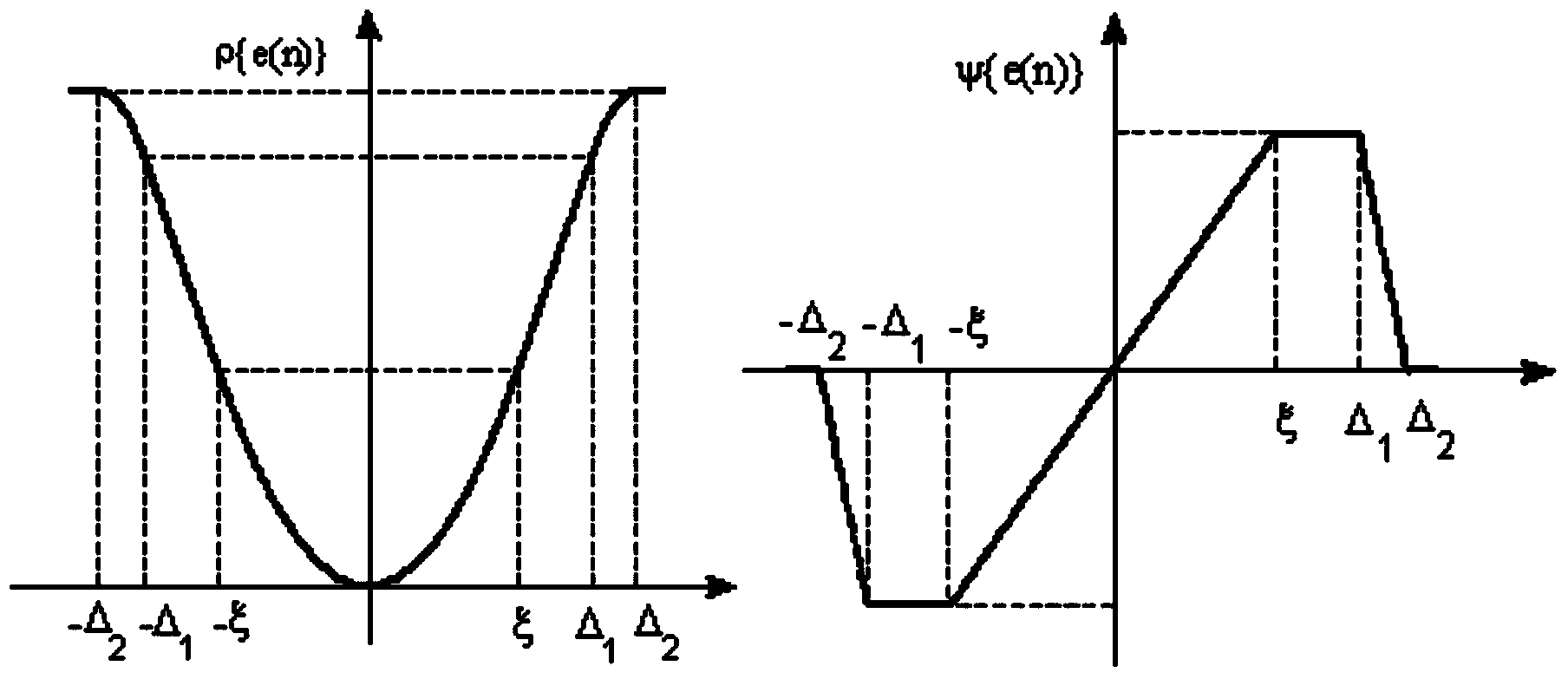M-estimation impulsive noise active control method
A control method and shock-like technology, which can be applied in adaptive control, general control system, control/regulation system, etc., and can solve problems such as algorithm robustness degradation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0033] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
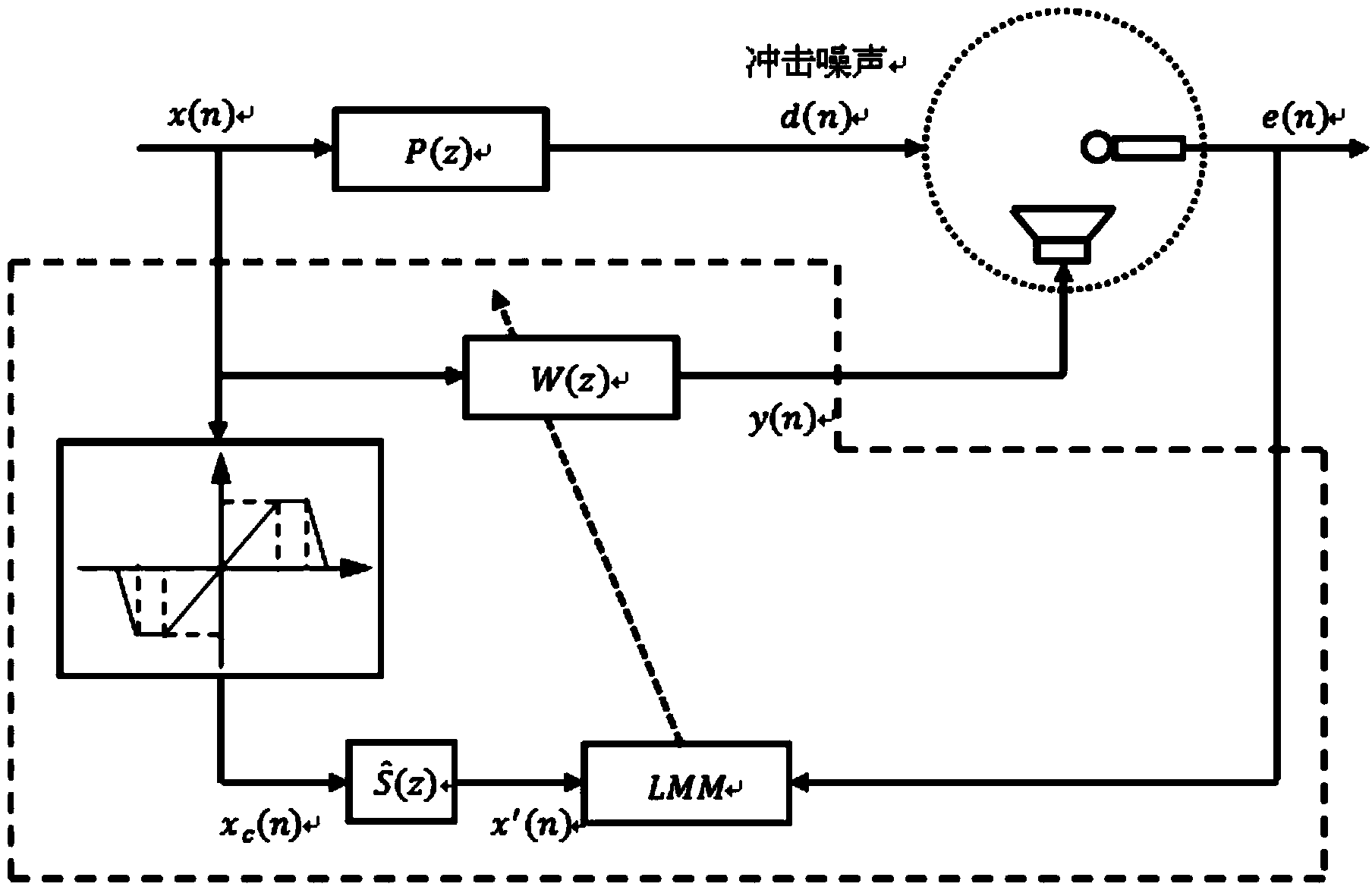
[0034] Such as Figure 1 to Figure 6 As shown, an active control method for shock-like noise based on M-estimation, the method uses the mean square value of the robust M-estimation of the error signal as a cost function, and introduces a threshold in the reference signal channel to limit the impact sample pair The impact of the iterative process of the algorithm, specifically including the following steps:
[0035] 1) Define the cost function J(n)=E[ρ{e(n)}], ρ{e(n)} is a highly robust M-estimation function, using the general Hampel three-segment gradient function;
[0036] 2) Estimate the threshold parameter of the M-estimation function;
[0037] 3) Set the threshold of the reference signal channel, and determine the truncation processing result x of the reference signal c (n);
[0038] 4) Update filter coefficients: W ( ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com