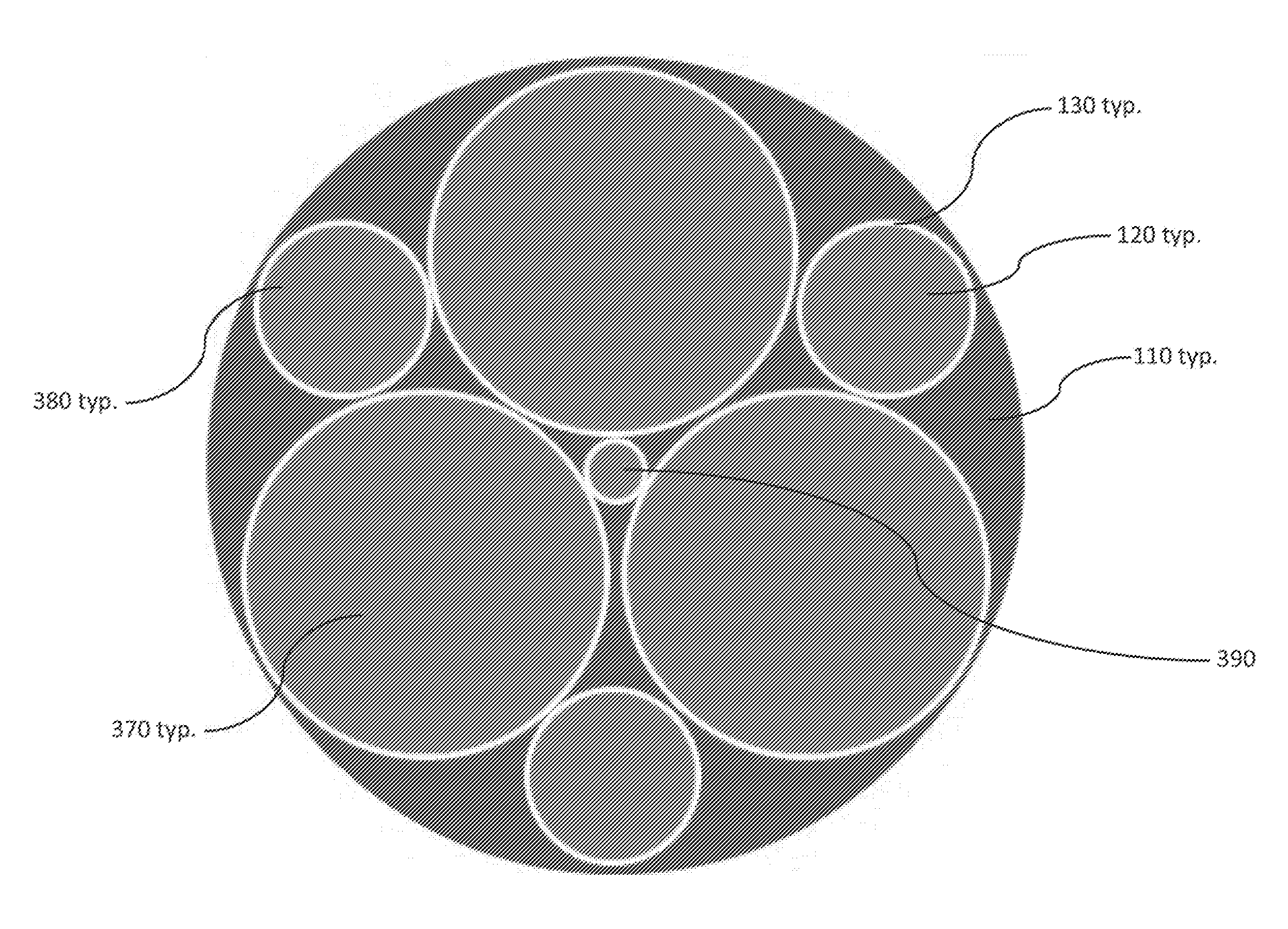Patents
Literature
232 results about "Shell element" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
