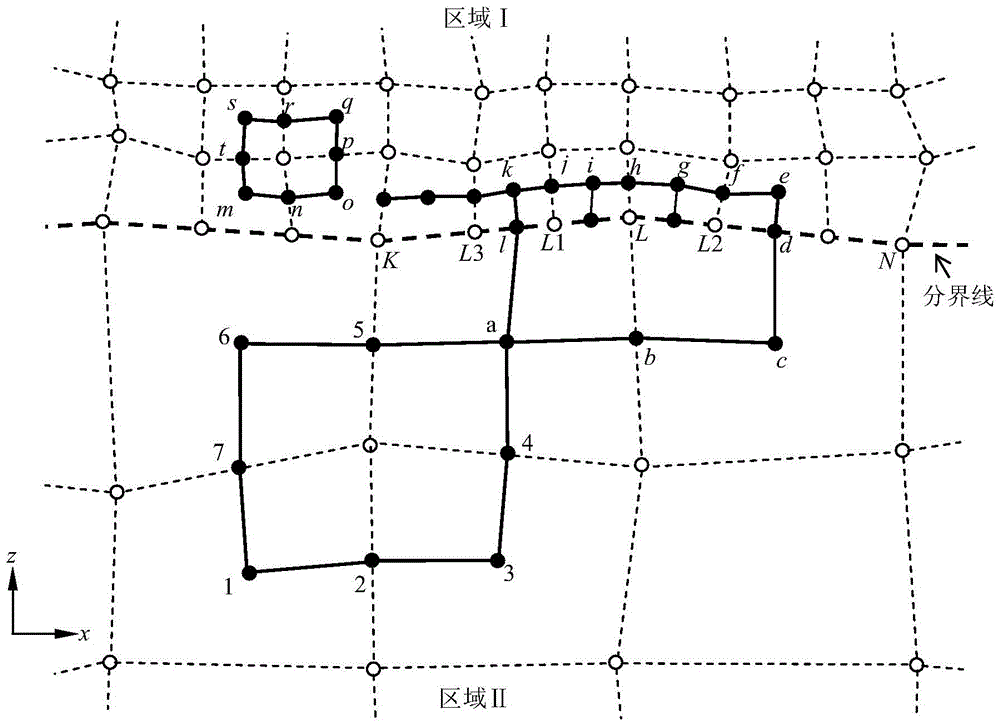
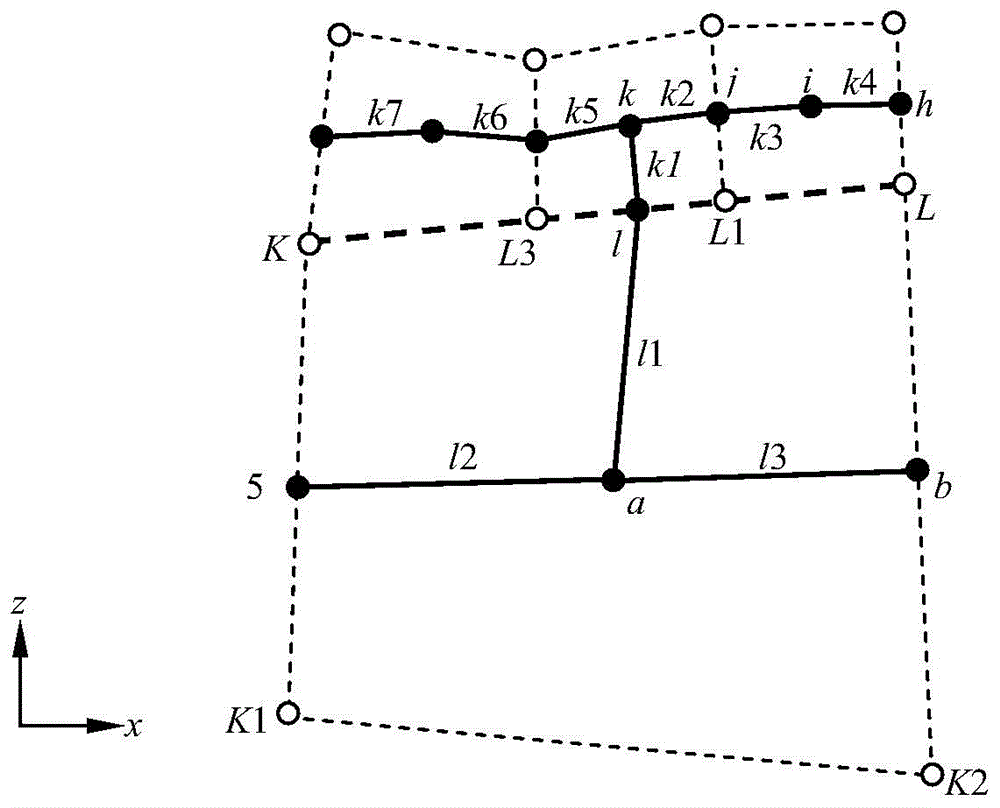
Grid grading method for near-surface ground motion simulation
A classification method and ground motion technology, applied in the fields of engineering wave theory and seismology, which can solve problems such as high requirements on grid shape and discreteness
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
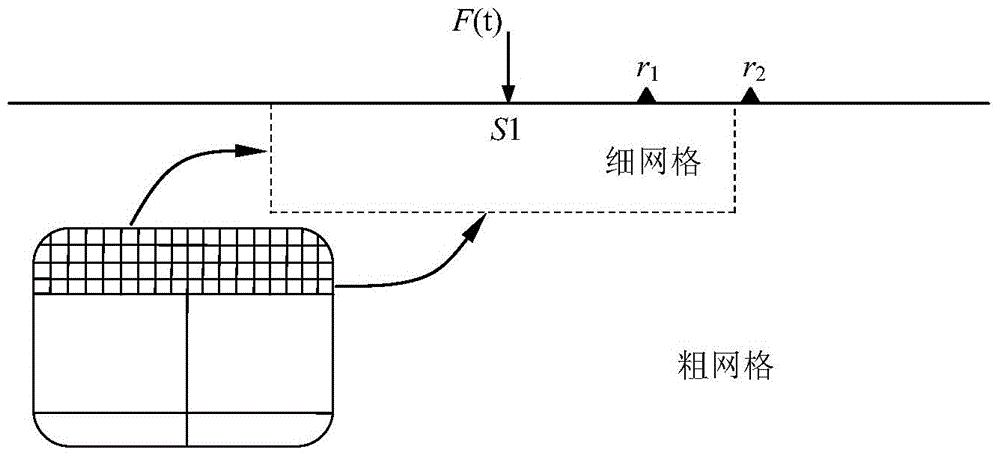
[0159] Example 1: Comparison with Lamb analytical solution results
[0160] image 3 It is the computational model compared with the Lamb analytical solution. In the figure, the force source F(t)=exp[-α(t-t 0 )], α=90 and t 0 = 0.3s. The smaller area of the calculation model is discretized with a 10m square grid, and the larger areas are discretized with a 30m, 50m, 70m and 90m square grid respectively. Two observation points r 1 and r 2 The distance from the loading point S1 is 2000m and 5310m respectively, and the observation point r 1 On a fine mesh surface, the observation point r 2 Located on the surface of the coarse grid and separated from the boundary line of the coarse and fine grid ( image 3 The dotted line in ) is 360m apart. The P wave velocity of the medium in the elastic half space is 5196m / s, the SV wave velocity is 3000m / s, and the density is 2300Kg / m 3 . The time step used in the calculation is 0.001s, and the calculation time is 4s.
[0161] ...
Embodiment 2
[0164] Example 2: Simulation of near-surface ground motion under complex site conditions
[0165] Figure 7 Computational models for sedimentary basins and undulating surfaces. In the figure, the observation point Ra is located at the apex of the left mountain peak, and the relative horizontal and vertical distances between the observation point Rc (located on the left edge of the basin) and Ra are 2.4km and 1.2km respectively; the observation point Rb is located at the apex of the right mountain peak , the relative horizontal and vertical distances between observation point Rd (located on the right edge of the basin) and Rb are 1.9km and 0.8km, respectively. Located on the mountainside on the left, a total of 19 observation points are set between observation points Ra and Rc; on the surface of the sedimentary basin, a total of 28 observation points are set between observation points Rc and Rd; on the right mountainside, observation point Rd A total of 12 observation points ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com