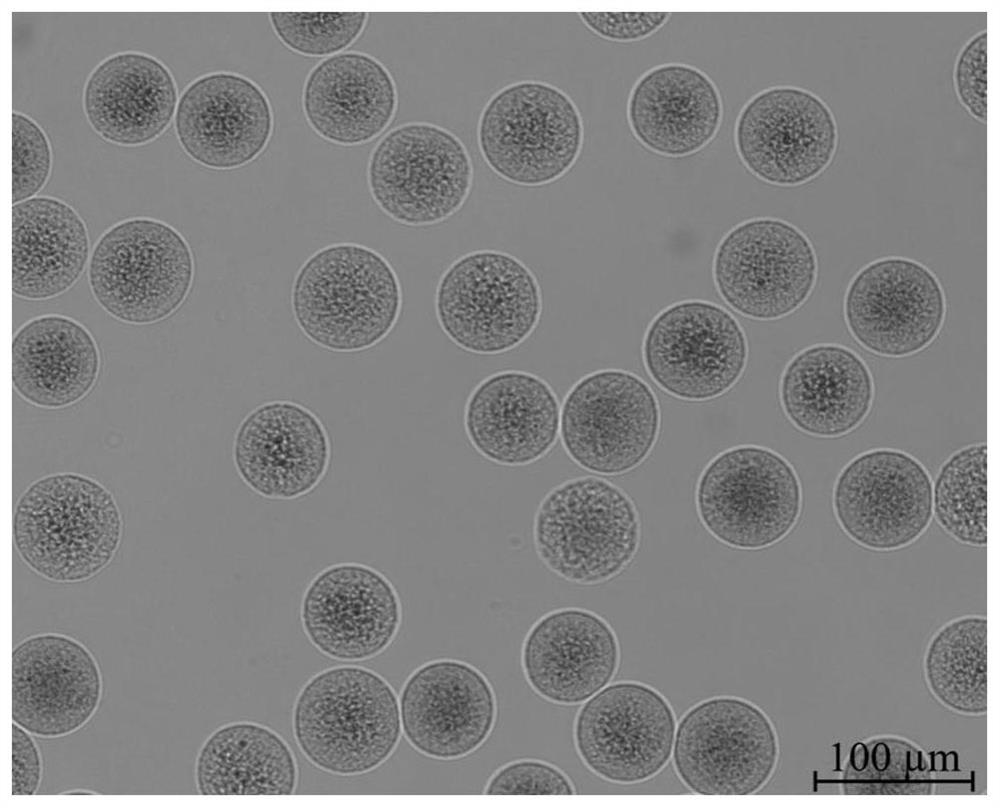
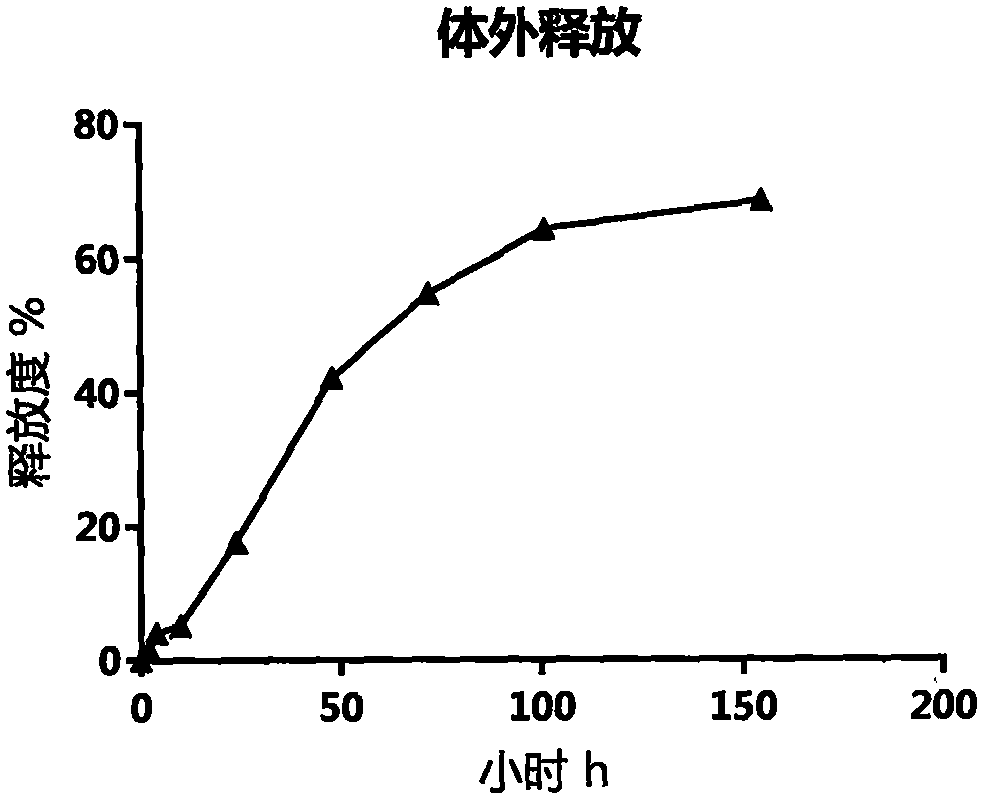
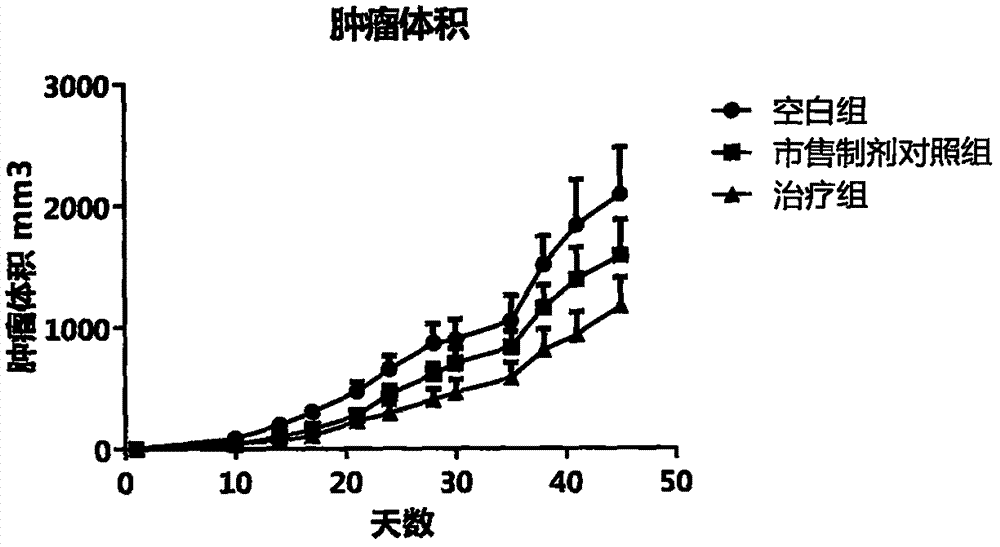
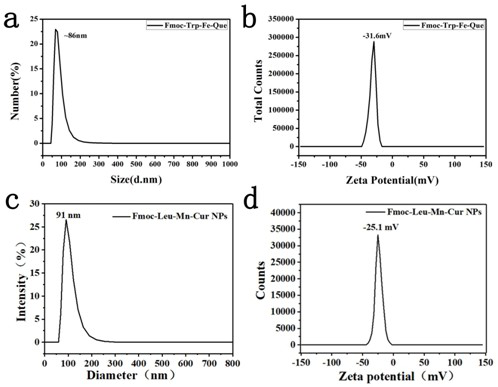
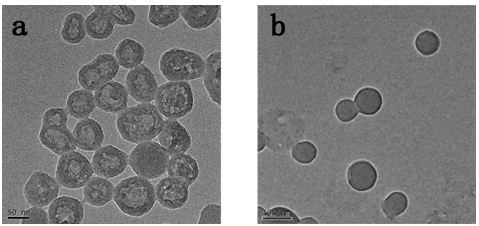
Patents
Literature
103 results about "Drug nanoparticles" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Methods and devices for the treatment of ocular diseases in human subjects
InactiveUS20150258120A1Reduce in quantityReduce severityOrganic active ingredientsPowder deliveryDiseaseMicroparticle
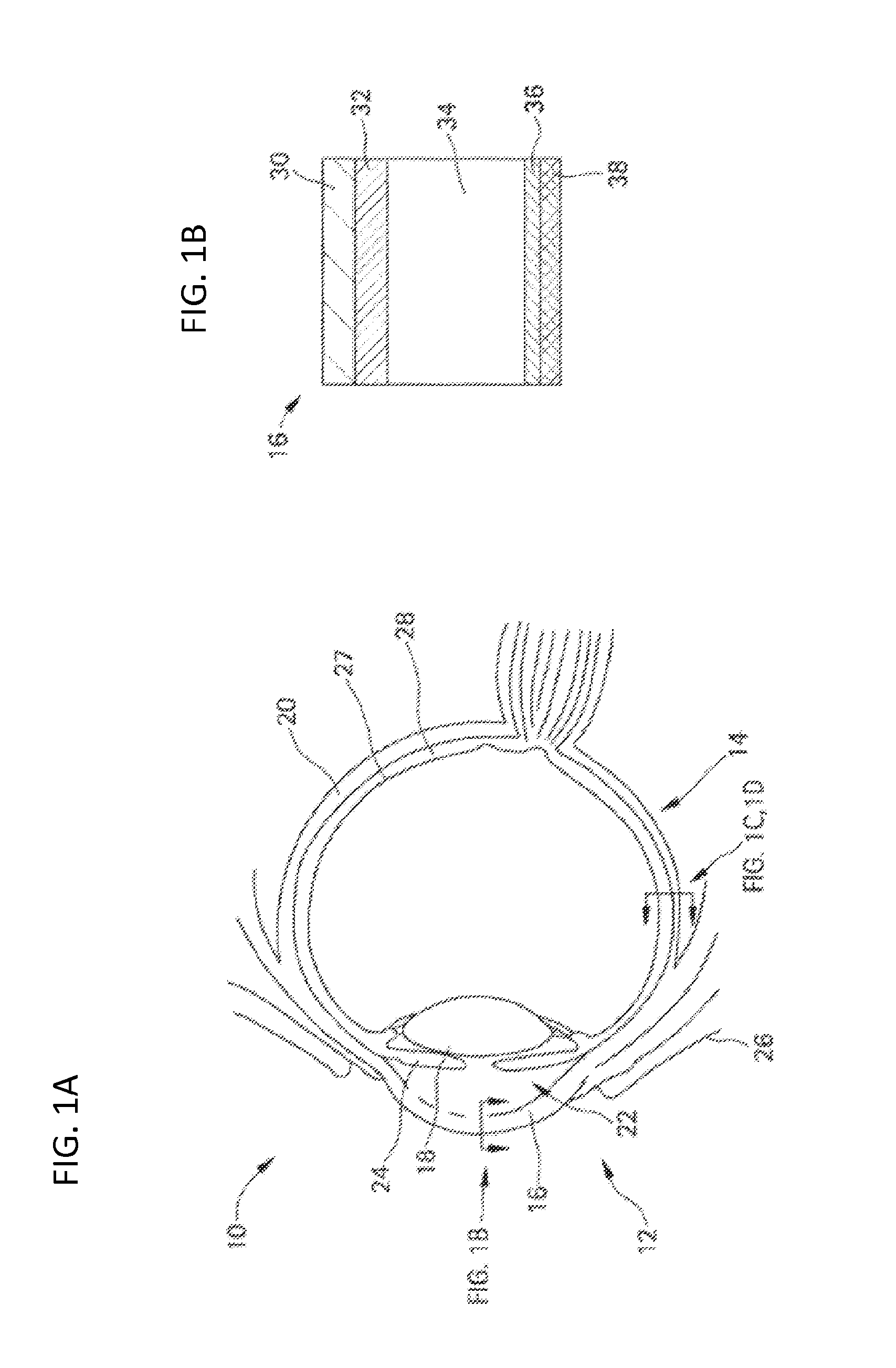
Methods and devices are provided for targeted non-surgical administration of a drug formulation to the suprachoroidal space (SCS) of the eye of a human subject for the treatment of a posterior ocular disorder or a choroidal malady. In one embodiment, the method comprises inserting a hollow microneedle into the eye at an insertion site and infusing a drug formulation through the inserted microneedle and into the suprachoroidal space of the eye, wherein the infused drug formulation flows within the suprachoroidal space away from the insertion site during the infusion. In one embodiment, the fluid drug formulation comprises drug nanoparticles or microparticles.
Owner:CLEARSIDE BIOMEDICAL
Nanoparticulate formulations and methods for the making and use therof
InactiveUS20090004262A1Remove obstaclesRelieving conditionPowder deliveryOrganic active ingredientsNanoparticleMicroparticle
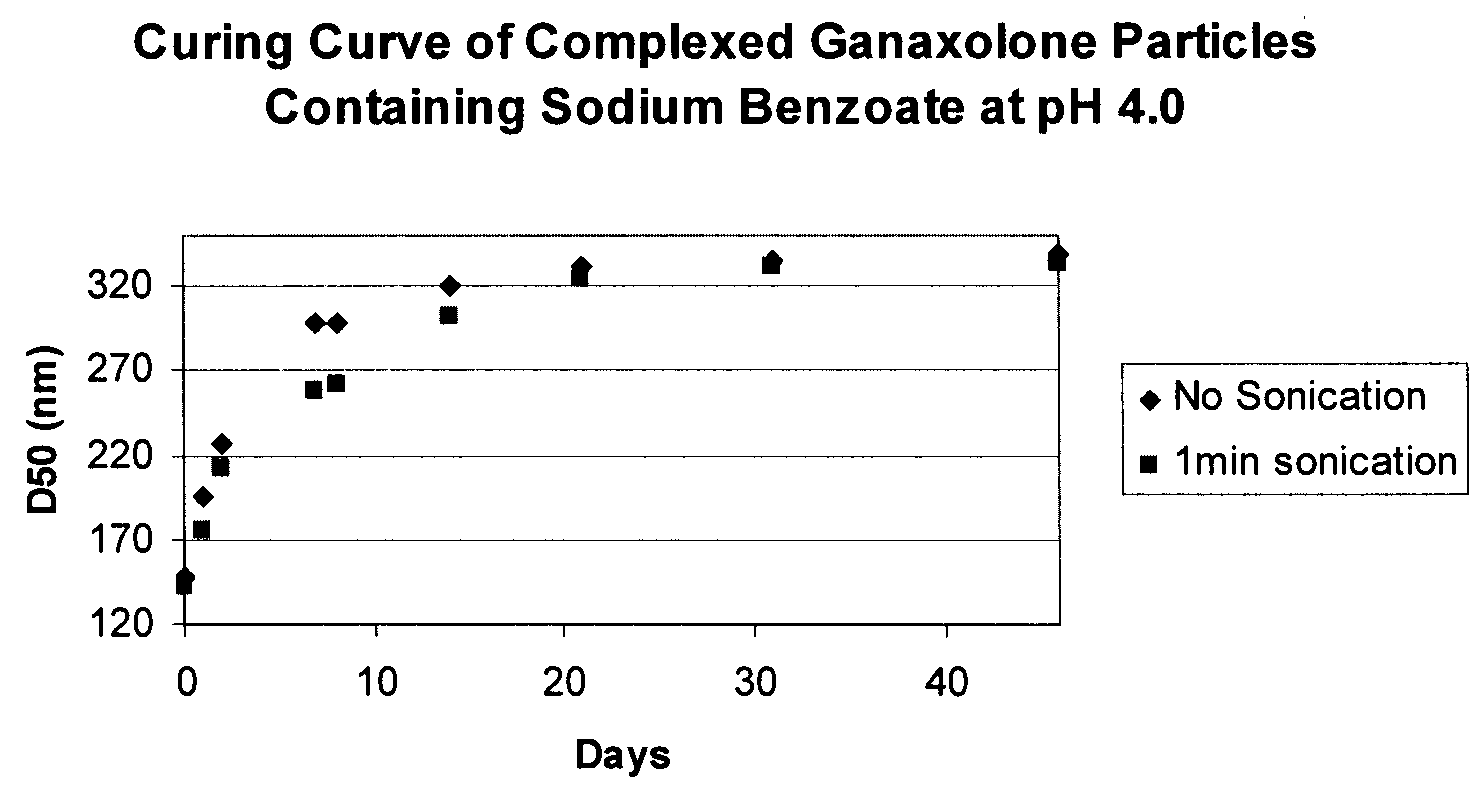
The present invention is directed to size-stabilized drug nanoparticulate compositions and methods of preparation thereof.
