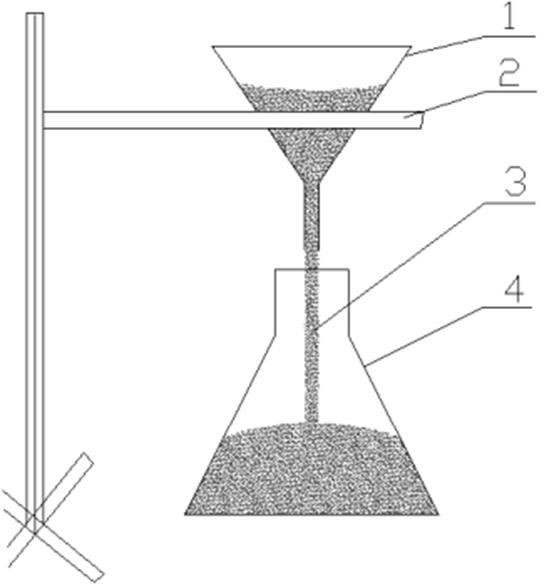
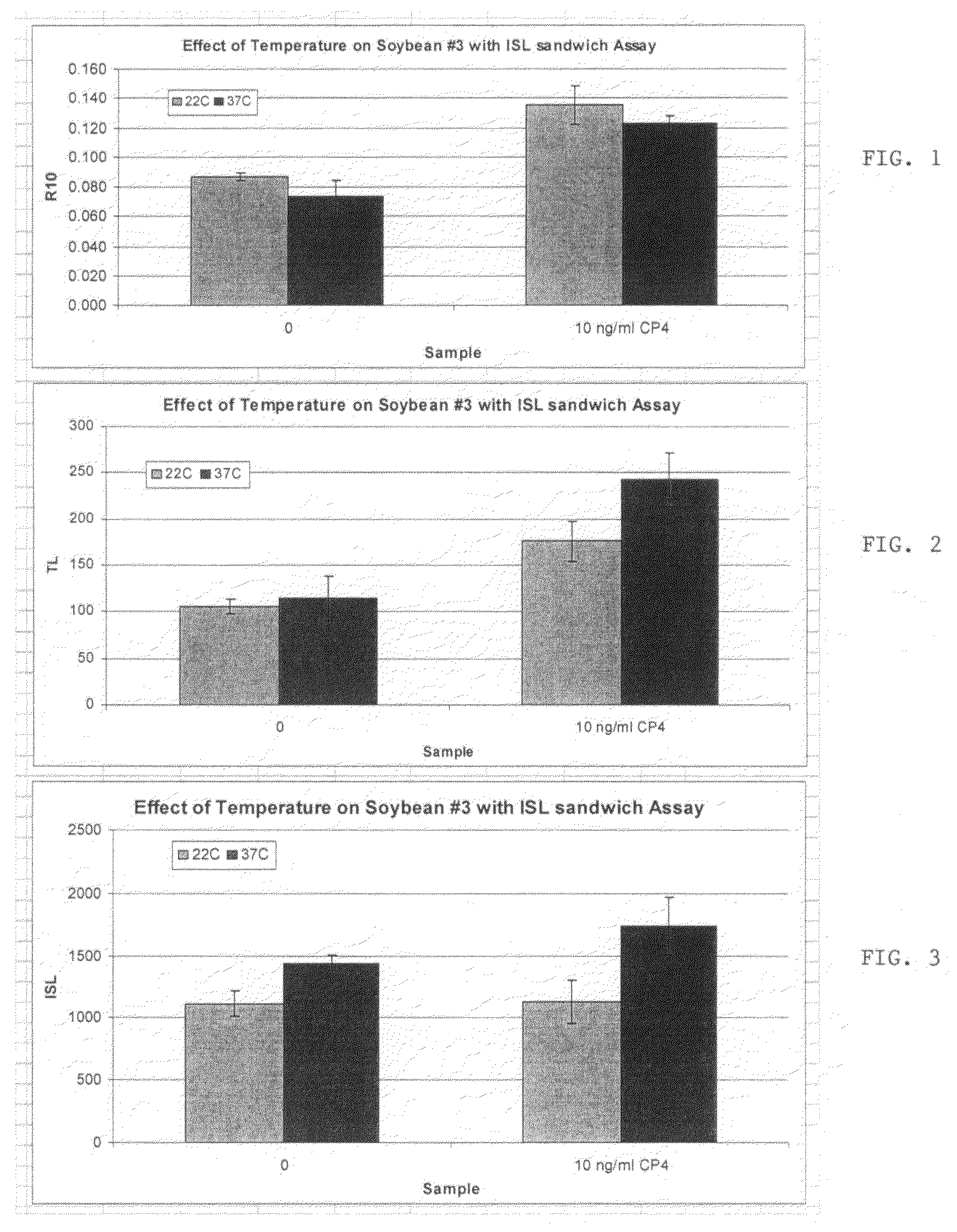
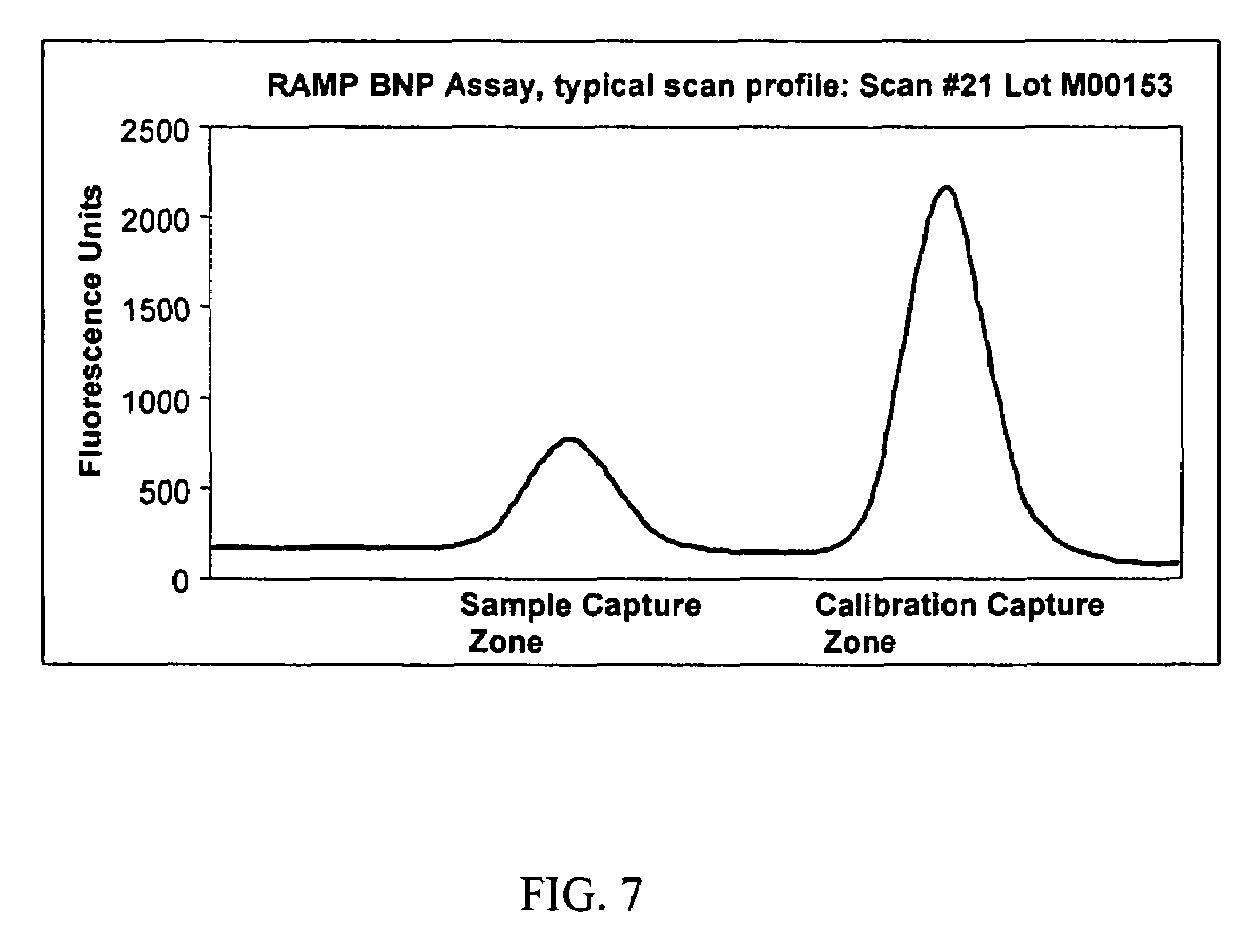
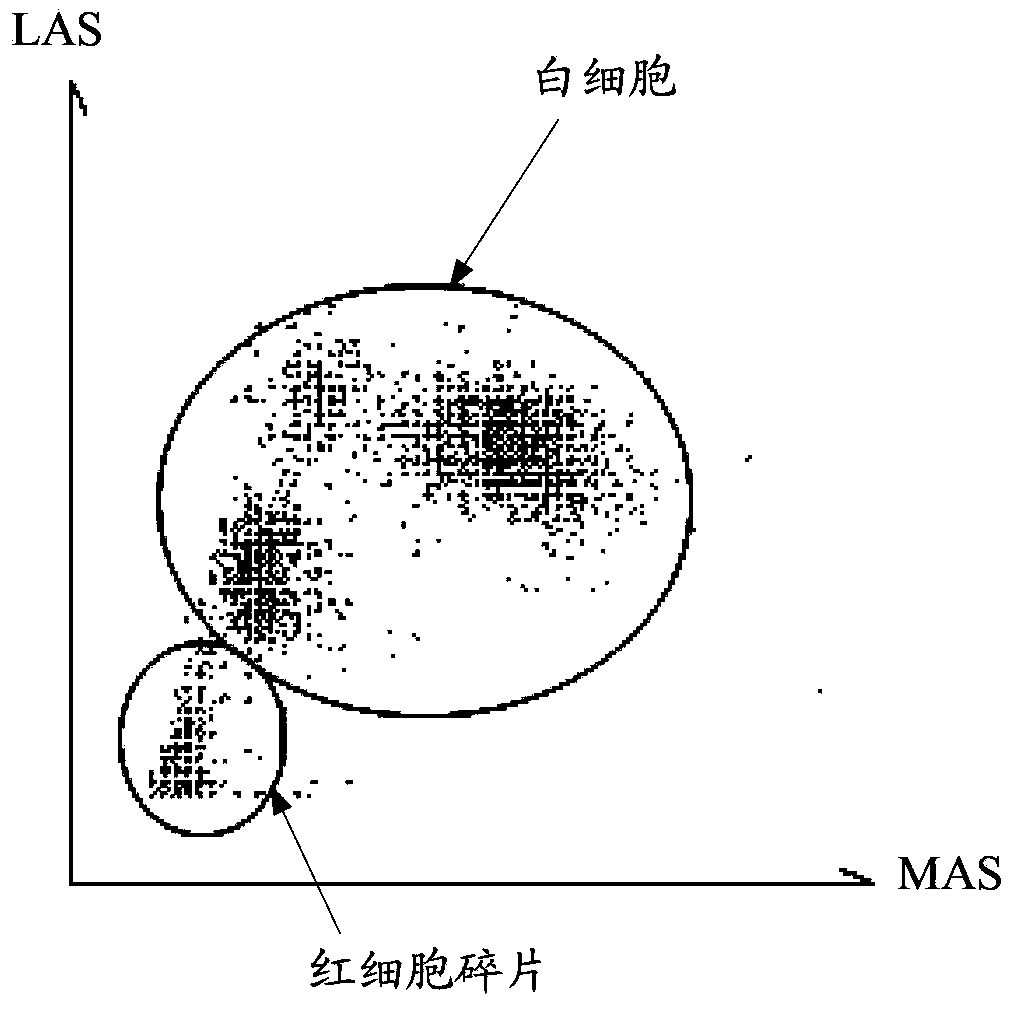
Patents
Literature
67 results about "Test particle" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In physical theories, a test particle, or test charge, is an idealized model of an object whose physical properties (usually mass, charge, or size) are assumed to be negligible except for the property being studied, which is considered to be insufficient to alter the behavior of the rest of the system. The concept of a test particle often simplifies problems, and can provide a good approximation for physical phenomena. In addition to its uses in the simplification of the dynamics of a system in particular limits, it is also used as a diagnostic in computer simulations of physical processes.
Integrated chip system for high-throughput sorting and counting detection of biological particles, and application
ActiveCN103191791AMeet the damageNo damageMaterial analysis by optical meansLaboratory glasswaresInertial effectLiquid Change
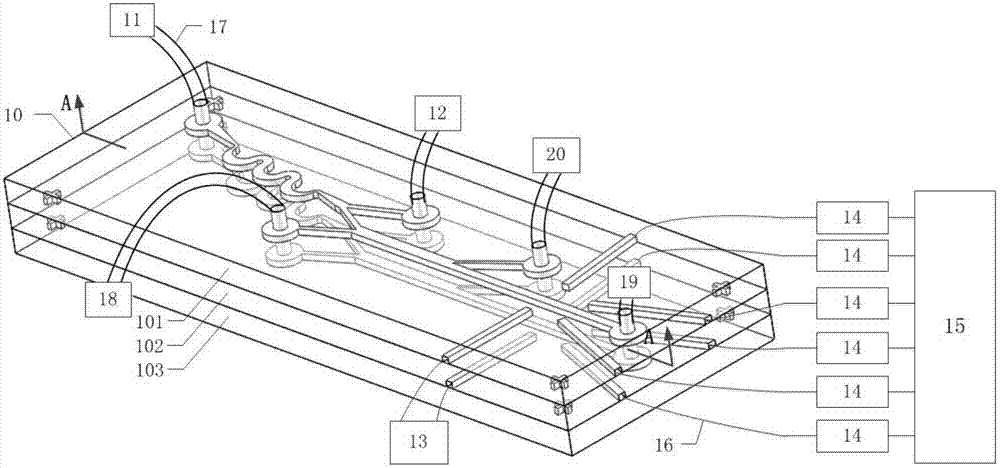
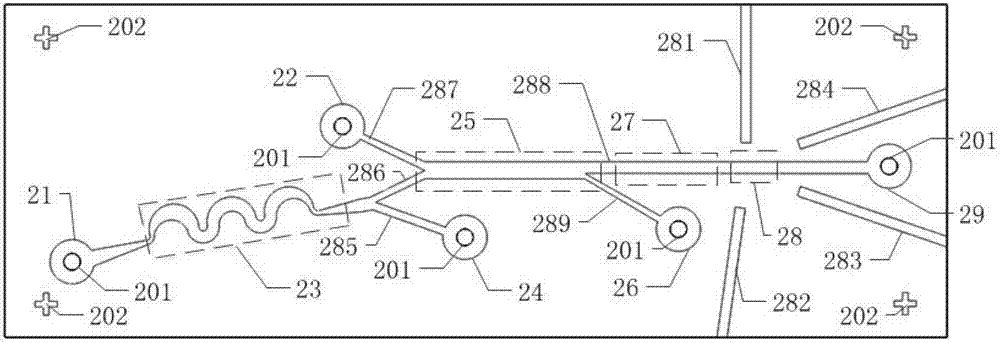
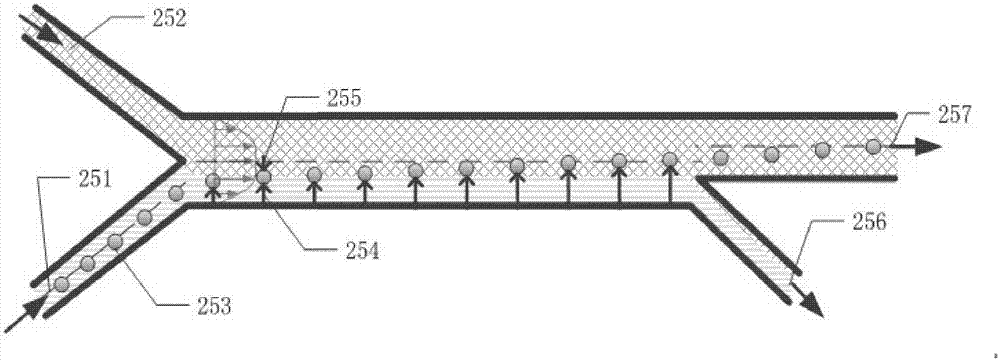
The invention discloses an integrated chip system for high-throughput sorting and counting detection of biological particles, and an application. The chip system comprises a main microfluidic chip, a micropipe, a sample liquid micropump, an exchange liquid micropump, a first waste liquid collecting device, a second waste liquid collecting device, a third waste liquid collecting device, laser emitters, photoelectric conversion devices, optical fibers and a computer, wherein the main microfluidic chip comprises an asymmetric curved flow path, a first branch channel, a second branch channel, a third branch channel, a main flow path, a branch flow path, aligning marks, etc. The system utilizes the asymmetric curved flow path to realize pre-focusing and sorting for the particles, utilizes a liquid changing flow channel to realize change of a carrier liquid of to-be-tested particles and particle cleaning, and utilizes a viscoelastic effect and an inertial effect of a viscoelastic fluid to realize focus of single equilibrium position of section centers of the particles. The system does not need a sheath liquid, complex pre-cleaning of the particles, and optical alignment, has advantages of high speed, high precision, integration, miniaturization, automation, low cost, simple production process, easy batch production, etc.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
System for testing particle moving speed based on single image
InactiveCN102393473AEnhance exposure intensityAvoid partial blurParticle size analysisFluid speed measurementCamera controlCamera lens
The invention discloses a system for testing the particle moving speed based on a single image. In the system, a continuous laser is taken as a laser light source, and a shift lens is taken as a camera lens; by adjusting the horizontal position of the shift lens, the shift lens is deviated from a sheet light source along the vertical direction by a certain angle, and the exposure intensity of a particle image is remarkably increased; and by adjusting an included angle between the shift lens and a camera sensitive surface, planes where the shift lens, the light sensitive surface of the camera and the sheet light source are intersected on a straight line, and clear imaging of all particles in a testing area is realized. In the invention, the exposure time is controlled by using the camera, changes of the speed and moving direction of the particles within the expose time can be reflected in real time only by acquiring a single image of the particle moving, and parameters such as speed change and distribution of particles in a flow field, particle diameter distribution of the particles and the like can be obtained by processing. The system has low equipment cost and low manufacturing cost, and can be applied to particle parameter testing of various atomization and flow fields.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
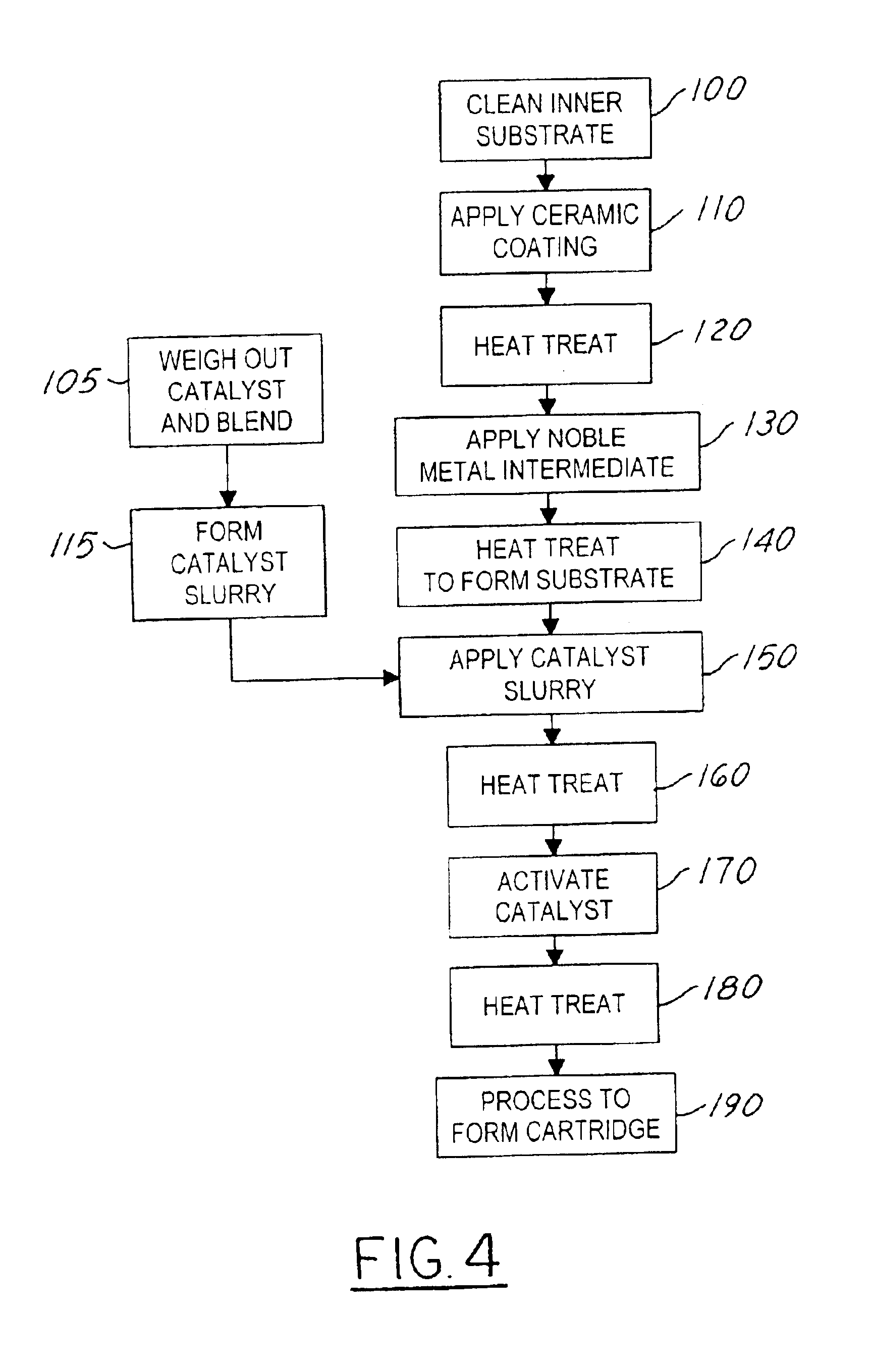
High-temperature catalyst for catalytic combustion and decomposition
InactiveUS6887821B2Solve low usageFast response timeCatalyst activation/preparationCombustion using catalytic materialHigh concentrationDecomposition
A robust, high temperature mixed metal oxide catalyst for propellant composition, including high concentration hydrogen peroxide, and catalytic combustion, including methane air mixtures. The uses include target, space, and on-orbit propulsion systems and low-emission terrestrial power and gas generation. The catalyst system requires no special preheat apparatus or special sequencing to meet start-up requirements, enabling a fast overall response time. Start-up transients of less than 1 second have been demonstrated with catalyst bed and propellant temperatures as low as 50 degrees Fahrenheit. The catalyst system has consistently demonstrated high decomposition effeciency, extremely low decomposition roughness, and long operating life on multiple test particles.
