Test Method for Characterizing the Effect of Cement-Based Materials-Aggregate-Substrate Interface on Carbonation Rate
A technology of cement-based materials and test methods, applied in the field of cement materials, can solve the problems of failure to consider the influence of aggregate transmission performance, failure to consider carbonization prediction models, etc., and achieve the effect of avoiding mutual influence
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0021] Embodiment 1: A kind of test method that characterizes the influence of cement-based material aggregate base material interface on carbonization rate, the mixing ratio of the cement slurry that adopts is
[0022] Water cement ratio
water / g
Cement / g
0.53
636
1200
[0023] The specific implementation steps are:
[0024] 1) Add 795g of distilled water and 1500g of cement successively to the slurry mixer, and stir evenly;
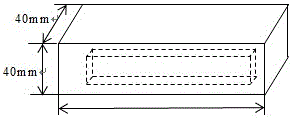
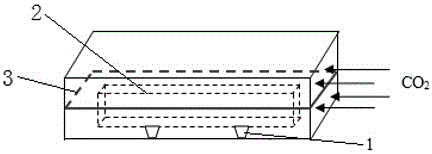
[0025] 2) Pour the stirred clean slurry into a 160mm×40mm×40mm (length×width×height) cement experiment forming mold, and put two small stones 1 with a height of 5mm along the length direction of the bottom in the mold;
[0026] 3) Prefabricated regular limestone flakes 2 (such as figure 1 Shown) the surface is coated with a layer of grout, and then as figure 2 As shown, slowly put it into the middle of the mold where the slurry has been poured, and place the small stone 1 on the bottom of the stone flake 2, so that...
Embodiment 2
[0031] Roughly the same as Example 1, the difference is that the proportion of the cement paste used is
[0032] Water cement ratio
water / g
Cement / g
0.35
420
1200
[0033] Add 345g of distilled water and 1500g of cement successively to the slurry mixer, and stir evenly. Put two pebbles 1 with a height of 10 mm in the mold along the length direction of the bottom, and apply a layer of cement slurry on the surface of the prefabricated regular granite slice 2 with a size of 5 mm × 20 mm × 150 mm, which has been washed and dried for 24 hours. Then slowly put it into the middle of the mold where the slurry has been poured, and place the small stone 1 on the bottom of the stone flake 2, so that the stone flake 2 is completely submerged in the slurry and keeps a distance of 10mm from the upper and lower slurry surfaces. Keep a distance of 5 mm between the left and right sides of the slurry as a laitance layer.
[0034] The measured carbonization ...
Embodiment 3
[0036] Roughly the same as Example 1, the difference is that the proportion of the cement paste used is
[0037] Water cement ratio
water / g
Cement / g
[0038] 0.23
276
1200
[0039] Step 1) Add 276g of distilled water and 1200g of cement successively to the slurry mixer, and stir evenly. Put two small stones 1 with a height of 8mm along the length direction of the bottom in the mold, and smear a layer of cement slurry on the surface of the prefabricated regular marble slice 2 with a size of 7mm×25mm×152mm that has been washed and dried for 24 hours in advance, Then slowly put it into the middle of the mold where the slurry has been poured, and place the small stone 1 on the bottom of the stone flake 2, so that the stone flake 2 is completely submerged in the slurry and keeps a distance of 8 mm from the upper and lower slurry surfaces. Keep a distance of 4mm between the left and right sides of the slurry as a laitance layer.
[0040]...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com