Owner:MARINUS PHARMA
Nanometer medicament microspheres
InactiveCN102885783AHigh encapsulation efficiencyImprove adhesionPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsGranular deliveryControlled releaseCell adhesion
The invention discloses nanometer medicament microspheres. The microspheres comprise a medicament, nanoparticles, a polymer and medicinal auxiliary materials. The invention further provides a preparation method of the nanometer medicament microspheres. The method comprises the following steps of: preparing a medicament and medicinal auxiliary materials into a nanometer medicament; adding the nanometer medicament into a polymer-containing organic solvent mixed solution for emulsifying; adding a nanometer medicament-in-oil mixed suspension into a water mixed suspension containing nanoparticles or containing nanoparticles and a surfactant for emulsifying to obtain an oil-in-nanoparticle mixed suspension-nanometer medicament-in-oil compound emulsion; and curing the obtained compound emulsion, and centrifugally collecting microspheres, wherein the obtained microspheres comprise the medicament, nanoparticles, the polymer and the medicinal auxiliary materials. An appropriate polymer material and an appropriate microsphere preparation method are selected, the prepared microspheres have high envelop rate, and a layer of self-assembled nanoparticles on the surfaces of the microspheres has the effects of improving cell adhesion and reducing inflammation and microencapsulation caused by local excessive acid and hydrophobic materials. The method disclosed by the invention can be applied to preparation of other medicament slow release or controlled release microspheres.
Owner:JINSHAN HOSPITAL FUDAN UNIV
Process For Preparing Powder Comprising Nanoparticles of Sparingly Soluble Drug
InactiveUS20100003332A1Improve bioavailabilityEnhanced particle size stabilityBiocidePowder deliverySide effectWater soluble drug
A powder comprising nanoparticles of a sparingly water-soluble drug prepared in accordance with the present invention exhibits enhanced bioavailability without generating adverse side effects caused by impurities, while the nano-particle size of the drug remains unchanged when administered. Accordingly, the powder can be useful for the development of a formulation of a sparingly water-soluble drug for oral and parenteral administration.
Owner:AMOREPACIFIC CORP
Preparation method for nano-granular solid dispersion of hydrophobic drug by high-voltage electrostatic spraying
InactiveCN102218019AIncrease surface areaDry fastPharmaceutical product form changeOrganic solventPharmaceutical drug
The invention relates to a preparation method for a nano-granular solid dispersion of a hydrophobic drug by high-voltage electrostatic spraying, which comprises the following steps of: mixing a hydrophobic drug, a drug-carrying polymer and an organic solvent at a mass ratio of (1-10): (10-20): (80-94) to prepare a consolute electric spraying solution; and then carrying out high-voltage electrostatic spraying while controlling the flow rate of the consolute electric spraying solution at 0.5-2.5 mL / h, the distance between a receiving board and a wire spraying port at 15-30cm and the voltage at 5-30kV to obtain the nano-granular solid dispersion of the hydrophobic drug. The preparation method is simple to operate, is low in cost, is environmentally-friendly and is suitable for industrial production; and the prepared solid dispersion of the hydrophobic drug not only can highly disperse a composite of a polymer and the drug into an amorphous state and has a nano-structural characteristic.
Owner:UNIV OF SHANGHAI FOR SCI & TECH
Medicinal transparent nano dispersant and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102188372ASimple processEasy to operateOrganic active ingredientsSolution deliveryMicro structurePrill
The invention relates to a medicinal transparent nano dispersant and a preparation method thereof. Water-insoluble medicinal nano particles are used as active ingredients, water is used as a dispersion medium, medicinal accessories are used as a colloidal dispersion system of a stabilizing agent, the concentration of the medicament is 0.1 to 10mg / mL, the mass ratio of the stabilizing agent to the medicament is (10-500): 100, and the average particle diameter of the medicinal particles is 20 to 90 nanometers. The method comprises the following steps of: dissolving the medicament into an organic solvent mutually soluble with water, adding the medicament solution into aqueous solution containing water-soluble medicinal accessories to obtain nano medicinal paste, performing spray drying on suspension, and adding the obtained nano and micro structure composite powder into the water to obtain the medicinal transparent nano dispersant. The method provided by the invention is simple in operation and low in cost, and has good industrialized production prospect; and the provided medicinal transparent nano dispersant has the advantages of good stability, high dissolution speed, high bioavailability and the like, and can be used for preparing soft capsules, injection and suspension.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Methods and devices for the treatment of ocular diseases in human subjects
ActiveUS20160206628A1Improve efficacyGood treatment effectPowder deliveryOrganic active ingredientsDiseaseMicroparticle
Methods and devices are provided for targeted non-surgical administration of a drug formulation to the suprachoroidal space (SCS) of the eye of a human subject for the treatment of a posterior ocular disorder or a choroidal malady. In one embodiment, the method comprises inserting a hollow microneedle into the eye at an insertion site and infusing a drug formulation through the inserted microneedle and into the suprachoroidal space of the eye, wherein the infused drug formulation flows within the suprachoroidal space away from the insertion site during the infusion. In one embodiment, the fluid drug formulation comprises drug nanoparticles or microparticles.
Owner:CLEARSIDE BIOMEDICAL
Biodegradable nanoparticle-entrapped oral colon-targeted micro-capsule and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103417515AObvious pH responseSignificant pH response characteristicsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsMicrocapsulesOral medicationPolyvinyl alcohol
The invention discloses a biodegradable nanoparticle-entrapped oral colon-targeted micro-capsule and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: 1, dissolving drugs and degradable polymers in an organic phase and taking a solution containing polyvinyl alcohol or sodium cholate as a water phase for preparing drug nanoparticles; 2, dissolving an enteric-coated material in absolute ethanol; 3, dispersing the drug nanoparticles in absolute ethanol in which the enteric-coated material is dissolved; 4, preparing edible oil; 5, dropwise adding ethanol liquid into the edible oil, stirring, solidifying, and volatilizing to remove absolute ethanol; 6, centrifuging suspension liquid, collecting the micro-capsule in a lower layer, and washing by normal hexane. The prepared oral colon-targeted micro-capsule has a remarkable pH response, drugs in the micro-capsule are hardly released under the acidic conditions, a capsule material is dissolved under the pH value of enteric canal, the drug nanoparticles are released, the nanoparticles can be transferred to a target point, and the drugs are slowly released, so that the absorption rate of oral administration is greatly increased, the bioavailability is improved, and the treatment effect is enhanced.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Method for preparing microspheres by using oil-in-nanoparticle mixed suspension-nanometer medicament-in-oil
InactiveCN102885784AHigh encapsulation efficiencyImprove adhesionPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsGranular deliveryControlled releaseCell adhesion
The invention discloses a method for preparing microspheres by using oil-in-nanoparticle mixed suspension-nanometer medicament-in-oil. The method comprises the following steps of: preparing a medicament and medicinal auxiliary materials into a nanometer medicament; adding the nanometer medicament into a polymer-containing organic solvent mixed solution for emulsifying; adding a nanometer medicament-in-oil mixed suspension into a water mixed suspension containing nanoparticles or containing nanoparticles and a surfactant for emulsifying to obtain an oil-in-nanoparticle mixed suspension-nanometer medicament-in-oil compound emulsion; and curing the obtained compound emulsion, and centrifugally collecting microspheres, wherein the obtained microspheres comprise the medicament, nanoparticles, the polymer and the medicinal auxiliary materials. An appropriate polymer material and an appropriate microsphere preparation method are selected, the prepared microspheres have high envelop rate, and a layer of self-assembled nanoparticles on the surfaces of the microspheres has the effects of improving cell adhesion and reducing inflammation and microencapsulation caused by local excessive acid and hydrophobic materials. The method disclosed by the invention can be applied to preparation of other medicament slow release or controlled release microspheres.
Owner:JINSHAN HOSPITAL FUDAN UNIV
Method of producing medicinal nanoparticle suspension
InactiveUS20080237376A1Enhance medicinal ingredient absorptionEfficient measurementOrganic active ingredientsPowder deliveryAdditive ingredientWater insoluble
A method of producing a medicinal nanoparticle suspension is provided, wherein a medicinal ingredient added in a suspending solution is ground to form nanoparticles of the medicinal ingredient by irradiating the suspending solution with a laser. The process is implemented after adding a poorly water-soluble or water-insoluble medicinal ingredient of a drug in a poor solvent to form the suspending solution.
Owner:ABSIZE INC
A process for making particles for delivery of drug nanoparticles
InactiveCN102164582ANo or slowed reunion growthImprove solubilityAntibacterial agentsPowder deliveryAnti solventExcipient
A process for making particles for delivery of drug nanoparticles is disclosed herein. The process comprises the steps of (a) forming a suspension of drug nanoparticles by mixing a precipitant solution with an anti-solvent solution under micro-mixing environment, where the formed nanoparticles have a narrow particle size distribution; (b) providing an excipient to at least one of the precipitant solution, the anti-solvent solution and the suspension of drug nanoparticles, the excipient being selected to maintain said drug nanoparticles in a dispersed state when in liquid form; and (c) drying the suspension of drug nanoparticles containing the excipient therein to remove solvent therefrom, wherein removal of the solvent causes the excipient to solidify and thereby form micro-sized matrix particles, each micro-sized particle being comprised of drug nanoparticles dispersed in a solid matrix of the excipient.
Owner:新加坡纳诺泰克药物科技有限公司
Preparation method of polypeptide/proteinic drug nanoparticle with high drug loading and high encapsulation efficiency
ActiveCN102552174AReduce usageWide variety of sourcesPowder deliveryPeptide/protein ingredientsCross-linkFreeze-drying
The invention discloses a preparation method of polypeptide / proteinic drug nanoparticle with high drug loading and high encapsulation efficiency. The method provided by the invention comprises the steps of: dissolving the drug, physiological compatible polymer material, cross-linking agent, and surfactant in aqueous phase, dissolving lipophilic surfactant in nonpolar solvent as oil phase, adding the aqueous phase in the oil phase, carrying out mechanical dispersion to form nano-emulsion; adding freeze-drying protective agent emulsion in the nano-emulsion; quick-freezing at an ultra-low temperature, freeze drying and removing water and the non-polar solvent to obtain the polypeptide / proteinic drug nanoparticle. In the method provided by the invention, the non-polar solvent with low toxicity is used, which is characterized of high freezing point and low boiling point, and is easy to be moved; heating process is avoided, and polypeptide or protein is not easily deactivated; the preparation process is simple, and easy for large-scale production; the polypeptide / proteinic drug nanoparticle is high in drug loading and encapsulation efficiency, and good in redispersibility, and is suitable for serving as drug carrier or intermediate.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Fatty-acid-binding alhumin-drug nanoparticle lyophilized preparation and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104127881ASpeed up entryImprove integrityPowder deliveryPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsWater solubleDrug nanoparticles
The invention discloses a fatty-acid-binding alhumin-drug nanoparticle lyophilized preparation and a preparation method thereof; by use of high affinity and stable binding characteristics of fatty acids and albumin specific sites, nanoparticles using the fatty acids as the core are prepared under the effects of high shearing forces, one or a plurality of ''water-insoluble'' or ''water-soluble '' drug in the form of ''solution'' or ''ultrafine nanoparticles'' is / are ''packaged'' or ''bound'' to obtain various types of nanoparticles suspensions, and the lyophilized preparation is obtained by removal of organic solvent, sterilization and drying. The fatty-acid-binding alhumin-drug nanoparticle lyophilized preparation is composed only by albumin, the drugs and the fatty acids, does not contain any accessories, and has the biological properties of high nanoparticles integrity and stability in a in vitro solution and in vivo blood circulation, , significant increase of drug content in gp60-rich receptor cells or tumor tissues, significant improvement of the LD50 (half lethal dose) and MTD (maximum tolerated dose) of load drugs, close of antigen sites of ''packaged'' or ''bound'' proteins, and the like.
