Solar sail transient dynamic analyzing method for determining effective propulsion acceleration breakage
A dynamic analysis and acceleration technology, applied in the field of transient dynamic analysis of solar sails, can solve the problems of large calculation error of the non-time-varying light pressure model, missing multiplication, and not considering the time-varying effect of light pressure.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
[0067] Example: Static finite element simulation analysis of 160m solar sail structure
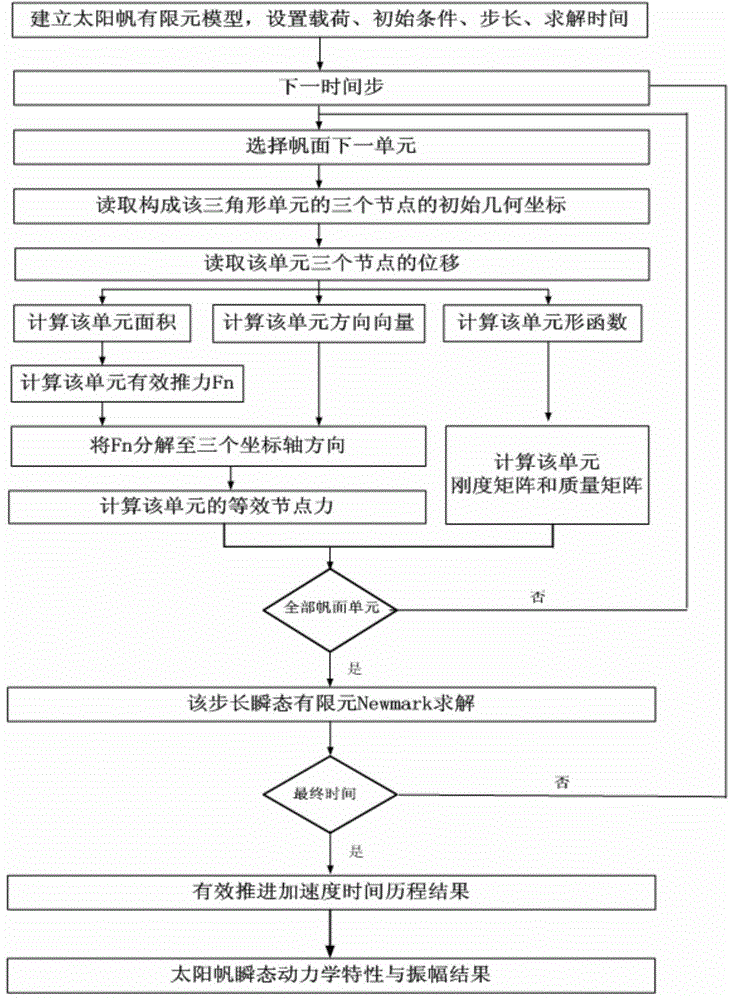
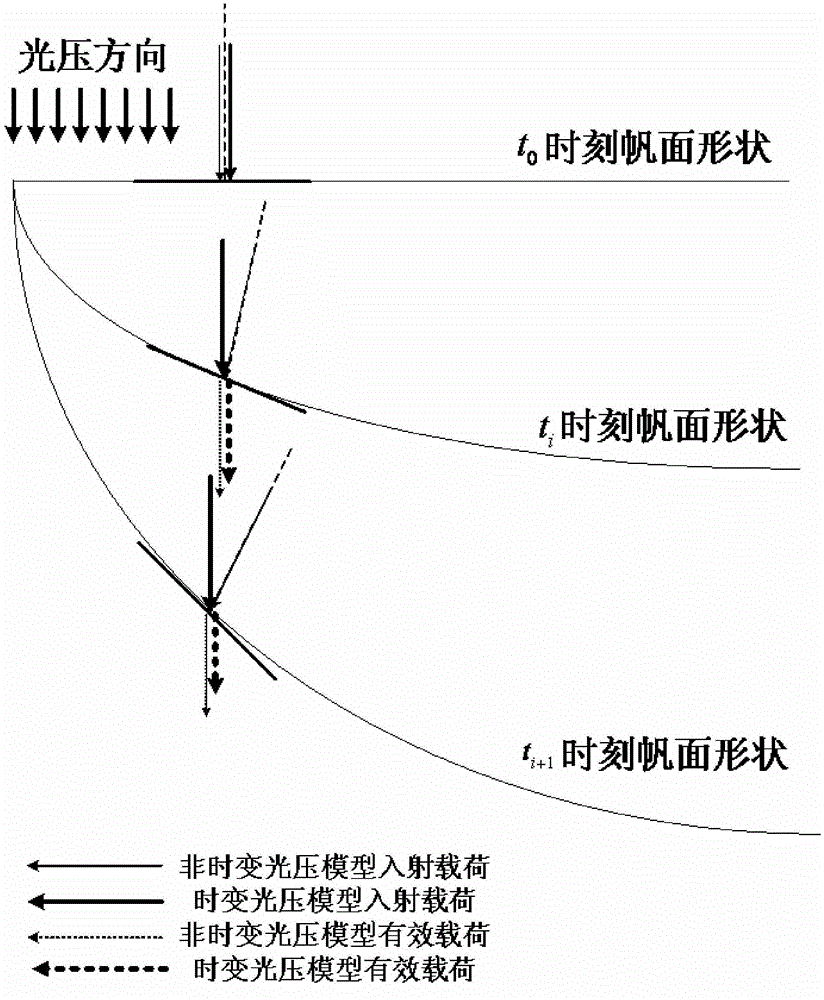
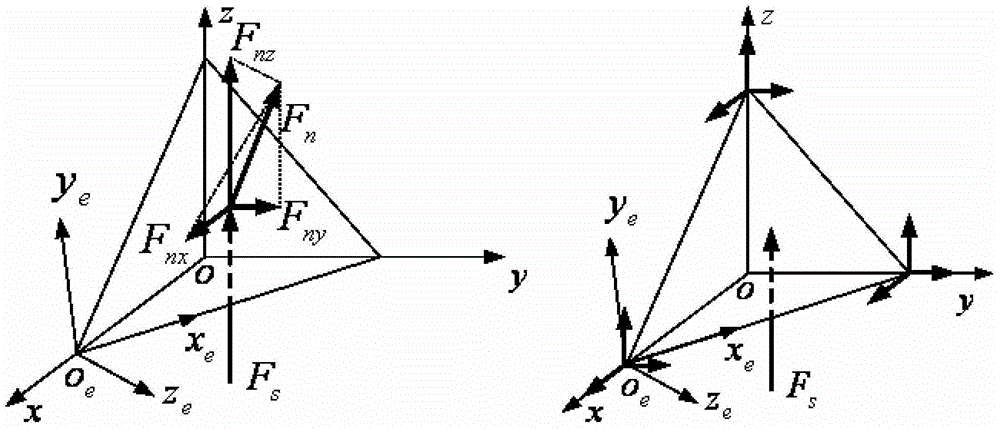
[0068] 1) Establish the finite element model of the solar sail, as shown in 4, which mainly includes: separately establish the support arm one-dimensional beam element and the sail surface two-dimensional triangular shell element model, set the square sail side length to 160m, and set the center body mass m center =100kg, end counterweight m vertex =12.4kg, the central body moment of inertia J center =0kg·m 2 , Support arm outer diameter D=300mm, wall thickness b=0.1mm, sail thickness h=1.5μm; set support arm material property E beam =210GPa, γ beam = 0.33, ρ beam =848kg / m 3 , Sail film material property E sail =2.5GPa, γ sail = 0.34, ρ sail =1420kg / m 3 ; Set the direction of prestress as two normal stresses in the sail surface, the magnitude is 50000Pa; Set the initial time t for solution 0 =0s, the final time t n = 400s and time step Δt = 0.5s, and the velocity and acceleration column...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com