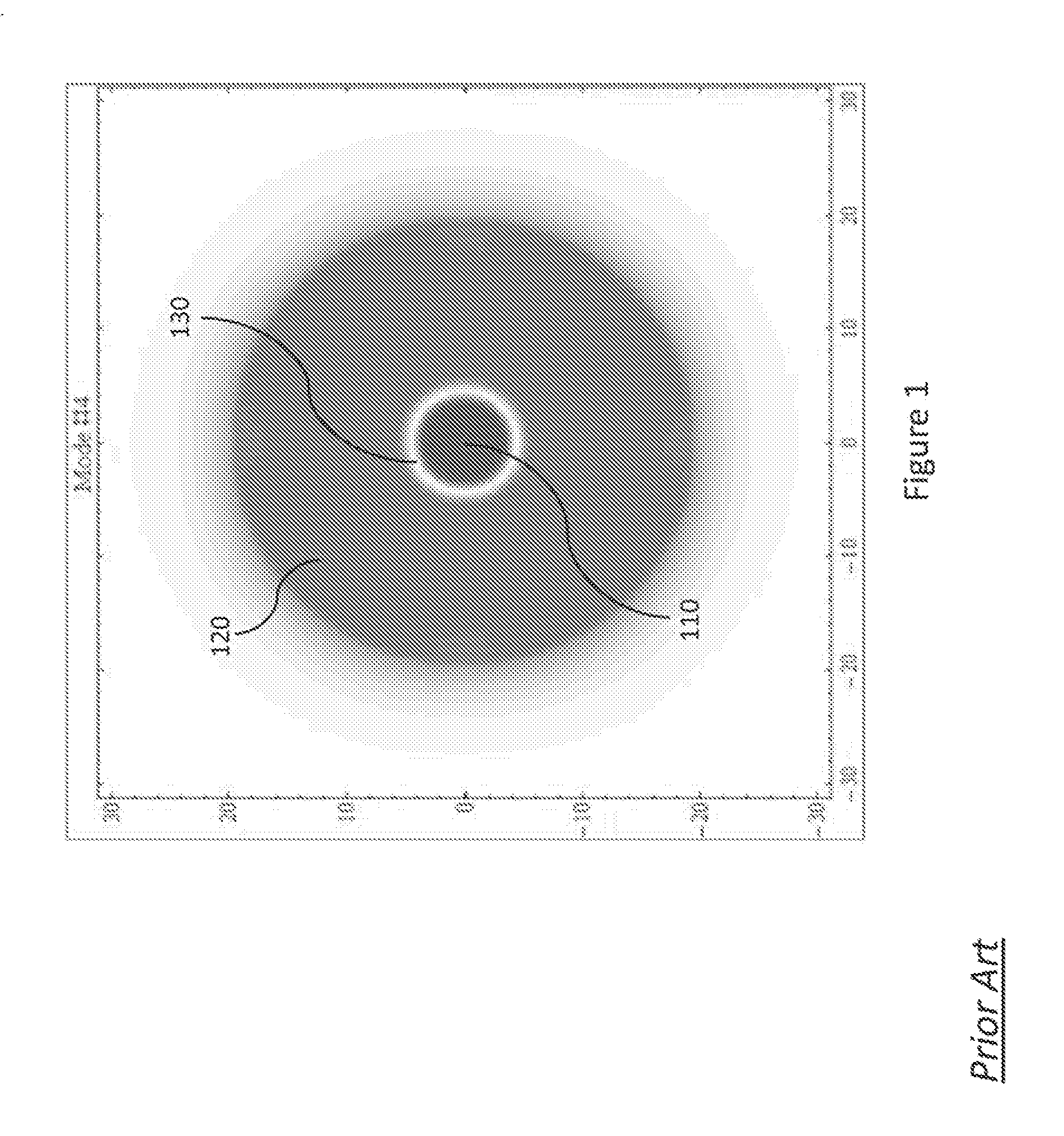
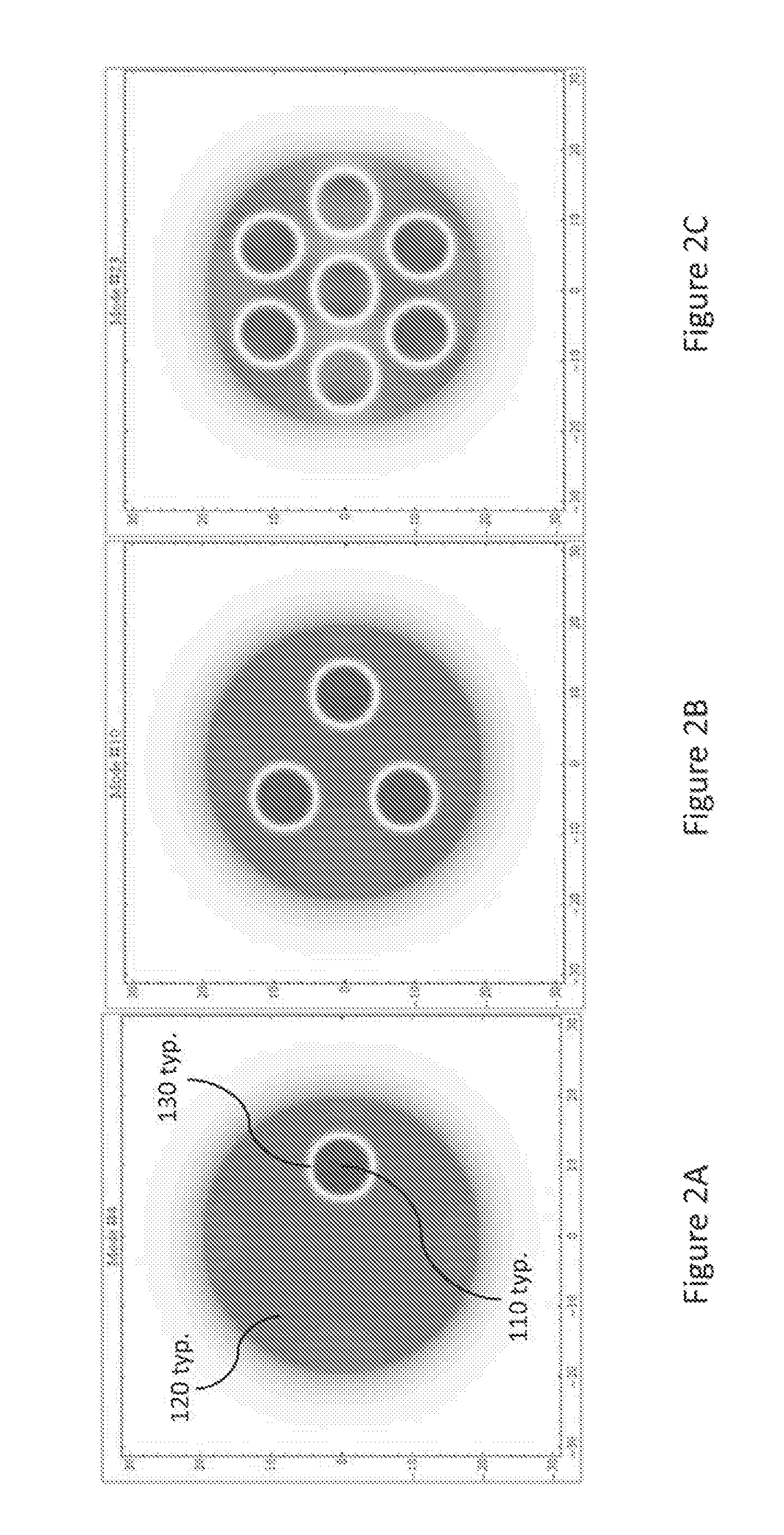
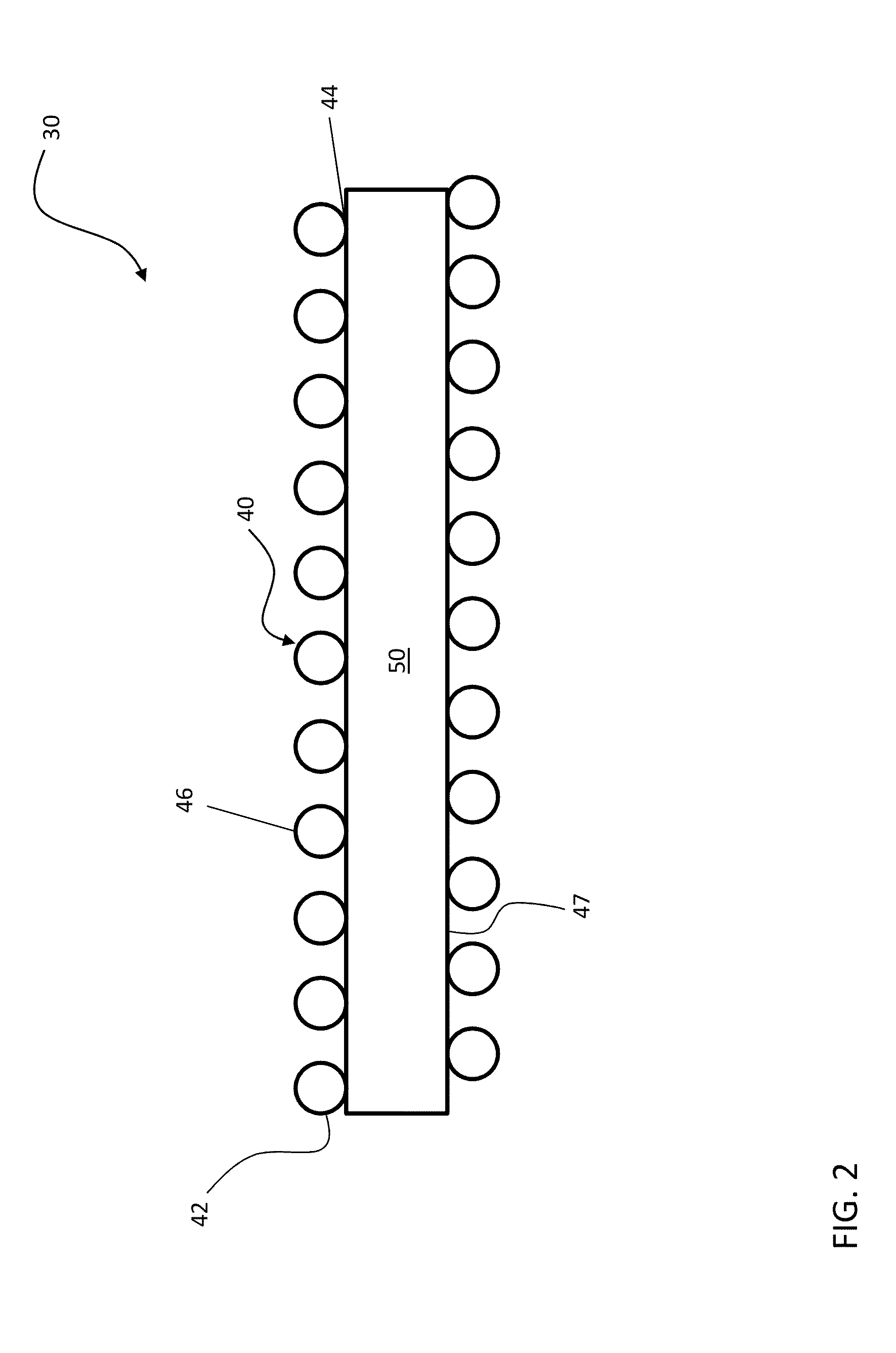
Shell elements are 4- to 8-node isoparametric quadrilaterals or 3- to 6-node triangular elements in any 3-D orientation. The General and Co-rotational shell element is formulated based on works by Ahmad, Iron and Zienkiewicz and later refined by Bathe and Balourchi.