Owner:TIANJIN PAIGE BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
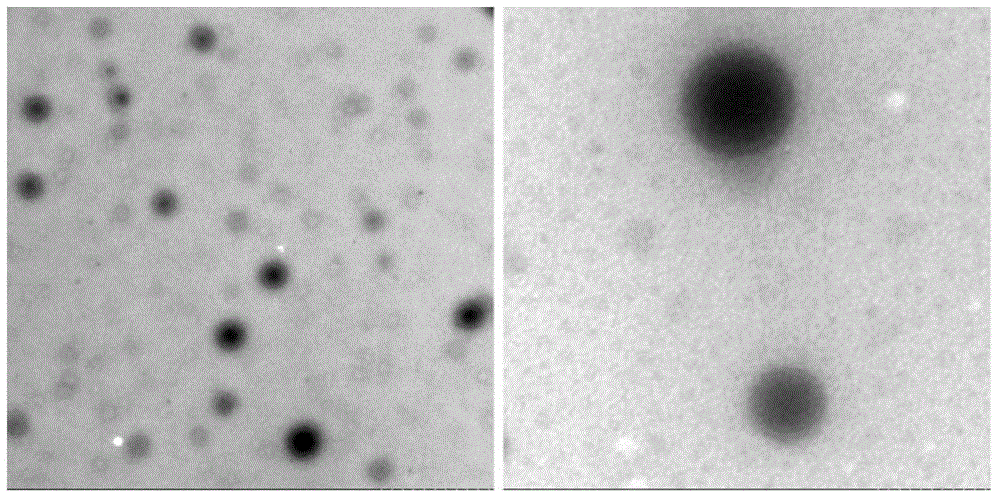
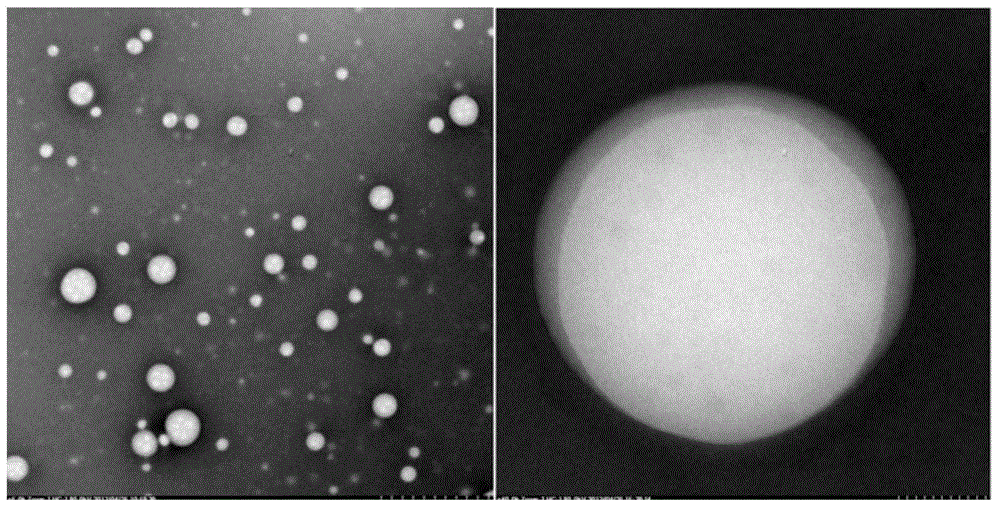
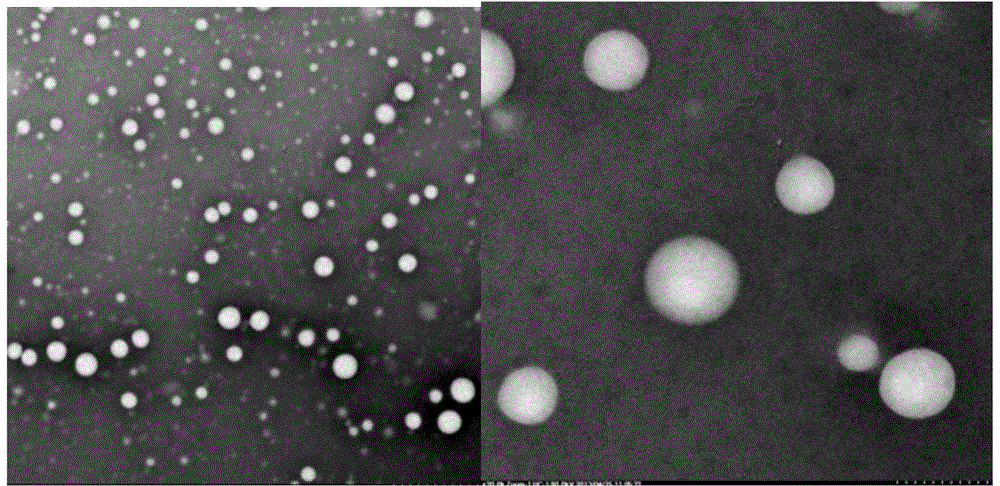
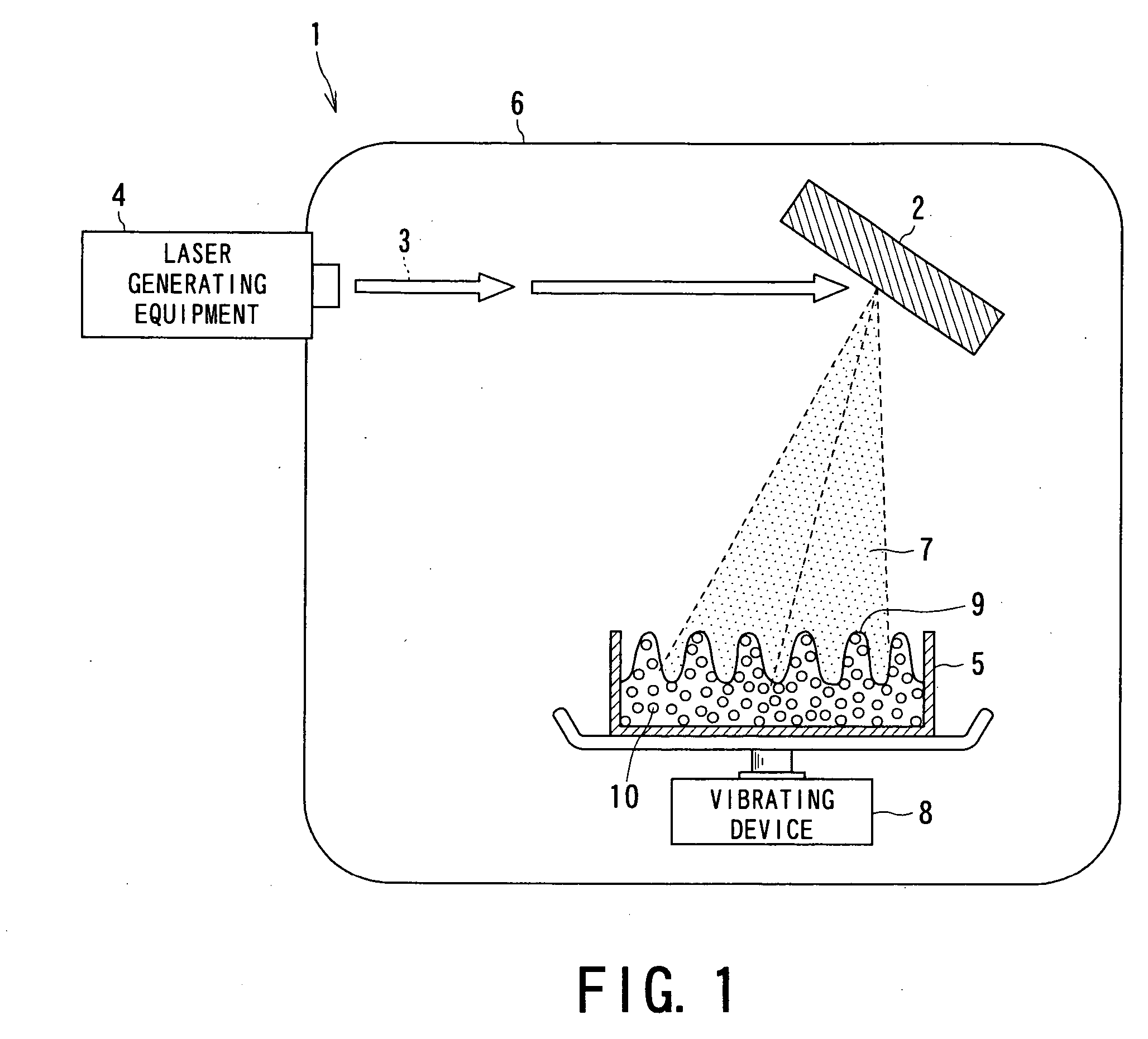
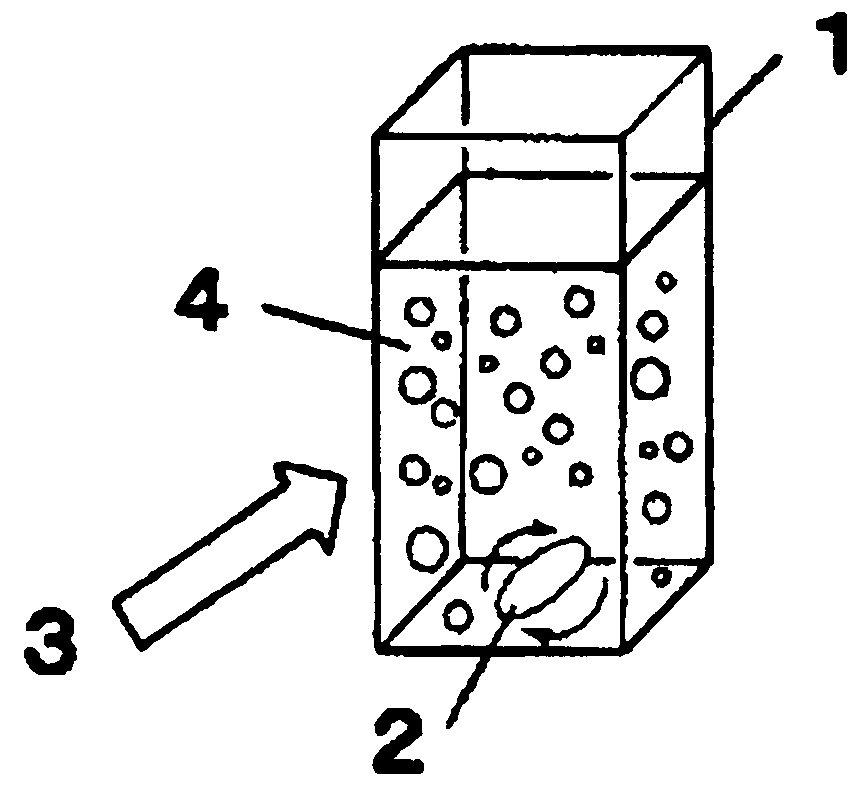
Drug nano-particle, method and apparatus for preparing pharmaceutical preparation using the particle
InactiveUS20060251584A1Easy to manufactureIncrease drug penetrationPowder deliveryGaseous substancesMedicineCompound (substance)
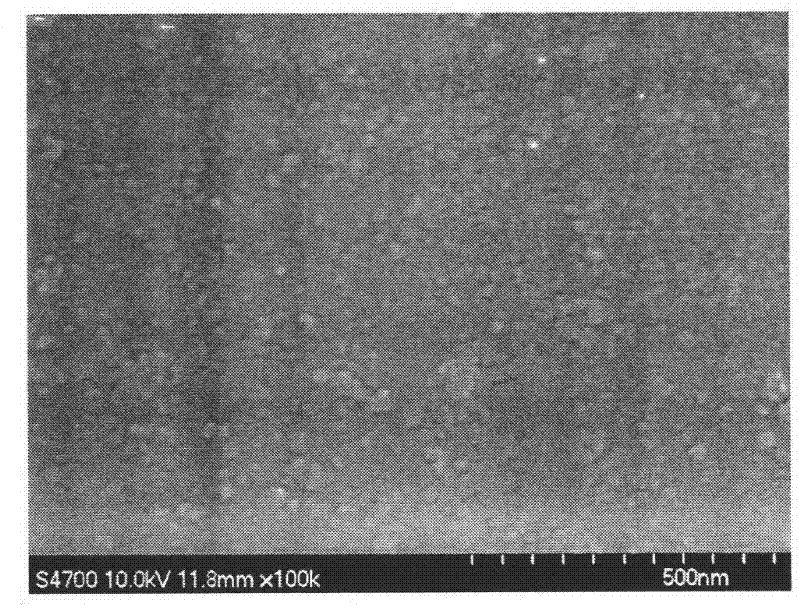
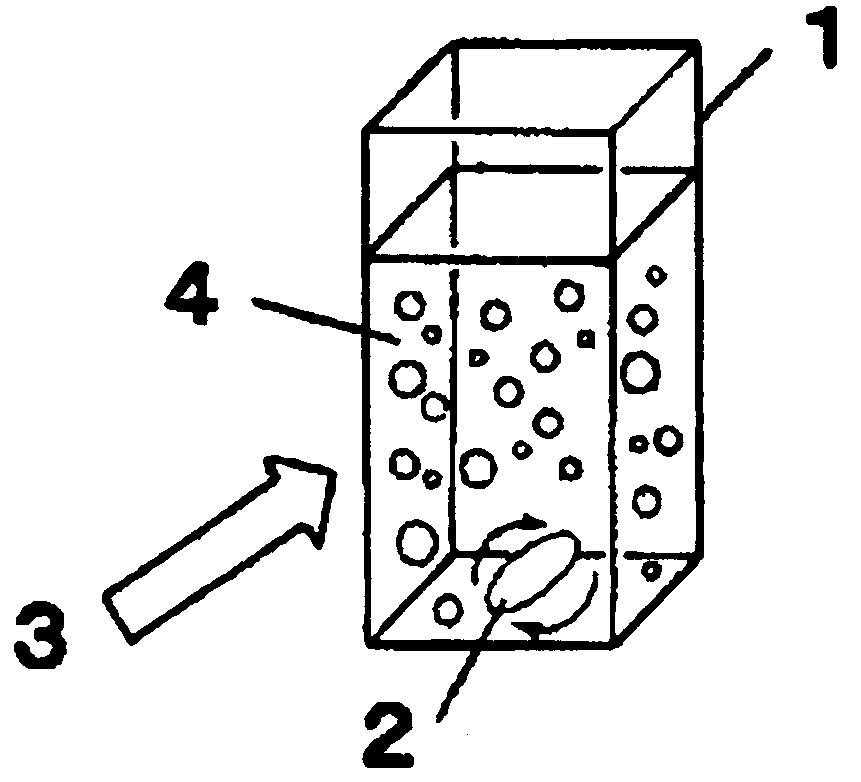
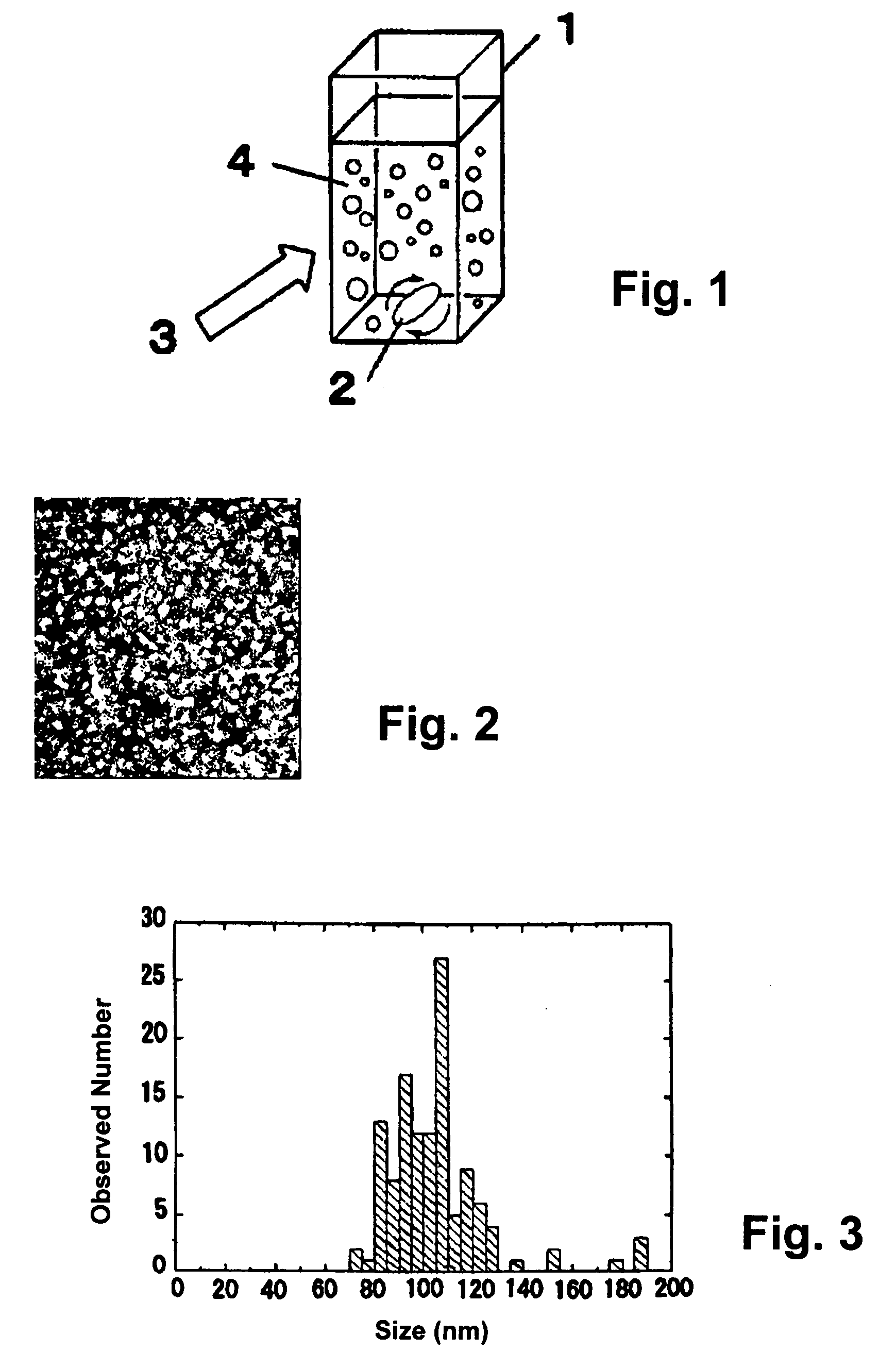
This invention provides a drug nanoparticle 7 obtained by irradiating laser beam 3 to a solid target 2 composed of drug powder so as to release the drug as downsized component particle from the solid target 2, wherein the drug nanoparticles 7 has an average diameter of 100 nm or less. According to the above structure, there can be provided: a drug nanoparticle having a high bioavailability, a high purity and an excellent handling property in a case where the drug nanoparticle is used as medical agent, agricultural chemical (agrichemical), chemical fertilizer or the like. The method of manufacturing the drug and the medical agent manufacturing apparatus are capable of effectively manufacturing the drug nanoparticles through simple manufacturing steps.