Owner:UNITED TECH CORP +1
Real-time microbial particle counter
InactiveCN103940709ARealize automated detectionSimple and fast operationParticle size analysisParticle suspension analysisEffect lightLaser-induced fluorescence
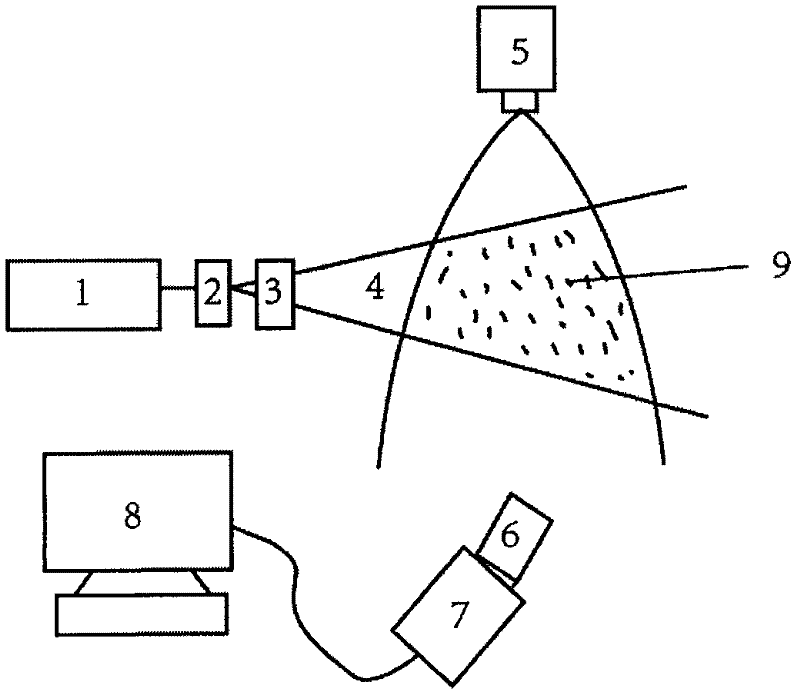
The invention discloses a real-time microbial particle counter comprising a light path, an air channel intersected with the light path, and a signal processing system connected with the light path, wherein the light path comprises a lighting light path for irradiating tested particles and a collecting light path arranged along the advancing direction of the lighting light path; the collecting light path also comprises a relay system for separating the light path and separately detecting separated light paths; the air channel is used for sampling the tested particles; the signal processing system is used for analyzing and processing a signal, and comprises a fluorescent preamplifier and a scattered light preamplifier. The concentration of microbial particles in air is monitored in real time by taking laser-induced fluorescence detection as the principle, the particle sizes and the biological attributes of the tested particles are judged by detecting the intensities of scattered light and fluorescence emitted by exciting light, and the particles in a sampling airflow are counted, so that the automatic detection on planktonic bacteria microorganisms is achieved, and the real-time microbial particle counter is simple and convenient to operate, strong in detection instantaneity, high in sensitivity and high in accuracy.
Owner:NANJING ZHONGKE SHENGUANG TECH
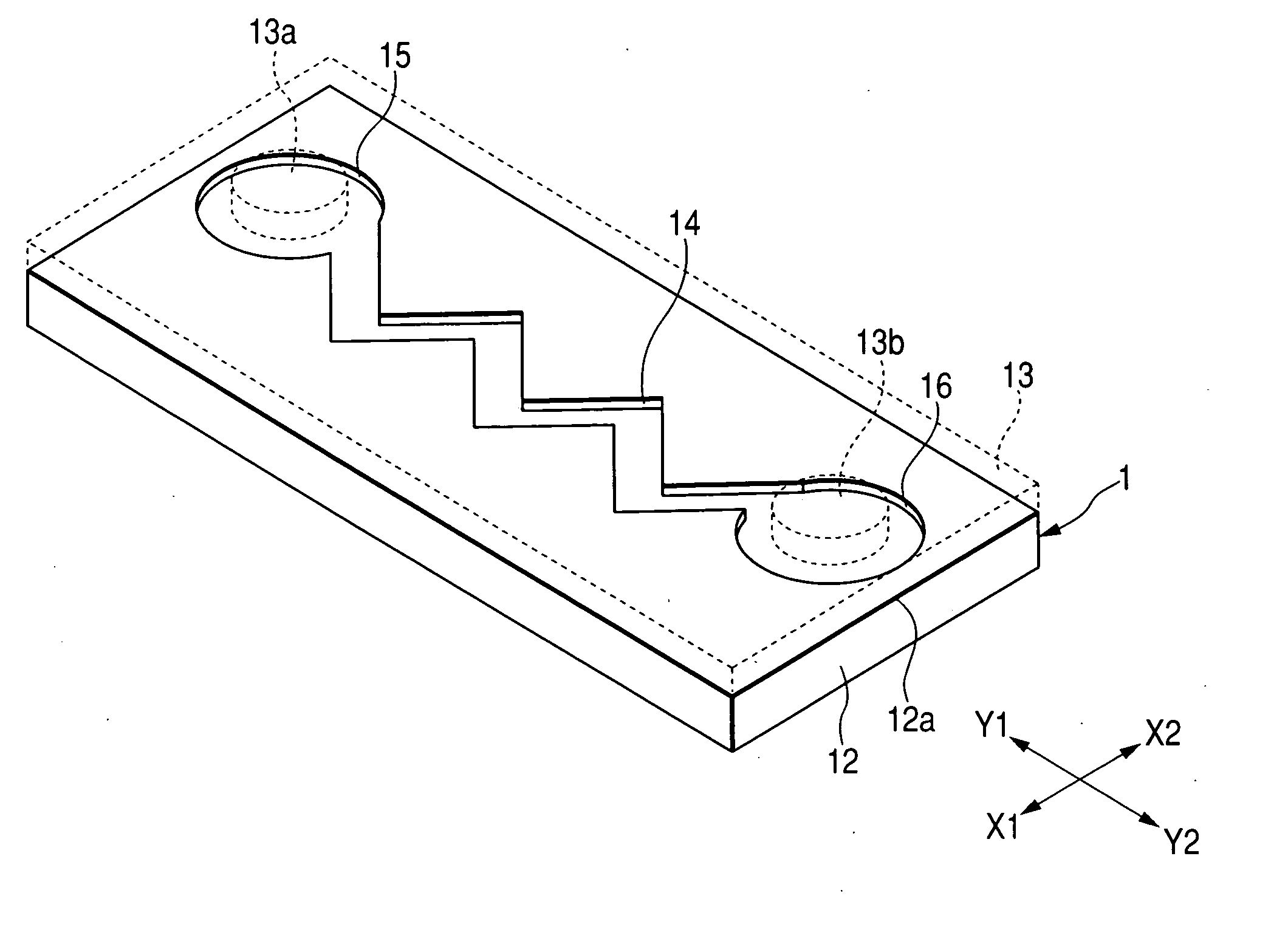
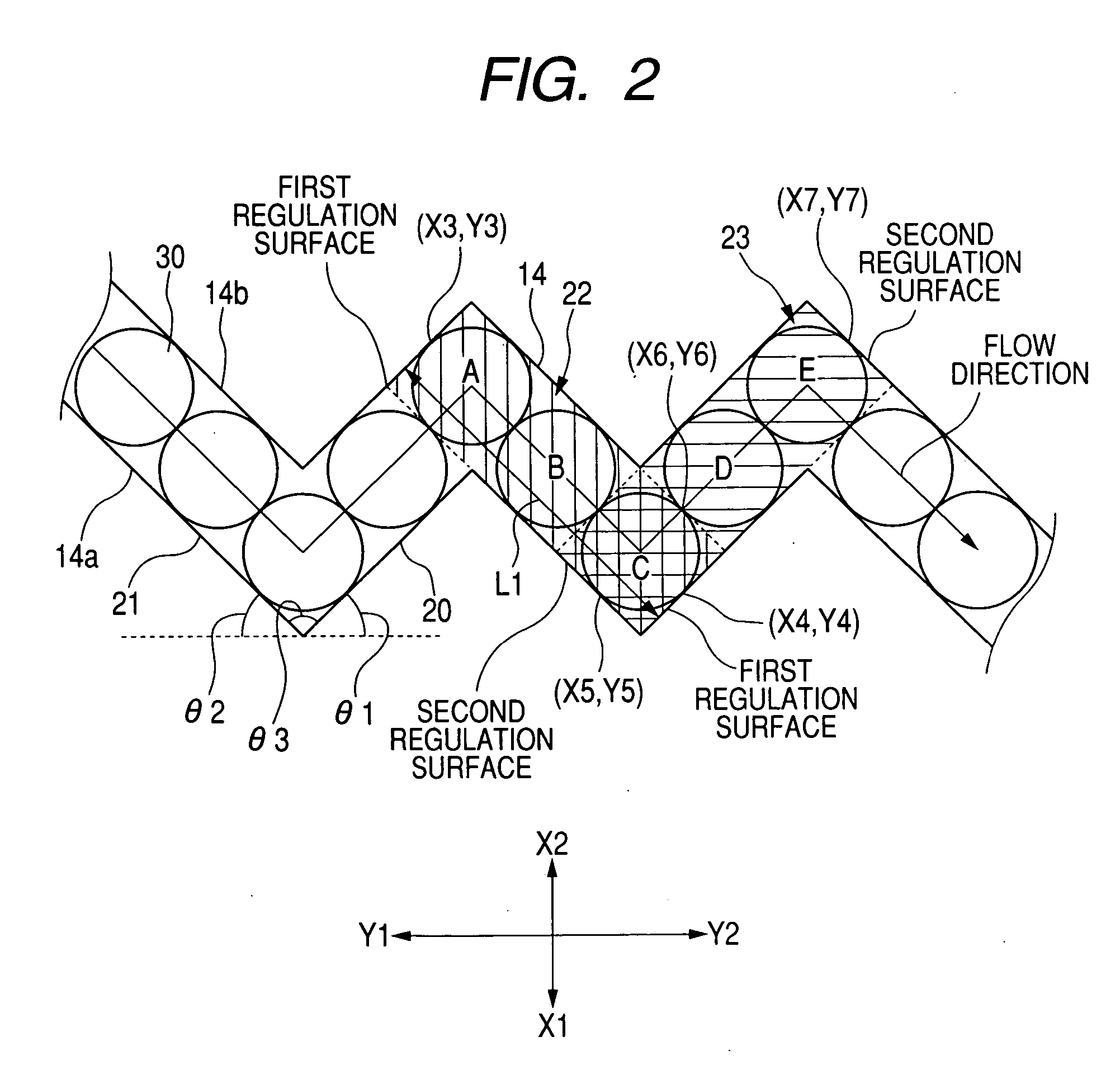
Structure for particle immobilization and apparatus for particle analysis
InactiveUS20130099143A1Reduce background noiseReduce crosstalk noiseAnalysis by electrical excitationPhotoelectric discharge tubesComputational physicsBackground noise
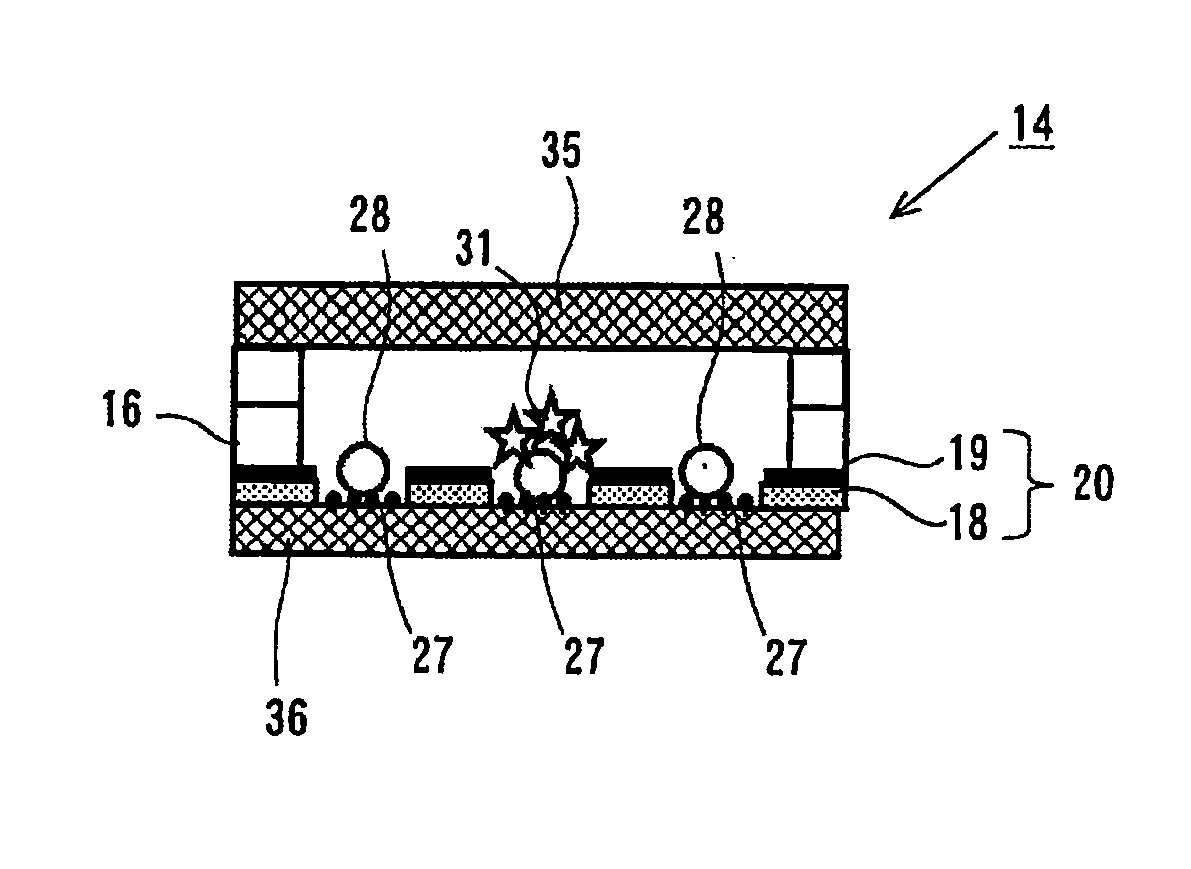
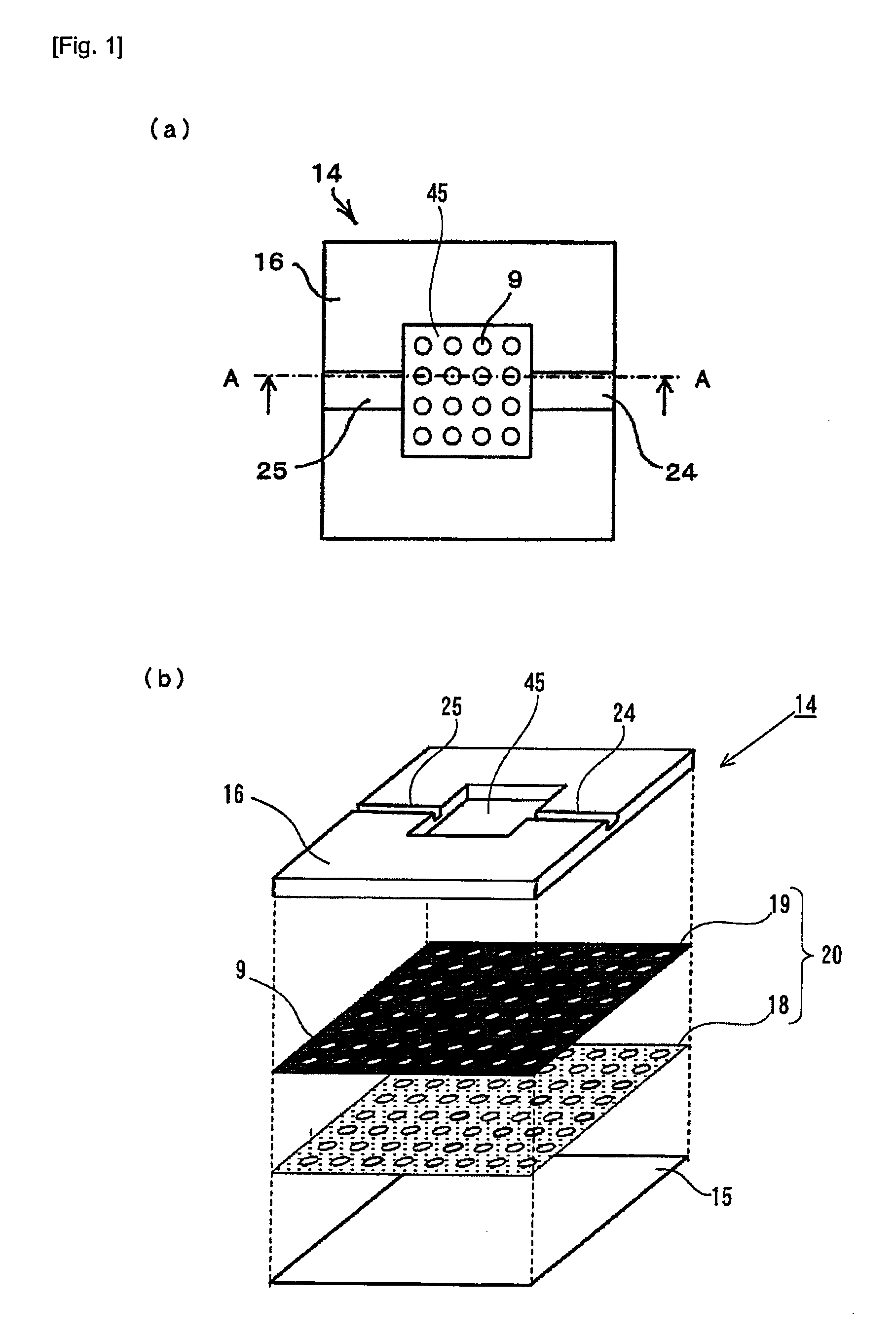
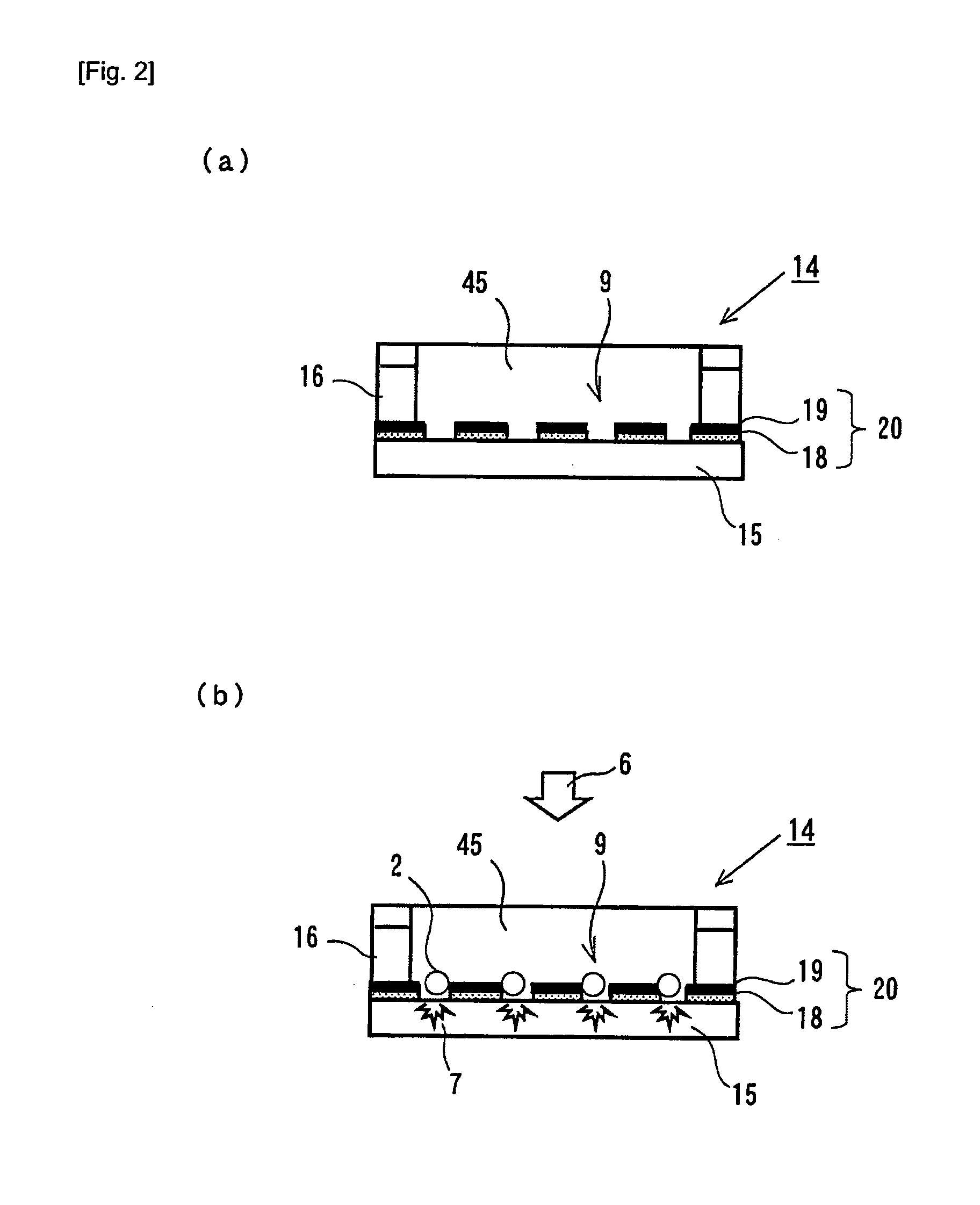
A structure 14 for particle immobilization has a plurality of holding holes 9 for holding respective test particles in order to detect light emitted from a substance which indicates the presence of a component for constructing each of the test particles, and the structure 14 for particle immobilization comprises a flat plate substrate 15, and a holding unit 20 which is arranged on the substrate 15 and which is formed with the plurality of holding holes 9. In this configuration, a light shielding film 19 which reduces light noise is provided for the substrate 15 or the holding unit 20 in order that the light noise such as the background noise and the crosstalk noise can be reduced, and a large number of test particles can be optically observed highly sensitively and highly accurately.