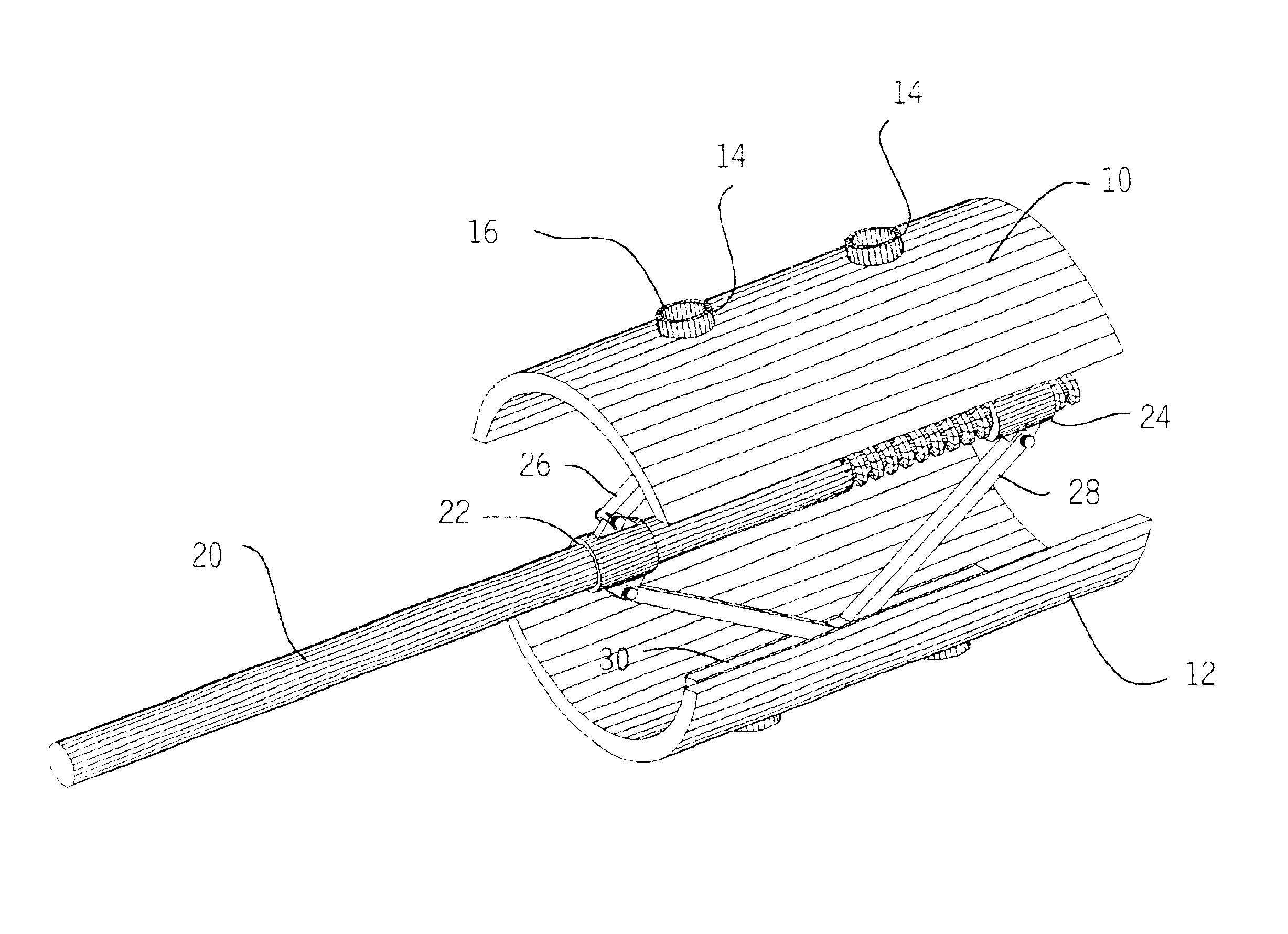
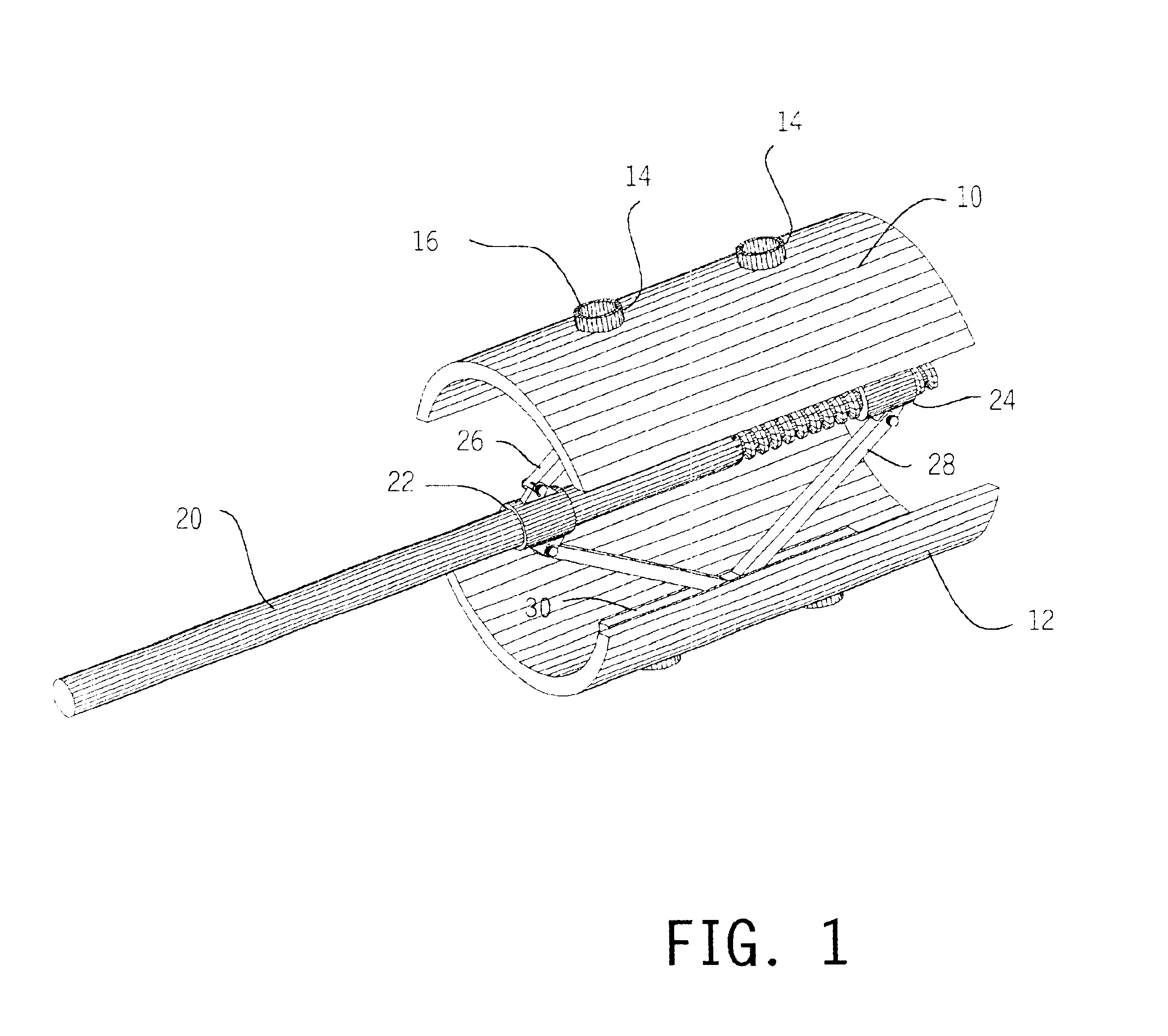
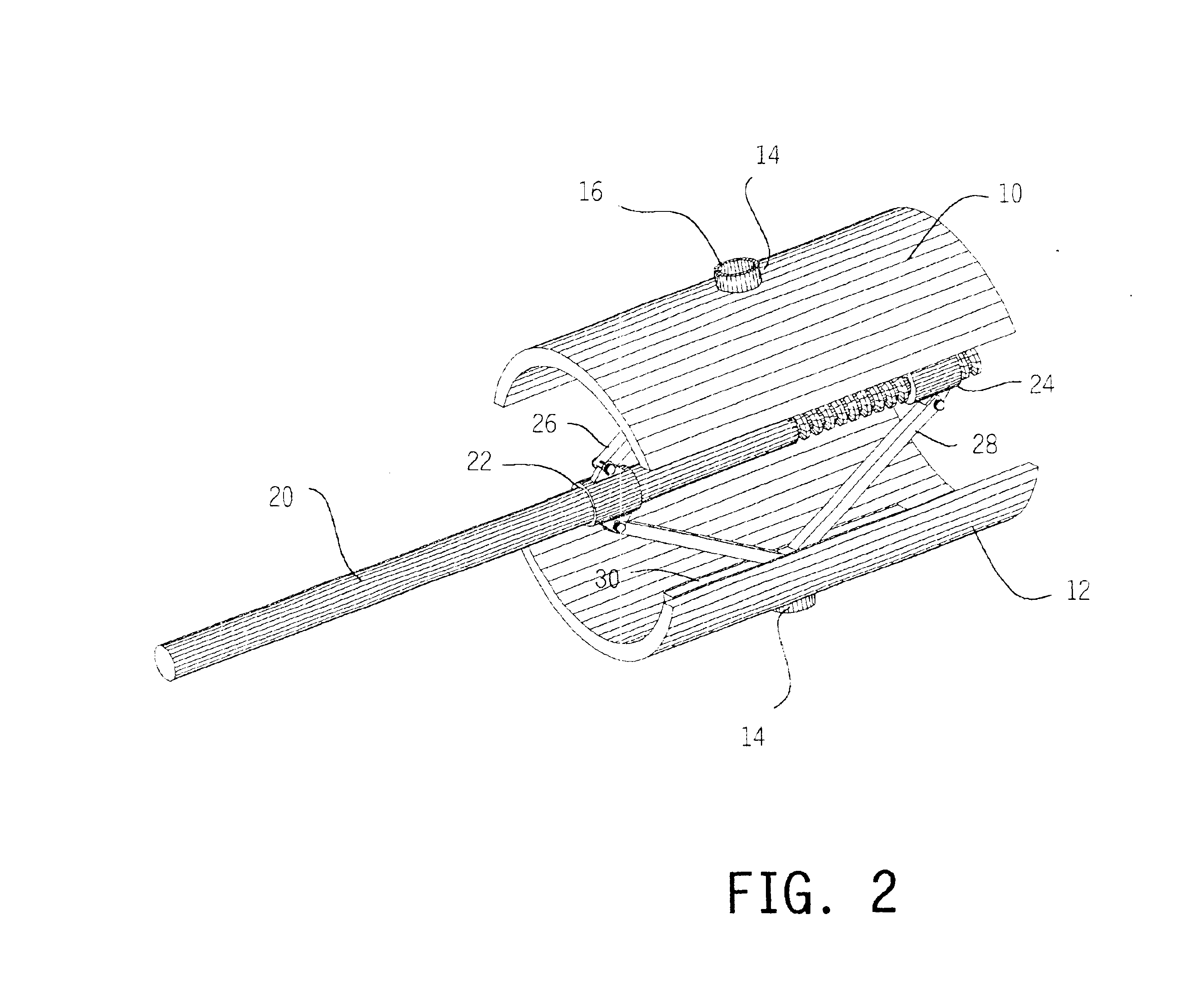