Owner:NARA MACHINERY
Structure and preparation method of liver-targeted platinum-loaded nanometer prodrug
ActiveCN106267229AAvoid non-specific adsorptionReduce the binding forceHeavy metal active ingredientsDigestive systemBiocompatibility TestingPt element
The invention discloses a liver-targeted platinum-loaded nanometer prodrug for treating liver cancers and a preparation method thereof. The liver-targeted platinum-loaded nanometer prodrug is prepared by taking sodium alginate with the good biocompatibility as a framework to be modified with glycyrrhetinic acid (GA) with a liver cancer cell targeting capacity and a tetravalent platinum compound (PtCl2(OH)2(NH3)2) through a self-assembly technique. In-vitro drug releasing and cytotoxicity tests prove that the platinum-loaded drug nanoparticles have the good blood stability and the intracellular slow-release effect and also have the tumor cell killing capacity. The nanometer prodrug is expected to be used for targeting treatment on the liver cancers and has a good application prospect in the biomedical field.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Drug-loaded microsphere and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN112603892AHigh encapsulation efficiencyHigh drug loadingPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsGranular deliveryControlled drugsMicrosphere
The invention discloses a drug-loaded microsphere and a preparation method thereof. The drug-loaded microsphere comprises nanoparticles containing active pharmaceutical ingredients and a framework material for wrapping a drug and controlling drug release, wherein the mass of the active pharmaceutical ingredients accounts for 1-80% of the mass of the whole microsphere; the encapsulation efficiency of the active pharmaceutical ingredients in the encapsulation process is 50-100%; and the particle size of the microspheres is 0.5-2000 [mu] m. The preparation method comprises the steps of precipitating the active pharmaceutical ingredients to form drug nanoparticles; then dispersing the drug nanoparticles in an oil phase to prepare an oil-in-water emulsion; and curing the oil-in-water type emulsion to form microspheres. The microspheres are relatively high in encapsulation efficiency and drug loading capacity, the treatment efficiency is improved, and extremely high application value is achieved.
Owner:CHINA PHARM UNIV
Double-drug albumin nanoparticles and preparation technology
InactiveCN109806241AGood effectSmall toxicityHydroxy compound active ingredientsMacromolecular non-active ingredientsSide effectMedicine
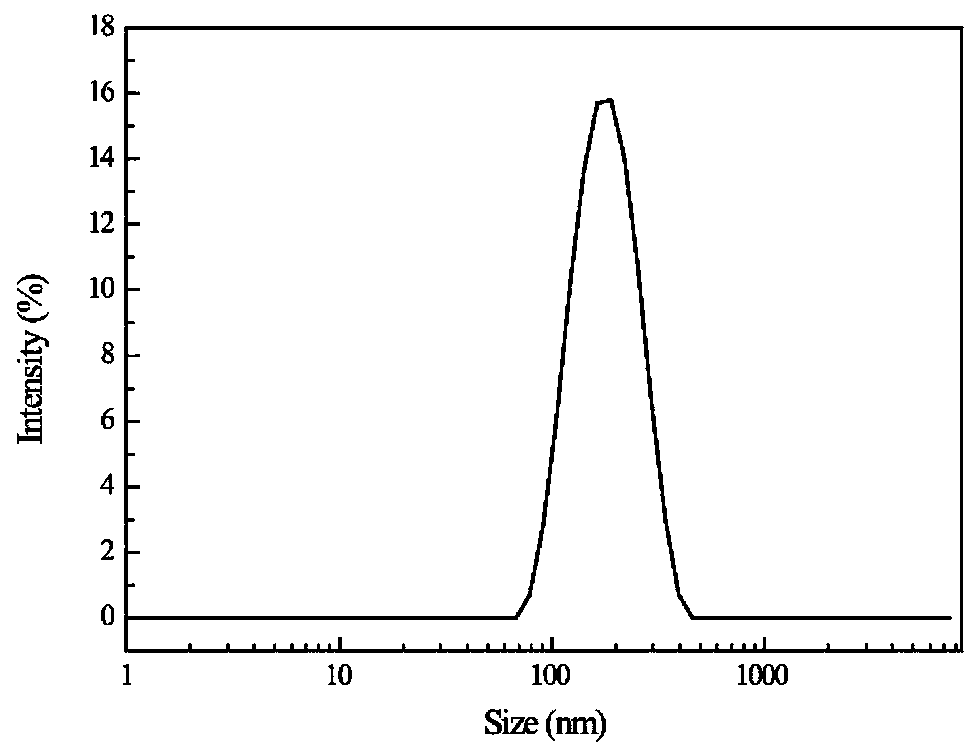
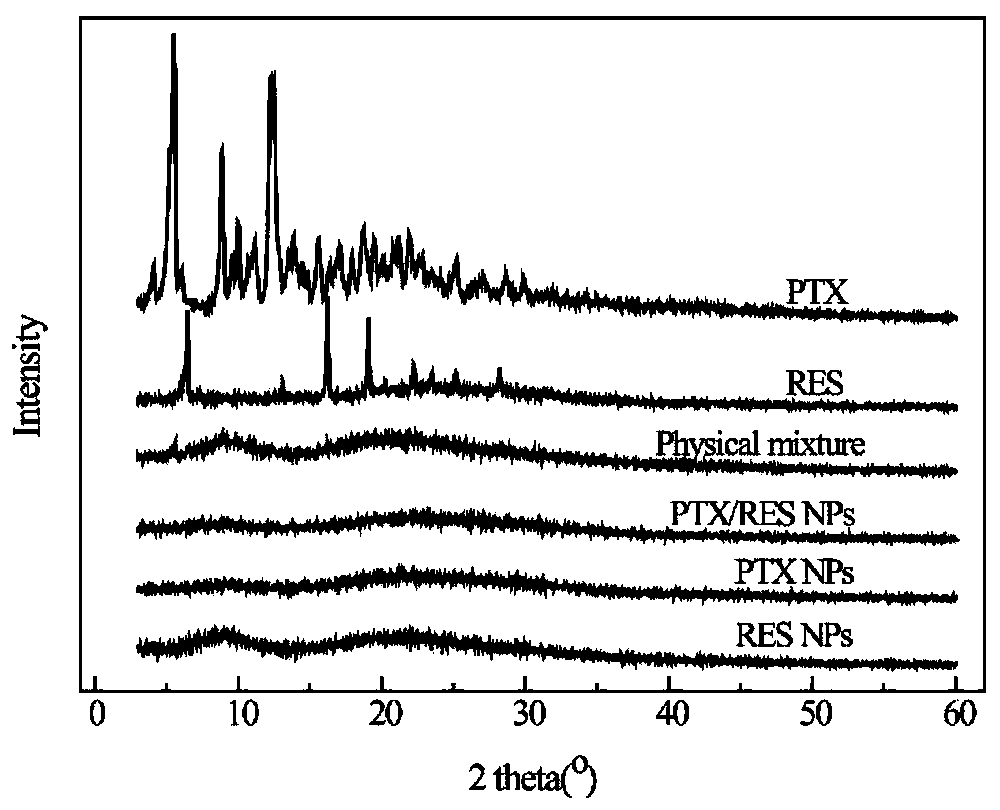
The invention provides paclitaxel / resveratrol albumin nanoparticles and a preparation technology. The preparation technology comprises the following steps: (1) preparing a paclitaxel and resveratrol storage solution; (2) preparing an albumin storage solution; (3) preparing double-drug albumin nanoparticles. According to the paclitaxel / resveratrol albumin nanoparticles, an anti-cancer drug paclitaxel and a bioactive substance resveratrol are combined to be administrated, so that the toxic side effect can be reduced and the anti-cancer effect is improved; the prepared double-drug albumin nanoparticles have the encapsulation efficiency of 99 percent and have good stability; the double-drug albumin nanoparticles provided by the invention can be released in sequence; the resveratrol is rapidlyreleased so that the effect of inhibiting P-gp is facilitated; a condition that the paclitaxel which is released subsequently is pumped out from tumor cells is avoided, so that the cytotoxicity on thedrug-resisting tumor cells is increased; an in-vitro cytotoxicity experiment of the double-drug albumin nanoparticles provided by the invention proves that the drug resistance of the tumor cells canbe reversed, and a cooperative anti-tumor effect of the paclitaxel and the resveratrol in the double-drug nanoparticles is realized.