Owner:TOSOH CORP
Particle airflow suspension laser ignition experiment device
InactiveCN104330519ATo achieve the purpose of the ignition processChemical analysis using combustionCombustorShoot
The invention discloses a particle airflow suspension laser ignition experiment device belonging to the technical field of solid rocket engines. The particle airflow suspension laser ignition experiment device enables particles to suspend in space in a combustor by means of tiny airflow, and the particles are not in contact with a metal wall plate, and are continuously heated and ignited by using a high-energy laser igniter. A gas environment is adjustable, single gas can be fed or different kinds of gases are simultaneously fed so that the purpose of testing particle ignition processes under different gas environments is achieved. Four transparent windows are arranged on the combustor, wherein two windows are observation windows and two windows are germanium glass windows; a working process is observed and tested by means of the two observation windows, laser generated by the laser igniter shoots into the combustor by means of the two germanium glass windows, the power of the laser igniter is regulated, and the particles suspending in the combustor are heated and ignited; a detailed process of particle ignition combustion are shot by means of the observation windows by using a high-speed photography system. The experiment device can be used for researching ignition and combustion characteristics of metal particles and nonmetal particles.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Target design for high-power laser accelerated ions
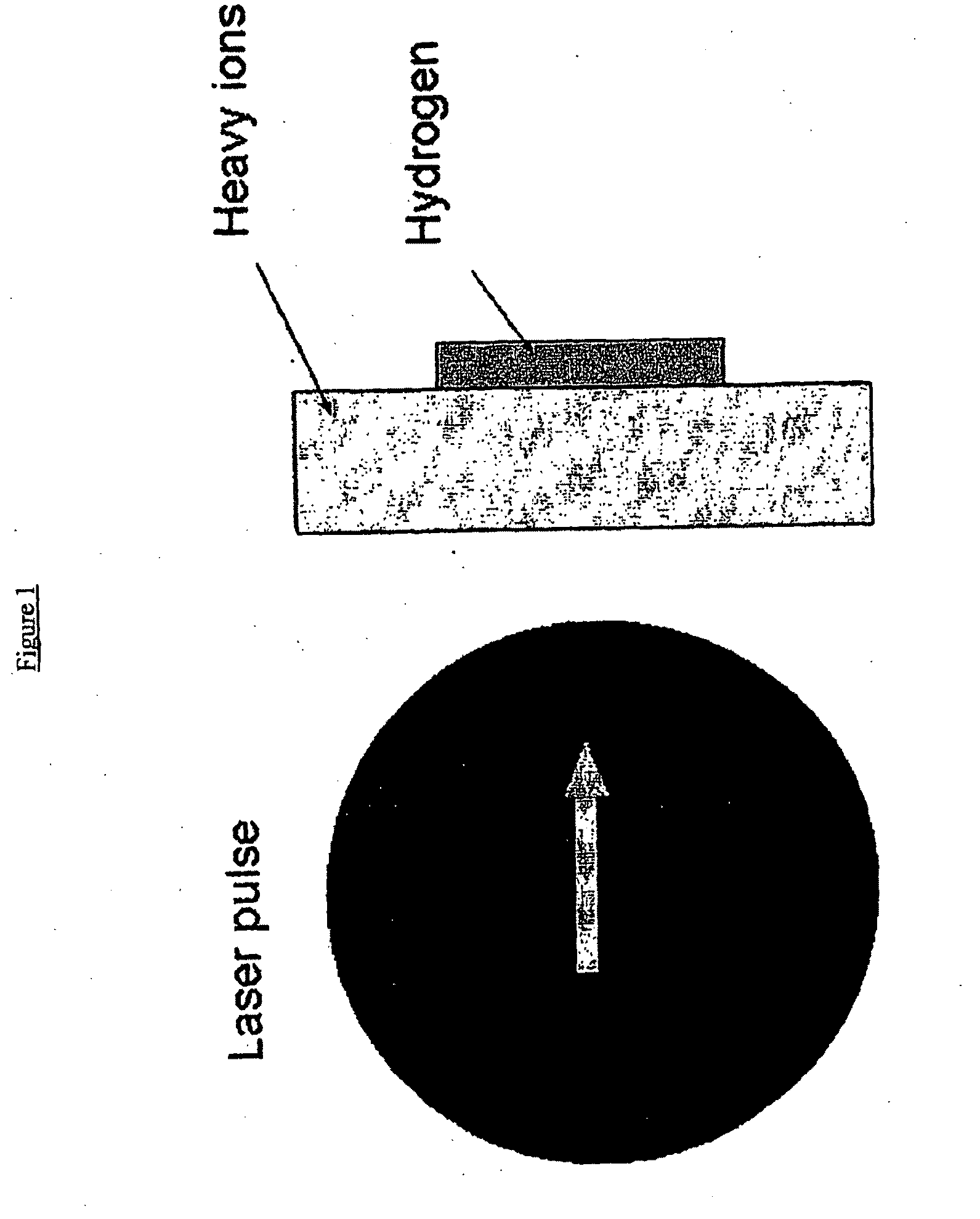
InactiveUS20090230318A1Maximizes energy distributionRadiation/particle handlingNuclear energy generationHigh power lasersHigh energy
Methods for designing a laser-accelerated ion beam are disclosed. The methods include modeling a system including a heavy ion layer, an electric field, and high energy light positive ions having a maximum light positive ion energy, correlating physical parameters of the heavy ion layer, the electric field, and the maximum light positive ion energy using the model, and varying the parameters of the heavy ion layer to optimize the energy distribution of the high energy light positive ions. One method includes analyzing the acceleration of light positive ions, for example protons, through interaction of a high-power laser pulse with a double-layer target using two-dimensional particle-in-cell (PIC) simulations and a one-dimensional analytical model. The maximum energy acquired by the accelerated light positive ions, e.g., protons, in this model depends on the physical characteristics of the heavy-ion layer—the electron-ion mass ratio and effective charge state of the ions. The hydrodynamic equations for both electron and heavy ion species solved and the test-particle approximation for the protons is applied. It was found that the heavy ion motion modifies the longitudinal electric field distribution, thus changing the acceleration conditions for the light positive ions.
Owner:FOX CHASE CANCER CENTER
Particle image speed measuring method based on convolutional neural network
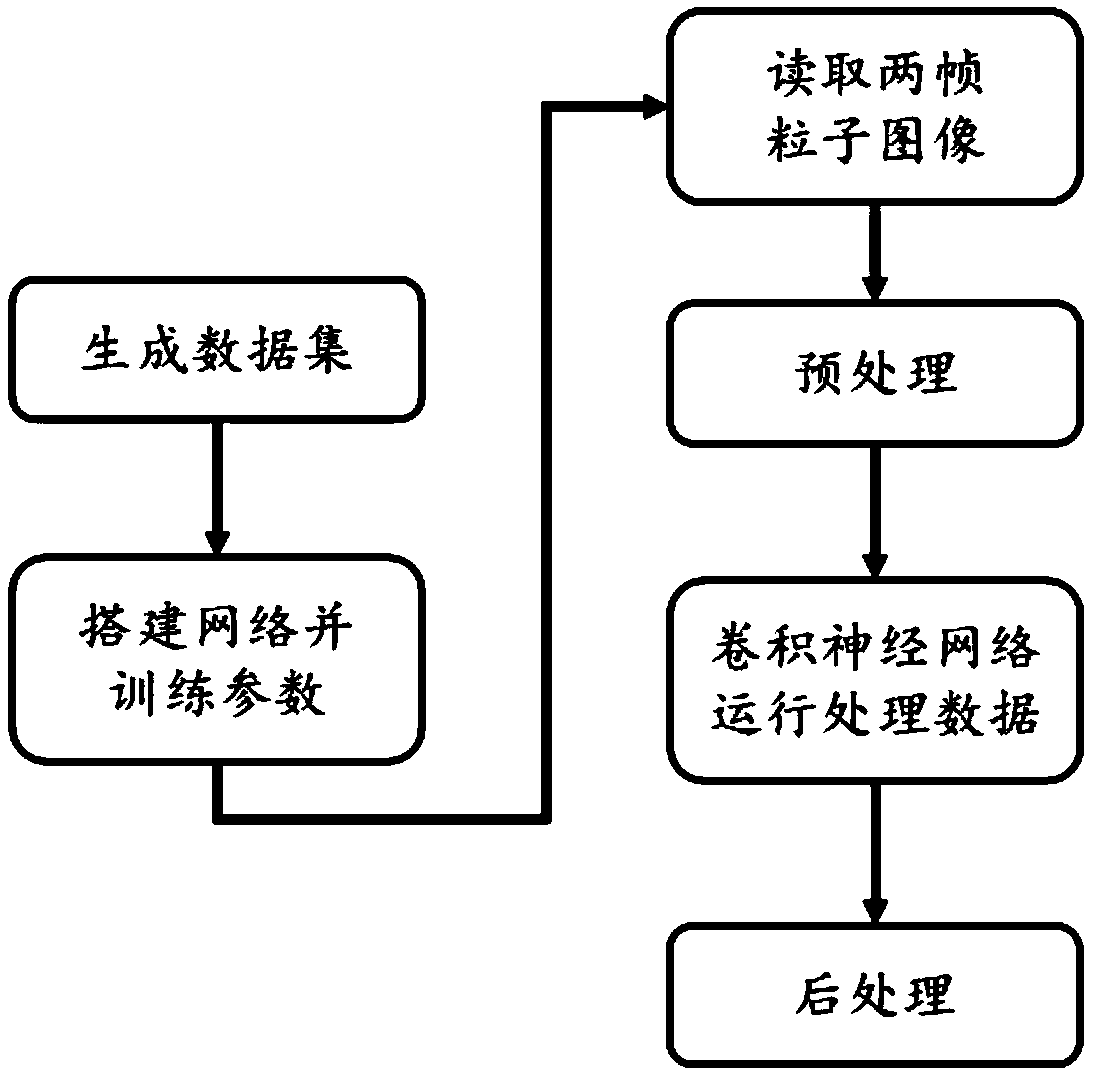
ActiveCN109669049AVelocity field estimationHigh precisionFluid speed measurementNeural architecturesNetwork modelTest particle
The invention discloses a particle image speed measuring method based on a convolutional neural network. The method solves the problem of extracting a speed field from a two-dimensional fluid particleimage by adopting a supervised learning method. The method comprises the steps of PIV data set generating, neural network model building, particle image reading, pre-processing, network operating andpost-processing, wherein PIV data can be generated in two modes: firstly, a known speed field generates the particle image, and secondly, an existing test particle image generates the speed field. The network model adopts the convolutional neural network, the PIV convolutional neural network model is obtained through training parameters, and the PIV convolutional neural network model inputs two images, and outputs the speed vector fields of every pixel in the images. The speed field with the high resolution and high precision can be obtained from the particle image by applying the method provided by the invention, and the computing efficiency of particle image speed measuring can be improved at the same time.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method for measuring granule fluid two-phase stream system heterogeneous texture parameter distribution
InactiveCN101042310AReduce the amount of calculationReduce computing timeHydrodynamic testingParticle flowMomentum
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Test particle simulation method for analyzing constraint performance of high-energy particles in Tokamak
ActiveCN111259599AQuick analysisQuick descriptionDesign optimisation/simulationNumerical stabilityEnergy particle
The invention discloses a test particle simulation method for analyzing the confinement performance of high-energy particles in Tokamak, and belongs to the field of magnetic confinement controlled nuclear fusion. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, dividing a two-dimensional triangular mesh according to input parameters such as a balanced magnetic field and a plasma profile; secondly, loading high-energy particle information, which comprises information such as position and speed, into a phase space; then, according to the full-orbit equation and the guide center orbit equation,the evolution of the particles along with time is solved, and a Monte Carlo method is adopted in the collision module; and finally, outputting information of all particles, and outputting informationsuch as particle distribution, energy flow and current after the information is processed by the post-processing module. According to the method, physical processes such as transportation and loss ofhigh-energy particles can be simulated, the calculation efficiency is high, the numerical stability is high, and the method is a stable and efficient numerical simulation method.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Method for testing particle packing density of concrete used powder
The invention provides a method for testing the particle packing density of concrete used powder, and the tight particle packing density degree of the concrete used powder can be tested through the ratio of the absolute volume of the mixing powder and the packing volume of powder in slurry. The method provided by the invention is simple to operate, scientific, and closer to the practical application condition, and can provide better guidance for the mix design of concrete.
Owner:CHINA STATE CONSTR READY MIXED CONCRETE CO LTD
Immunoassay employing two-step internal calibration reaction
ActiveUS7659086B2Accurate measurementBioreactor/fermenter combinationsAnalysis using chemical indicatorsAnalyteTwo step
Methods for quantitatively measuring the amount of an analyte of interest in a fluid sample, and kits useful in the methods, are disclosed. The methods comprise sandwich assays, and utilize an internal calibration reaction that closely mimics the reaction of test particles by the use of a two-step reaction.
