Recognizing method and recognizing system of particles in blood sample and blood cell analytic instrument
A blood sample and particle technology, applied in the field of medical devices, can solve the problems of the influence of counting and classification accuracy, the decrease of the accuracy of blood cell analyzer test results, etc., and achieve the effect of improving accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0034] This embodiment is mainly combined with the light scattering method for classifying and counting white blood cells in a blood sample.
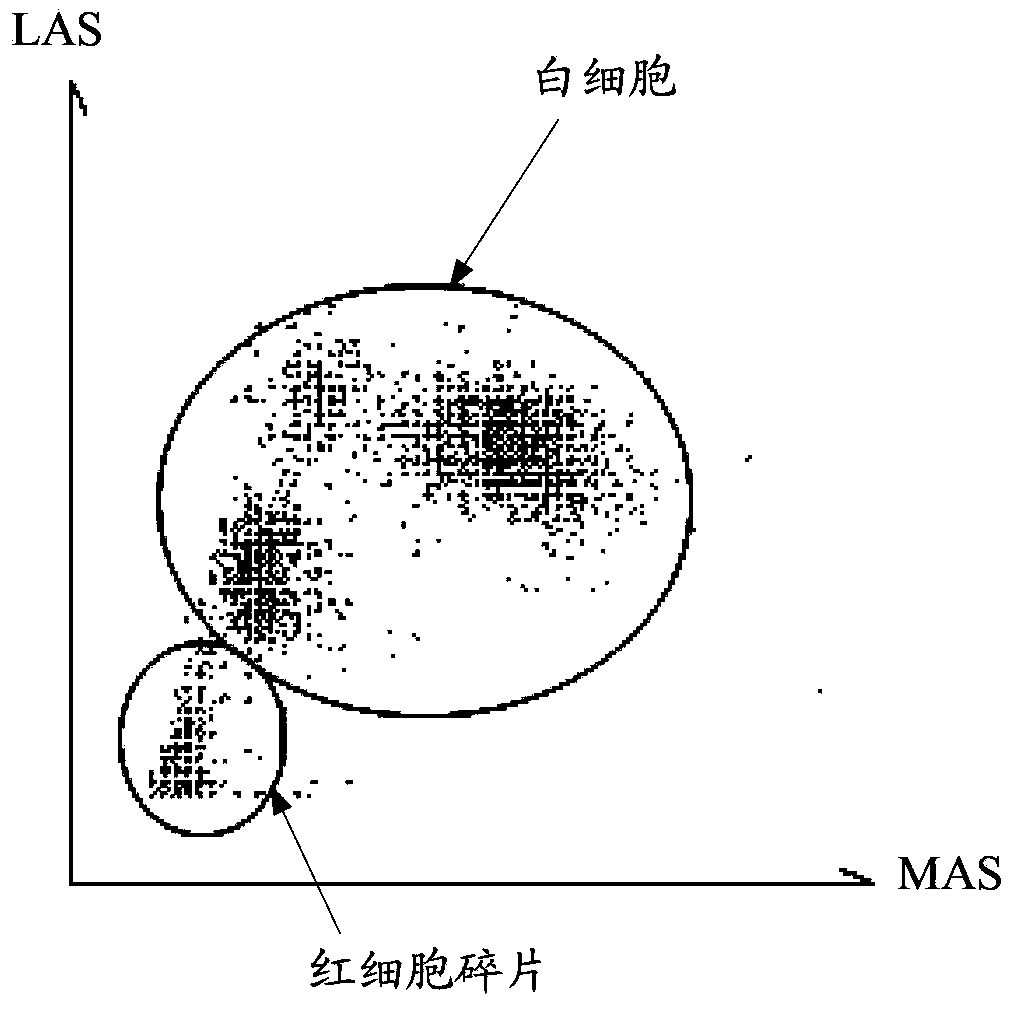
[0035] Before implementing the method for identifying particles in blood samples in this embodiment, it is also necessary to pre-determine and store a preset area, the preset area is corresponding to the first scattered light generated by the reference particle due to irradiation and reflects the complexity information of the reference particle. The amplitudes of the four electrical pulses and their equivalent width indicator values are jointly determined, and the preset area can be reflected in the following width-angle-amplitude scatter diagram. Specifically, the reference particles can be white blood cells or simulated particles of white blood cells. Before the hematology analyzer leaves the factory, first select the DIFF channel on the hematology analyzer, and use the light scattering method to count the reference particles in the ...