Owner:LIAOCHENG UNIV
Tanshinone IIA polylactic acid nano particles and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101310717APromote decompositionReduce solubilityOrganic active ingredientsPowder deliveryFreeze-dryingTanshinone IIA
The invention pertains to pharmaceutical field and relates to a tanshinone IIA polylactic acid drug-loaded nanoparticle preparation and a preparation method of the preparation. The active component of the carrier drug nanoparticles of the invention is tanshinone IIA, the carrier drug nano-material is polylactic acid, the range of the particle size of the nanoparticle size is 50nm to 300nm, the carrier drug amount of the nanoparticles is 1 percent to 30 percent, and the encapsulation rate of the nanoparticles is 70 percent to 90 percent. The carrier drug nanoparticles can be prepared into a freeze-dried powder injection. The preparation of the invention can improve the dispersion degree of the drug in carrier material, enhance the dissolution of the drug, improve the bioavailability, change the process in vivo of the drug, increase the liver target and have great significance on the injection drug delivery of tanshinone. The problem of easy drug leakage of liposomes, microemulsion and other preparations can be simultaneously better solved.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV OF TRADITIONAL CHINESE MEDICINE PUTUO DISTRICT CENT HOSPITAL
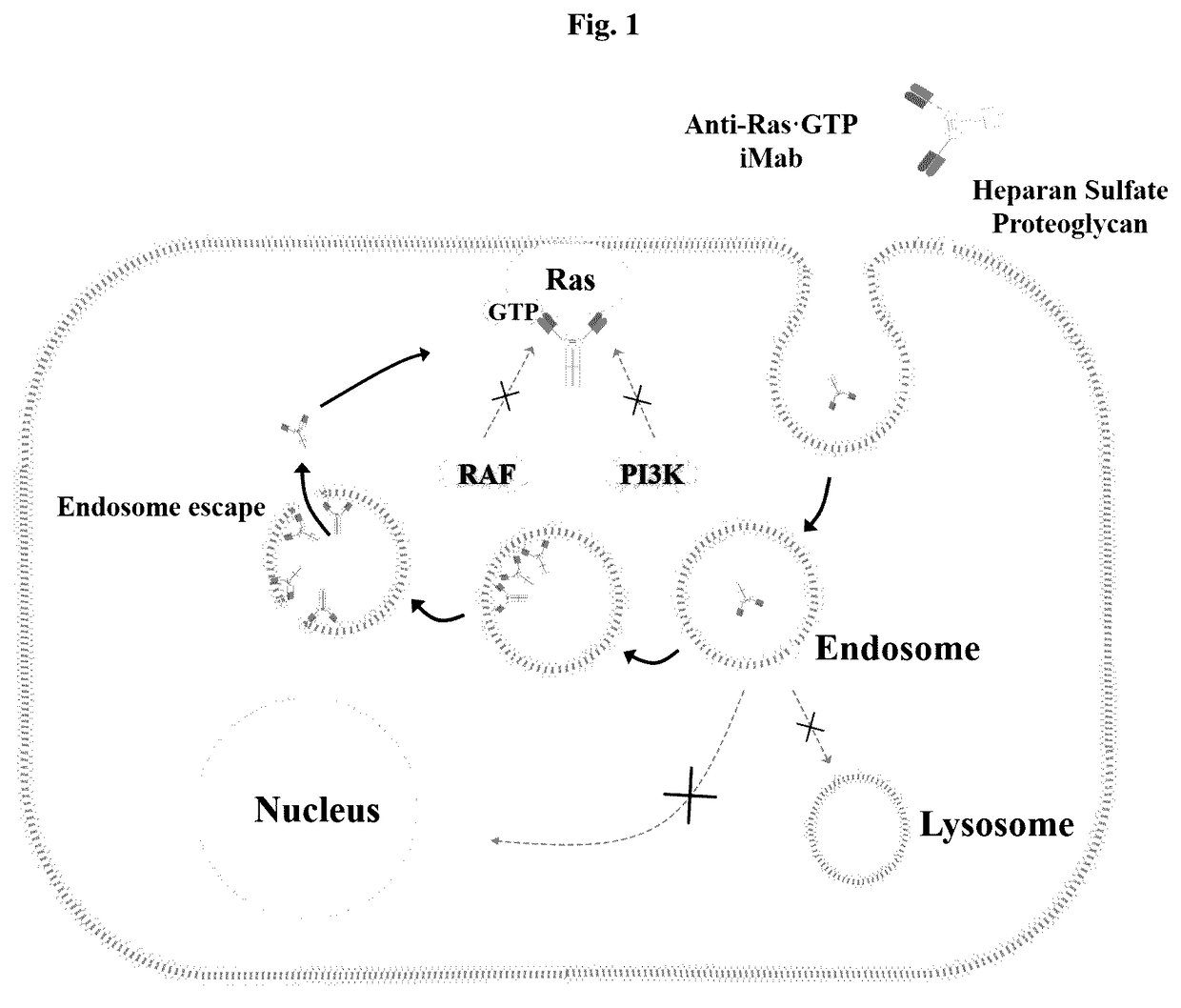
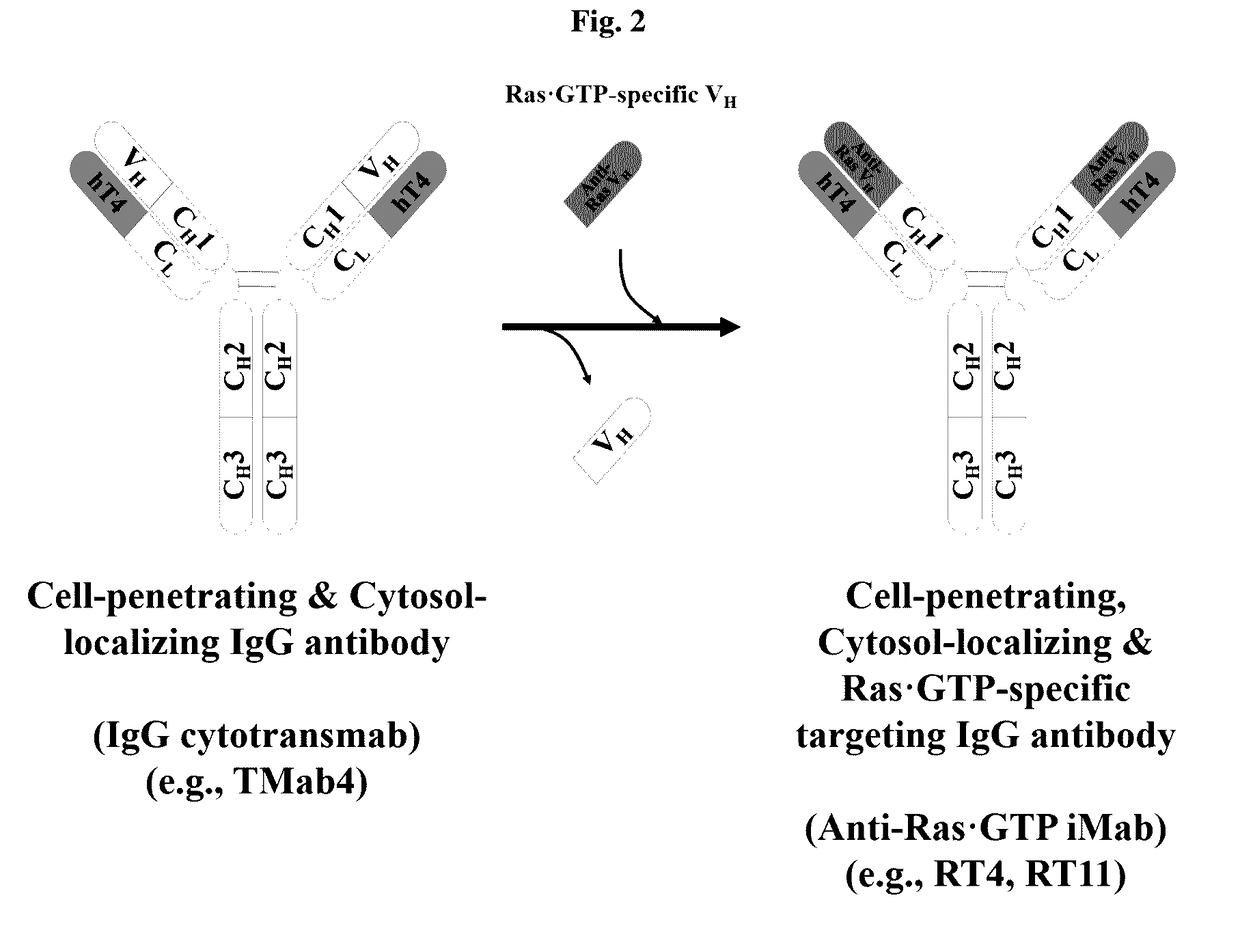
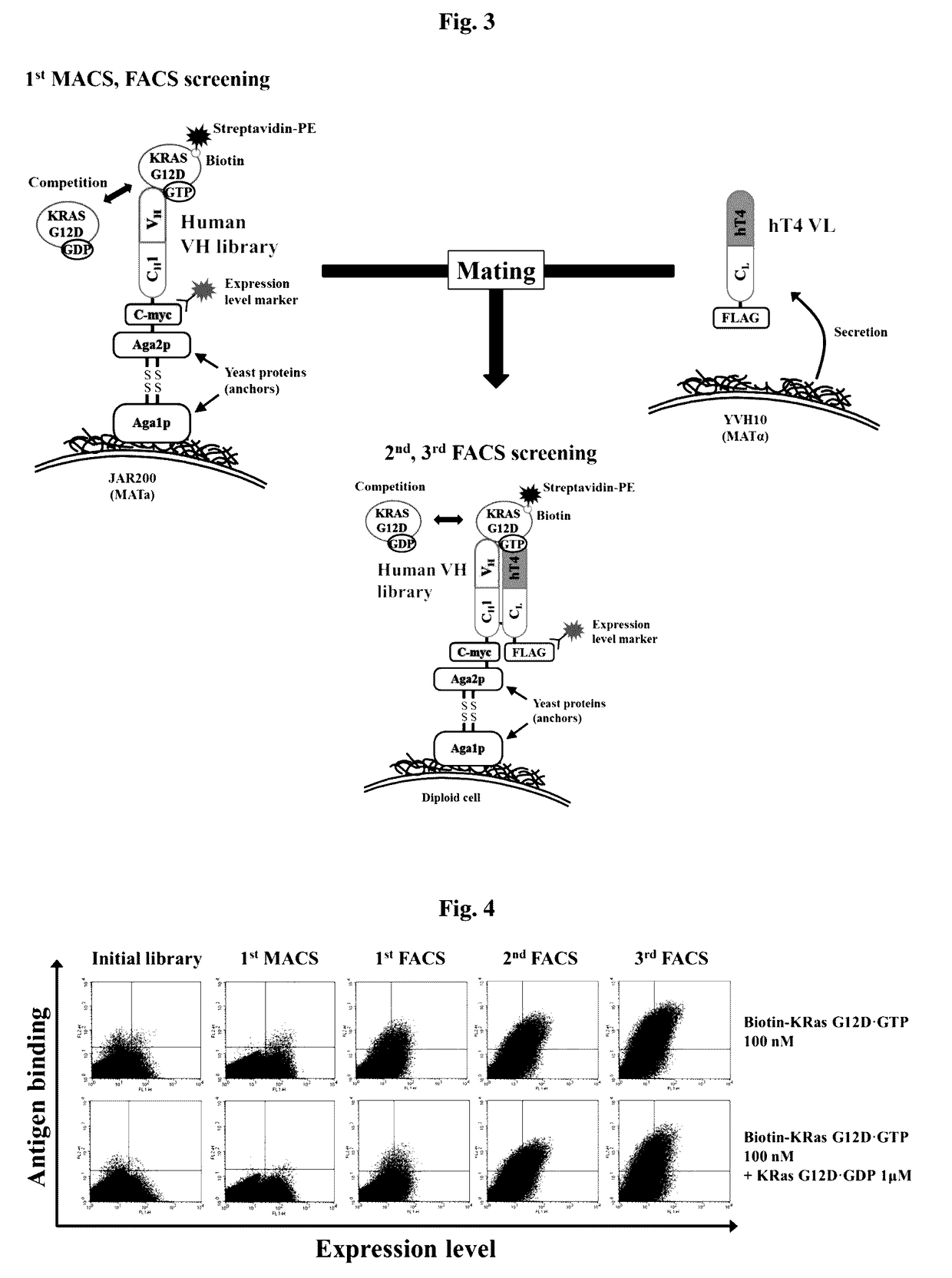
Method for inhibiting intracellular activated ras using intact immunoglobulin-type antibody having cytosol-penetrating ability and use thereof
ActiveUS20170158777A1Inhibitory activityNo cytotoxicityCompound screeningHybrid immunoglobulinsDiseaseCytoplasm
The present invention relates to a method for inhibiting intracellular activated RAS using an intact immunoglobulin-type antibody having the ability to penetrate the cytosol. The present invention also relates to a heavy-chain variable region (VH) which induces an intact immunoglobulin-type antibody to actively penetrate the cytosol of living cells through endocytosis and endosomal escape and to bind to activated RAS in the cytosol, and to an antibody comprising the same. The present invention also relates to a method of inhibiting the growth of cancer or tumor cells and a method of treating cancer or tumor, by use of the antibody. The present invention also relates to a method for screening a heavy-chain variable region that binds specifically to RAS in the cytosol. The present invention also relates to a biologically active molecule fused to the antibody and selected from the group consisting of peptides, proteins, small-molecule drugs, nanoparticles and liposomes. The present invention also relates to a composition for prevention, treatment or diagnosis of cancer, comprising: the antibody; or a biological active molecule fused to the antibody and selected from the group consisting of peptides, proteins, small-molecule drugs, nanoparticles and liposomes. The present invention also relates to a polynucleotide that encodes the light-chain variable region and the antibody.According to the present invention, the method for inhibiting intracellular activated RAS using an intact immunoglobulin-type antibody having the ability to penetrate the cytosol is achieved by allowing the antibody to penetrate living cells and to specifically recognize activated (GTP-bound) RAS in the cytosol. Thus, the antibody can target activated (GTP-bound) RAS in the cytosol of living cells and inhibit the activity of the RAS.Furthermore, the antibody light-chain variable region according to the present invention and an antibody comprising the same is able to penetrate living cells and localize in the cytosol, without having to use a special external protein delivery system. Particularly, the antibody light-chain variable region according to the present invention can easily interact with various human heavy-chain variable regions (VHs) and has the ability to penetrate the cytosol and remain in the cytosol, and an intact IgG-type monoclonal antibody comprising the light-chain variable region can penetrate cells and localize in the cytosol, and shows no cytotoxicity non-specific for target cells.The antibody heavy-chain variable region according to the present invention and an antibody comprising the same can selectively inhibit mutations of the major drug resistance-related factor RAS of conventional various tumor therapeutic agents, and can exhibit synergistic anticancer activity with conventional therapeutic agents. In addition, the cytosol-penetrating, intact immunoglobulin-type antibody according to the present invention can penetrate cells and remain in the cytosol, without affecting the high specificity and affinity of a human antibody heavy-chain variable region (VH) for antigens, and thus can localize in the cytosol which is currently classified as a target in disease treatment based on small-molecule drugs, and at the same time, can exhibit high effects on the treatment and diagnosis of tumor and disease-related factors that show structurally complex interactions through a wide and flat surface between protein and protein.
Owner:ORUM THERAPEUTICS INC
Method of producing medicinal nanoparticle suspension
InactiveUS7597278B2Good effectPromote absorptionOrganic active ingredientsPowder deliveryWater insolubleAdditive ingredient
A method of producing a medicinal nanoparticle suspension is provided, wherein a medicinal ingredient added in a suspending solution is ground to form nanoparticles of the medicinal ingredient by irradiating the suspending solution with a laser. The process is implemented after adding a poorly water-soluble or water-insoluble medicinal ingredient of a drug in a poor solvent to form the suspending solution.