Owner:RESPONSE BIOMEDICAL CORP
Recognizing method and recognizing system of particles in blood sample and blood cell analytic instrument
ActiveCN104297135AImprove accuracyEliminate the effects ofIndividual particle analysisWhite blood cellParticle identification
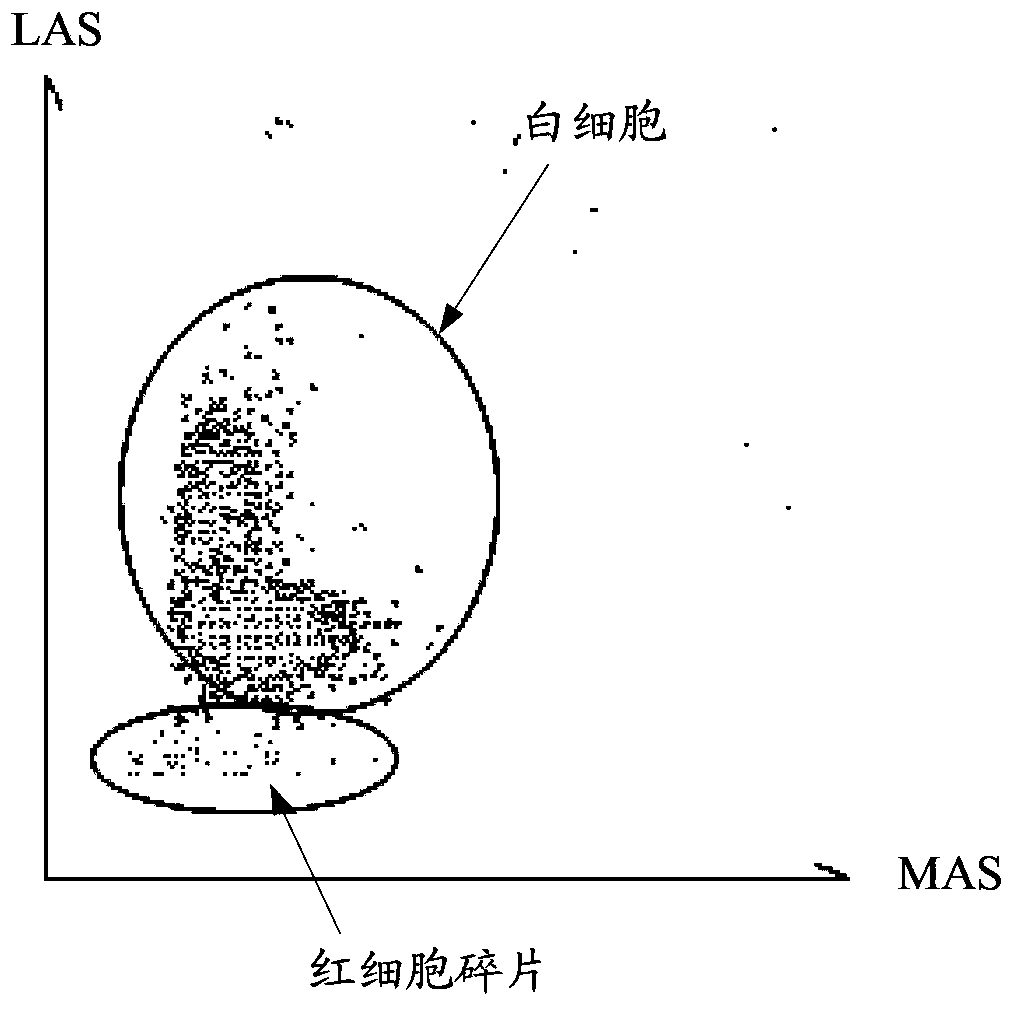
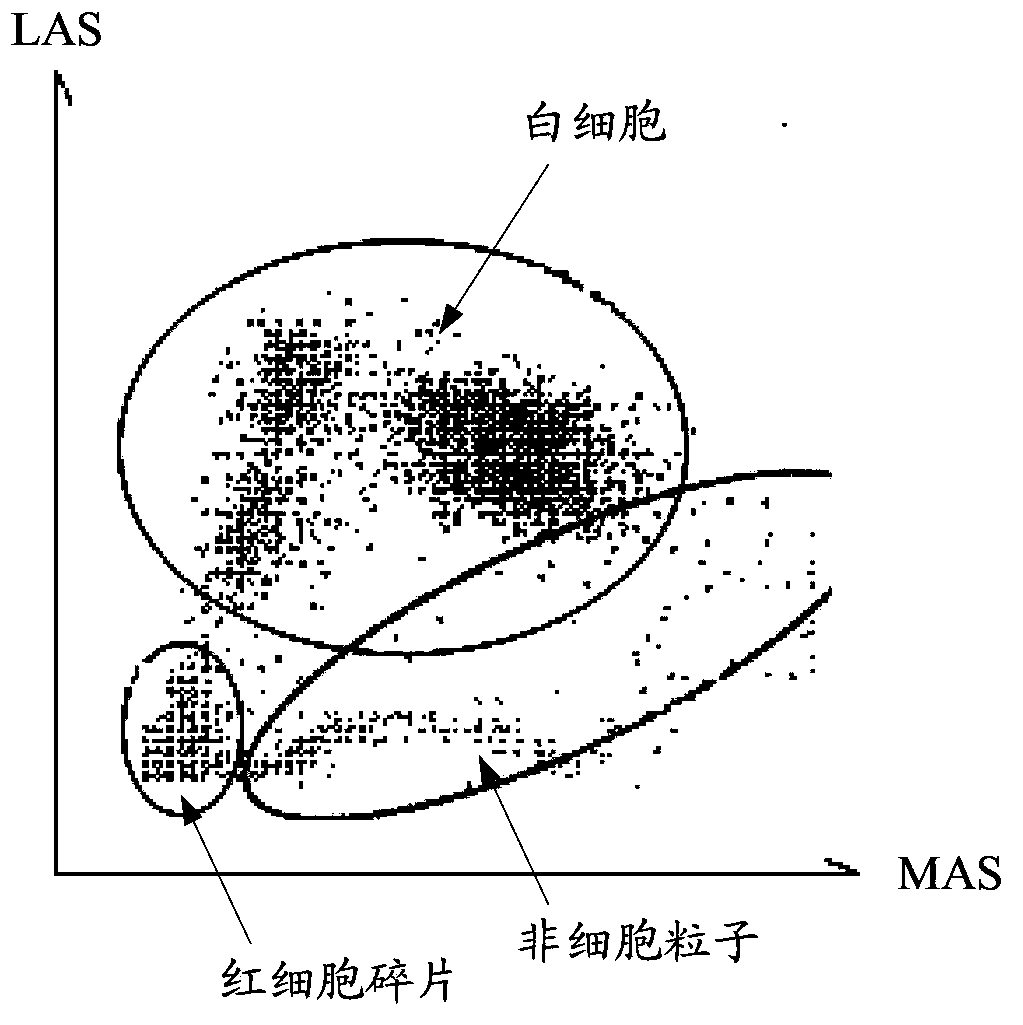
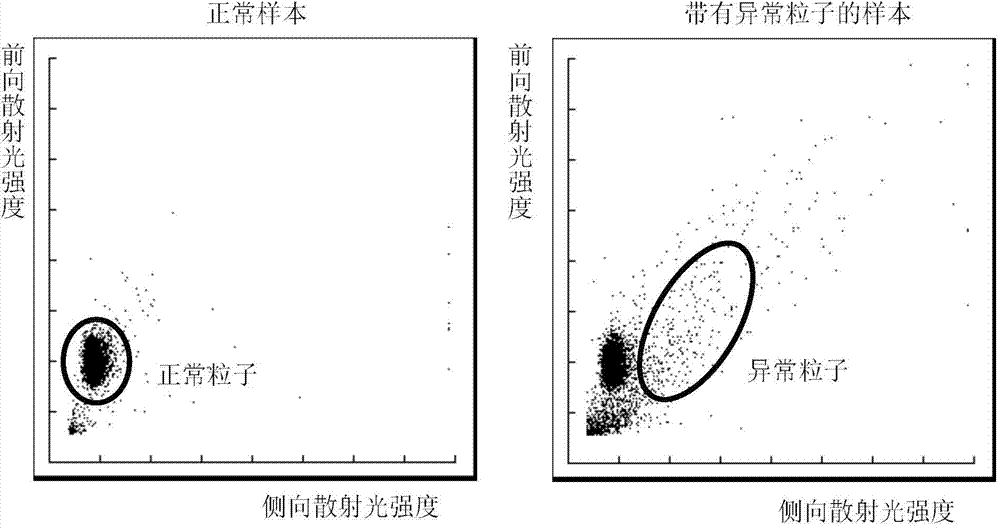
In the application, a recognizing method and a recognizing system of particles in a blood sample and a blood cell analytic instrument are disclosed. Firstly, according to an electronic pulse corresponding to a light scattering signal generated by irradiation on to-be-tested particles in the blood sample, a leukocyte group is recognized from the blood sample; and then an equivalent width indicating value of the to-be-tested particles in the blood sample is determined with correspondence to the electronic pulse by the light scattering signal which reflects size information of the to-be-tested particles; a scatter diagram of the equivalent width indicating value to electronic pulse amplitudes of information which reflects a complex degree of the to-be-tested particles is established; and non-cell particles are recognized from the leukocyte group in a manner of comparing the to-be-tested particles with a preset area in the scatter diagram. By means of the technical scheme, the non-cell particles in the blood sample can be recognized, thereby finally eliminating influence of the non-cell particles on leukocytes and improving recognizing accuracy of the particles in the blood sample.
Owner:CHENGDU SHEN MINDRAY MEDICAL ELECTRONICS TECH RES INST +1
Method for rapidly predicting aerodynamic characteristics of low-orbit spacecraft having complex shape
ActiveCN105975677AMeet real-time requirementsFast Computing Storage RequirementsSpecial data processing applicationsMomentumEnergy exchange
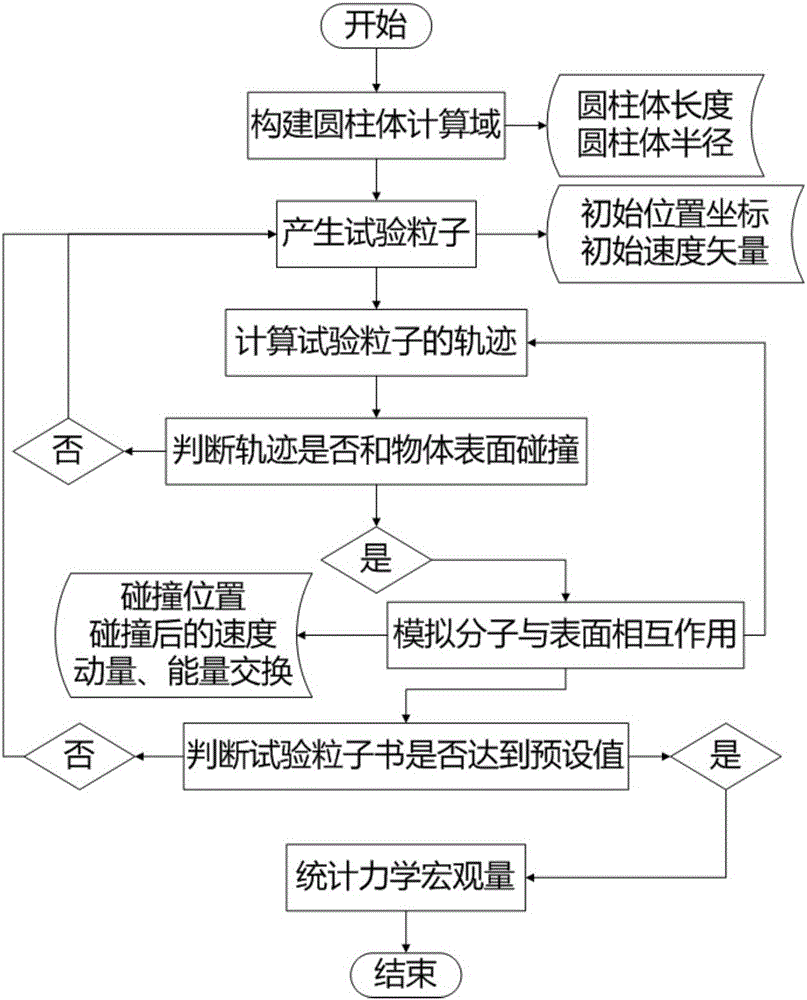
The invention relates to a method for rapidly and accurately predicting aerodynamic characteristics of a low-orbit spacecraft having a complex shape. The method comprises the following steps of: firstly, constructing a big enough computational domain, wherein the spacecraft is positioned in the computational domain; and a test particle is generated at the boundary; then, tracking and simulating the movement locus and the collision process after the test particle till the test particle flies out the computational domain or collides the surface of the spacecraft, and computing momentum and energy exchange of the test particle and the surface of the object and continuously tracking the test particle if the test particle is collided with the surface; and finally, repeating the process till the number of the test particles is large enough, such that convergence of a computing result is ensured, and counting an aerodynamic characteristic rule of the spacecraft in a flying environment, such that design of the spacecraft is carried out.
Owner:CHINA ACAD OF AEROSPACE AERODYNAMICS
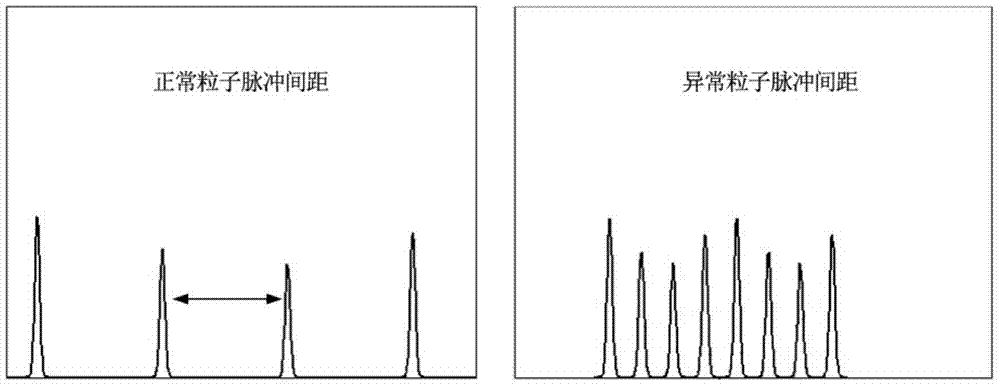
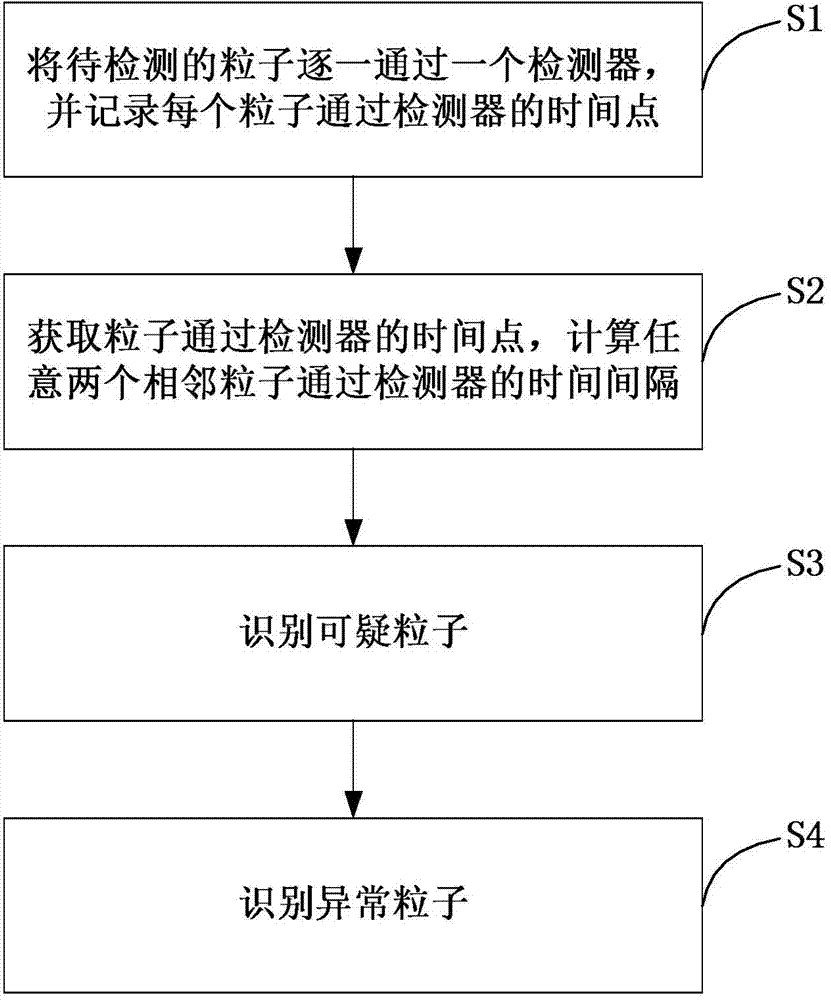
Method and system for recognizing abnormal particles and cell analyzer thereof
ActiveCN104515725AEasy to identifyImprove accuracyIndividual particle analysisInformation supportClinical diagnosis
The invention provides a method and a system for recognizing abnormal particles and a cell analyzer thereof. The method includes following steps: S1: enabling to-be-test particles to pass through a detector one-by-one and recording a time point of each particle passing through the detector; S2: calculating a time interval between any two adjacent particles passing the detector; S3: recognizing a doubtful particle; and S4: recognizing an abnormal particle. In the method, the system and the cell analyzer thereof, a characteristic that a pulse interval generated by abnormal particles is not in conformity with a statistic principle is employed for simply and efficiently recognizing the abnormal particles and further excluding recognized abnormal particles. By means of removal of the abnormal particles, accuracy of a particle counting result can be significantly improved, thereby providing accurate information support to clinical diagnosis.
Owner:SHENZHEN MINDRAY BIO MEDICAL ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
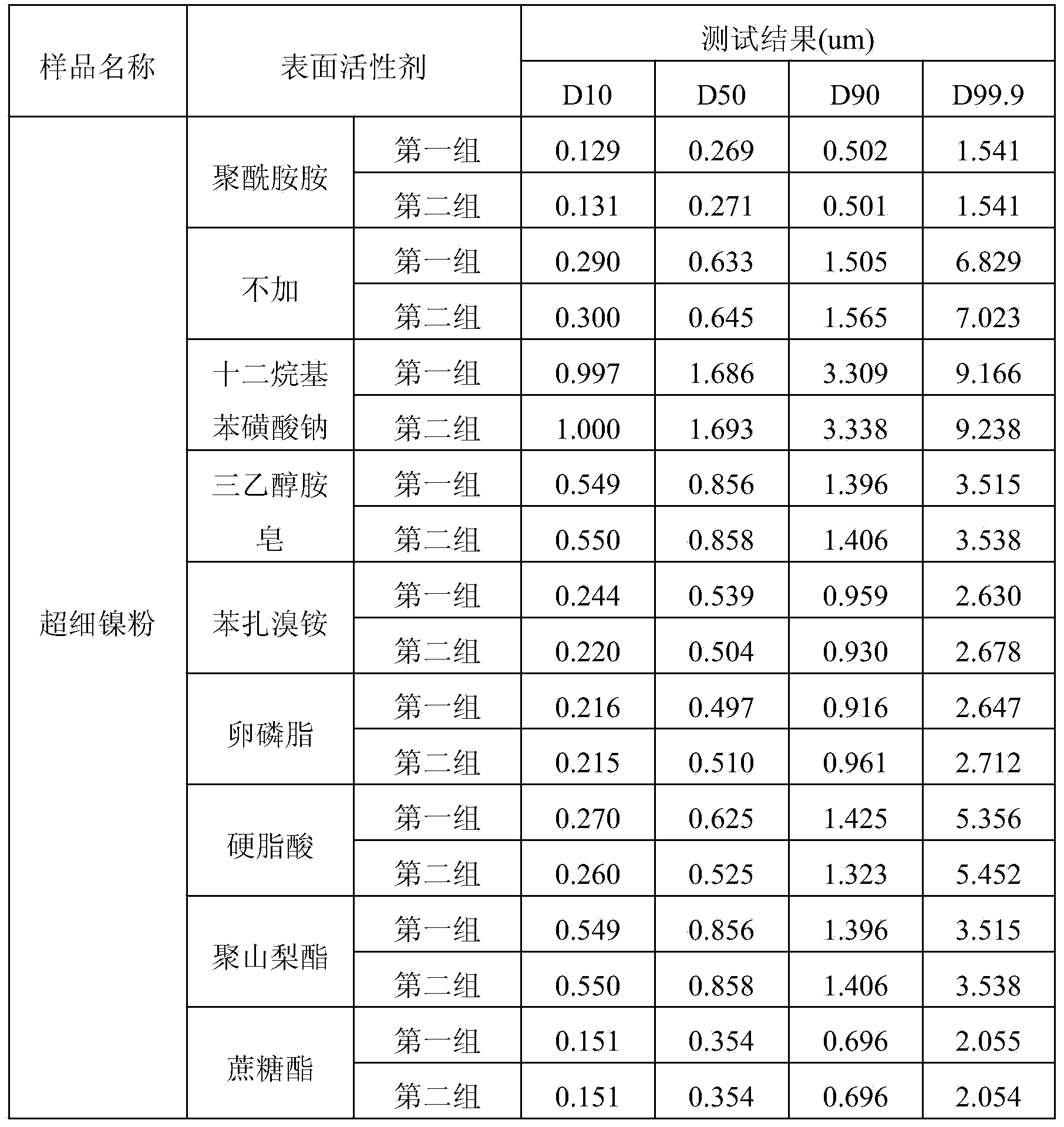
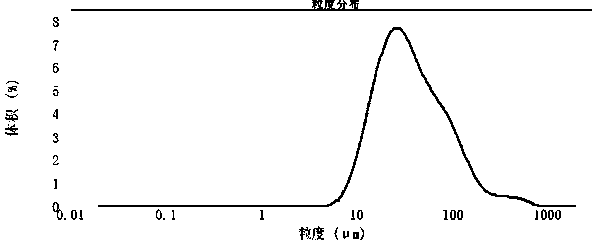
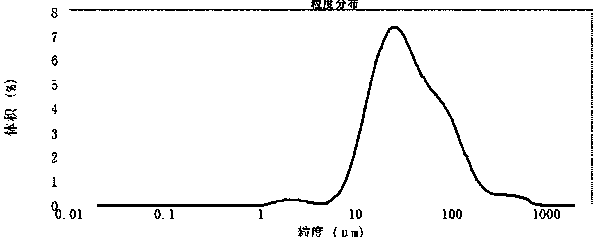
Method for testing particle size distribution of superfine nickel powder
The invention provides a method for testing particle size distribution of superfine nickel powder. The method comprises the operation steps as follows: preparing a polyamidoamine solution with the mass-to-volume percent of 0.5-20% with reverse osmosis water; enabling a laser particle size distribution detector to be located in a stable detection state; preparing a superfine nickel powder solution with the mass-to-volume percent of 0.01-1% with the reverse osmosis water, adding the polyamidoamine solution, wherein the adding amount of the polyamidoamine solution to the amount of reverse osmosis water in the superfine nickel power solution is (0.5-2 ml):150 ml; then dispersing the mixture with an ultrasonic stirrer for 15-20 min; detecting the liquid obtained in the last step by the laser particle size distribution detector to obtain the particle size distribution condition of the superfine nickel power. According to the method, the polyamidoamine is selected as a surfactant, so that the superfine nickel powder is good in hydrophilic property, and the actual particle size distribution condition of the superfine nickel power can be reflected more truly.
