A kind of primer and method for distinguishing larvae of A. lepidus and A. sylvaticus using est microsatellite markers
A technology of microsatellite markers and primer pairs, which is applied in the field of agricultural biology and can solve problems such as the inability to construct EST microsatellite markers
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
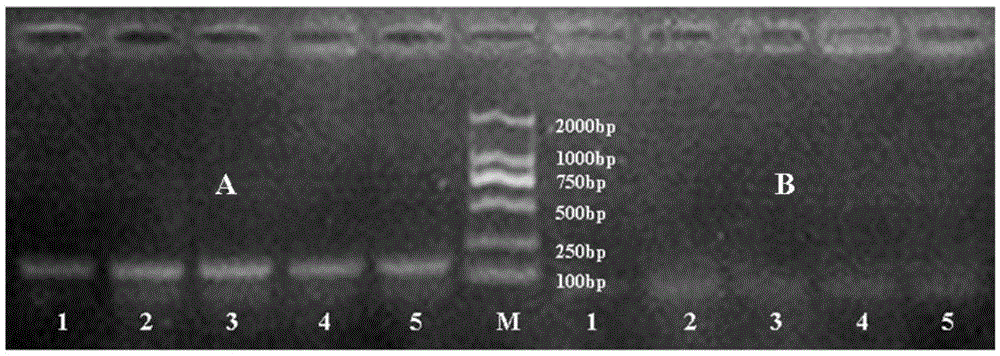
[0026] Chive tardigrades described in Example 1 were collected in 11 districts in Shandong Province in 2012;
Embodiment 2
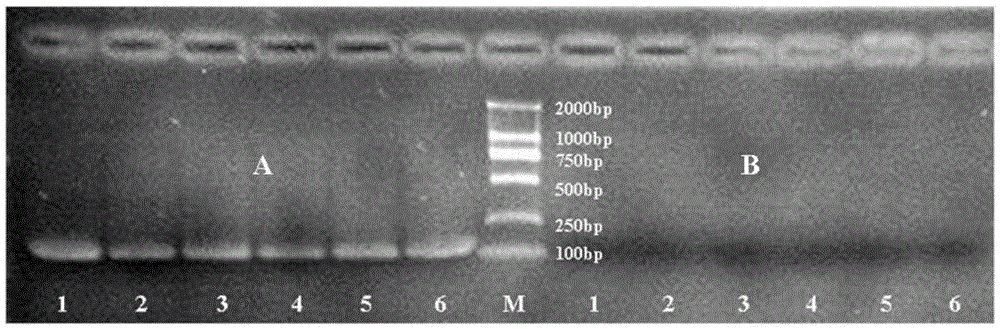
[0027] In Example 2, A and B described in A and B were collected in 2012 respectively in Yiyuan District, Zibo City, Shandong Province and Changle District, Weifang City, Shandong Province;
Embodiment 3
[0028] A, B described in the embodiment 3 Chive tardigrade and Heterophthalmia were collected respectively in 2012 in Jining City, Shandong Province and Fei County, Linyi City, Shandong Province;
[0029] The above samples are all according to (Shi Baocai, Lu Hong, Gong Yajun, etc., 2010. Identification and control of Chive tardigrades. Chinese Vegetables, 11:21-22.; Zhang Hongrui, Zhang Xiaoyun, Shen Dengrong, etc., 2008. Edible fungi The biological characteristics of the fungus Bradysiadifformis. Chinese Edible Fungi, 27 (6): 54-56.) The above-mentioned Bradysiadifformis and different Bradysiadifformis were morphologically identified.
[0030] The instrument described in the embodiment is a Nikon SMZ745T stereo microscope, which is a common commercially available product.
[0031] Example 1
[0032] Constructed and sequenced the transcriptome library of T.
[0033] Firstly, the total RNA was extracted from the larvae of T. chileensis, and the extracted RNA was subjected to...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com