Global synchronization pulse width modulation system and method of distributed grid-connected inverter system
一种脉宽调制、全局同步的技术,应用在脉冲持续时间/宽度调制、交流网络电路、单网平行进料安排等方向,能够解决不能控制公共并网点注入电网电流谐波、公共并网点电压畸变、总谐波畸变不确定等问题,达到实现全局同步脉宽调制、消除谐波电流无序叠加、减少影响的效果
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
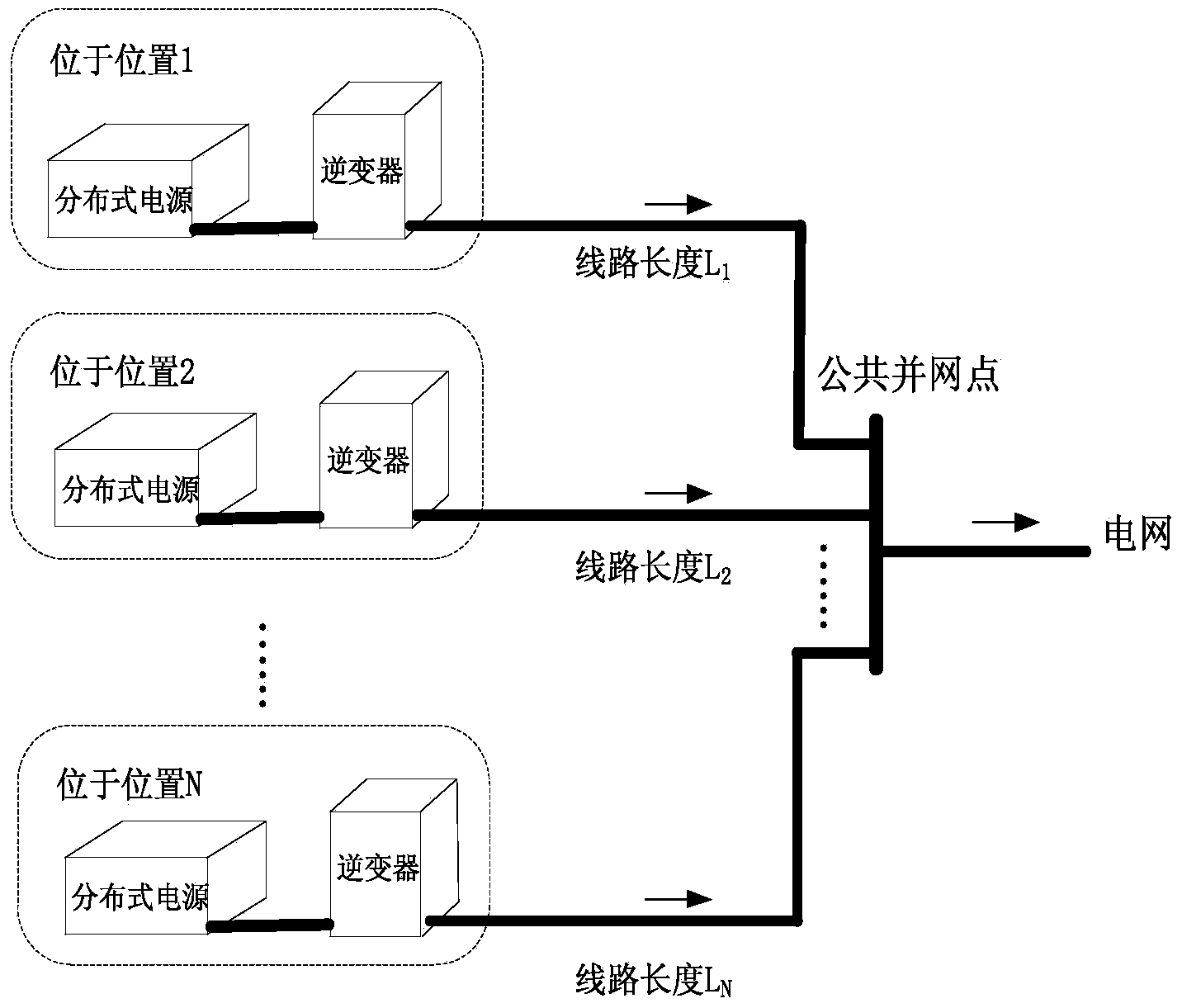
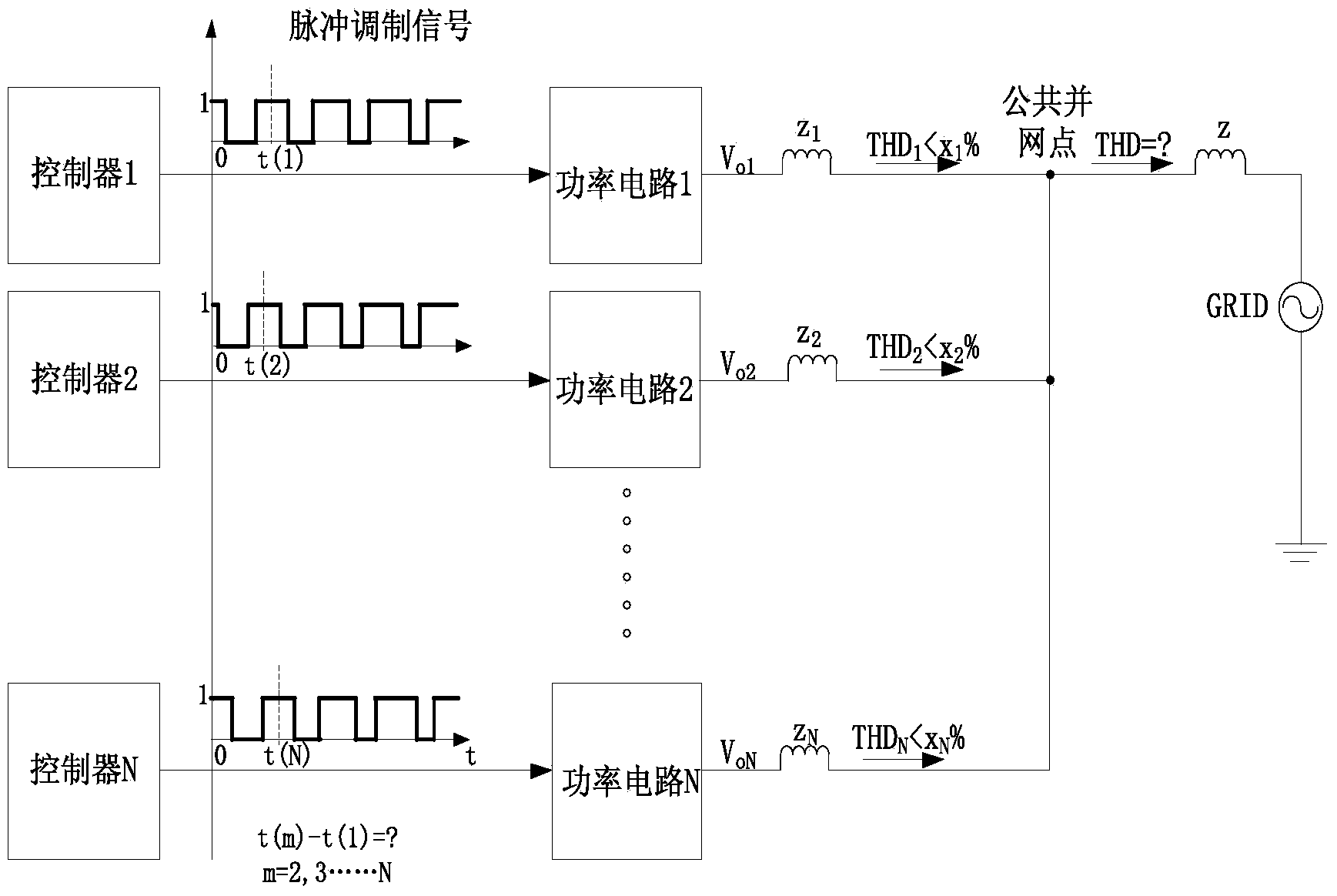
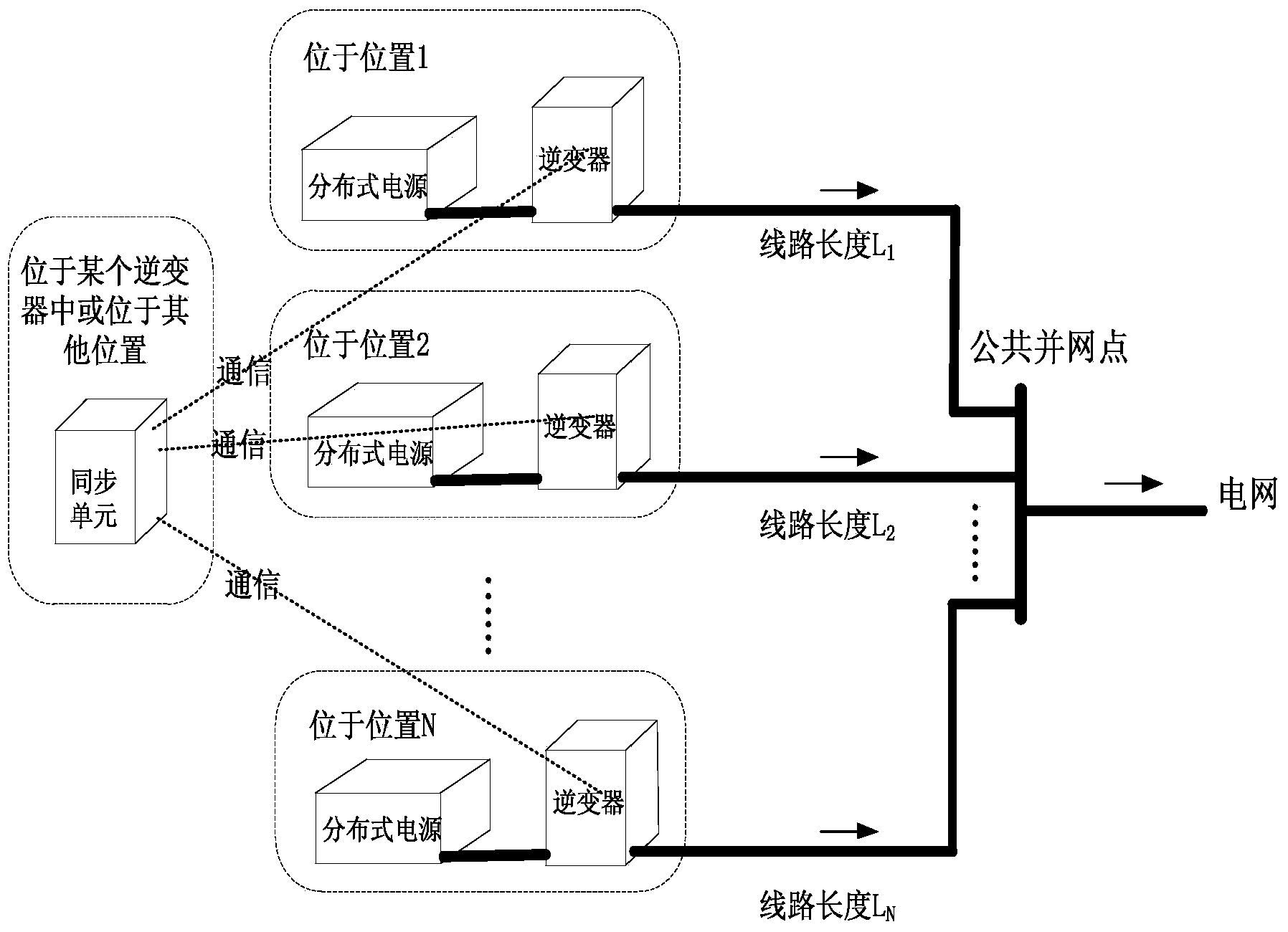
[0109] Corresponding to the situation where the inverters are not grouped, there are 4 inverters in the system connected to the common grid-connected point, the switching frequency is 20k, the DC side voltage is Vdc, and the inductance between the common grid-connected point is L, wrong Inverters are grouped, N=4, m=1,2,3,4.
[0110] In step 11, the synchronization unit obtains the switching frequency of each inverter, the DC side voltage, and the reactance to the common grid connection point.
[0111] The time of one switching cycle is:
[0112] T c = 1 20 × 10 3 = 50 μs