Owner:JIANGSU BOQIAN NEW MATERIALS
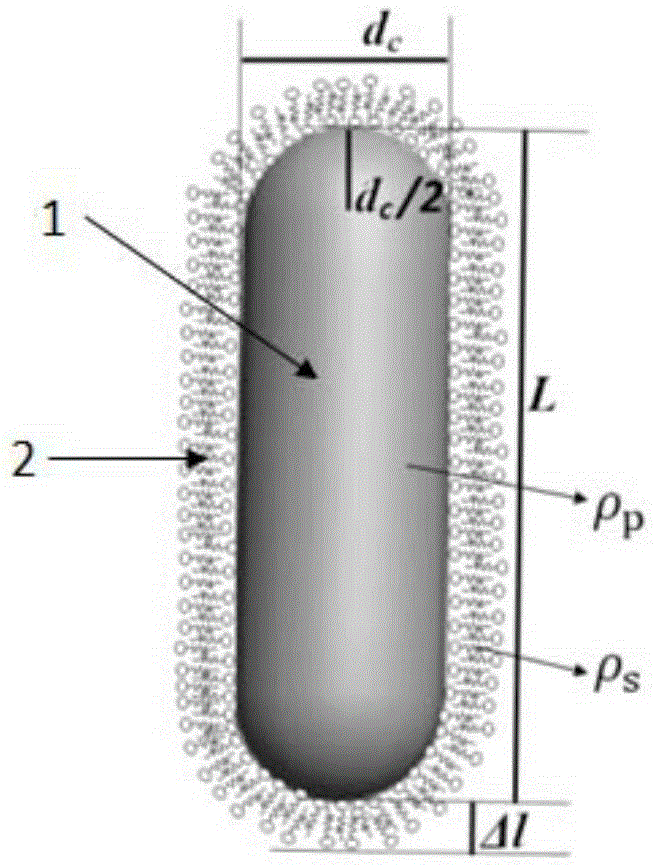
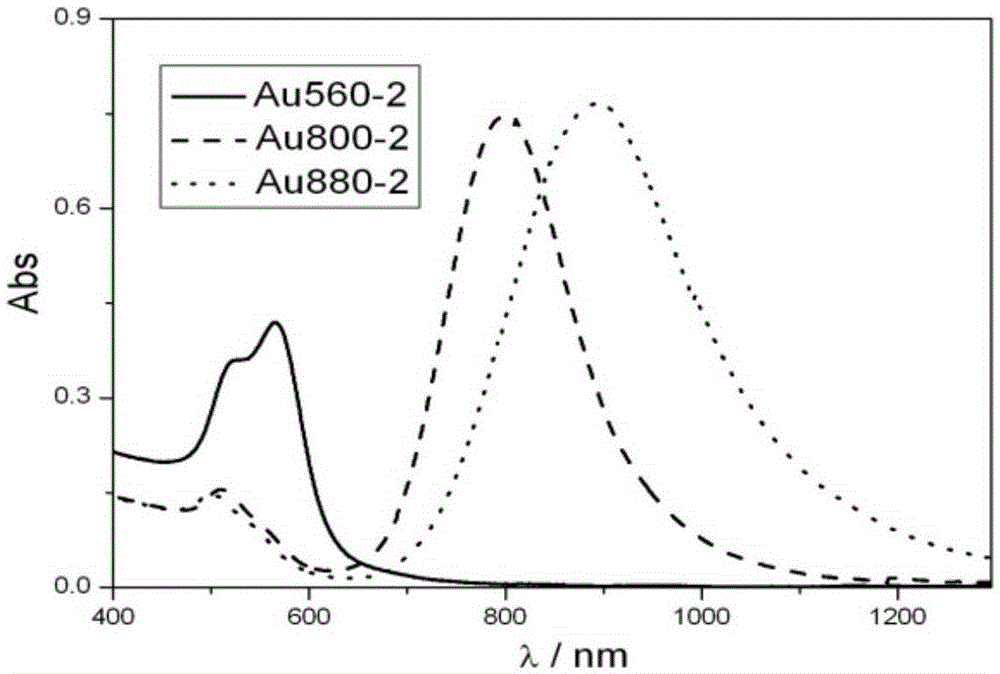
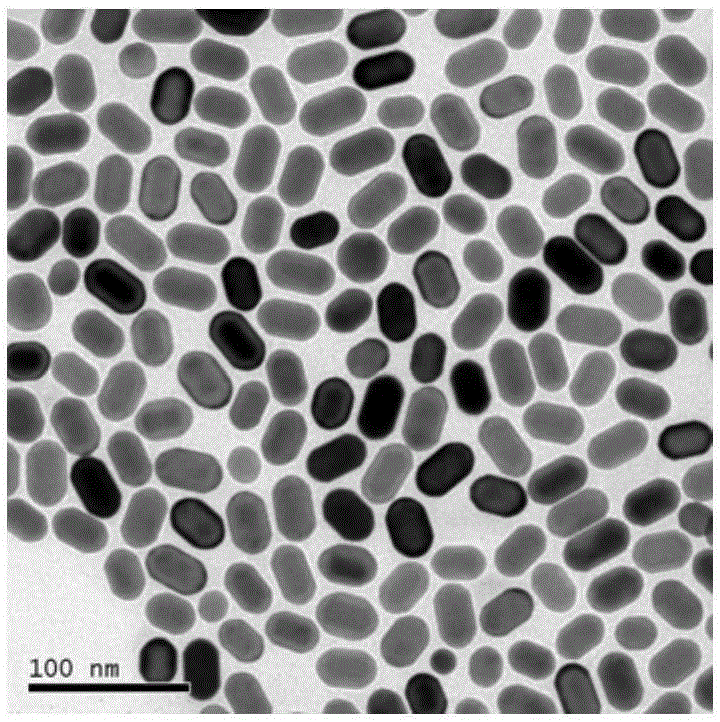
Determination method for geometrical shape of rod-like nano-particle
ActiveCN105300857ASimple test methodGood repeatabilityParticle size analysisCircular discGold nanorod
The invention relates to a determination method for the geometrical shape of a rod-like nano-particle. The determination method comprises the following steps: (1) dispersing the rod-like nano-particle in a surfactant solution so as to obtain a rod-like nano-particle dispersion liquid; (2) determining the absorption peak of the rod-like nano-particle dispersion liquid by using an ultraviolet spectrophotometer; (3) injecting the rod-like nano-particle dispersion liquid into a disc centrifugal nano-particle size analyzer and carrying out determination by using a differential centrifugal sedimentation process so as to obtain a test particle size dm; (4) calculating the diameter dc of the rod-like nano-particle according to a formula (II); and (5) calculating the length l of the rod-like nano-particle according to a formula (III). According to the invention, the disc centrifugal nano-particle size analyzer is used to determine the geometrical shape of the rod-like nano-particle for the first time, so preparation is made to research on the rod-like nano-particle; and the determination method is simple, has good repeatability and small deviation and can test tens of thousands of gold nanorods at one time, and data obtained through the method has better statistical significance and representativeness.
Owner:THE NAT CENT FOR NANOSCI & TECH NCNST OF CHINA
Granularity detection device
InactiveCN105067491AReliable resultsEasy to move and assembleParticle size analysisOptoelectronicsDecentralised system
The invention relates to a granularity detection device which comprises a laser diffraction system, a sample injection system and a dispersion system, wherein the laser diffraction system comprises a laser system, a receiving system and a test region; the laser system and the receiving system are respectively mounted at the two ends of the base; the laser system is connected with the receiving system through a cable; a test region is an opening region arranged between the laser system and the receiving system. By adoption of modular design, before test, the dispersion system and the sample injection system are used for dispersing a sample, so that the sizes of tested particles are representative, and the obtained result is reliable and accurate; moreover, the three modules are combined, so that movement and assembling are facilitated; by adoption of an optical theory, detection and analysis of the granularity distribution of emulsion, suspension, aerosol, powder and particles are realized in a fastest way; the granularity detection device is high in test speed, wide in test range, high in repetitiveness and authenticity and easy and convenient to operate.
Owner:SUZHOU SABO IND DESIGN
Micron-size particle autorotation speed test method and device in liquid swirling flow field
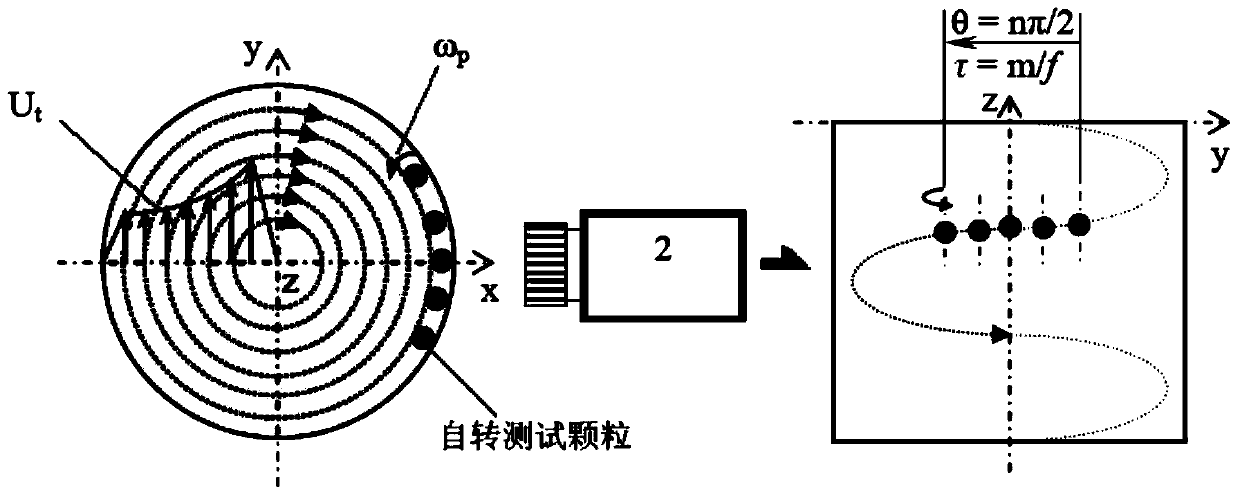
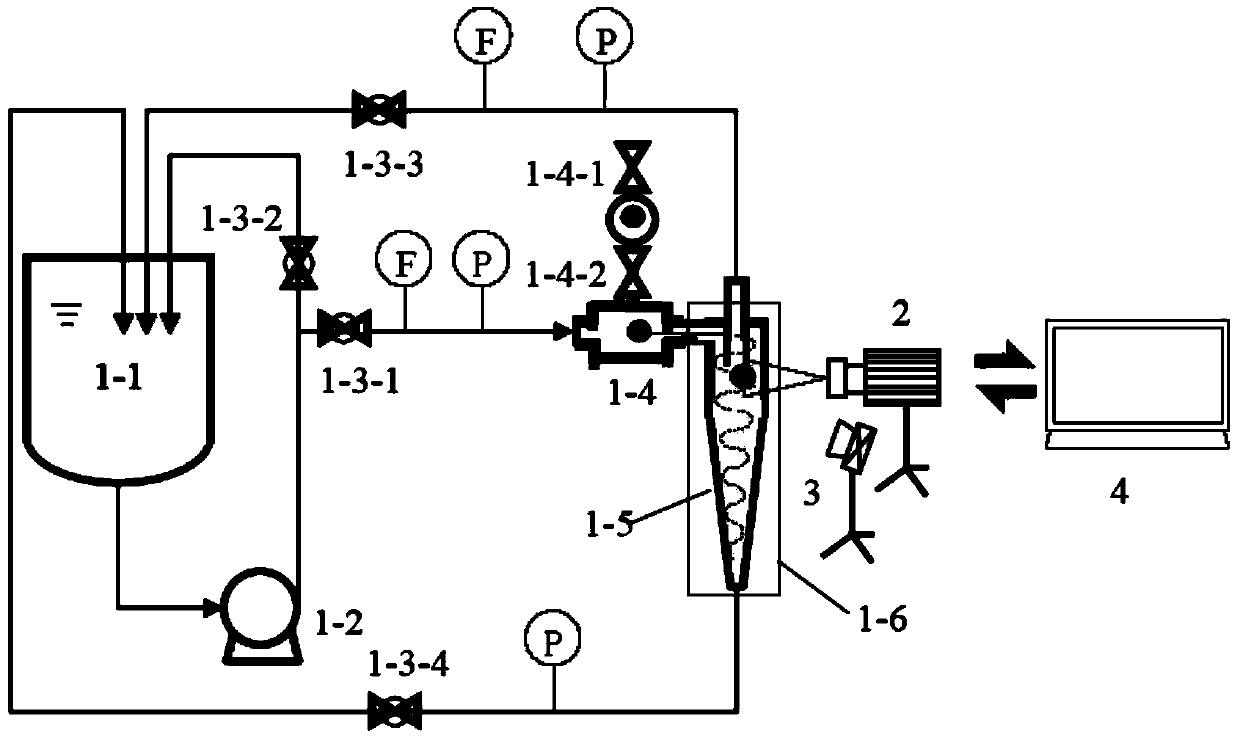
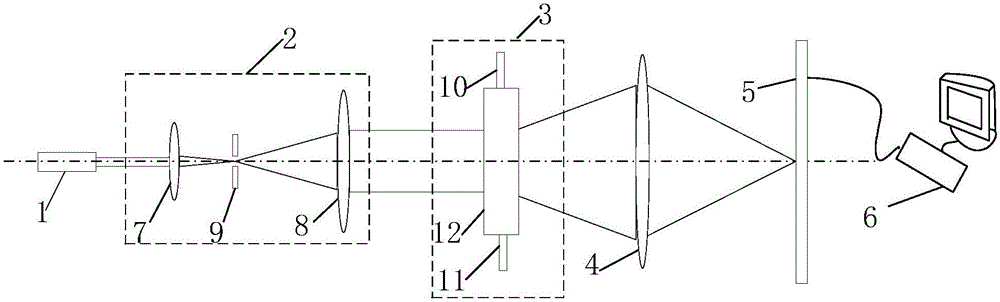
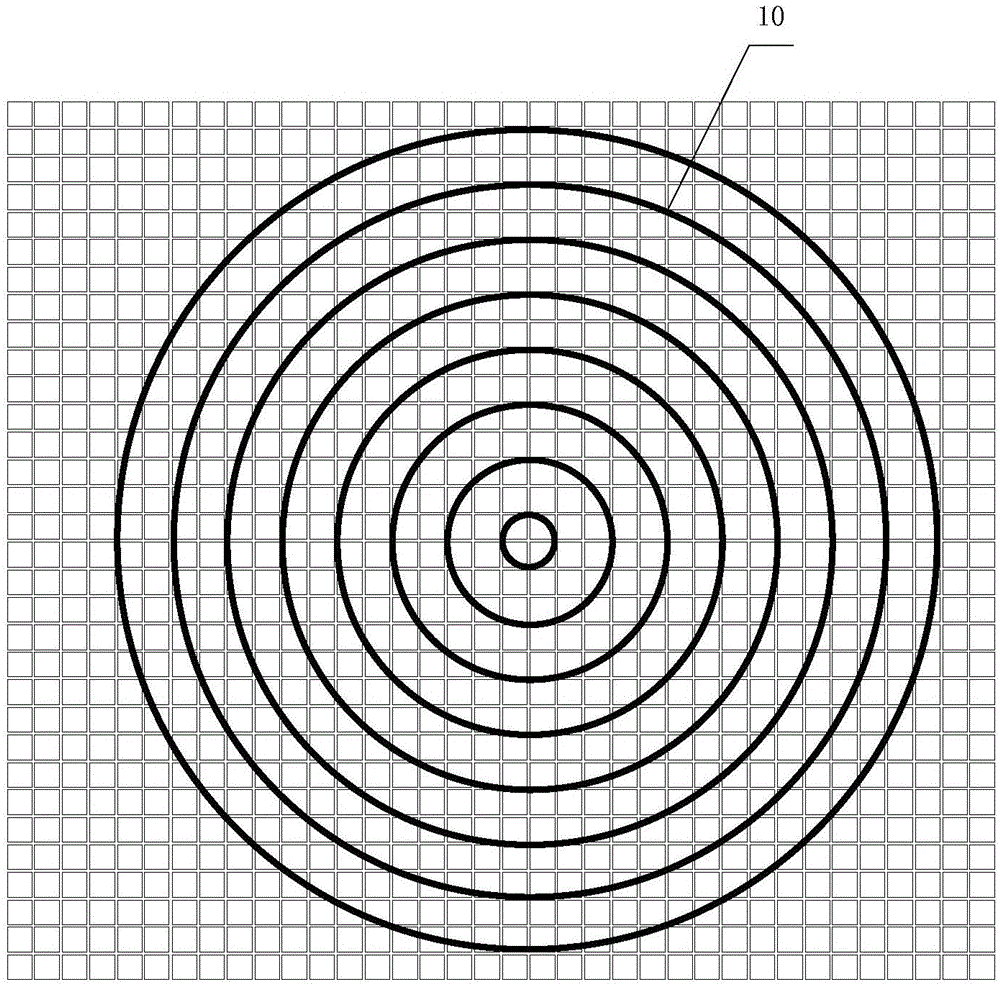
ActiveCN104049100AImprove visibilityAccurate measurementDevices using optical meansSpeed testEngineering
The invention relates to a micron-size particle autorotation speed test method and device in a liquid swirling flow field, and provides the micron-size particle autorotation speed test method in the liquid swirling flow field. The method comprises the steps that (1) transparent or semi-transparent particles which are equal in diameter, are arranged in a center symmetry mode and are provided with two inner cores are selected as autorotation test particles; (2) a high-speed image pickup system is adopted for recording the two-dimensional movement process of the particles in the liquid swirling flow field, and an image sequence of particle movement is obtained; (3) the autorotation speed of the particles is determined by analyzing the overlapping and separating frequency of projections of the two inner cores in the particles in the obtained image sequence. The invention further provides the micron-size particle autorotation speed test device in the liquid swirling flow field.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Laser particle analyzer and method for testing particle size distribution
