Low-secretion protease a saccharomyces cerevisiae strain and construction method thereof
A technology of Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain and protease, which is applied in the field of bioengineering, can solve the problems of abnormal temperature sensitivity of bacteria, temperature sensitivity, and influence on the growth and polarity transport of reproductive cells, so as to increase the fermentation speed, improve the foam retention, fermentation performance and good growth performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0067] Example 1: Construction of low-secretion protease A Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain WS5
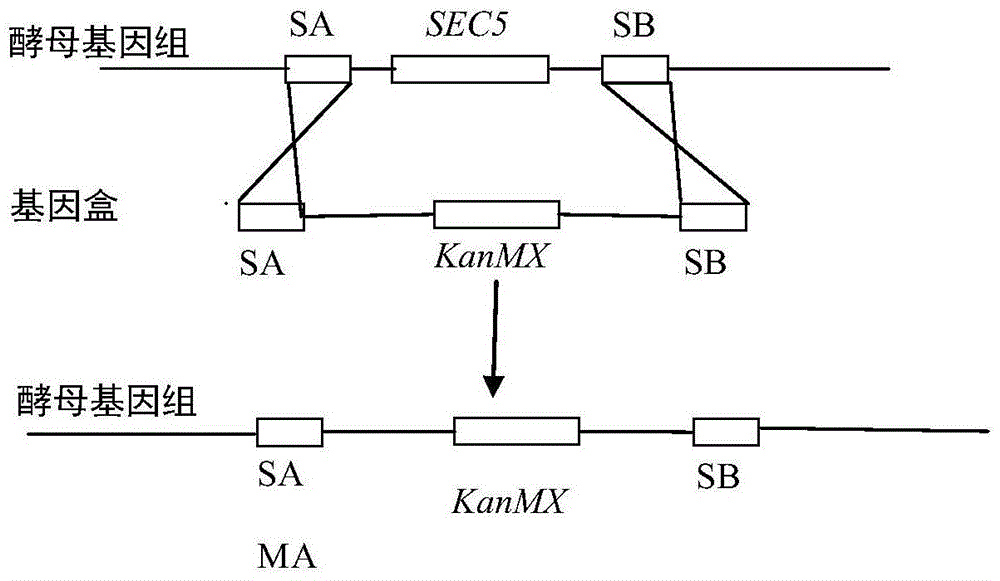
[0068] The starting strain W303-1A was constructed by two homologous recombination methods to construct recombinant genetically engineered strains.
[0069] According to the yeast genome data in Genebank and the integrated plasmid sequence, the primers in the following examples were designed.
[0070] Table 1 Primers used in this example
[0071]
[0072]
[0073] Note: The underlined part indicates the enzyme cutting site
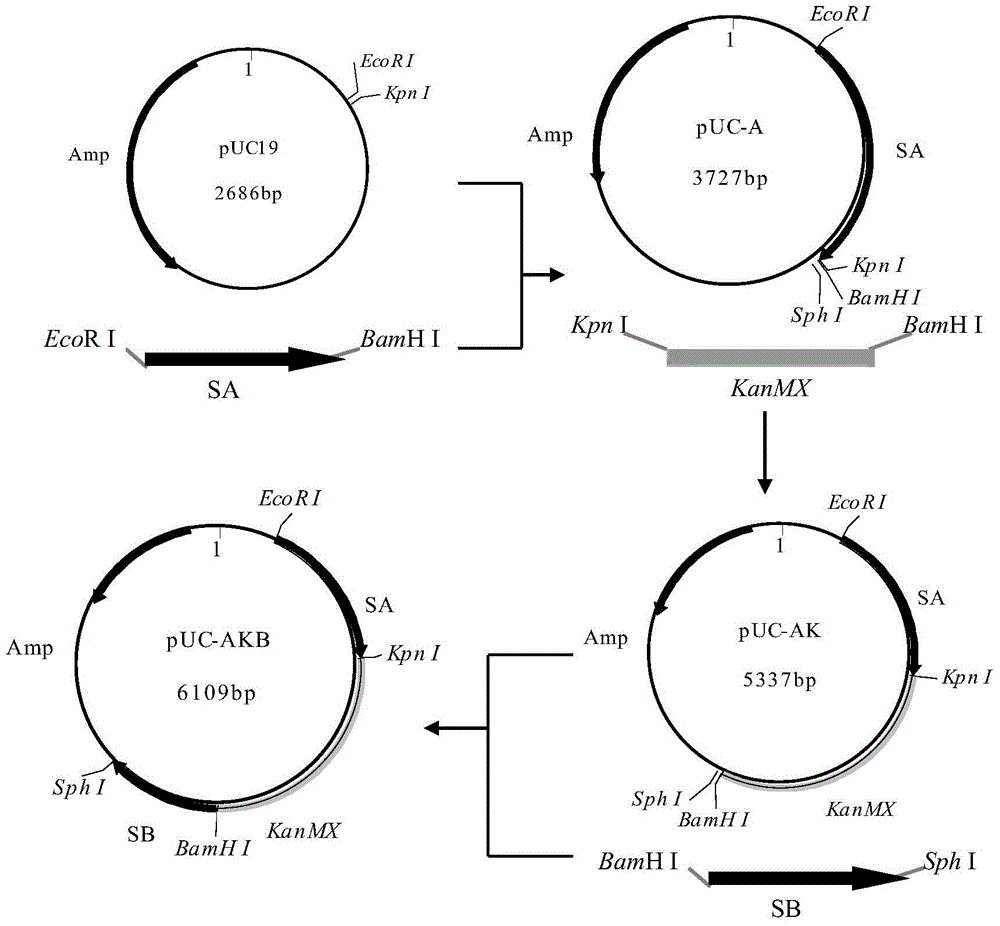
[0074] (1) Construction of recombinant plasmid pUC-AKB
[0075] The construction process of the recombinant plasmid pUC-AKB is as follows: figure 1 shown.
