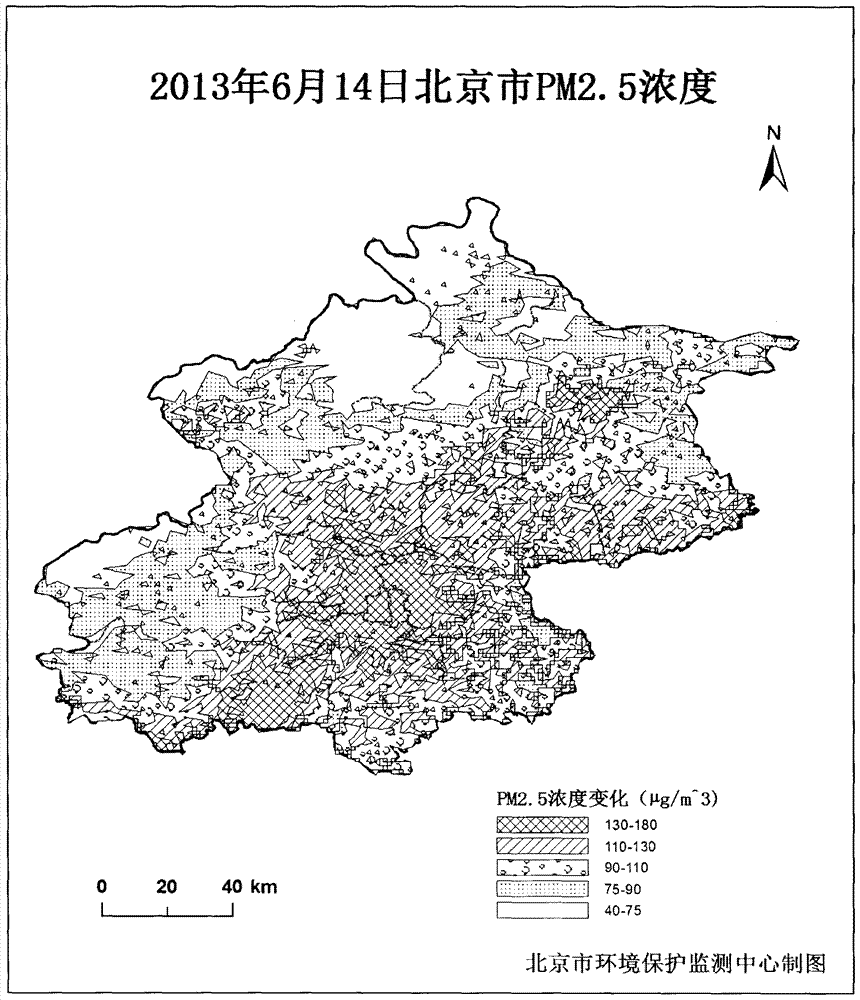
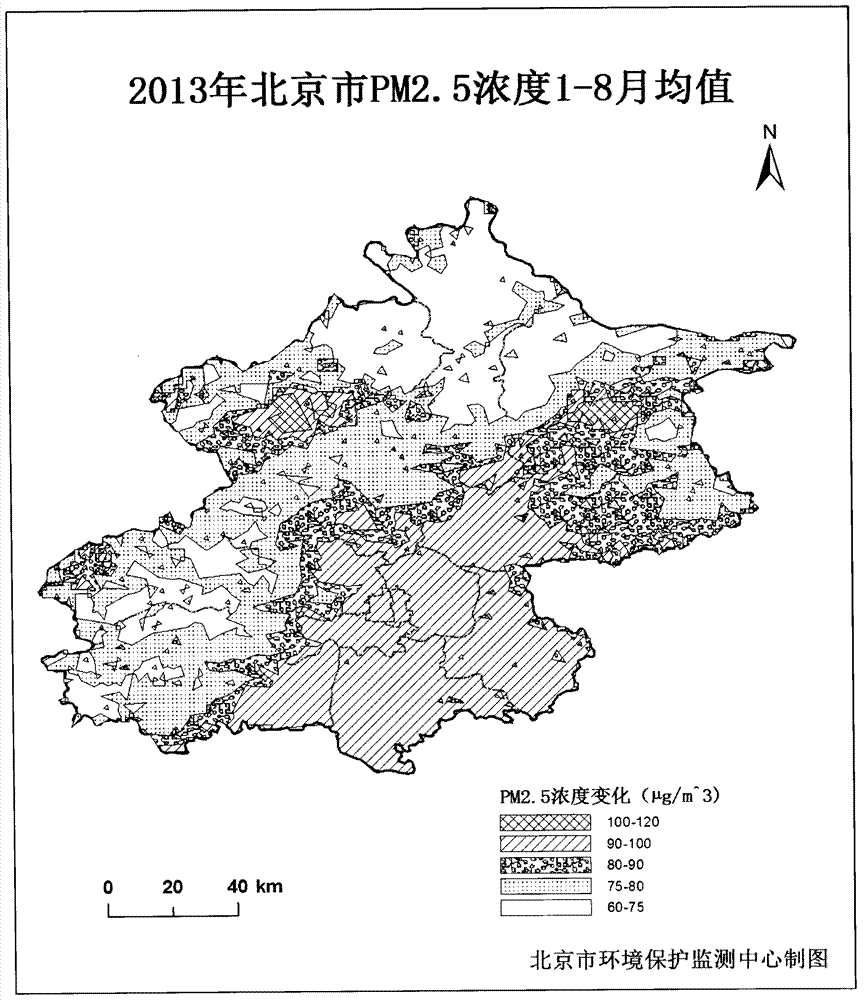
Method for monitoring mass concentration of near-surface fine particulate matter by satellite remote sensing
A technology of mass concentration and fine particles, which is used in measurement devices, particle suspension analysis, suspension and porous material analysis, etc. It can solve the problems of large monitoring deviation, accumulation of errors, and inability to effectively adapt to improve accuracy and inversion. The effect of accurate data
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0037] A method of using satellite remote sensing to monitor the mass concentration of fine particulate matter near the ground, using the visible light and infrared light channels carried on the satellite to obtain satellite monitoring data of each monochromatic light;
[0038] Step 1: Calculate the apparent albedo of each monochromatic light through the satellite monitoring data of each monochromatic light;
[0039] What needs to be explained here is that the monochromatic light here is red light with a wavelength of 0.66 μm, blue light with a wavelength of 0.47 μm, and near-infrared light with a wavelength of 2.1 μm. The color light channel receives red light, the blue light monochromatic light channel receives blue light, and the near-infrared light monochromatic light channel receives near-infrared light.
[0040] This method uses the satellite to receive the red light with a wavelength of 0.66 μm, the blue light with a wavelength of 0.47 μm and the near-infrared light wit...
Embodiment 2
[0064] Compared with embodiment 1, embodiment 2 is further improved on the basis of embodiment 1, and the point of improvement is that the number of monitoring points is several (such as 10, 20, 35, 50, etc.).
[0065] Taking Beijing as an example, several monitoring points are distributed in different areas of Beijing according to the actual situation.
