Thermal energy recycling process based on viscose staple fiber drying waste heat
A technology of viscose staple fiber and waste heat, which is applied in the processing of textile materials, textiles and papermaking, and the removal of liquid/gas/steam, etc. It can solve the problems of single layout, short process, and poor utilization rate, so as to reduce steam consumption, Reduce the loss of heat energy and accelerate the effect of water evaporation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
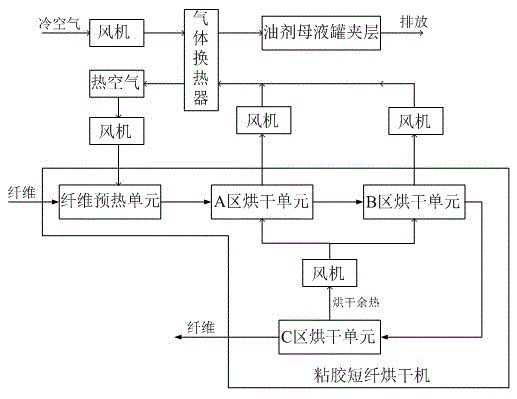
[0033] The present invention proposes a heat energy reuse process based on viscose staple fiber drying waste heat. In this embodiment, the heat energy reuse process is a process of classifying and reusing the waste heat of viscose staple fiber dryer. The heat energy and humidity contained in the waste heat of each unit of the staple fiber dryer are different. The viscose staple fiber dryer is divided into areas, which can be divided into fiber preheating units, high-temperature waste heat units and drying waste heat units connected in sequence. In actual operation, the following steps can be used for processing:
[0034] (1) Classification processing: According to the above-mentioned regional division results, the waste heat generated by each unit is collected separately, that is, fans are respectively installed on the air outlets of the high-temperature waste heat unit and the drying waste heat unit, and the high-temperature waste heat generated by the high-temperature waste h...
Embodiment 2
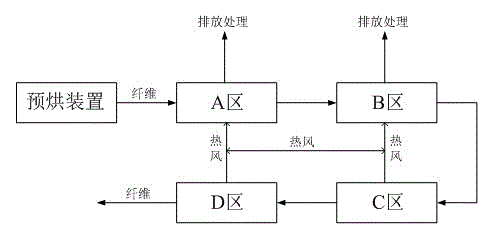
[0037] The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that this embodiment is applicable to the viscose production industry with a production capacity of about 50,000 tons / year. In its production process, the viscose staple fiber dryer includes A, B, C Three drying areas, that is, the A area drying unit, the B area drying unit and the C area drying unit connected to the fiber preheating unit in sequence. In the actual production process, the A area drying unit and the B area drying unit The unit is a high-temperature waste heat unit, and the temperature of the high-temperature waste air generated is 85°C and the humidity is 98%. %.
[0038] In actual operation, the following steps can be used for processing:
[0039] (1) Classification treatment: Install fans on the air outlets of the drying units in A, B, and C respectively to collect the high-temperature residual air generated by the drying units in A and B respectively. And the drying residual air produced by ...
Embodiment 3
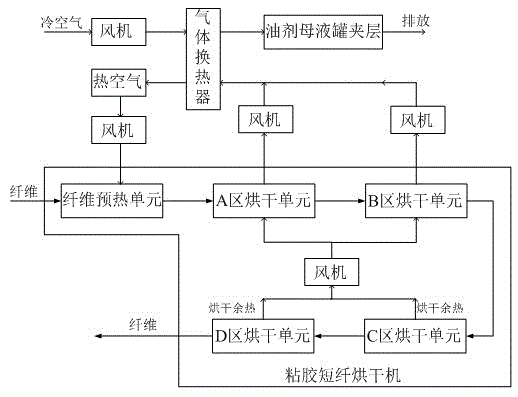
[0042] The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that this embodiment is applicable to the viscose production industry with a production capacity of about 100,000 to 120,000 tons / year. Taking the production of viscose with a production capacity of 100,000 tons / year as an example, in its production process Among them, the viscose staple fiber dryer includes four drying areas A, B, C, and D, that is, it includes the A area drying unit, the B area drying unit, and the C area that are connected to the fiber preheating unit in sequence. Drying unit and D area drying unit. In the actual production process, the A area drying unit and the B area drying unit are high-temperature waste heat units, and the temperature of the high-temperature waste air generated is 95°C and the humidity is 99.9%; C The drying unit in the area and the drying unit in the D area are drying waste heat units. Among them, the temperature of the drying residual air generated by the drying unit in...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com