Owner:ABSIZE INC
Drug targeting system, method of its preparation and its use
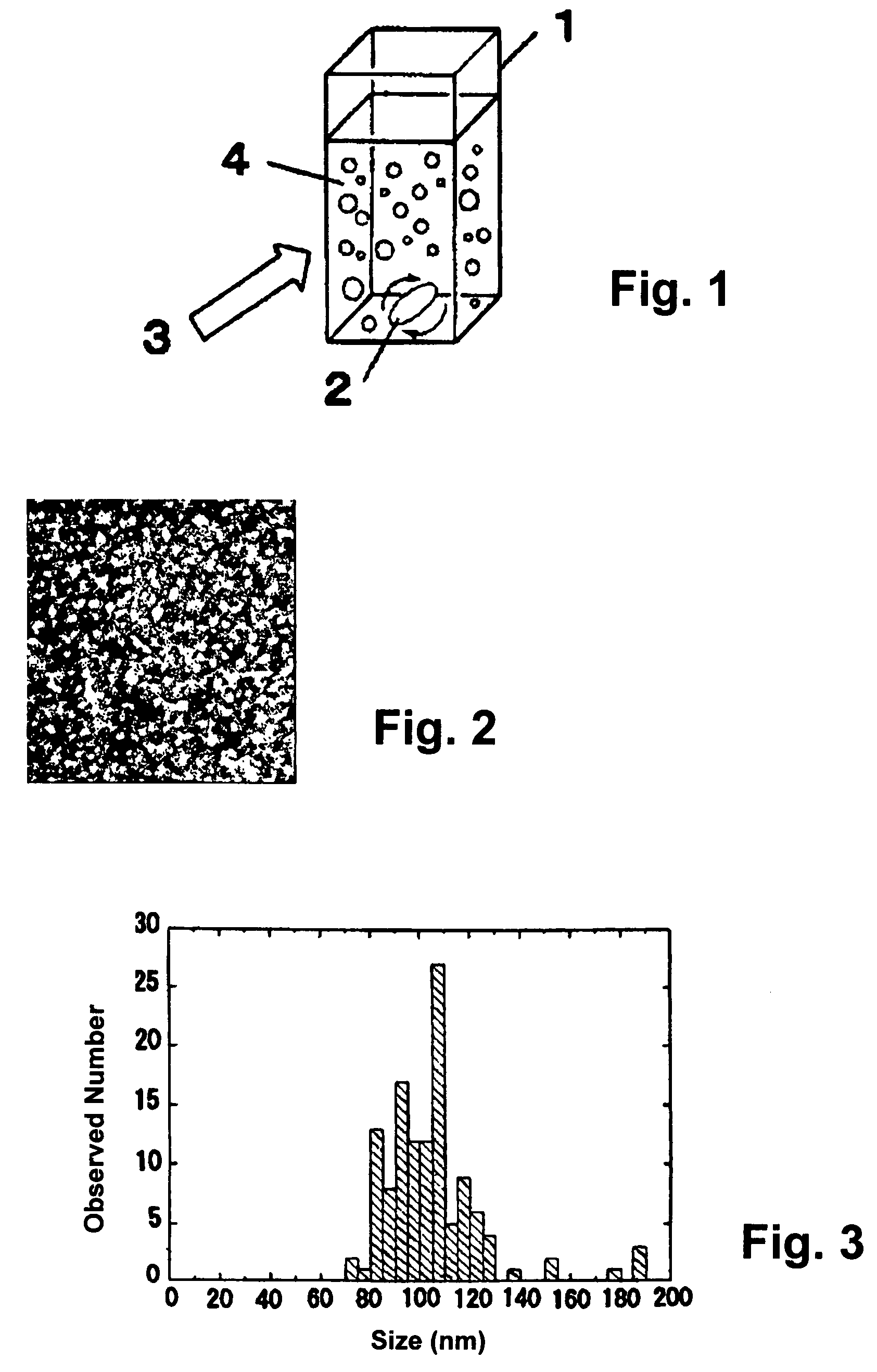
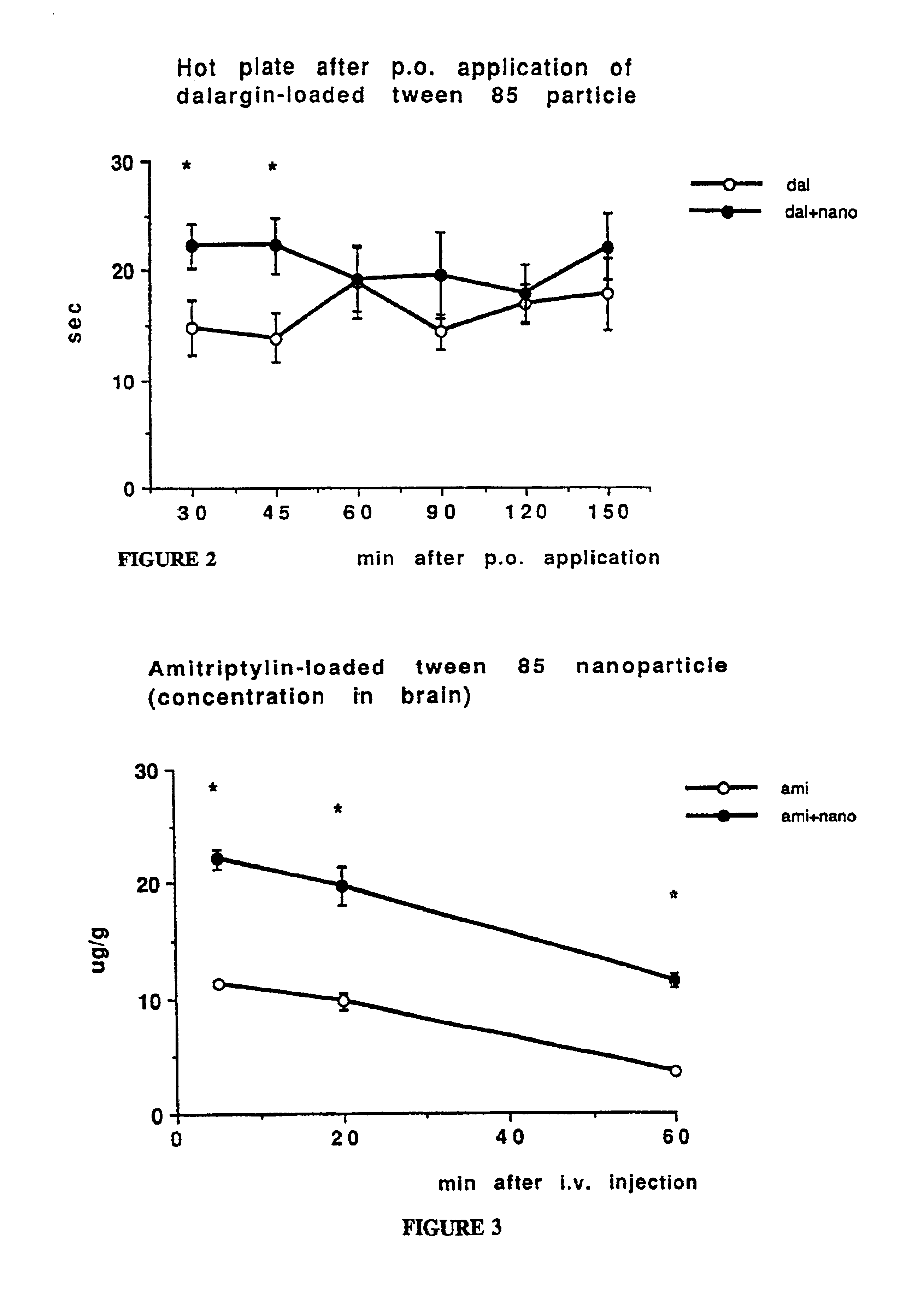
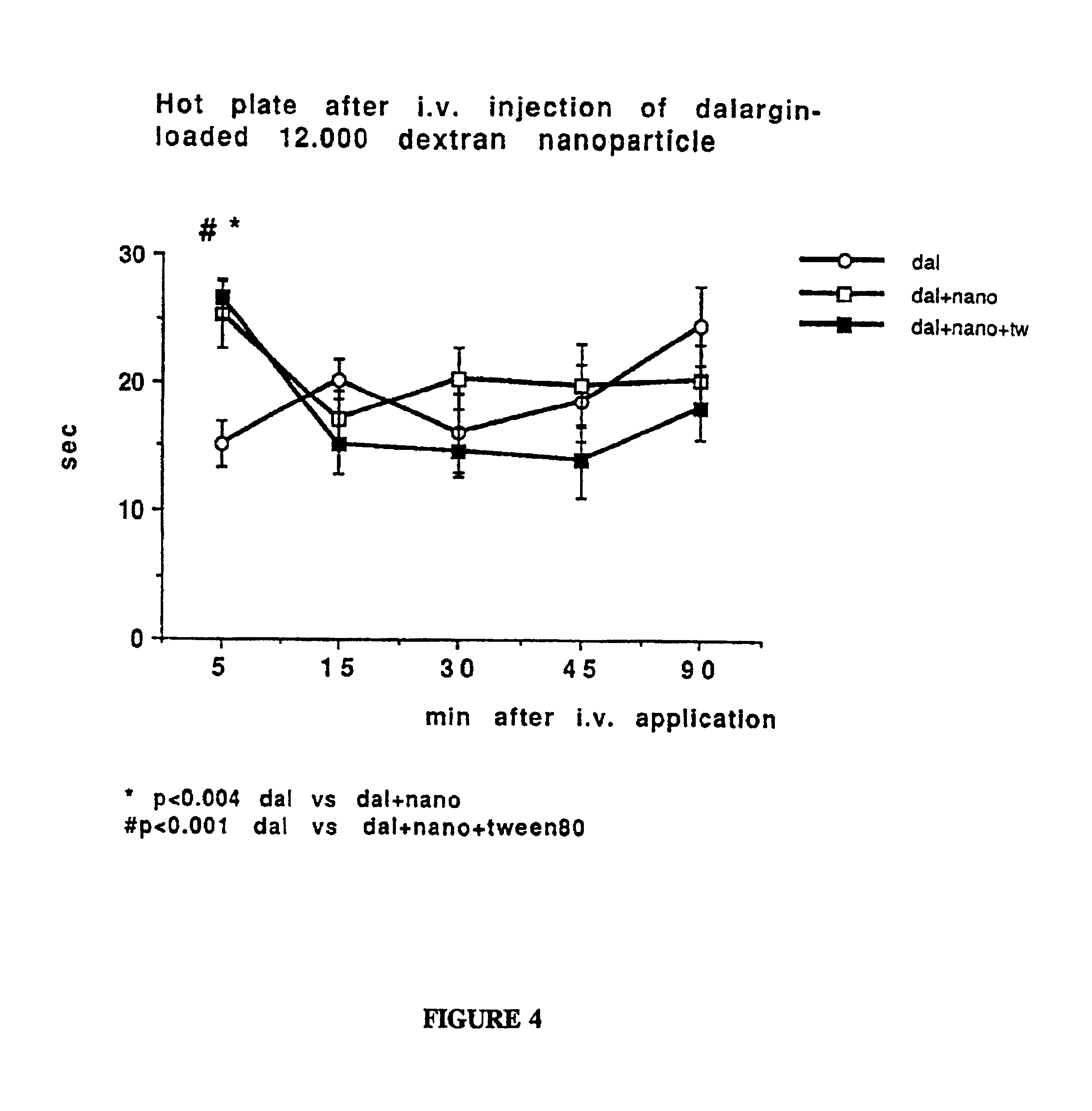
InactiveUS7025991B2Conveniently deliverHigh ratePowder deliveryNervous disorderPharmacological actionDrug action
A composition and method of fabrication are presented with which nanoparticles may be used as a tool to deliver drugs to a specific target within or on a mammalian body. Specifically, by using stabilizers other than Dextran 70.000 during the polymerization process, according to the present invention, surfactants, which were deemed necessary coating material in the prior art, are no longer required. This is a significant simplification of the fabrication procedure. Many substances are useful as stabilizers, but the preferred stabilizers comprise Dextran 12.000 or polysorbate 85. In the present invention a drug is either incorporated into or adsorbed onto the stabilized nanoparticles. This drug / nanoparticle complex is then administered to the organism on any route such as by oral application, injection or inhalation, whereupon the drug exerts its effect at the desired site of pharmacological action. In a novel medical treatment process, the drug / nanoparticle complex may be administered preferably either by intravenous injection or by oral application. The resulting drug action, which does not occur or which occurs only to an insufficient extent when the drug is administered alone, shows that when linked to said nanoparticles drugs can reach a specific target within or on the mammalian body. The usefulness of the present invention as a universal approach to deliver any drug or diagnostic agent to a specific target within or on the mammalian body was demonstrated by experiments showing an unexpected transfer of the drug across the blood brain barrier.
Owner:NANODEL TECH GMBH
A drug nanoparticle delivery system
InactiveCN107260683ANo or slowed reunion growthAntibacterial agentsPowder deliveryOral medicationMicrometer
The invention relates to a drug nanoparticle delivery system comprising skeleton particles formed from solidified auxiliary materials, and drug nanoparticles wrapped in the auxiliary materials and scattered in the skeleton particles independently. The particle size of the skeleton particles is 1-10 micrometers and the average particle size of the drug nanoparticles is 50-1000 nanometers. Compared with conventional preparations, the preparations provided by the invention have a higher dissolution rate and dissolution degree. The preparations have high bioavailability when being absorbed by human bodies and are suitable for oral administration of mammals.