[0113] Δt(1)=(1-1)T c / 4=0μs
[0114] Δt(2)=(2-1)T c / 4=12.5μs
[0115] Δt(3)=(3-1)T c / 4=25μs
[0116] Δt(4)=(4-1)T c / 4=37.5μs
[0117] Step 12, locate the synchronization time interval for 1 minute, ...
Embodiment 2
[0122] Corresponding to the situation where the inverters are not grouped, there are 5 inverters in the system connected to the common grid-connected point, the switching frequency is 20k, the DC side voltage is Vdc, and the inductance between the common grid-connected point is L, wrong Inverters are grouped, N=5, m=1,2,3,4,5.
[0123] In step 21, the synchronization unit obtains the switching frequency of each inverter, the DC side voltage, and the reactance to the common grid connection point.
[0124] Divided into two groups for control,
[0125] Group 1 The time for one switching cycle is:
[0126] T c = 1 20 × 10 3 = 50 μs
[0127] Δt(1)=(1-1)T c / 5=0μs
[0128] Δt(2)=(2-1)T c / 5=10μs
[0129] Δt(3)=(3-1)T c / 5=20μs
[0130] Δt(4)=(4-1)T c / 5=30μs
[0131] Δt(5)=(4-1)T...
Embodiment 3
[0137] Step 31: In the case of grouping inverters, there are 11 inverters in the system connected to the common grid connection point, and the switching frequency is 40k, but when the DC side voltage and the reactance to the public grid connection point are different, group them The label, the DC side voltage parameters and reactance parameters of each inverter are shown in Table 1. Here, an example is used for analysis, which does not represent the actual parameter value. Here, according to one method, the V in each group dcm / L m They are divided into 4 groups by the method of sum and similarity, and the groups are shown in Table 1. Inverters 1, 2, and 3 are the first group, inverters 4, 5, and 6 are the second group, and inverters 7, 8, 9 is the third group, inverters 10 and 11 are the fourth group, N=4, m=1, 2, 3, 4.
[0138] Table 1
[0139]
[0140] T c = 1 40 × ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com