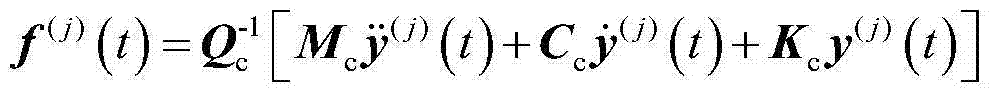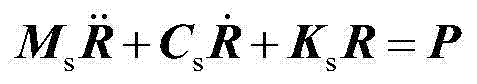Time domain identification method of random dynamic loads
A random dynamic, time domain identification technology, applied in special data processing applications, instruments, electrical digital data processing, etc., can solve the problem of load identification results deviation, inability to consider the randomness of external loads, etc., to achieve intuitive methods and computational efficiency. high effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
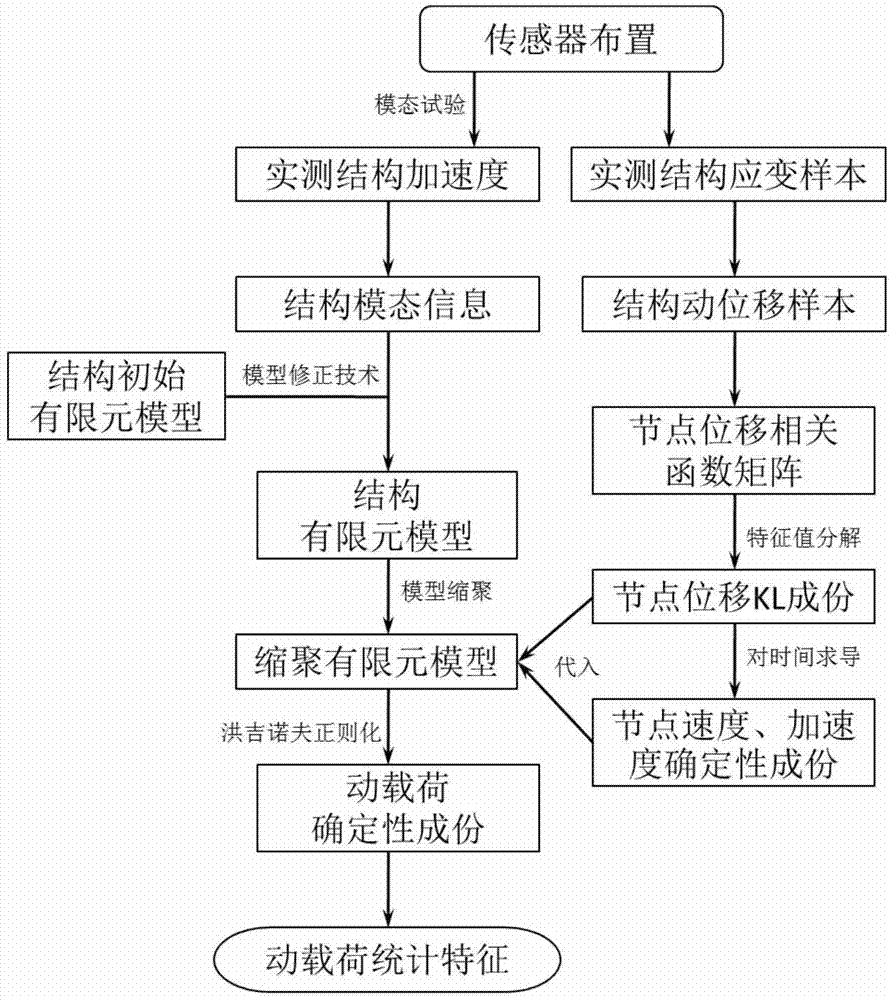
[0028] Embodiment: the random dynamic load identification method of the present invention comprises the following steps:
[0029] (1) Arrange strain and acceleration sensors on the engineering structure, and measure the dynamic strain and acceleration response samples of the structure;
[0030] (2) Establish a structural finite element model for the engineering structure, and then carry out model condensation to obtain the structural finite element model after condensation and the position matrix Q of the load after condensation that matches the corresponding degrees of freedom of the measured dynamic strain response signal c , the finite element model of the structure after polycondensation includes the mass matrix M after polycondensation c , the damping matrix C after polycondensation c and the stiffness matrix K after polycondensation c ;
[0031] First, the initial finite element model of the engineering structure is established; for the engineering structure, the dyna...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com