Decoupling SVPWM (space vector pulse width modulation) based fault tolerance control method for open-winding PMSM (permanent magnet synchronous motor) driving system
A fault-tolerant control and drive system technology, applied in the direction of motor generator control, electronic commutation motor control, control system, etc., can solve the problems of fault-tolerant control system such as complex program and inapplicability, and achieve the effect of voltage utilization
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0025] Below in conjunction with specific embodiment, further illustrate the present invention, should be understood that these embodiments are only used to illustrate the present invention and are not intended to limit the scope of the present invention, after having read the present invention, those skilled in the art will understand various equivalent forms of the present invention All modifications fall within the scope defined by the appended claims of the present application.
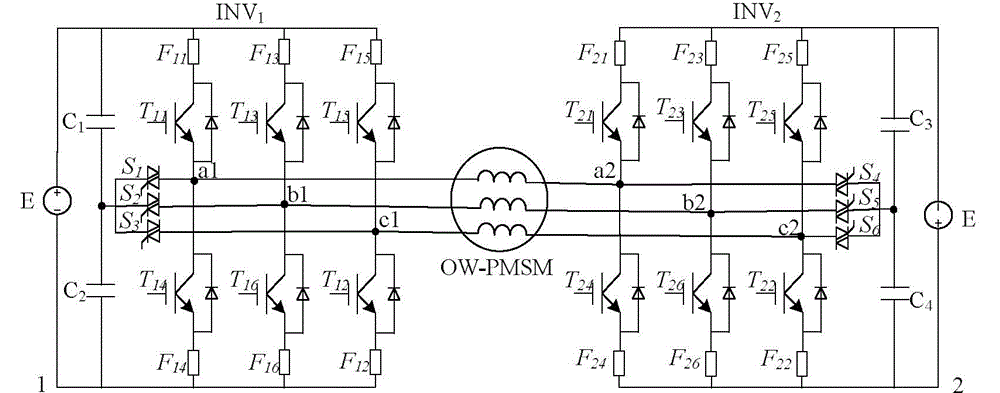
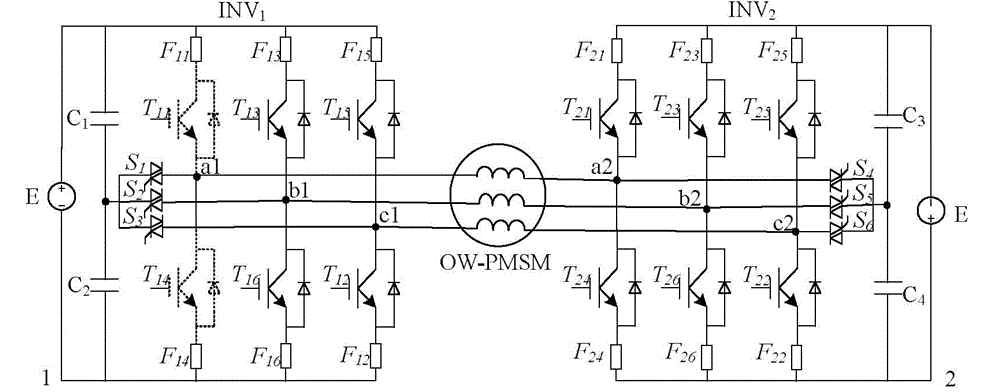
[0026] In order to facilitate the understanding of the technical solution of the present invention, firstly, the effective voltage vector output by the three-phase open-winding PMSM dual-inverter drive system in normal operation is introduced. figure 1 Structural diagram of the open-winding three-phase PMSM drive system for dual power supplies, the power supply voltages DC1 and DC2 of the dual inverters are both E.
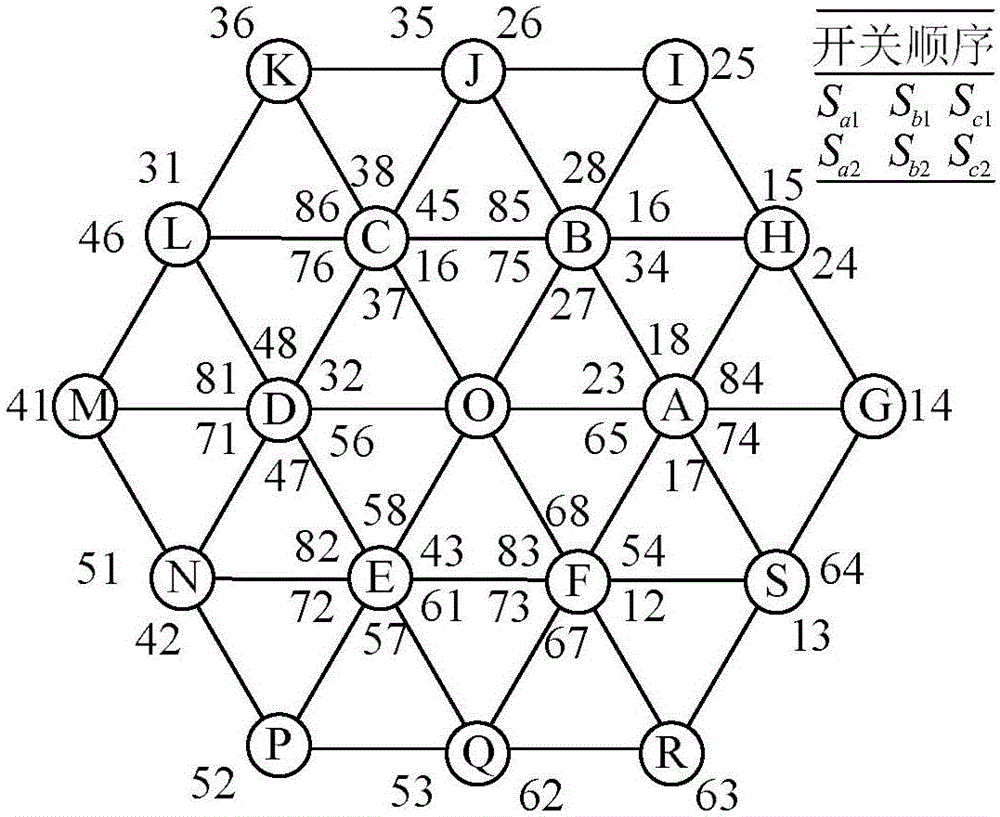
[0027] There are two switch states for each phase arm of the dual inverter system...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com