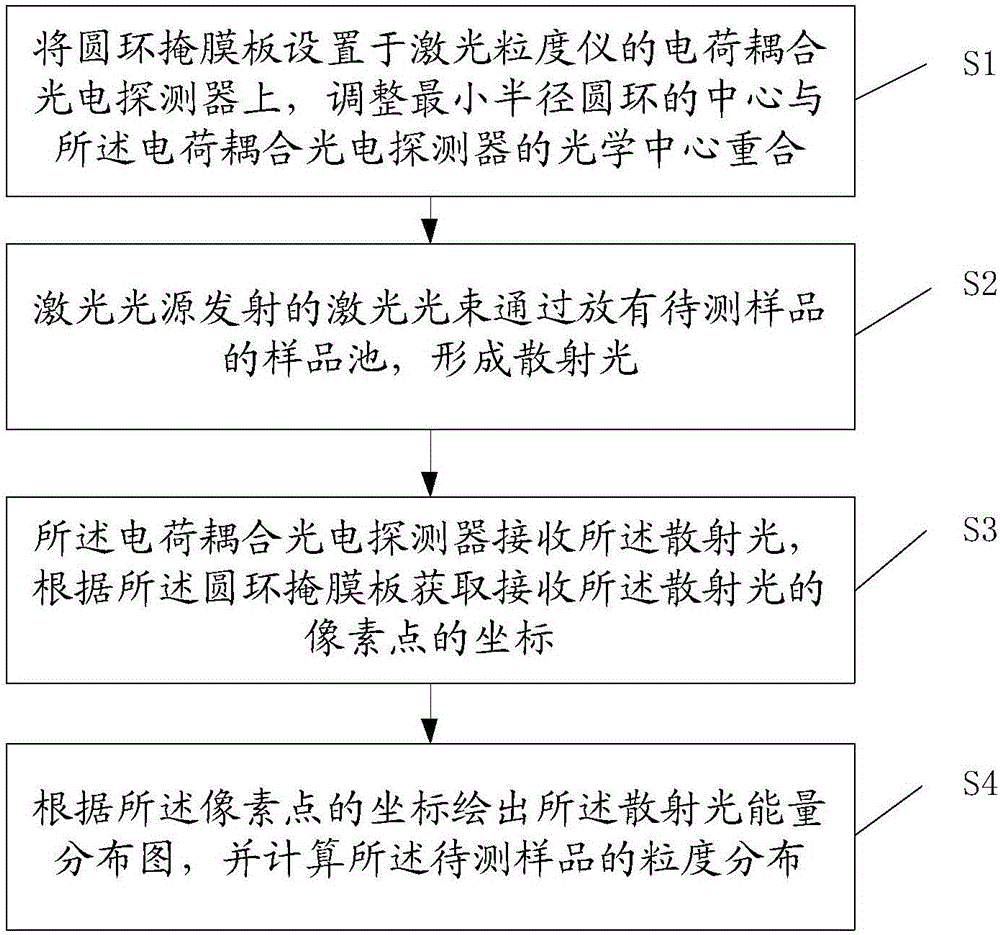
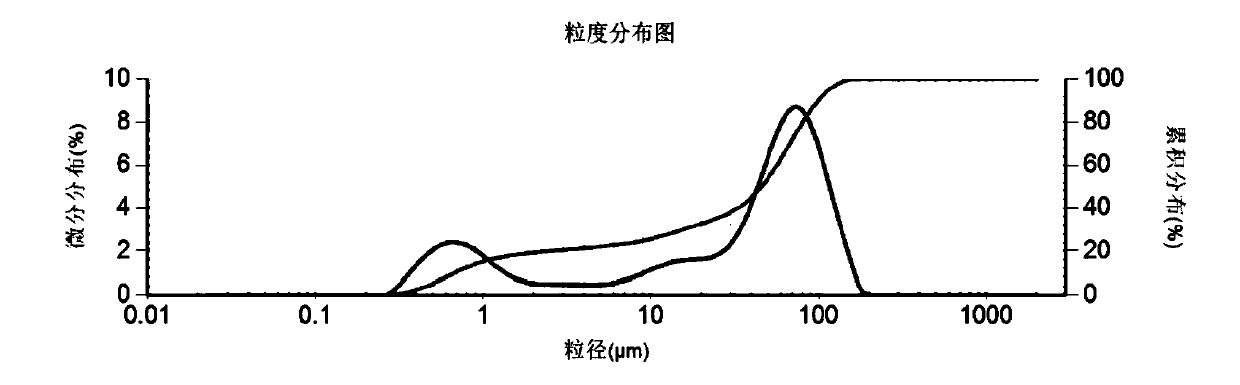
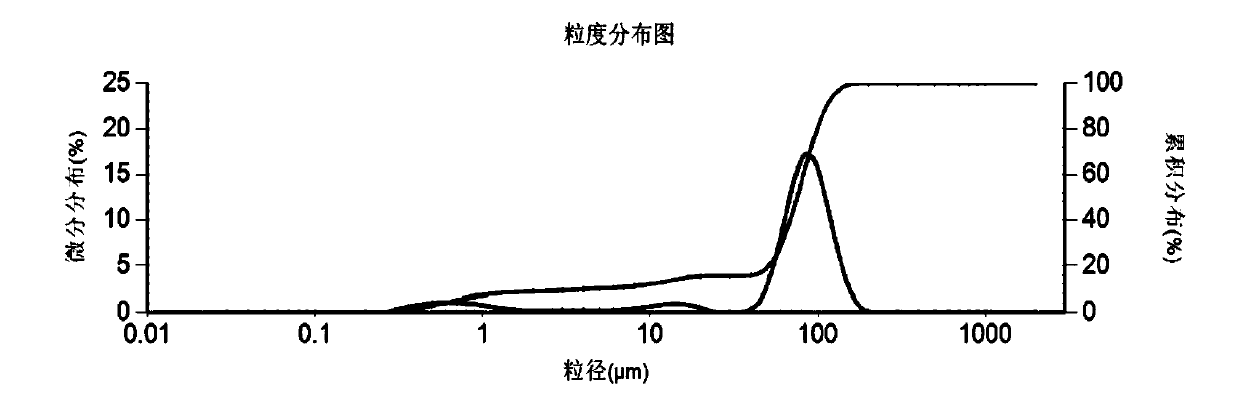
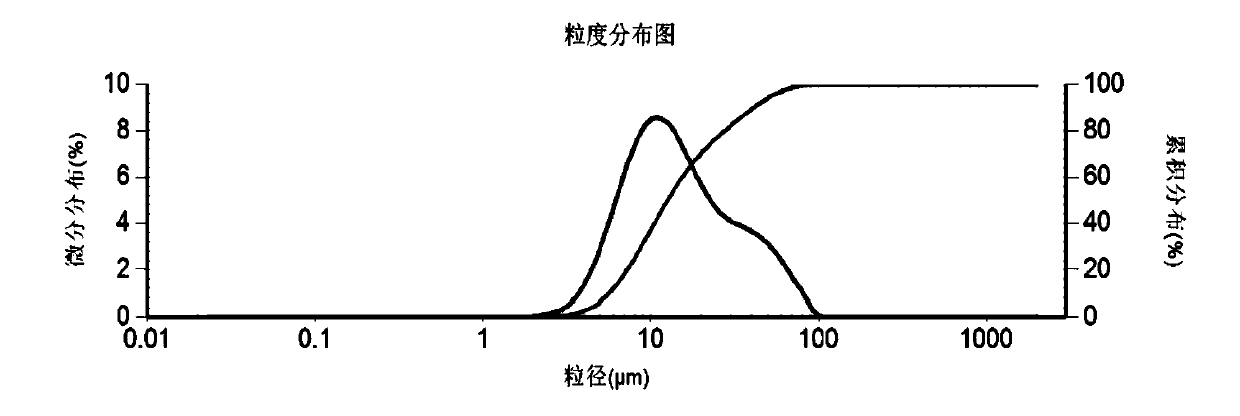
The invention discloses a laser particle analyzer which comprises a laser light source for transmitting a laser beam, a sample pool for accommodating a to-be-tested sample, a charge coupling photoelectric detector and a calculator, wherein the charge coupling photoelectric detector is used for receiving scattered light generated after the laser beam penetrates the to-be-tested sample and converting the scattered light into a scattered light energy distribution diagram, and the surface of the charge coupling photoelectric detector is provided with a ring mask plate; and the calculator is used for calculating grain size distribution of the to-be-tested sample according to the scattered light energy distribution diagram. The goal of using the ring mask plate is to obtain corresponding positions of each pixel receiving the scattered light more visually, conveniently extract energy of the scattered light according to the position corresponding to each pixel, quickly draw the scattered light energy distribution diagram, and accelerate the speed of calculating the grain size distribution of the to-be-tested sample. The invention further provides a method for testing the grain size distribution, and the method has aforementioned effects.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for testing particle size and particle size distribution of aluminum trihydride
The invention provides a method for testing the particle size and particle size distribution of aluminum trihydride. The method applies a wet laser diffraction method to test the particle size and particle size distribution of AlH3. The method comprises the steps that (1) a dispersion medium is added into the aluminum trihydride, and the dispersion medium is a lecithin-butyl acetate solution withthe mass fraction being (1-3)% or a nonylphenol polyoxyethylene ether-butyl acetate solution with the mass fraction being (1-3)%; (2) combined ingredients in the step (1) are dispersed, and thus a completely-dispersed AlH3 suspension system is prepared; and (3) the particle size and particle size distribution of the aluminum trihydride in a suspension treated in the step (2) are measured through awet laser particle analyzer. According to the method, the relative standard deviation of the multiple measuring results of the particle size is not greater than 5%, and the precision of the method isgood.
Owner:HUBEI INST OF AEROSPACE CHEMOTECHNOLOGY
Method for testing particle size and particle size distribution of 5-aminotetrazole
ActiveCN107894378AGood precisionImprove applicabilityParticle size analysis5-AminotetrazoleTest particle
The invention relates to a method for testing the particle size and the particle size distribution of 5-aminotetrazole, wherein the particle size and the particle size distribution of an organic synthesis intermediate 5-aminotetrazole are tested by a wet laser diffraction method. According to the method, 5-AT particle size test is performed by using a trichloromethane solution containing 0.2-0.4%of sodium dodecylbenzenesulfonate and 0.1-0.2% of ethylphenyl polyethylene glycol as a dispersion system at an ultrasonic dispersion time of 5-10 min. According to the present invention, the relativestandard deviation of the multiple median particle size measurement results is not more than 6%, the precision of the method is good, and the wet laser diffraction method for testing the particle sizeof 5-AT has good applicability and can be used for the test of the particle size of 5-AT so as to be used for the quality control of the product.
