Second Pulse Synchronization Method Based on Merging Unit SV Packet Sampling Number Learning
A sampling sequence number and message sampling technology, applied in electrical components, time-division multiplexing systems, multiplexing communications, etc., can solve problems such as large time errors, insufficient reliability, and inability to protect the timing of measurement and control devices. Achieve seamless switching and improve resampling accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach
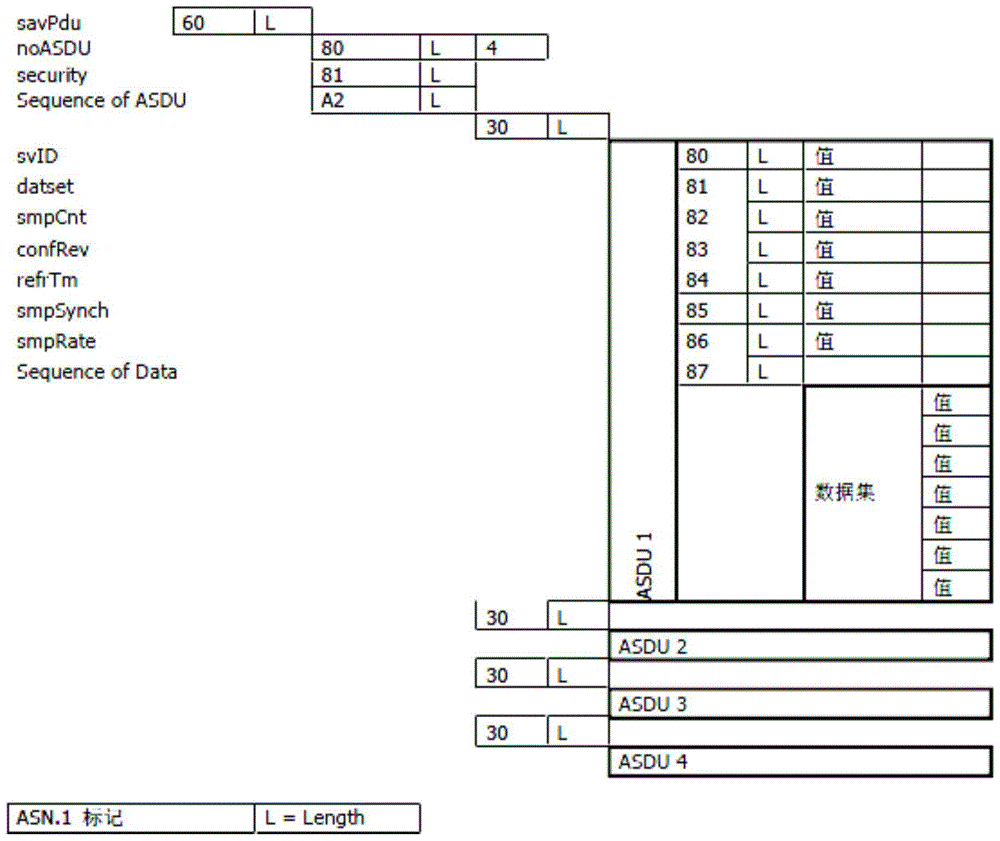
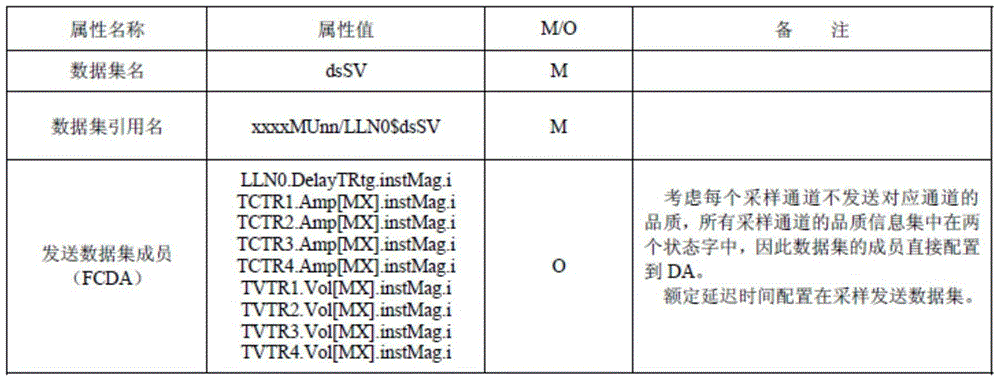
[0074] The synchronous merging unit is selected as the time reference source by judging the validity of the sampling number of the merging unit, and the time of the rising edge of the second pulse and the second pulse width can be calculated through the sampling number, rated delay time, and transmission delay. In order to achieve the above purpose, The specific embodiment of the present invention is as follows:
[0075] 1) Protection measurement and control devices (including but not limited to protection devices, measurement and control devices, integrated protection measurement and control devices, and station domain protection and control devices) can be analyzed and identified through the merging unit SV message without the need for external synchronous clock signals to cooperate with access Synchronization flag and sampling sequence number;
[0076] 2) Select at least two sets of merging units whose synchronization flag is 1 to calculate the validity of their sampling se...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com