[0066] The "actual situation" mentioned here means that it can be evenly distributed in the entire area of Beijing, or it can be distributed according to the actual situation (areas with a large flow of people have a higher density of monitoring points than areas with a small flow of people).
[0067] Correction method:
[0068] Statistics of PM monitored by each monitoring point 2.5 Mass concentration (PM), and these values correspond to the data of the aerosol extinction contribution corresponding to the point, and plot it on a two-dimensional coordinate system.
[0069] Further, according to the points drawn on the t...
Embodiment 3
[0072] The difference between embodiment 3 and embodiment 2 is only that the correction method is different,
[0073] Correction method:
[0074] PMs monitored in the field 2.5 The mass concentration is PM S , according to the coefficient k, the satellite retrieved PM of each field monitoring point is calculated, and the PM of each field monitoring point S One-to-one correspondence with PM, and draw it on the two-dimensional coordinate system, according to PM S / PM draws a point on the two-dimensional coordinate system, fits a linear straight line on the two-dimensional coordinate system, and calculates PM based on the linear straight line S The relational formula between PM and PM S = a·PM+b.
[0075] PM in this method S It is basically equal to the value of PM.
[0076] What needs to be emphasized here is that this method is preferably used in a certain area (such as Beijing, Tianjin, Shanghai, Nanjing, Hangzhou, Chongqing, Fuzhou, Guangzhou, Shenzhen, Wuhan, etc.). ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| wavelength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| wavelength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| wavelength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com