Method of observing samples with a fluorescent microscope
A fluorescence microscope and electron microscope technology, applied in the field of observing samples with a fluorescence microscope, can solve the problems of destroying samples, damage, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
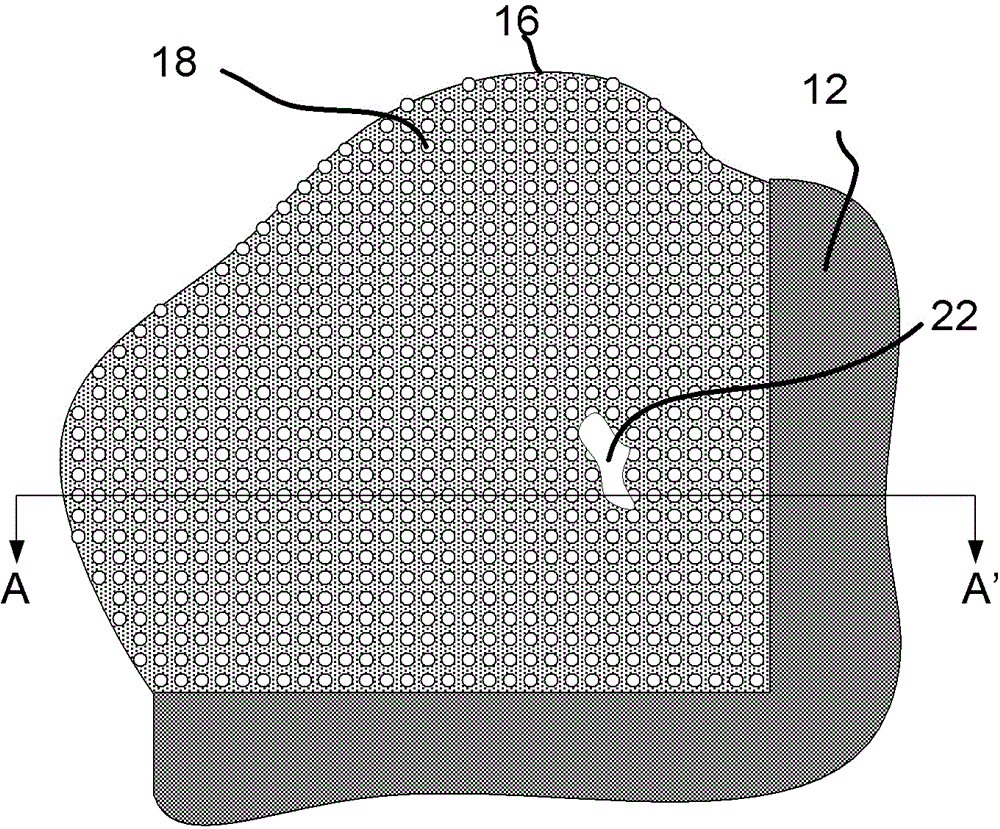
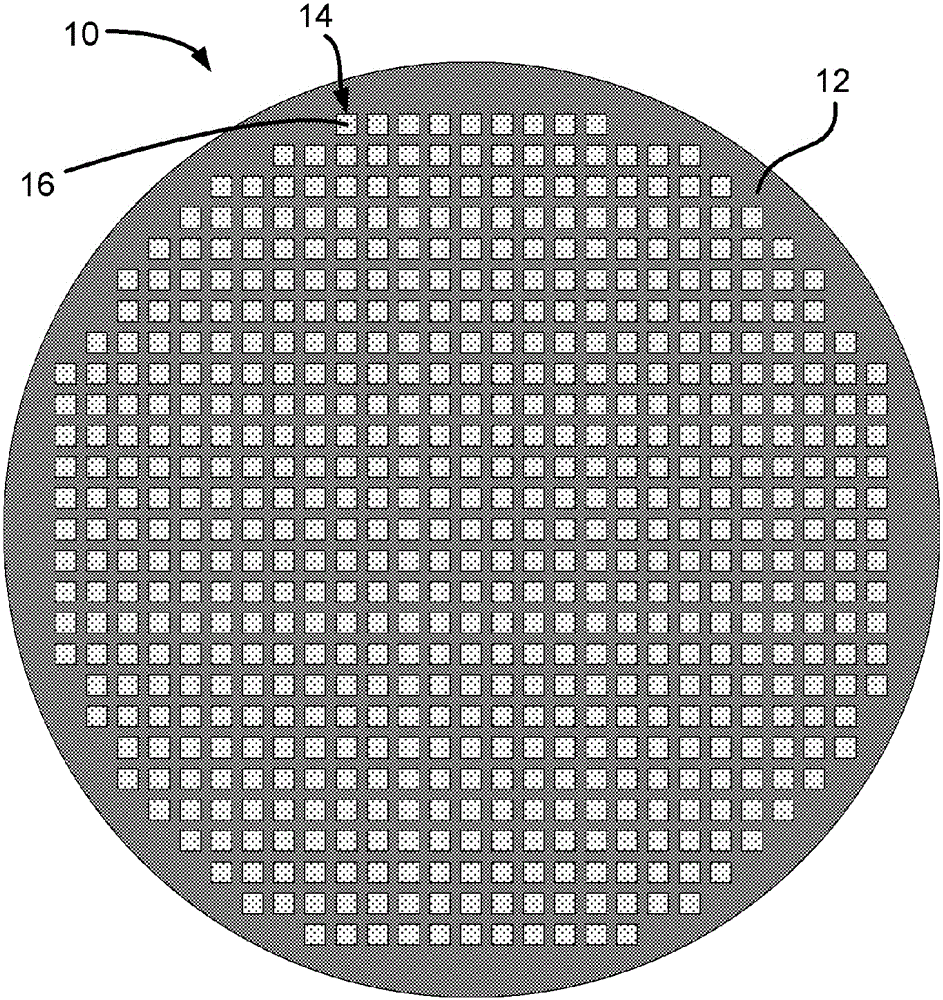
[0037] Figure 1A The top view of the TEM grid is schematically shown.
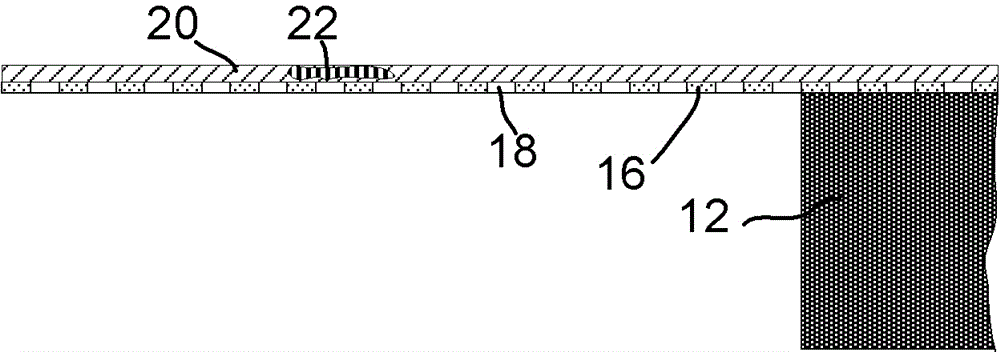
[0038] TEM grid 10 is a circular thin copper foil (copper foil) 12 with a thickness of about 25 μm and a diameter of 3.05 mm. The foil exhibits a large number of holes 14 (eg 400 per inch) and a thin carbon film 16 on which a sample can be placed. Copper and carbon not only provide support but also conductivity to avoid charging.
[0039] Note that grids with coarser or finer meshes, other materials (gold, nickel, (carbon-coated) plastics), other forms of holes (slots, hexagons) or Forms other than thin circular foils (see eg US Patent Nos. US 7,767,979 and US 7,034,316).
[0040] Note also that the holes may exhibit thin carbon layers, eg 3 nm layers. This is based on the fact that LARSON is not sufficient to absorb light or provide a conductive path from the sample to ground (the holder of the grid).
[0041] The film does not have to be a carbon film, essentially for the present invention the fil...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com