Owner:新加坡纳诺泰克药物科技有限公司
Preparation and application of 5-aminolevulinic acid-camptothecin micromolecular prodrug
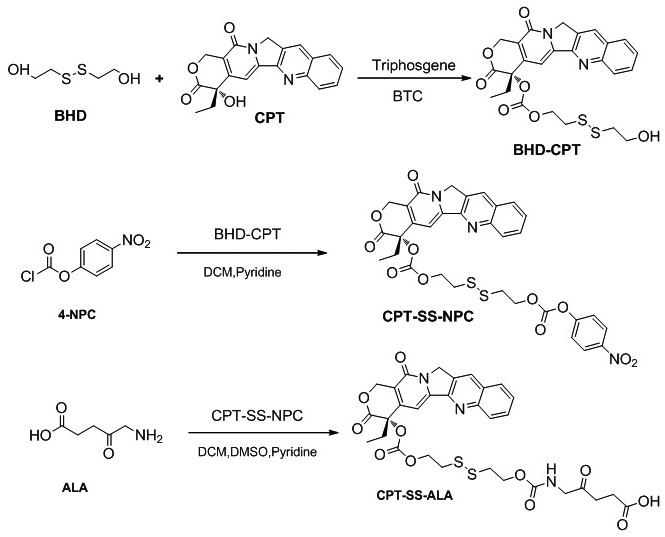
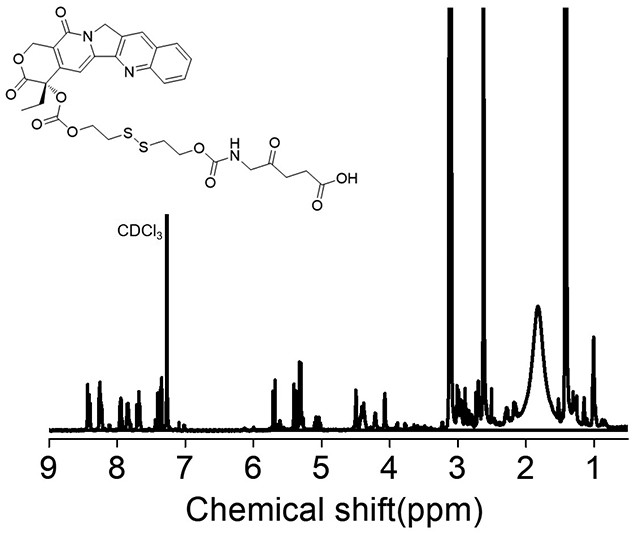
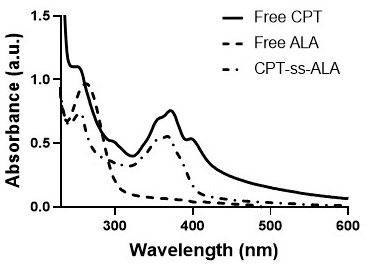
InactiveCN111840574AIncrease upload volumeHigh selectivityOrganic active ingredientsEnergy modified materialsDisulfide bondingChemo therapy
The invention discloses preparation and application of a 5-aminolevulinic acid-camptothecin micromolecular prodrug. A preparation method comprises the following steps: (1) preparing a disulfide bond-containing camptothecin monomer BHD-CPT; (2) preparing CPT-SS-NPC; and (3) reacting a photosensitizer ALA with CPT-SS-NPC to prepare CPT-SS-ALA. Benefited from the amphiphilic structure of the drug conjugate, the drug conjugate can be self-assembled in water to form nanoparticles, and has the advantages of high micelle stability, controllable micelle shape, high drug loading capacity, low toxic andside effects, good drug controlled release and the like. In a reductive tumor microenvironment, disulfide bonds in the drug nanoparticles are broken, a chemotherapeutic drug CPT is released, meanwhile, the photosensitizer ALA continues to generate singlet oxygen under laser irradiation to kill cancer cells, and multi-modal synergistic treatment of tumors is achieved.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIV
Quantitative nano aerosol and method of manufacturing the same
The invention relates to a nanometer grain and rationed nanometer aerosol utilizing the nanometer grain and their preparation method. With comprehensive microemulsion technology and fast drying technology, prepare a plurality of chemical drugs and biologic particles into nanometer grain, so as to enhance the transfer efficiency via lung intake. To be specific, evenly distribute the liquid for dissolving the drug in another non-mixing solvent under the action of surfactant with microemulsion technology. Then, evaporate all the liquid with fast drying technology to get the nanometer grain of drug. The nanometer grain of drug can evenly disperse in a fluid with propellent, so as to get the nanometer preparation of aerosol. The nanometer preparation has stable transfer capacity for the lung intake of drug and can be applied to drugs with lung transfer, oral transfer or nostril transfer.
Owner:NANTONG RUIKANGDA BIOTECH CO LTD
Polypeptide and nucleic acid drug nanoparticles containing same
ActiveCN103804473ADown-regulated expressionLow toxicityOrganic active ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsLiver cancerDrug transfer
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Polymer nanocarrier capable of promoting endocytosis and cell nucleus targeting and preparation method of polymer nanocarrier
InactiveCN106619571ASmall toxicityEnsure safetyHeavy metal active ingredientsOrganic active ingredientsPolyesterNanocarriers
The invention discloses a polymer nanocarrier capable of promoting endocytosis and cell nucleus targeting and a preparation method of the polymer nanocarrier. The polymer nanocarrier material is an amphipathic block polymer, a hydrophobic end is a polyester capable of being biologically degraded and absorbed, a hydrophilic chain segment is polyethylene glycol with a terminal linked with polypeptide capable of promoting endocytosis and cell nucleus targeting, the polypeptide is modified by a small molecule, and an amido bond, linked with the polypeptide, of the small molecule responds to a faintly acid environment of tumors, so that the endocytosis and the nucleus targeting drug delivery are promoted; and a cell nucleus can be targeted by virtue of a cell nucleus targeting signal. The polymer nanocarrier material and medicines can form medicine-carrying nanoparticles in water through self-assembling, and the preparation method is simple.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
Antineoplastic agent containing hydrophobic chemotherapeutic drug nano-particles and fibrin glue
InactiveCN106974896AReduce dosing frequencyImprove complianceOrganic active ingredientsSolution deliveryFibrin glueChemotherapeutic drugs
The invention belongs to the field of pharmaceutic preparations, and relates to an antineoplastic agent containing hydrophobic chemotherapeutic drug nano-particles and fibrin glue. The antineoplastic agent can be a pharmaceutic preparation composed of hydrophobic chemotherapeutic drug nano-particles and fibrin glue, and can also be an oncotherapy agent prepared from a hydrophobic chemotherapeutic drug nano-particle preparation and a fibrin glue preparation right before use. The antineoplastic agent can be used for local drug delivery after tumor excision, and can make local drug concentration stay at a high level for a long time.
Owner:BEIJING DELI FURUI MEDICAL SCI & TECH
Preparation and application of anti-Alzheimer disease (AD) peptide-metal-drug self-assembled nanoparticles
ActiveCN112641956AImprove stabilityHigh efficiency loadPowder deliveryNervous disorderDiseaseRos scavenging
The invention discloses preparation and application of anti-Alzheimer disease (AD) peptide-metal-drug self-assembled nanoparticles, and belongs to the field of nano material preparation and biomedical application. The peptide-metal-drug nanoparticles are prepared in a self-assembly mode by taking coordination effect and hydrophobic effect as driving force. The peptide-metal-drug self-assembled nanoparticles have the advantages of being simple in preparation process, controllable in particle size and potential, good in water solubility, high in drug loading rate, good in biocompatibility, biodegradable and the like. The self-assembled nanoparticles show remarkable inhibition and degradation effects on A[beta] protein fibrosis, excellent ROS scavenging capacity, activity inhibition of beta-secretase and other functions at low dosage concentration, so that the peptide-metal-drug self-assembled nanoparticles have huge potentials as a multi-target and multi-channel drug for treating AD.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
Method for producing solid-lipid composite drug particles
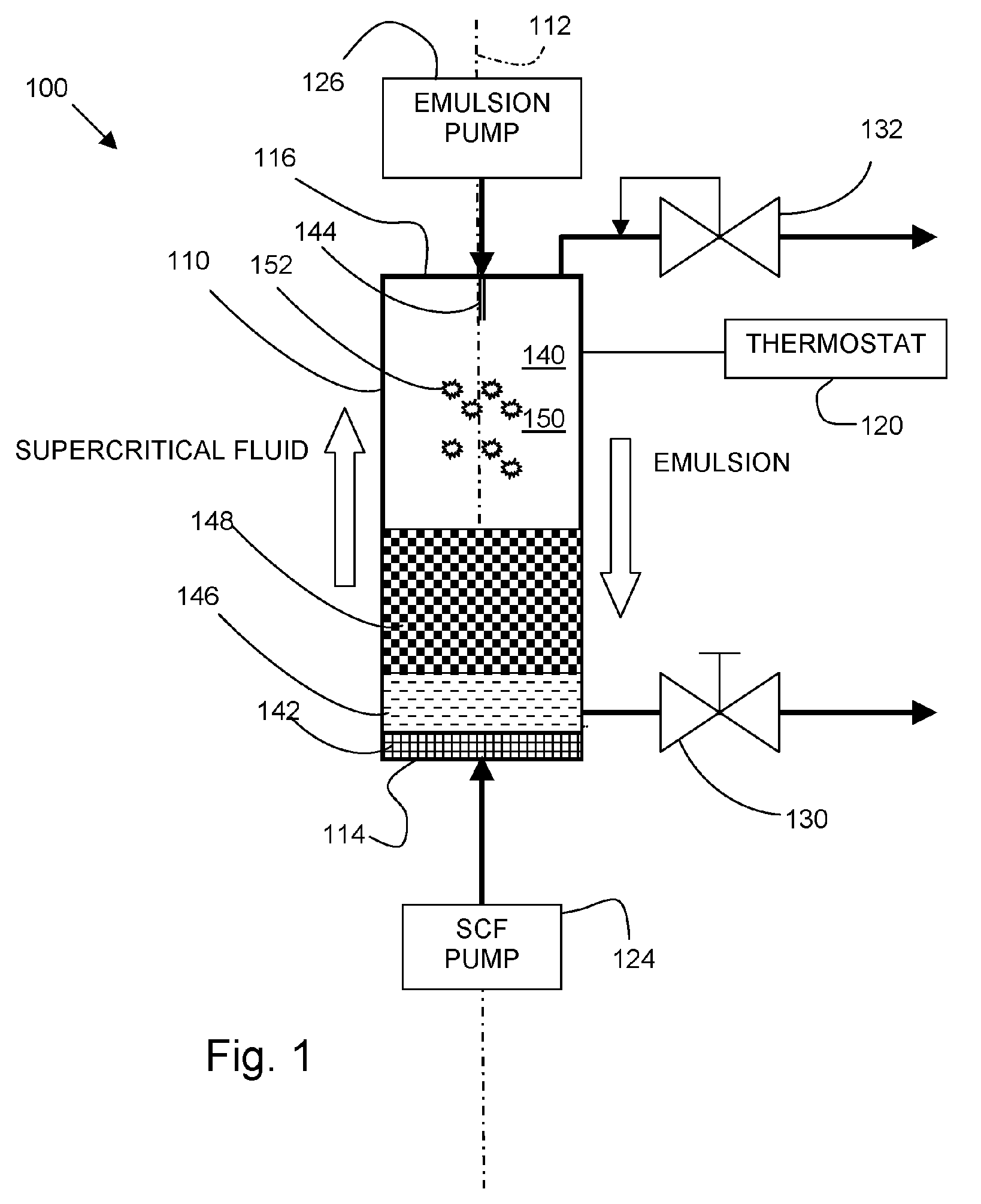
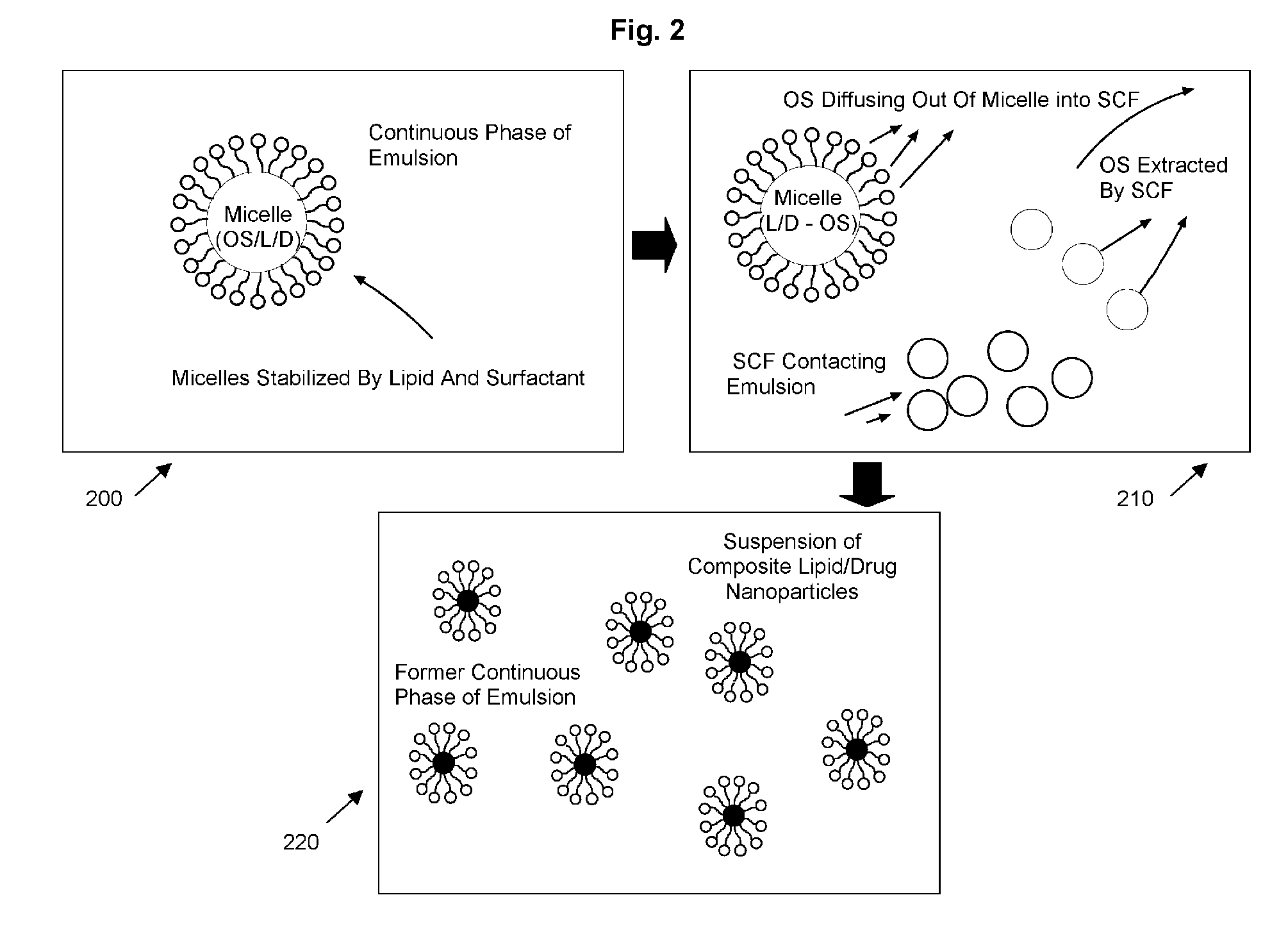
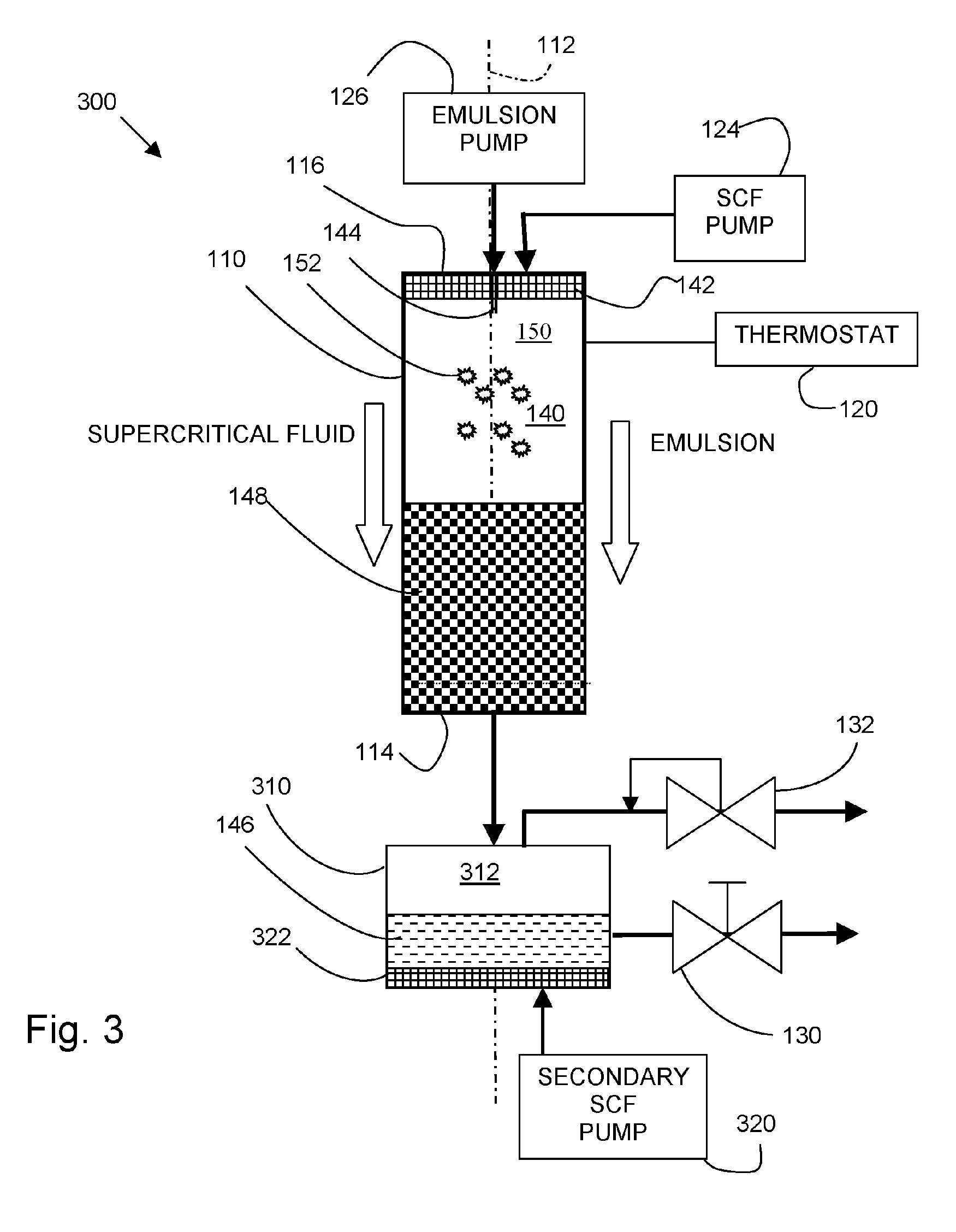
InactiveUS20060008531A1High drug loadingLow temperature processingPowder deliverySolvent extractionLipid formationEmulsion
A method of producing solid composite lipid / drug nanoparticles that includes the steps of: (1) dissolving a lipid and a drug in a suitable organic solvent to form a solution; (2) emulsifying the solution in a liquid to form an emulsion having a discontinuous phase of micelles comprising the organic solvent, the drug and the lipid, and a continuous phase comprising the liquid; and (3) contacting the emulsion with a supercritical fluid under conditions suitable to keep the supercritical fluid in a supercritical state, whereby the supercritical fluid extracts the organic solvent from the micelles, causing them to precipitate as organic-solvent free solid composite lipid / drug nanoparticles suspended or dispersed in the liquid.
