An independent current sharing circuit suitable for multi-channel parallel LED strings
A circuit and current sharing technology, which is applied in the layout of electric lamp circuits, electric light sources, electrical components, etc., can solve the problems of uneven current, different V-I characteristics of multiple LED strings, and the inability to achieve independent current sharing of circuits, and achieve a simple structure. , The effect of efficient and autonomous current sharing
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
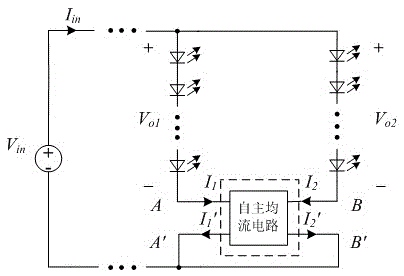
[0026] The schematic diagram of the independent current equalizing circuit of the present invention is as attached figure 1 , 3 Shown:
[0027] 1) pair attached figure 1 In the circuit shown, when the two currents are uneven, there must be a potential difference between A and B (at this time, when there is no independent current equalizing circuit control, the schematic diagram of the V-I characteristic curve of the two LED strings is as attached Image 6 shown). attached figure 1 The two potentials of points A and B correspond to the attached image 3 Middle port A, B potential;
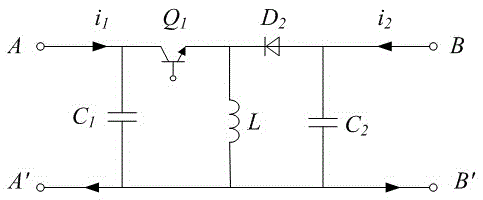
[0028] 2) The present invention is attached to the traditional Buck-Boost circuit figure 2 improved on the basis of figure 2 The independent current equalizing circuit is composed of capacitors C1, C2, inductor L, diode D2 and switch tube Q1. It can only realize the one-way power transmission function of one port input and one port output. According to this working principle, if the D2 b...
Embodiment 2
[0038] The present invention can also adopt as attached Figure 4 In the circuit design shown, in order to control the working state of the Buck-Boost circuit and realize two-way current sharing, it is necessary to measure the voltage across the capacitors C3 and C4 at the same time.
[0039] 1) The example is attached image 3 On the basis of the circuit, in order to collect the potential information of ports A and B, a circuit is connected between the two ports, in which C3 and D3 are connected in series, D4 and C4 are connected in series, and the two series branches are connected in parallel to form the circuit, as shown in the attached Figure 4 As shown, when the circuit is working, the working state of the circuit is controlled with the voltage at both ends of C3 and C4 as a reference;
[0040] 2) As attached image 3 As shown, when the potential of port A is high, D3 is turned on, D4 is turned off, C3 stores energy, and the voltage at both ends of C3 is positive. The ...
Embodiment 3
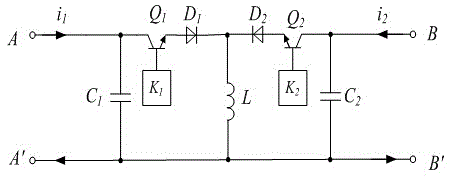
[0044] The present invention can also adopt as attached Figure 5 The autonomous current sharing circuit shown can realize autonomous current sharing by collecting the potentials of the two ports of the Buck-Boost circuit.
[0045] 1) Different from Embodiment 2, when the autonomous current sharing circuit is working, it can directly collect the potentials of ports A and B for comparison, and the two ports are respectively connected to the input terminals of the voltage comparator, and the voltage comparator generates level signals to switches K1 and K2 The tube controller, the switch tube controller finally runs the drive unit, thereby controlling the working status of Q1 and Q2;
[0046] 2) When the two currents are uneven, the voltage signal must be high or low. When the measured potential of the A terminal is high, the voltage comparator sends a signal to the controller K1, and the switch tube controller K1 controls Q1 to work in the switch state, duty The ratio is 0.5, a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com