Nanoparticulate formulations and methods for the making and use therof
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Preparation of USP Simulated Gastric and Intestinal Fluid
Simulated Intestinal Fluid (SIF)
[0352]Monobasic potassium phosphate (6.8 g) and sodium hydroxide (0.616 g) are added into 250 ml of distilled water in a 1000 ml volumetric flask and swirled until dissolved. 700 ml distilled water is added and the pH checked. The pH is adjusted to pH 6.8+ / −0.1 by adding either 0.2N sodium hydroxide or 0.2N hydrochloric acid and the volume is brought to 1000 ml.
Simulated Gastric Fluid (SGF)
[0353]Sodium chloride (2 g), 750 ml distilled water, and 7.0 ml of concentrated hydrochloric acid are added into a 1000 ml volumetric flask. The flask is swirled to mix and the volume brought to 1000 ml with distilled water. The pH should be approx. 1.2.
example 2
Particle Size Measurement Method
[0354]The following methods and settings for particle size measurement were used for all D50 values for ganaxolone and phenyloin.
Particle Size Method Using Horiba Laser Scattering Particle Size Distribution Analyzer LA-910
[0355]Particle size measurement using Horiba laser scattering particle size distribution analyzer is generally well known for those skilled in the art. It is important that the parameters be kept constant when measuring different samples if they are used for comparison purposes. For ganaxolone and phenyloin nanoparticulate compositions, instrument settings and sample preparation method are described below:
Instrument Settings and Parameters:
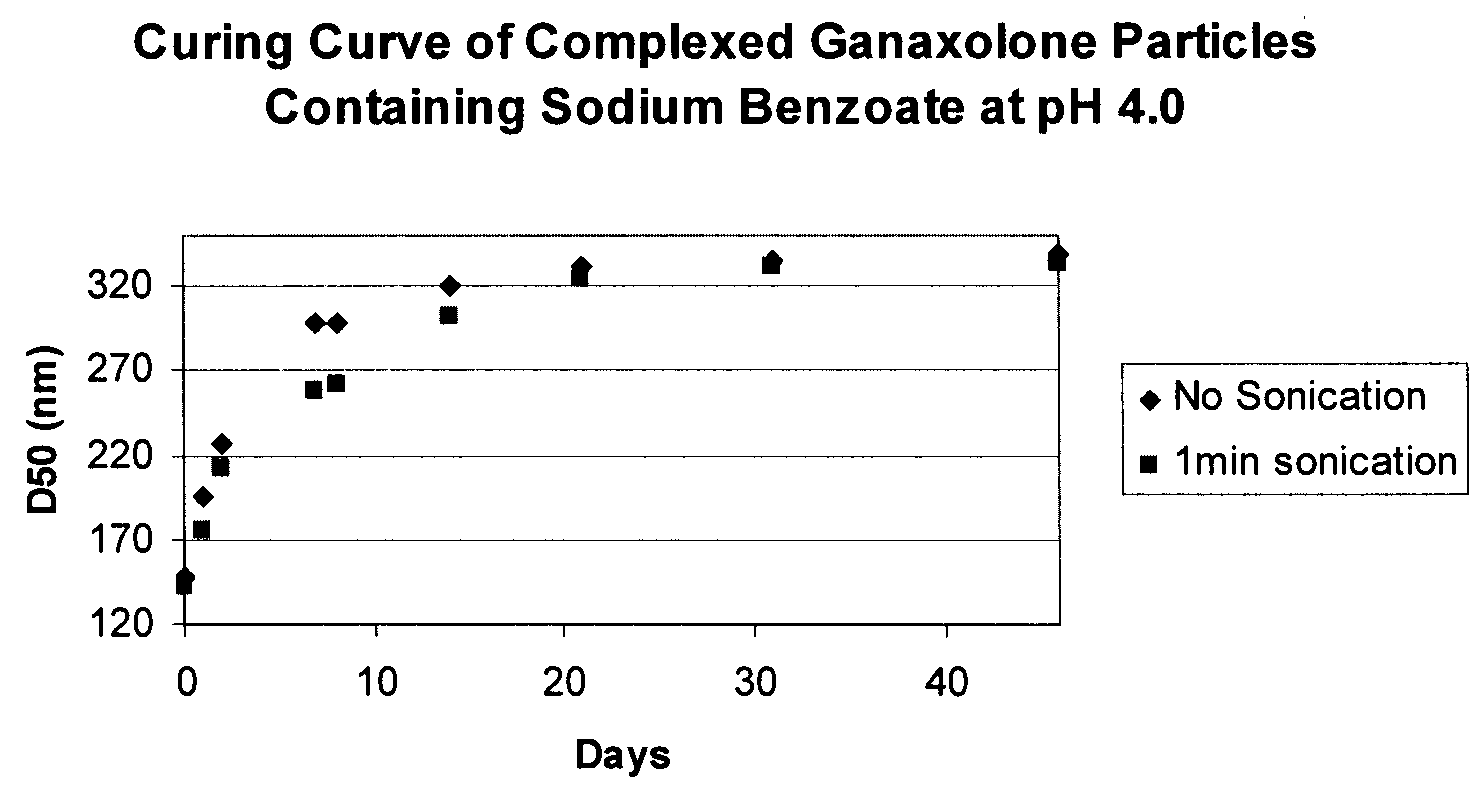
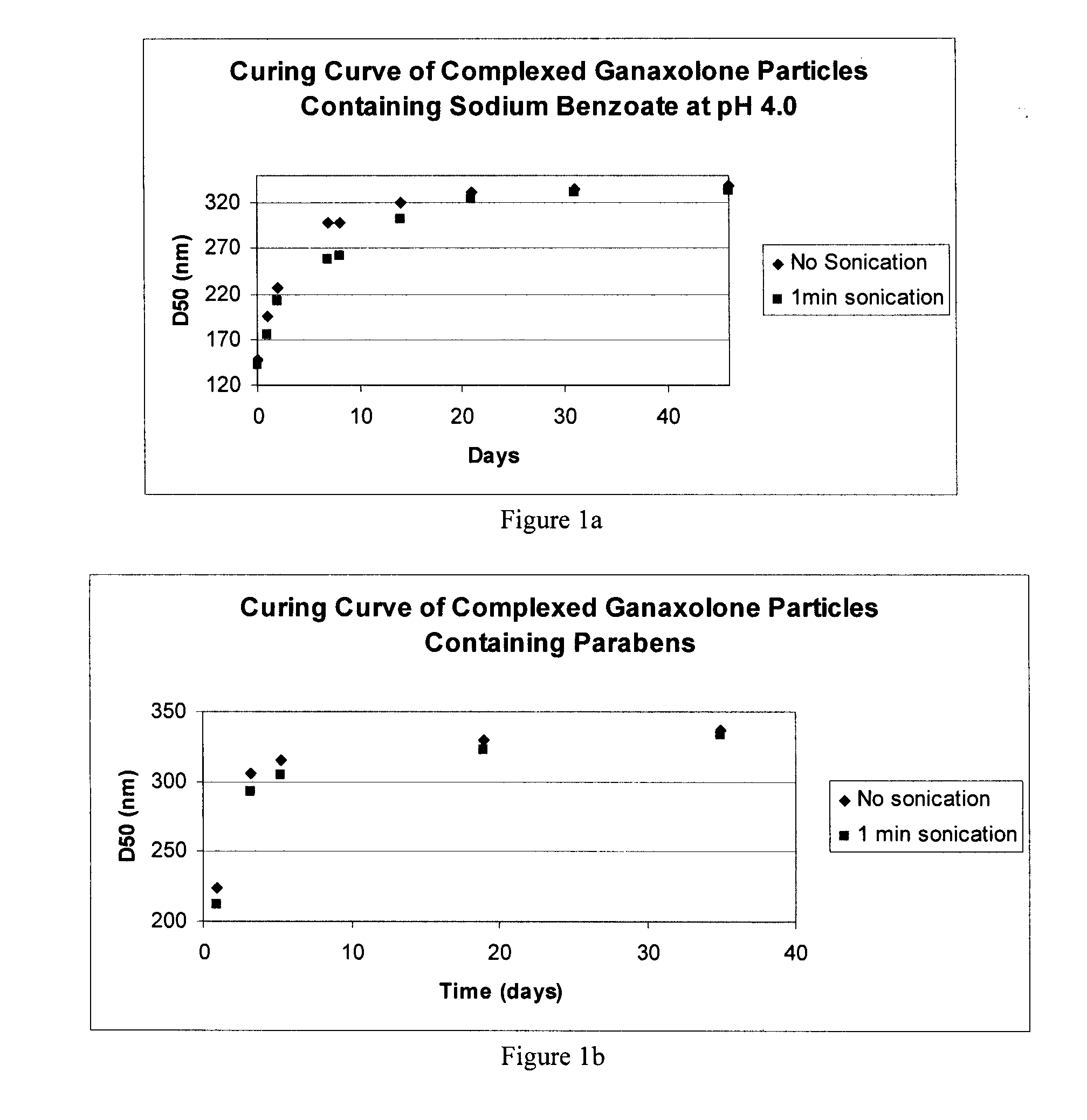
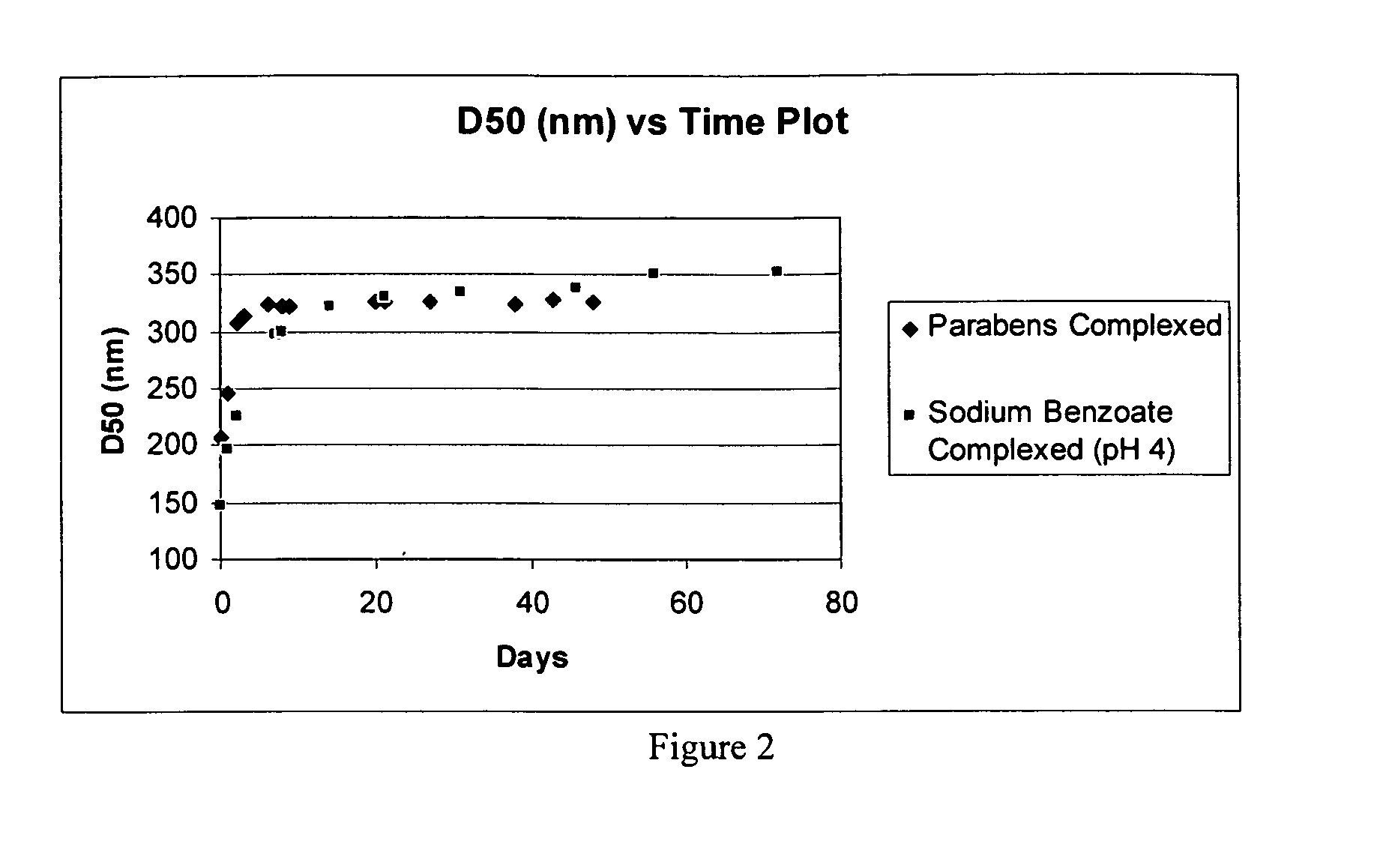
[0356]Measure Conditions: Circulation=4; ultrasonic time=1; agitation=1; sampling times: red laser=10, blue lamp=2; preferred % transmittance: blue lamp=75-80%; blank: red laser=10, blue lamp=2. For D50 values after sonication, the sonication power is set to low and the sonication time is 1 minute....
example 2a
Sample Preparation and Particle Size (D50) Determination
[0359]For concentrated nanoparticle drug suspensions, dilute the nanoparticulate composition with deionized water to approximately 5 mg / mL API concentration. Shake well for 15-30 seconds. Add 120 mL of deionized water to the chamber, turn agitation and recirculation settings on. Transfer the nanoparticulate suspension via a pipette to the sample chamber in sufficient quantity to reach the transmittance range of 75-80% blue lamp. If a suspension or stability indicating dispersion is at a concentration of approximately 0.5 mg / ml do not further dilute if not necessary and use directly for particle size measurement. Transfer the sample to be measured via a pipette to up to the desired transmittance range (75-80% blue lamp). Take a measurement and collect the D50 value. This will be the unsonicated particles size. Sonicate for 1 min and take a measurement again to collect D50 value. This will be the particle size after 1 minute soni...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com