Owner:FERRO CORP
Encapsulation and high loading efficiency of phosphorylated drug and imaging agents in nanoparticles
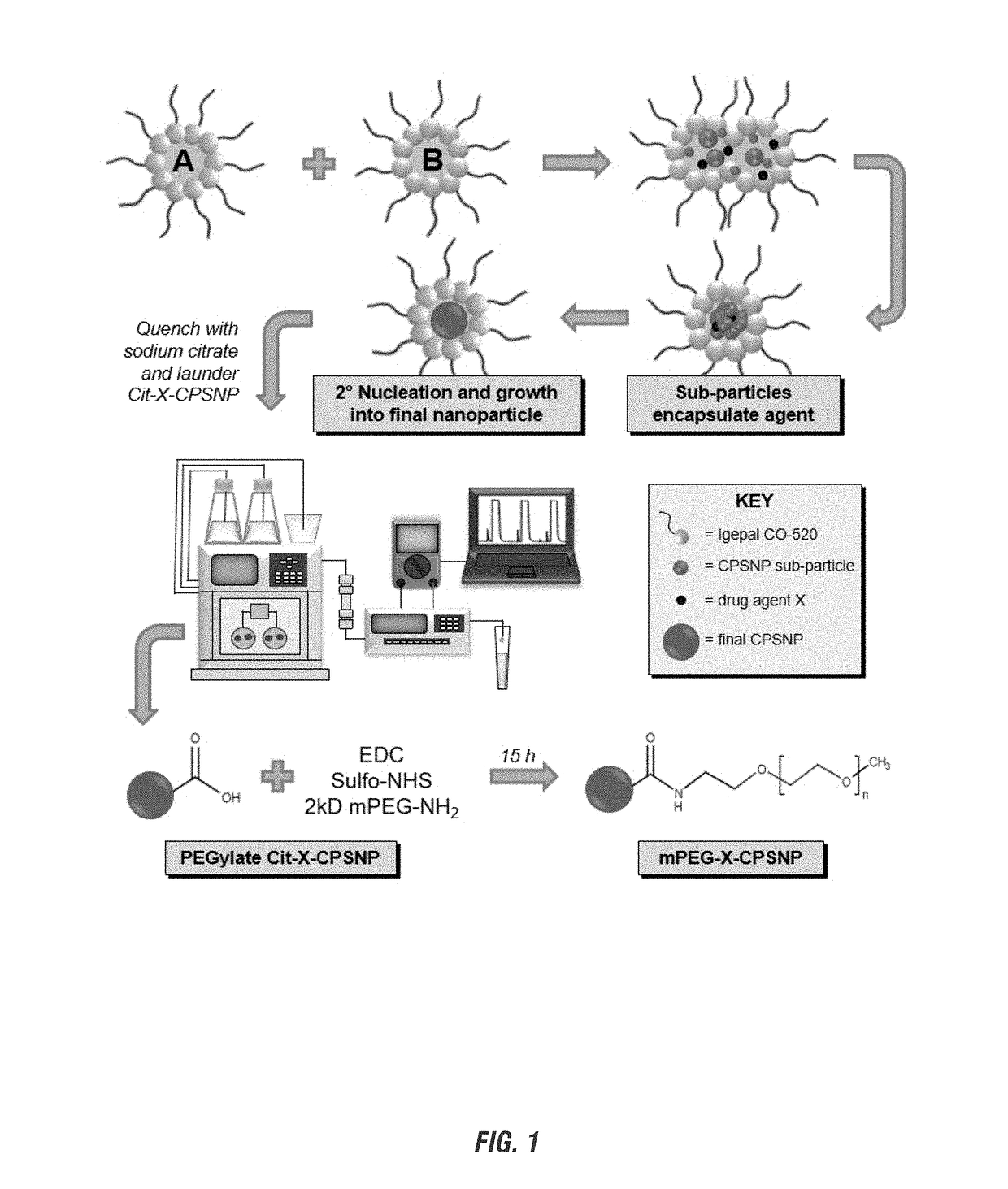
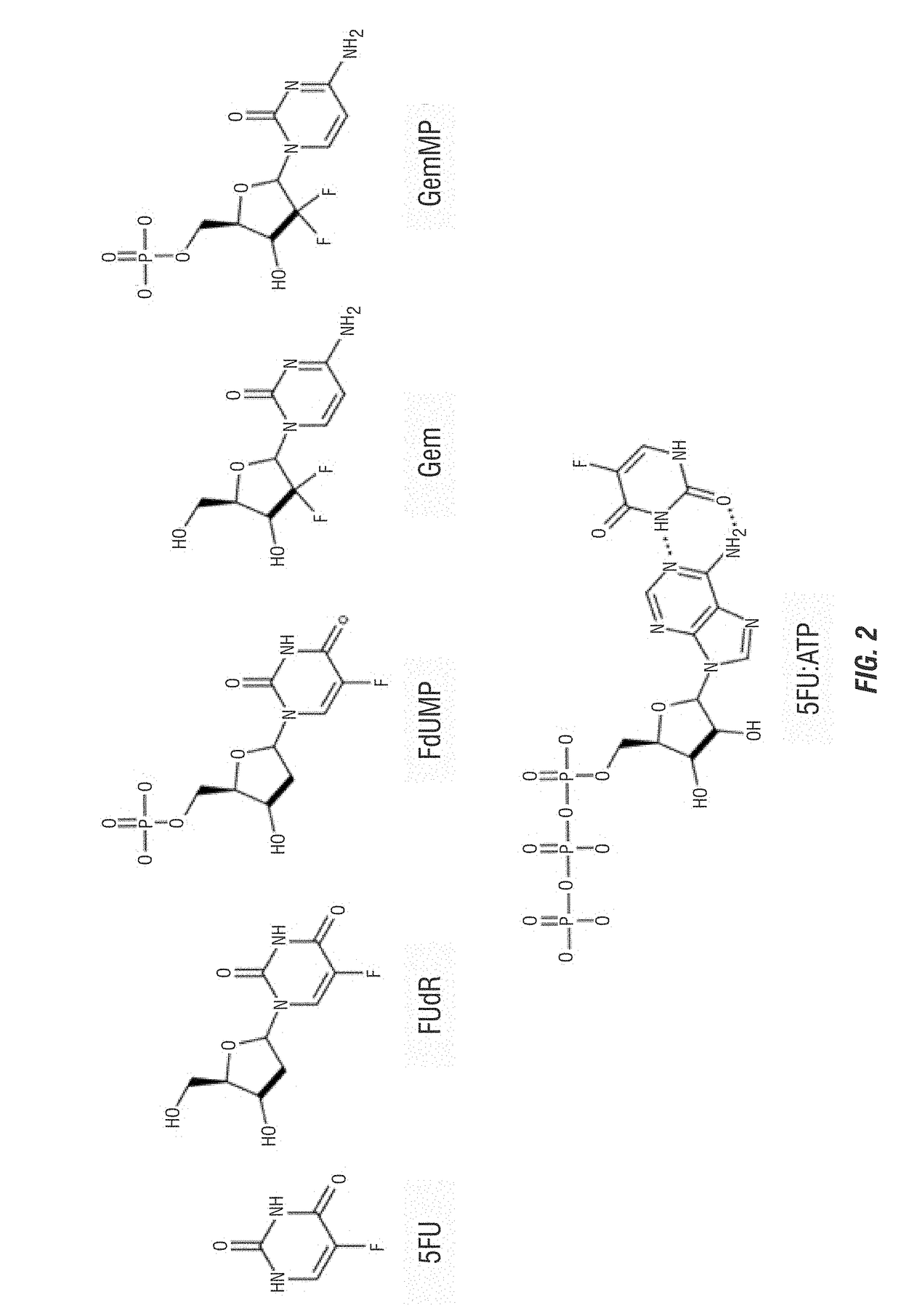
InactiveUS20170209478A1Improve loading efficiencyImprove efficiencyOrganic active ingredientsSpecial deliveryMetaboliteCancer cell
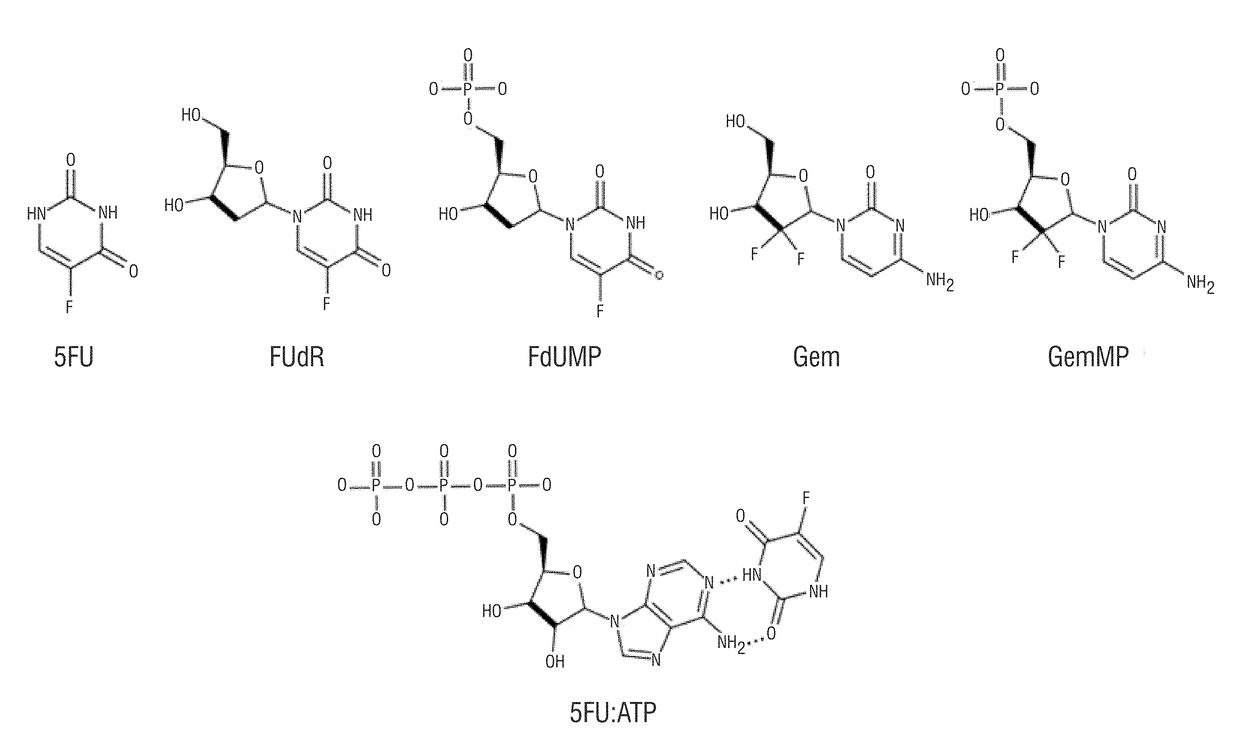
Method of producing nanoparticle of drug and imaging agents are provided. The phosphorylated encapsulated drugs and imaging agents could be encapsulated at therapeutic levels, were encapsulated at higher amounts. The CPSNPs were more effective in treating cancer, in reducing cancer proliferation, arresting cancer cell growth than when not in the form of a CPSNP, and showed efficacious treatment of cancer cells at far lower dosage than free molecules. Calcium phosphosilicate and phosphate nanoparticles are disclosed and their method of use. The methods and nanoparticles are particularly efficacious where CPSNPs were used to encapsulate 5-FU metabolites such as FdUMP and gemcitabine metabolites.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com