Photoelectrocatalytic method for treating heavy metal complex waste water and recovering heavy metal therefrom
A technology of heavy metal ions and photoelectric catalysis, applied in the field of water treatment, can solve the problem of insufficient attention and research on the cathode effect, and achieve the effect of effective treatment
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0053] Embodiment 1: to the processing of Cu-EDTA simulated waste water
[0054] This embodiment uses Cu-EDTA to simulate wastewater, wherein the initial concentration of Cu-EDTA is 20mg / L, and the NaClO of 10mmol / L 4 as background electrolyte. The Cu-EDTA simulated wastewater is treated by the photocatalytic method of the present invention, only the electrochemical oxidation method, and only the photocatalytic oxidation method.
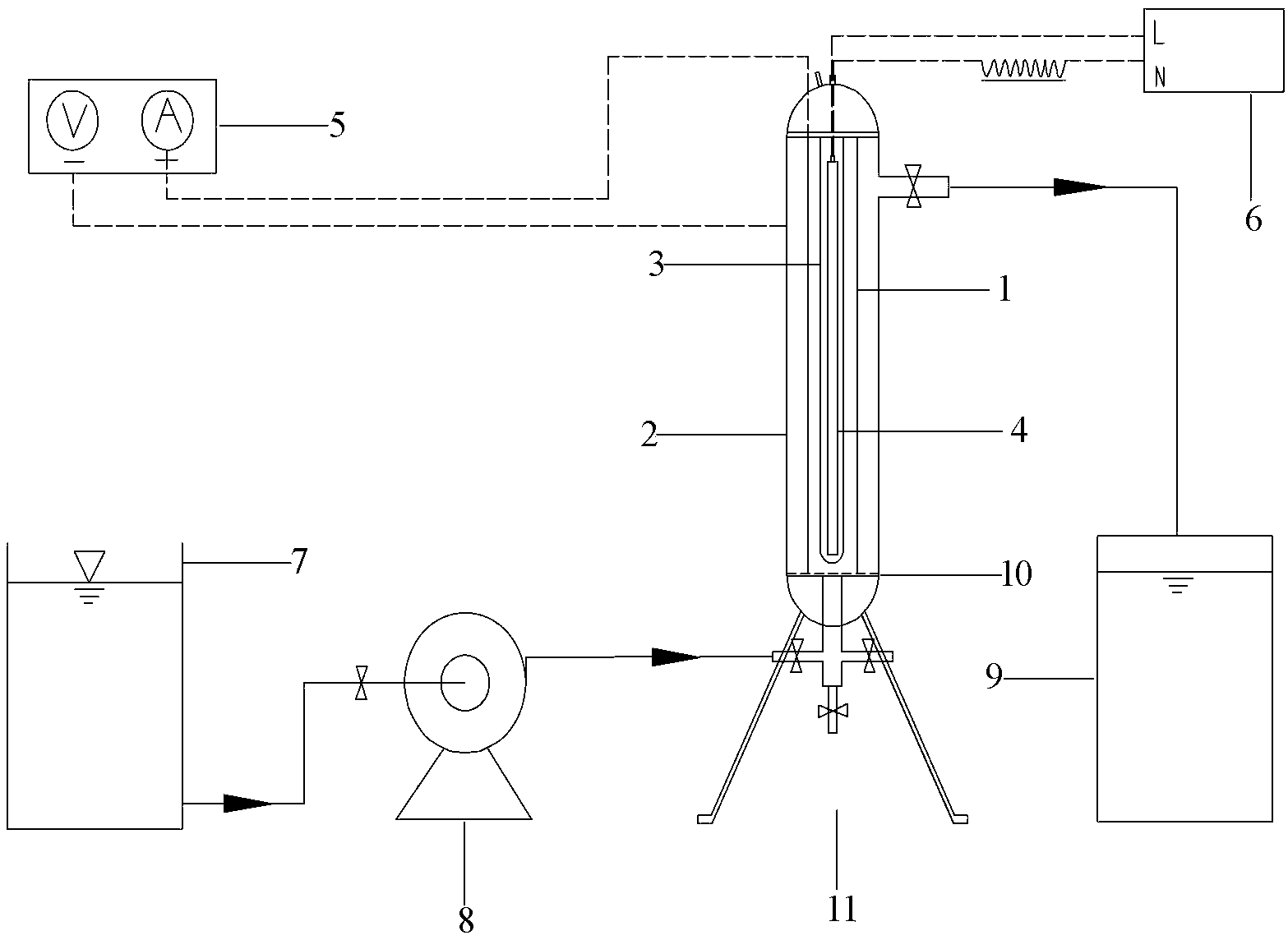
[0055] The processing steps using the photoelectrocatalytic method of the present invention are: figure 1 As shown in the photoelectric reactor, open the water inlet valve, turn on the peristaltic pump 8, open the water outlet valve, fill in the water containing Cu-EDTA to be treated, when the water outlet valve overflows, turn off the peristaltic pump 8; turn on the electrode DC power supply 5, turn on The low-pressure mercury lamp AC power supply 6 adjusts the rotating speed of the peristaltic pump 8 to control the residence time, and the photoel...
Embodiment 2
[0058] Embodiment 2: to the processing of Pb-EDTA simulated waste water
[0059] The present embodiment adopts Pb-EDTA simulated waste water, wherein the initial concentration of Pb-EDTA is 0.1mmol / L, TOC (total organic carbon content) is 12mg / L, the NaClO of 10mmol / L 4 as background electrolyte. The photoelectric catalysis method of the invention is used to treat Pb-EDTA simulated wastewater.
[0060] The processing steps using the photoelectrocatalytic method of the present invention are: figure 1 For the photoelectric reactor shown, open the water inlet valve, turn on the peristaltic pump 8, open the water outlet valve, fill in the water containing Pb-EDTA to be treated, when the water outlet valve overflows, turn off the peristaltic pump 8; turn on the DC power supply 5, and turn on the low pressure The mercury lamp AC power supply 6 adjusts the rotating speed of the peristaltic pump 8 to control the residence time, and the photoelectric oxidation reaction begins. Under...
Embodiment 3
[0061] Embodiment 3: to the treatment of Ni-EDTA simulated waste water
[0062] This embodiment uses Ni-EDTA to simulate wastewater, wherein the initial concentration of Ni-EDTA is 0.05mmol / L, and the NaClO of 10mmol / L 4 as background electrolyte. The Ni-EDTA simulated wastewater is treated by the photoelectric catalytic method of the invention.
[0063] The processing steps using the photoelectrocatalytic method of the present invention are: figure 1 As shown in the photoelectric reactor, open the water inlet valve, turn on the peristaltic pump 8, open the water outlet valve, fill in the water containing Ni-EDTA to be treated, when the water outlet valve overflows, turn off the peristaltic pump 8; turn on the DC power supply 5, and turn on the low pressure The mercury lamp AC power supply 6 adjusts the rotating speed of the peristaltic pump 8 to control the residence time, and the photoelectric oxidation reaction begins. Under the condition of pH=9.0, adjust the power of t...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| power | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com