Owner:HUBEI INST OF AEROSPACE CHEMOTECH
Method for testing particle size of specific plastic titanium dioxide by particle size analyzer
The invention discloses a method for testing particle size of specific plastic titanium dioxide by a particle size analyzer, and especially relates to a method for testing the particle size of specific plastic titanium dioxide by the particle size analyzer in metallurgy and chemical engineering domains. The method for testing the particle size of specific plastic titanium dioxide by the particle size analyzer includes steps of A, adding titanium dioxide in a solvent and preparing to be titanium dioxide solution; B, adding dispersing agent in the titanium dioxide solution; C, dispersing treatment; D, performing sampling detection and testing the particle size; controlling concentration of titanium dioxide, wherein the amount of titanium dioxide added in step A is 0.1-0.5g, and the solvent amount is 50 mL. Through selecting solvent and adjusting the dispersing treatment technique, the method has good dispersing performance, and the solution benefiting to test is obtained; the testing result is approached to the real particle size of a product.
Owner:PANGANG GROUP RESEARCH INSTITUTE CO LTD
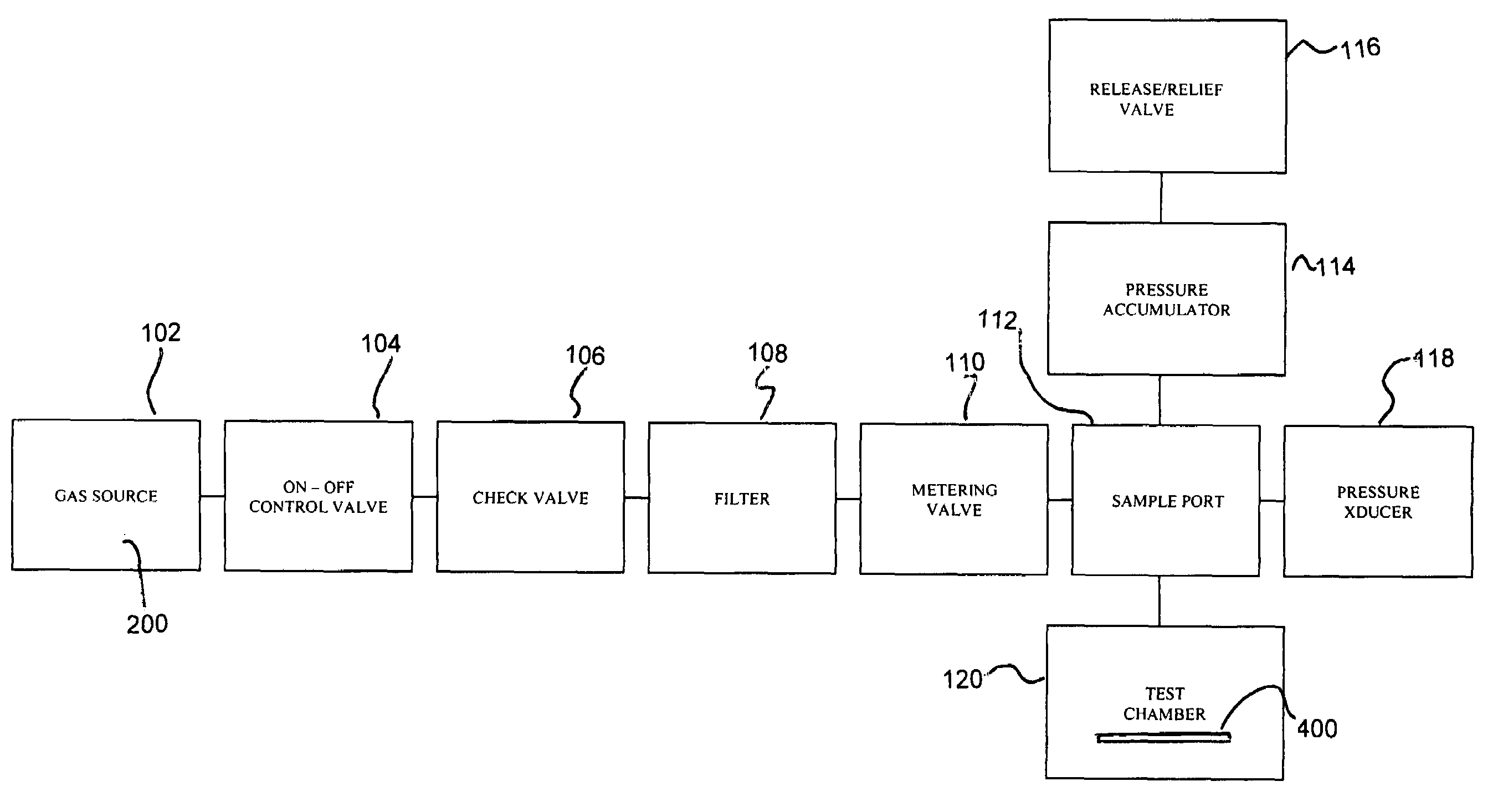
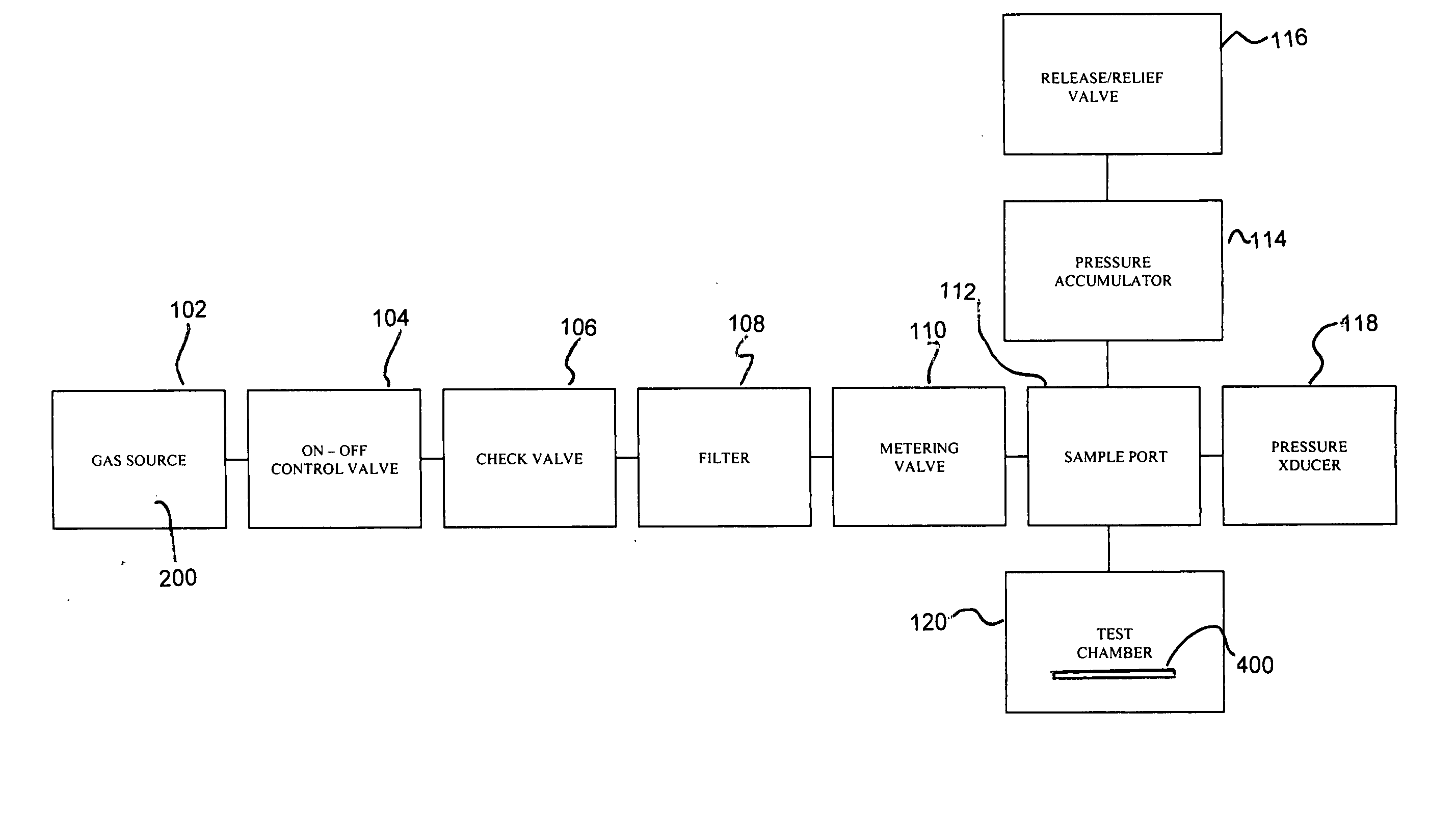
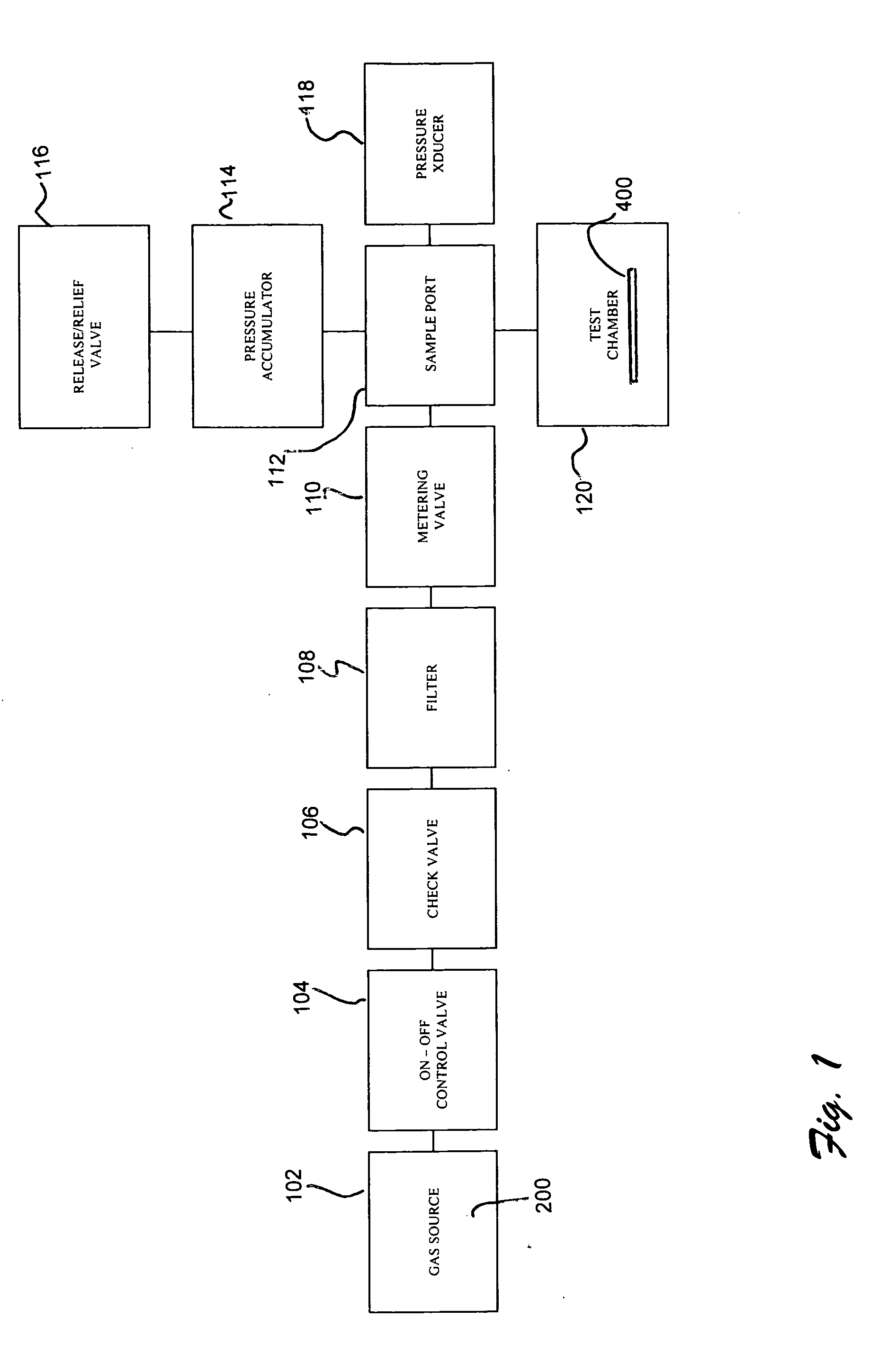
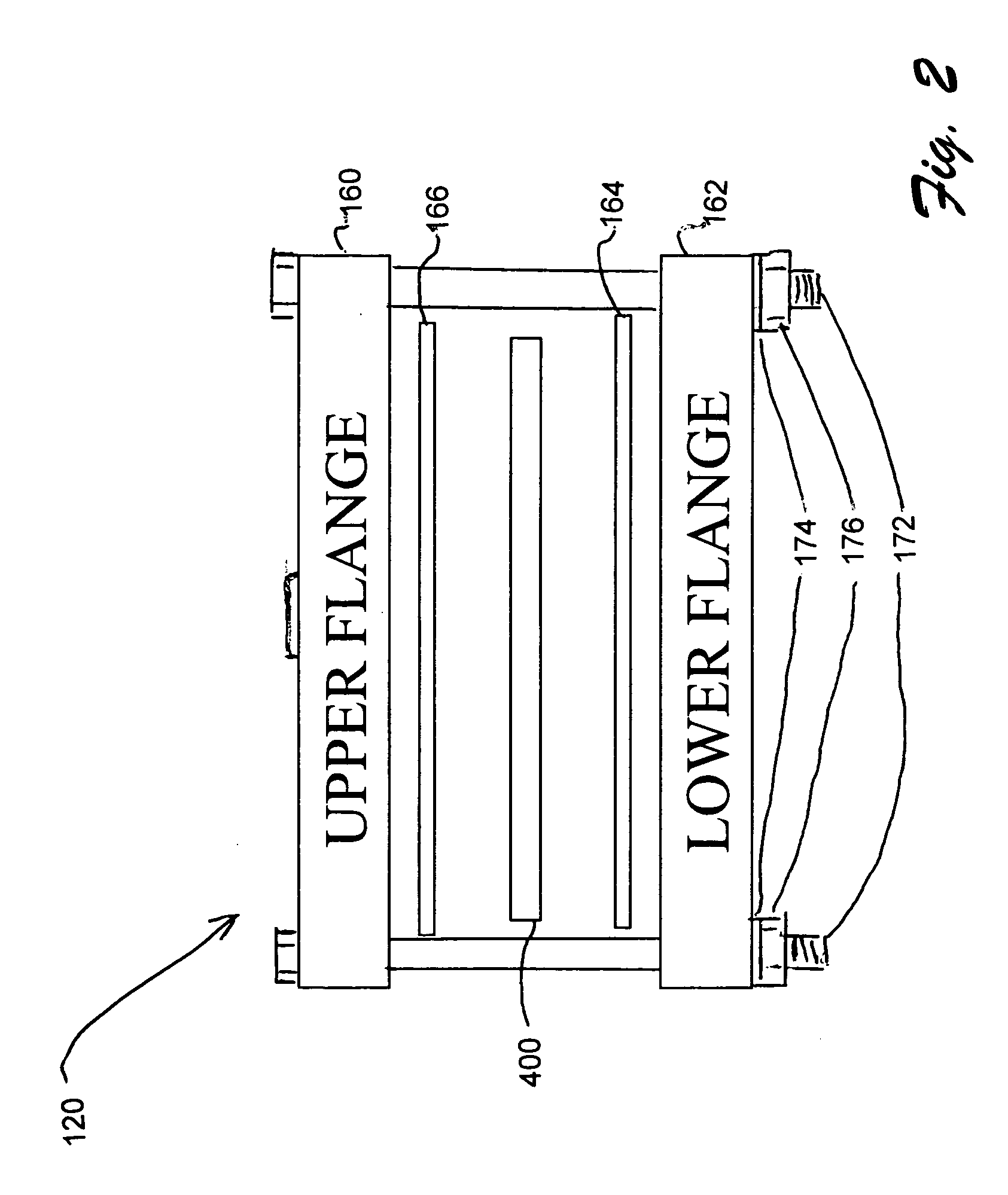
Material porosity pressure impulse testing system
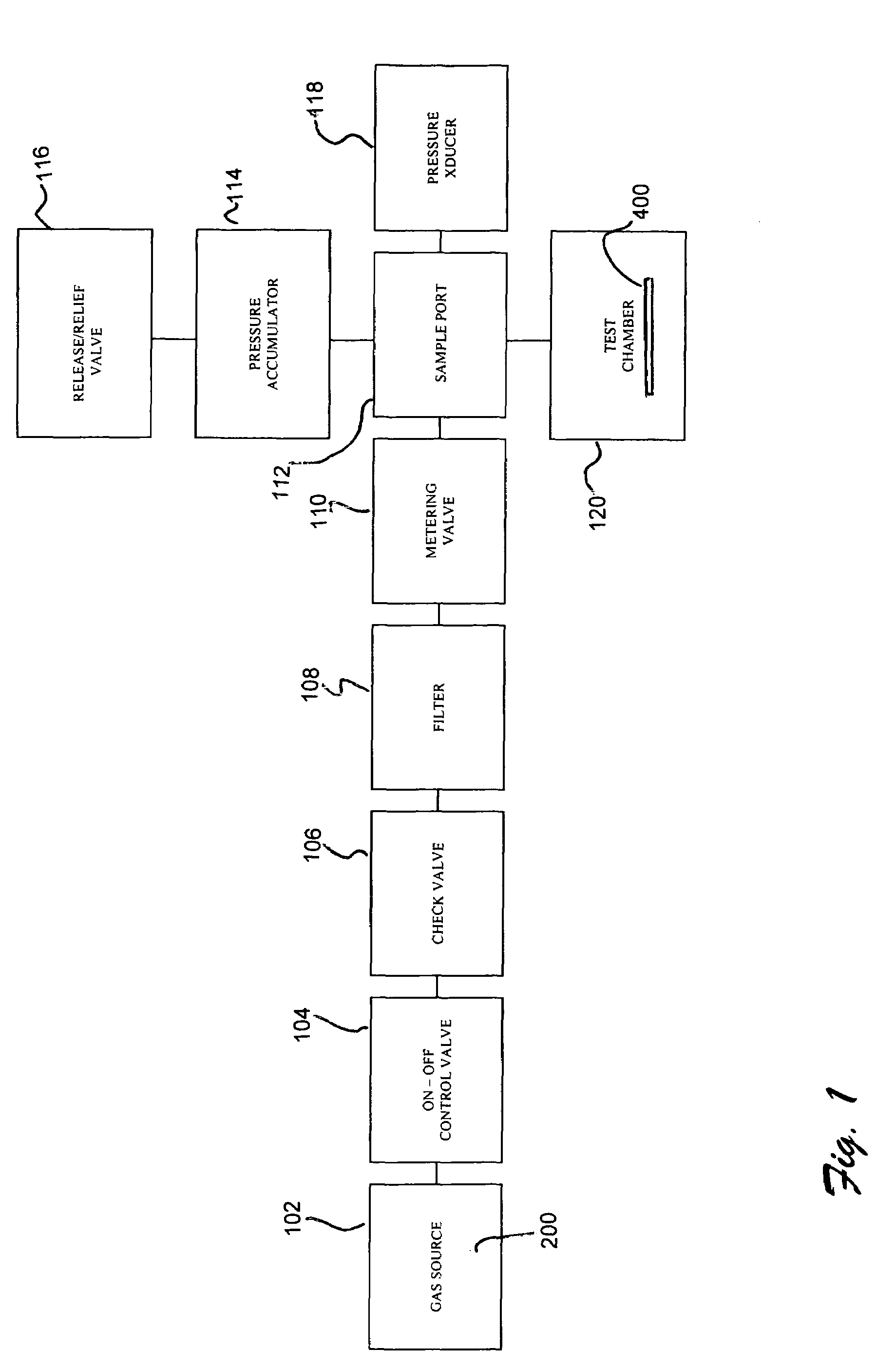
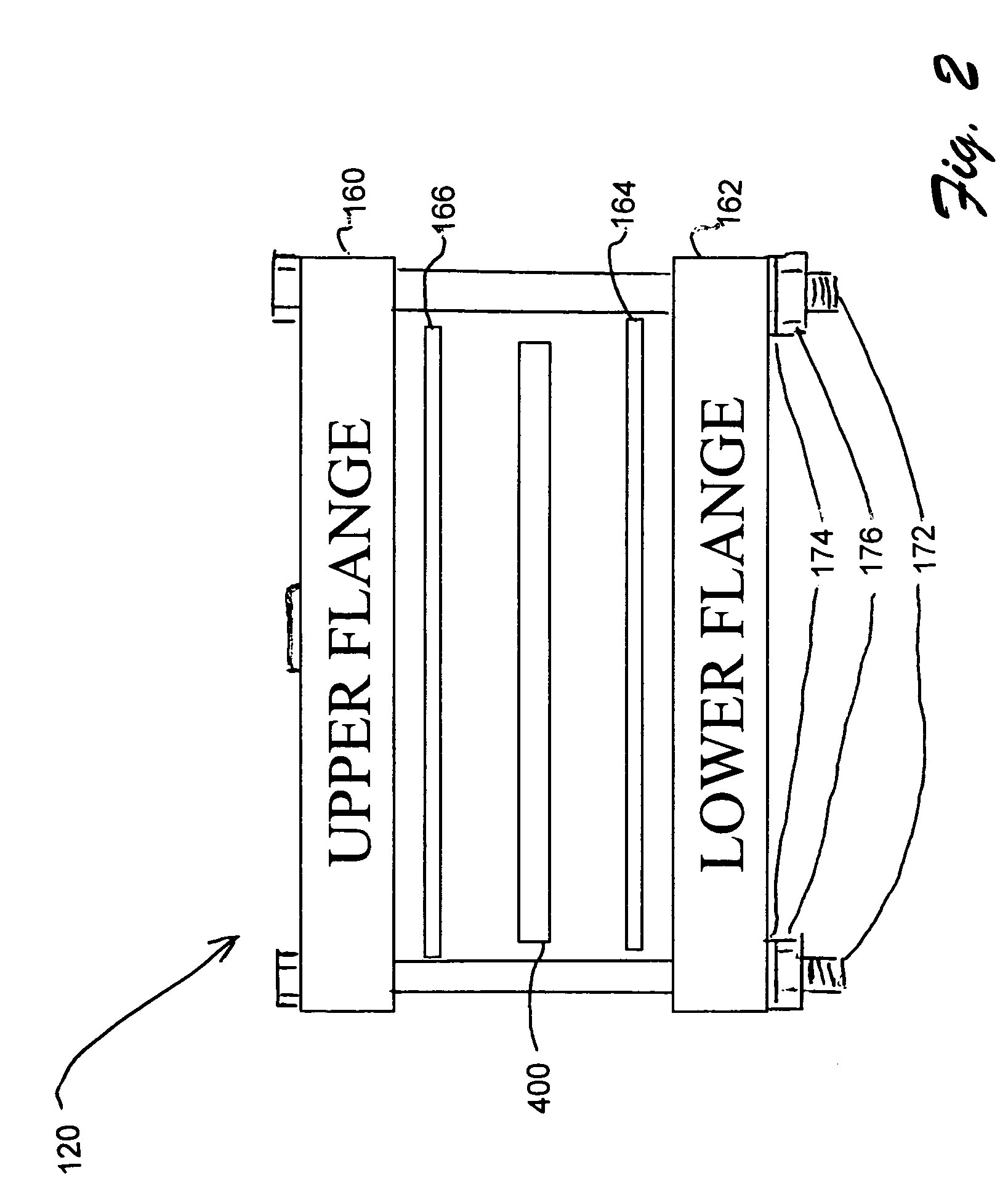
InactiveUS7274447B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsDiffusionPorosity
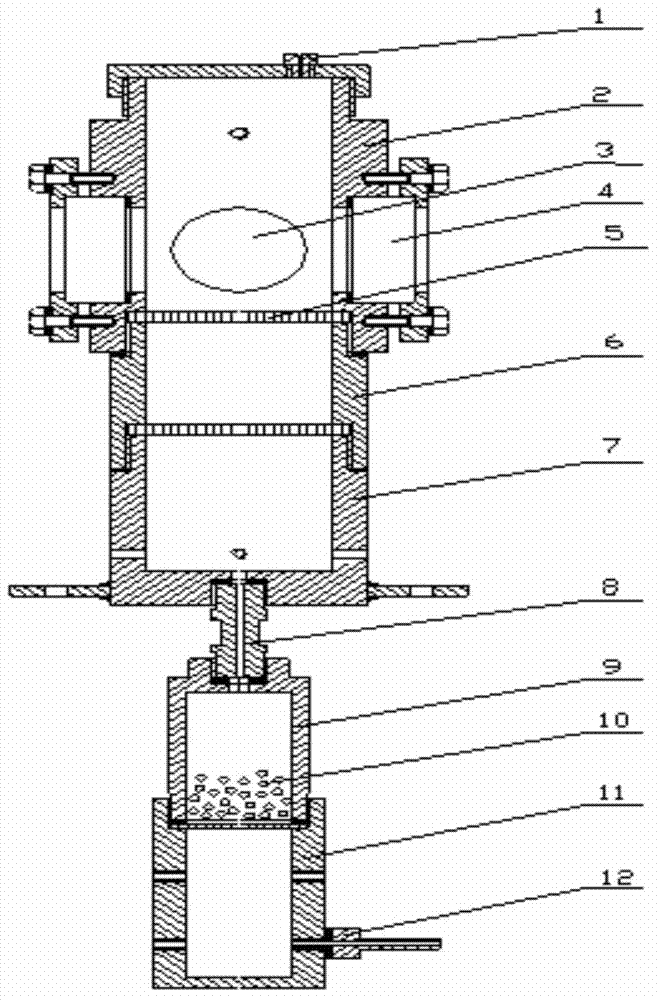
A system and method for determining porosity of a material enables rapid testing of materials by detecting test particle penetration. The material is held by a test chamber wherein a test particle solution covers a surface of the material. The test chamber is pressurized to a predetermined pressure, predetermined temperature and for a predetermined time. After the pressure is released the test particle penetration / diffusion into the material is then detected through differential fluorescence of the test particle.
Owner:SWCE
Method for testing particle size and particle size distribution of linezolid raw medicine
The invention provides a method for testing the particle size and the particle size distribution of a linezolid raw medicine. The method has the advantages that the wet laser diffraction method is adopted for testing, and the raw medicine to be tested is prepared into a test suspension with a polysorbate-80 aqueous solution serving as a dispersant and a linezolid raw medicine saturated aqueous solution serving as a dispersion medium, so that the problems that solid powders of the linezolid raw medicine are bulked, are likely to be agglomerated, and have low possibility of dispersion and high possibility of foaming upon stirring in the dispersion medium are solved; and the testing process is simple and convenient, and experimental results are highly repeatable and precise, so that the method can be used for particle size testing in production and application processes of the linezolid raw medicine, and effective technical measures can be further provided for the product quality controlin the processes.
Owner:深圳万乐药业有限公司
Material porosity pressure impulse testing system
InactiveUS20050279948A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsDiffusionPorosity
A system and method for determining porosity of a material enables rapid testing of materials by detecting test particle penetration. The material is held by a test chamber wherein a test particle solution covers a surface of the material. The test chamber is pressurized to a predetermined pressure, predetermined temperature and for a predetermined time. After the pressure is released the test particle penetration / diffusion into the material is then detected through differential fluorescence of the test particle.