Embodiment 2
[0054] The difference between this embodiment and embodiment one mainly lies in:
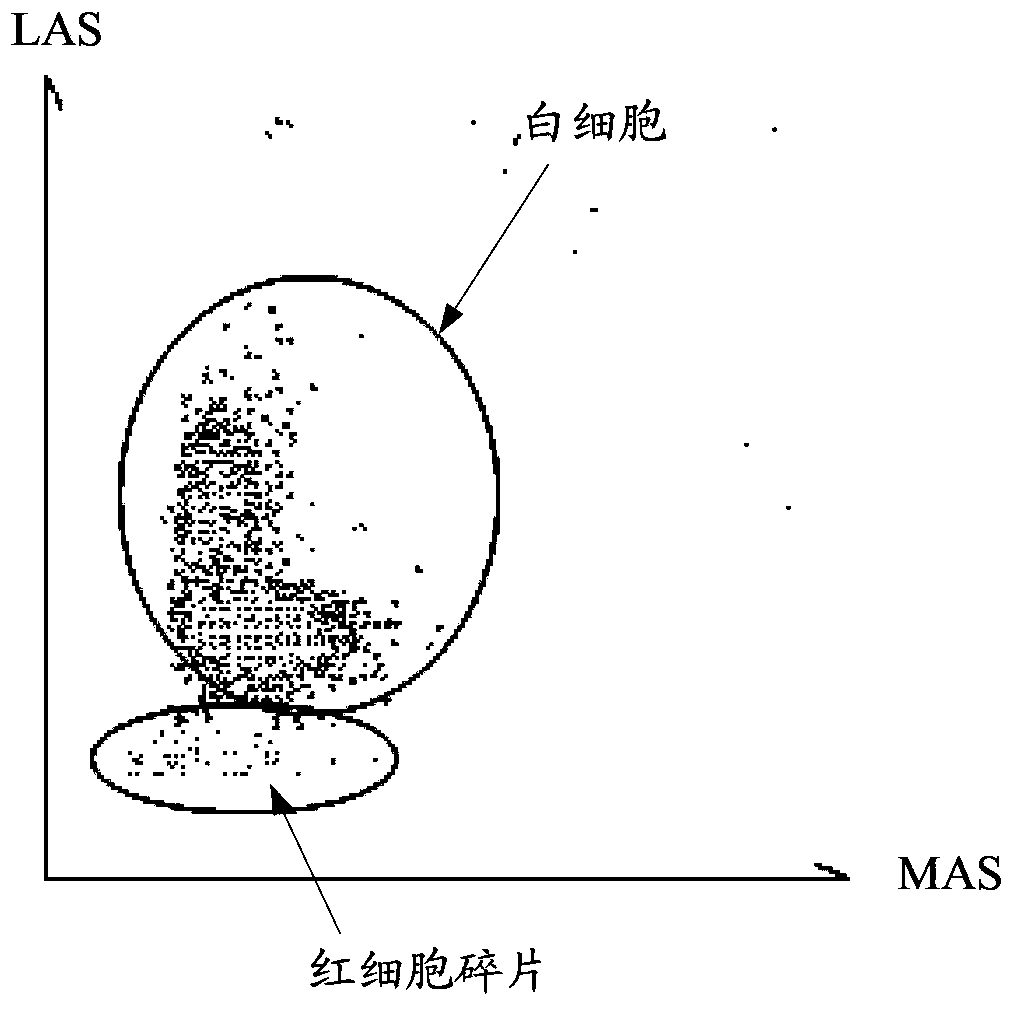
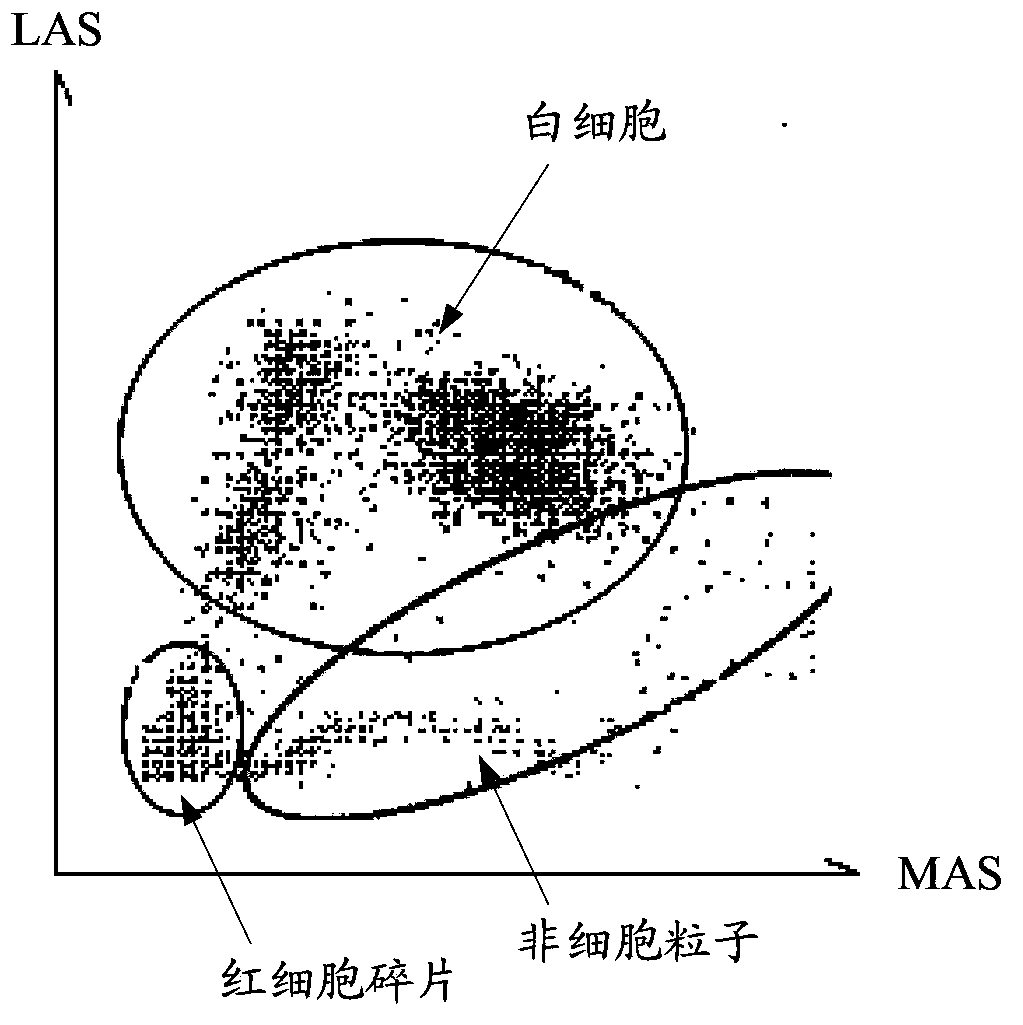
[0055] In this embodiment, the scatter diagram of the width, angle and amplitude obtained by detecting the blood sample in the BASO channel of the hematology analyzer is as follows: Figure 9 As shown, the figure includes a white blood cell area 902 and a non-cell particle area 903 separated by an identification boundary 901 , the white blood cell area 901 is located on the right side of the identification boundary 901 , and the non-cell particle area 903 is located on the left side of the identification boundary 901 .
[0056] It should be noted that the preset area under the DIFF channel in Embodiment 1 is different from the preset area under the BASO channel in this embodiment, and thus the identification boundaries corresponding to the preset area are also different. In addition, under the BASO channel, since there are relatively few red blood cell fragments, it is also possible to choose no...
Embodiment 3
[0058] The difference between this embodiment and any embodiment in Embodiments 1 and 2 is:
[0059] In the identification method of this embodiment: first, the sample liquid can be transported to the flow chamber in the counting system of the blood cell analyzer, so that the particles to be measured in the sample liquid pass through the optical detection area in the flow chamber one by one, when the optical system in the optical system When the light beam generated by the light source is irradiated on the particle to be measured and light scattering occurs, the two detectors convert the two sub-beams at two angles into two electric pulses, and the ratio of the area to the amplitude of the electric pulse is calculated to obtain the Measure the equivalent width indication value of the particle. Then form the corresponding relationship between the equivalent width indication value of the particle, the amplitude of the first electric pulse and the amplitude of the second electric...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com