[0076] ① Using the total DNA of the yeast strain W303-1A as a template, the upstream sequence SA of the SEC5 gene was amplified by PCR with primers SA1 and SA2;
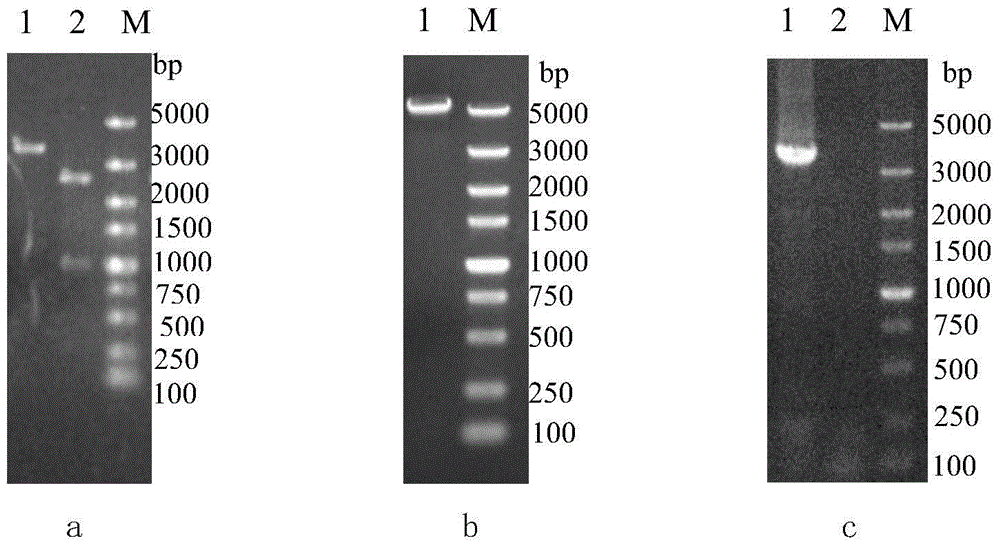
[0077] PCR reaction conditions: 95°C for 5min; 94°C for 45s; 61°C for 45s; 72°C for 30s, 30 cycles; 72°C for 10min, 0.8% agarose gel e...
Embodiment 2
[0100] Example 2: Construction of low-secretion protease A Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain SS5-2
[0101] The starting strain S6 was constructed by two homologous recombination methods to construct recombinant genetically engineered strains. The primers used in this example are the same as those in Example 1.
[0102] (1) Knockout of one allele of SEC5
[0103] Using the recombinant plasmid pUC-AKB obtained in Example 1-(1) as a template, the recombinant gene cassette SA-KanMX-SB fragment was obtained by PCR amplification. Using the method described in Example 1-(2), the recombination cassette was introduced into the starting strain S6 to obtain an allelic knockout recombinant strain SS5K-1. Extract the genome of SS5K-1 as a template, and carry out PCR amplification with primers S1U / S1D and S2U / S2D respectively to obtain 1276bp (nucleotide sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO: 2) and 1715bp (nucleotide sequence The band shown in SEQ ID NO: 3); and the band of 1276bp and 1715bp ca...
Embodiment 3
[0110] Embodiment 3: Fermentation experiment of low-secretion protease A Saccharomyces cerevisiae WS5
[0111] The starting strain W303-1A and the recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae laboratory strain WS5 were simultaneously subjected to beer fermentation experiments. Nitrogen source deficient wort production process: Weigh a certain amount of crushed malt, saccharify at 65°C according to the material-water ratio of 1:4 until the iodine test is completed, adjust the apparent sugar content to 5°Brix with a sugar meter, and then add glucose to The appearance Brix is 10°Brix. Centrifuge the cultivated seed solution to obtain yeast slurry, put it into nitrogen-deficient wort medium according to the inoculum size of 0.8%, and let it stand for fermentation at 16° C. for 5 days.
[0112] (1) Protease A activity and bubble retention of low-secretion protease A strain WS5
[0113] The foam persistence of the starting strain W303-1A and the recombinant strain WS5 was determined by ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com