Owner:SWCE
Plate and test method using the same
InactiveUS20060057709A1Improve accuracyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsElectrical and Electronics engineeringTest particle
Owner:ALPS ALPINE CO LTD
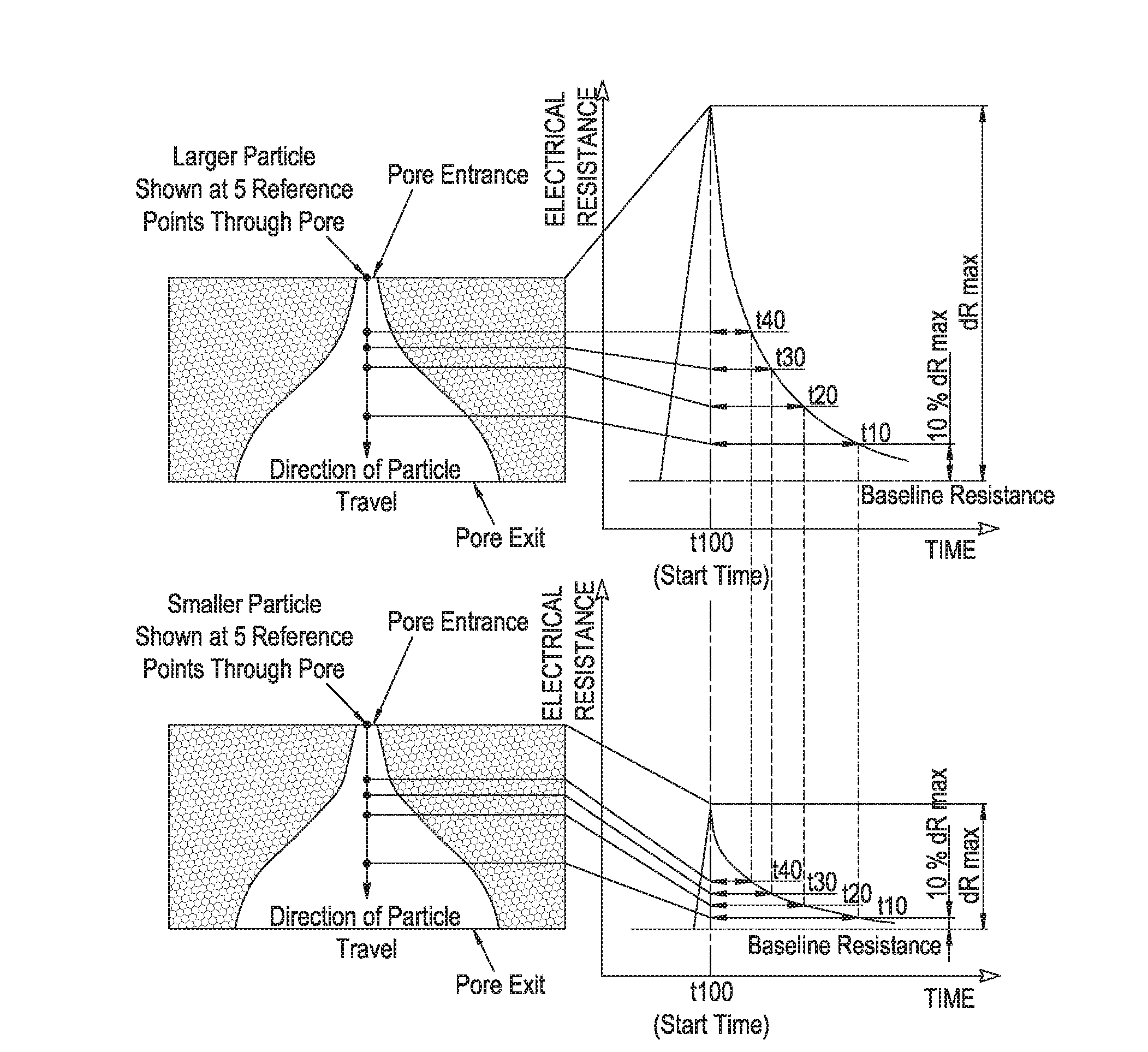
Measurement of particle charge
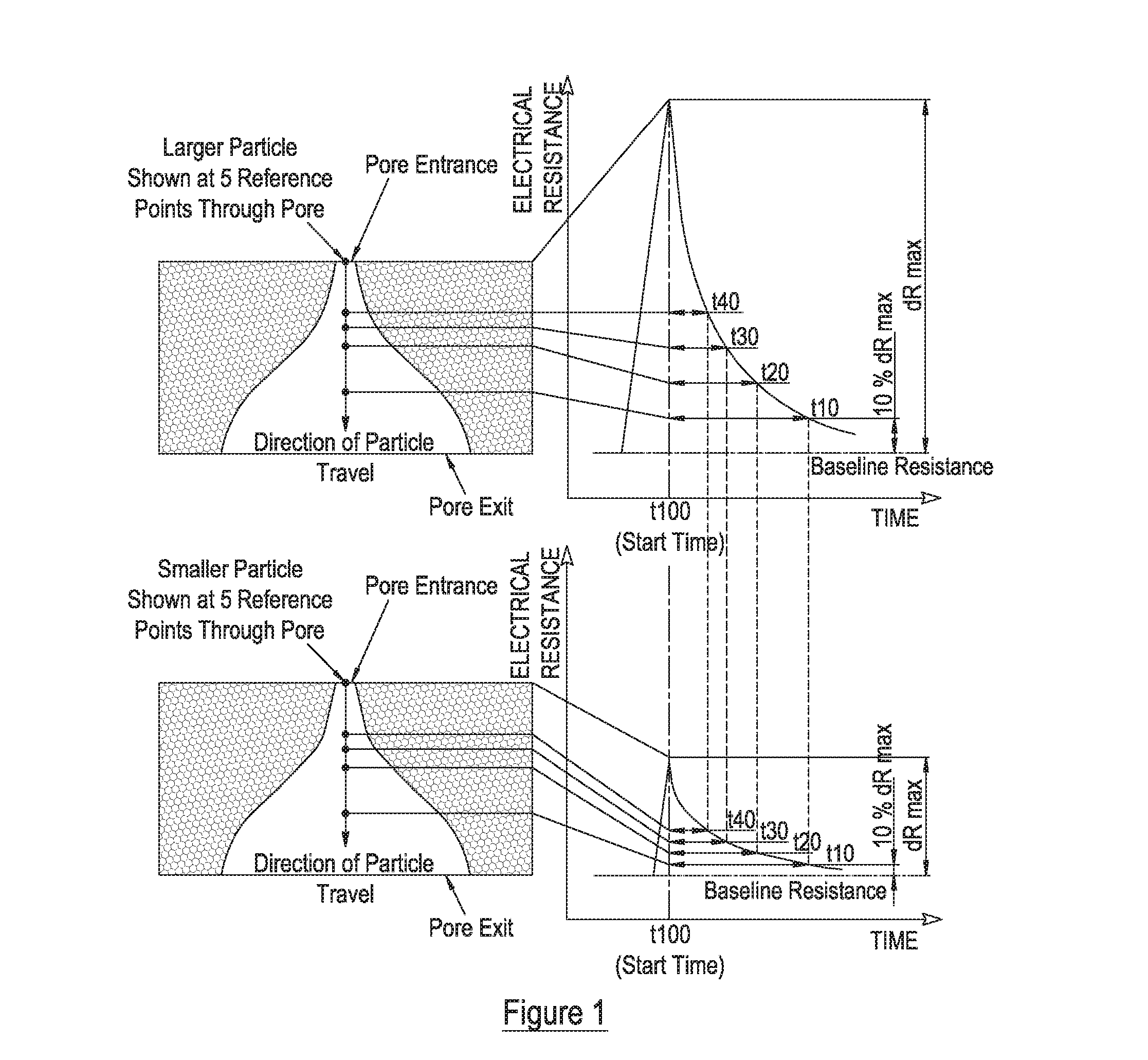
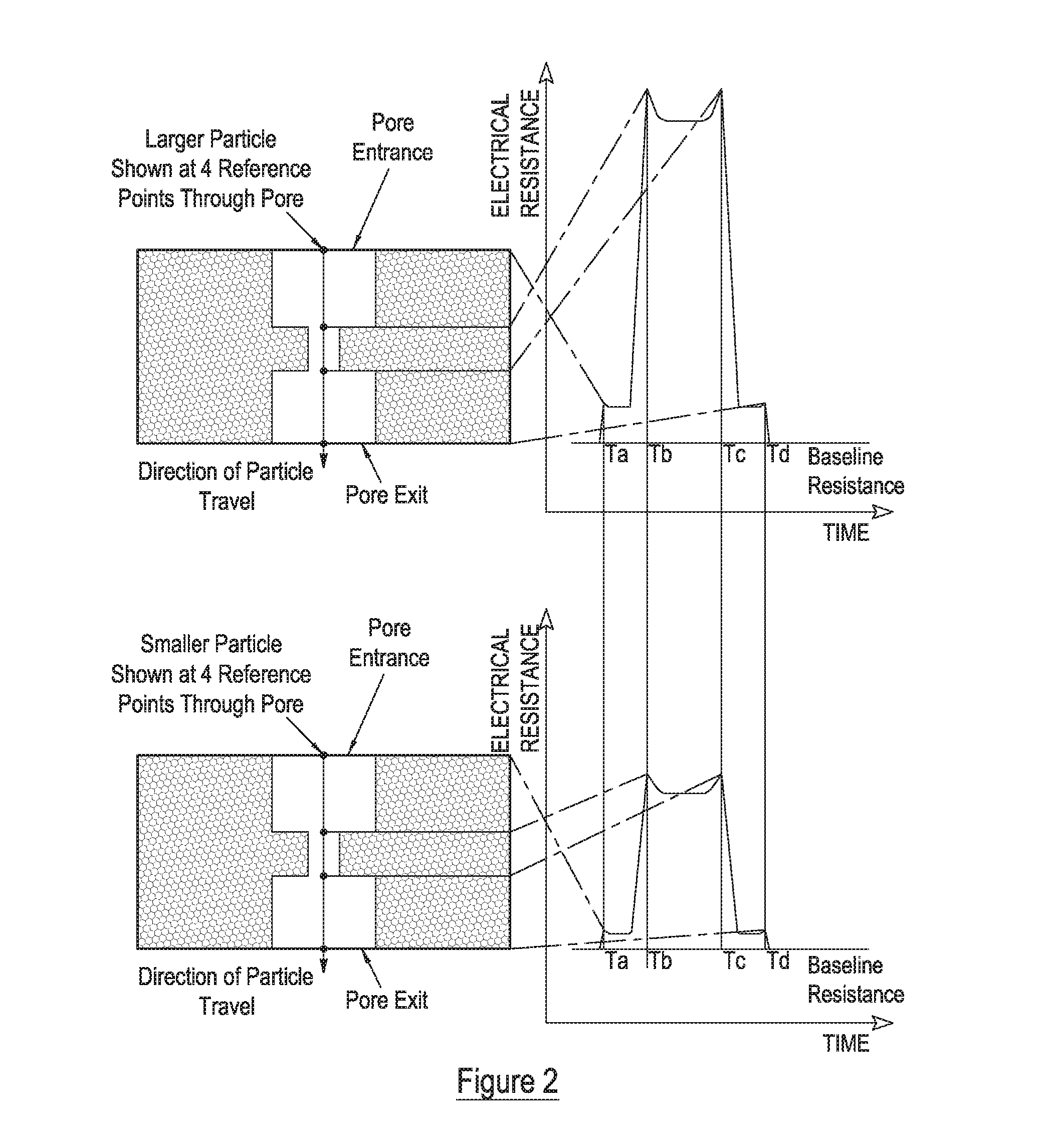
ActiveUS20160223492A1Accurate measurementIncrease opportunitiesMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansElectrical measurementsElectricityMechanics
Owner:IZON SCIENCE
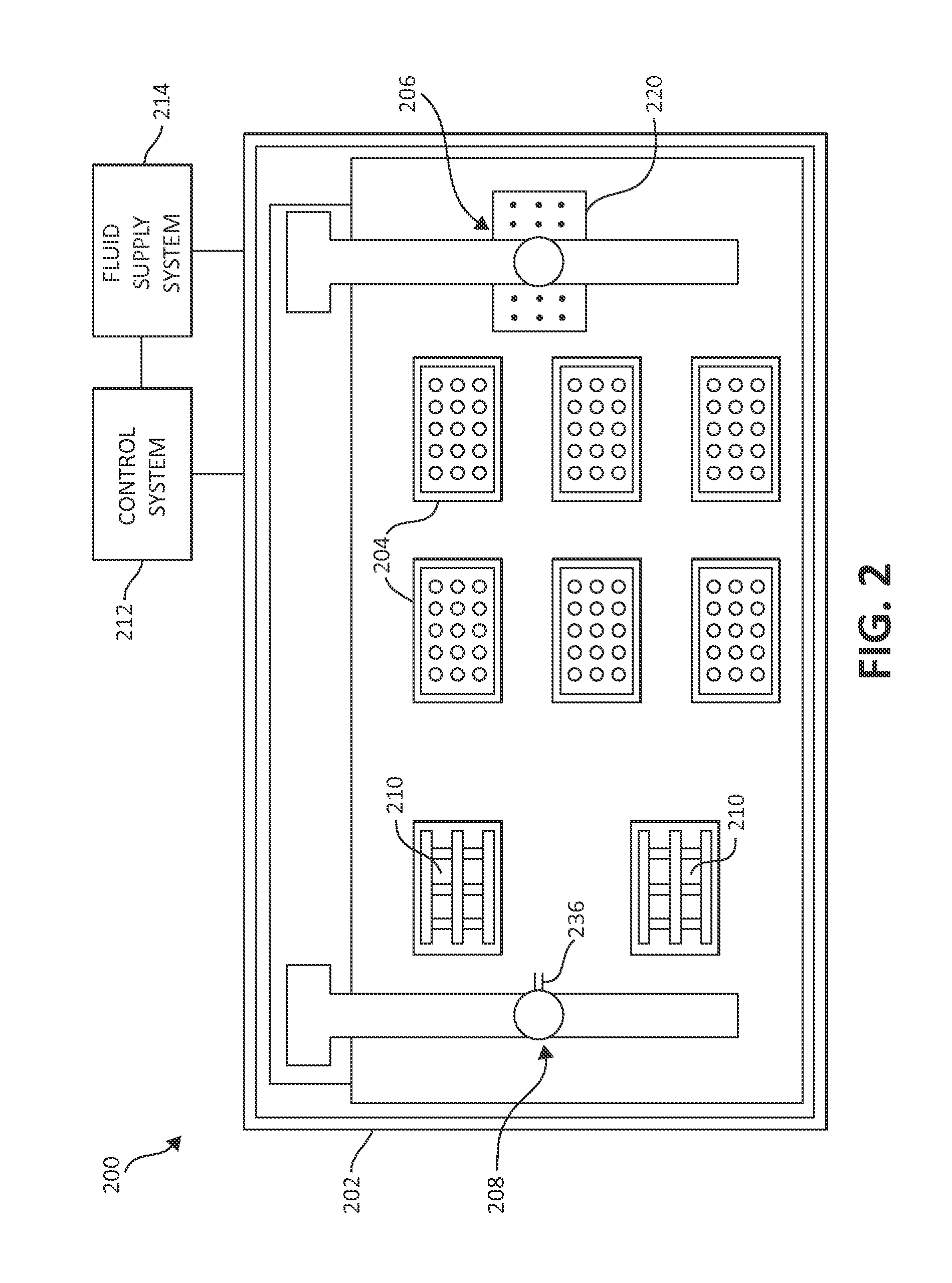
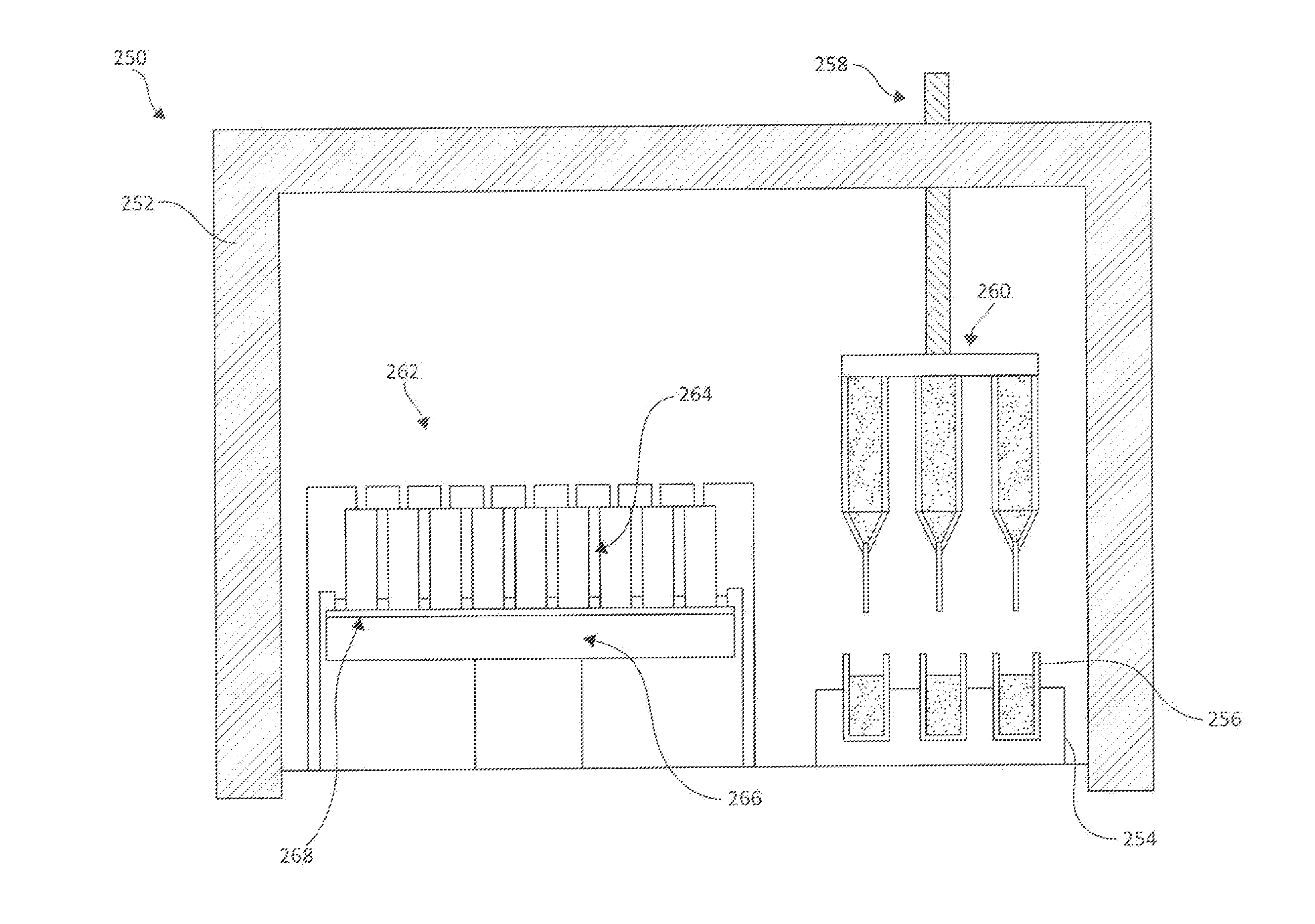
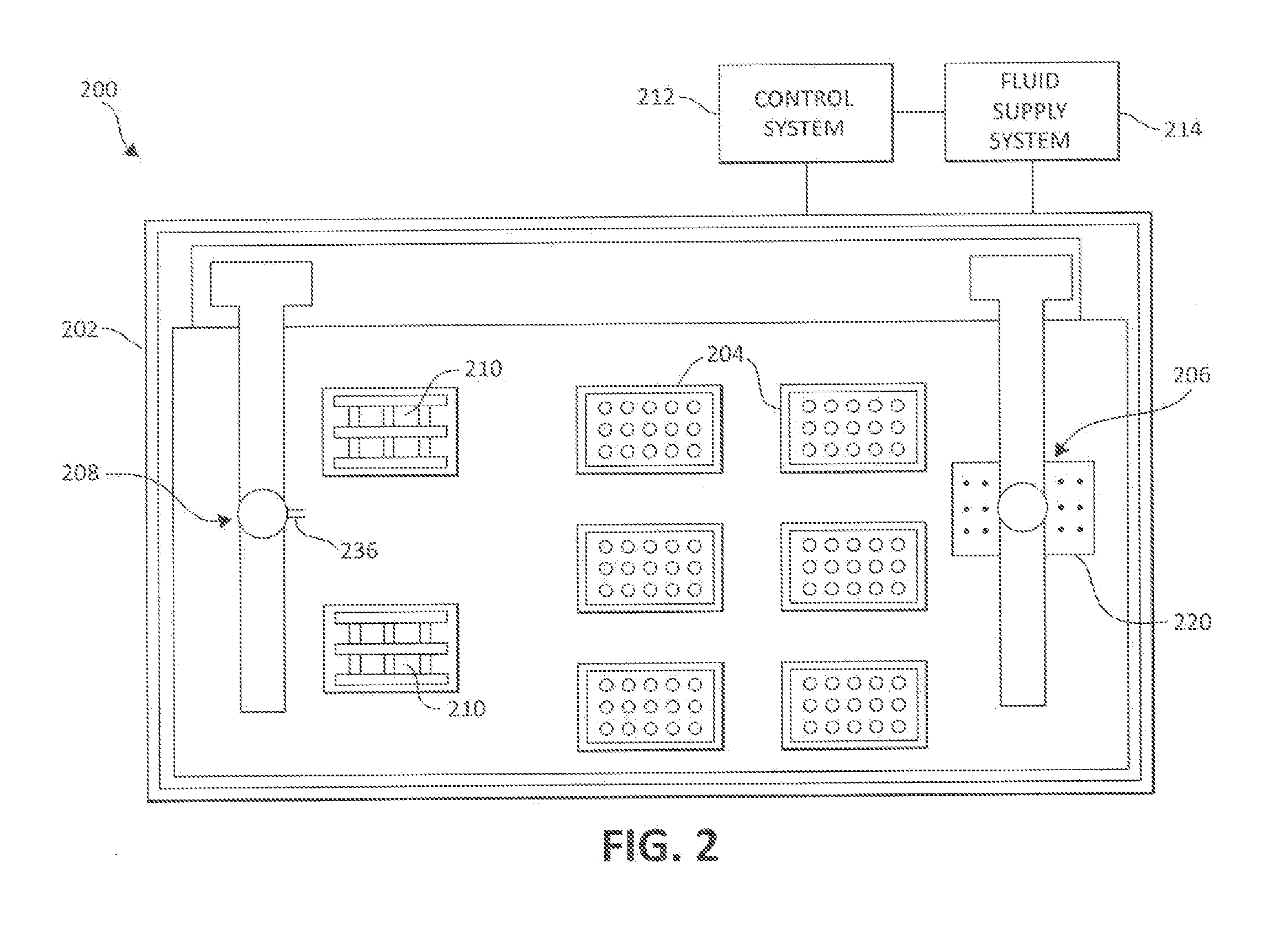
High-Throughput Combinatorial Dip-Coating Apparatus and Methodologies
InactiveUS20110151105A1Liquid surface applicatorsSequential/parallel process reactionsCombined methodDip-coating
Embodiments of the current invention describe a high performance combinatorial method and apparatus for the combinatorial development of coatings by a dip-coating process. The dip-coating process may be used for multiple applications, including forming coatings from varied sol-gel formulations, coating substrates uniformly with particles to combinatorially test particle removal formulations, and the dipping of substrates into texturing formulations to combinatorially develop the texturing formulations.
Owner:INTERMOLECULAR
High-Throughput Combinatorial Dip-Coating Apparatus and Methodologies
InactiveUS20120156498A1Sequential/parallel process reactionsLiquid surface applicatorsCombined methodDip-coating
Embodiments of the current invention describe a high performance combinatorial method and apparatus for the combinatorial development of coatings by a dip-coating process. The dip-coating process may be used for multiple applications, including forming coatings from varied sol-gel formulations, coating substrates uniformly with particles to combinatorially test particle removal formulations, and the dipping of substrates into texturing formulations to combinatorially develop the texturing formulations.
Owner:INTERMOLECULAR
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com