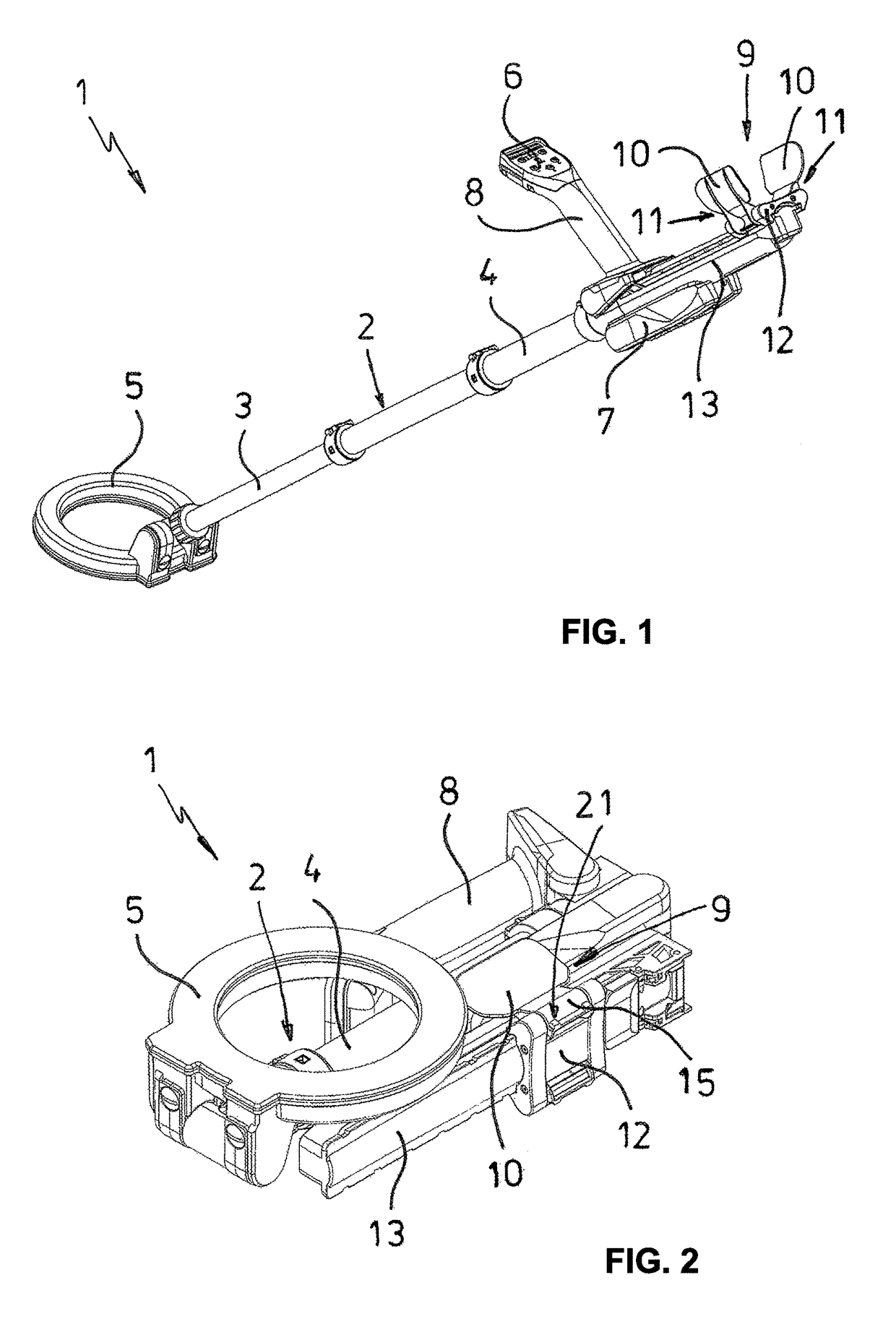
Vertebral body end plate cutter
InactiveUS6840944B2Easy to integrateEasy to manufactureFractureEndoscopic cutting instrumentsProsthesisEngineering
Precision recesses are cut in the end plates of vertebral bodies by inserting into the disc space a cutter having a pair of shell elements provided with cutting edges shaped to match bone growth apertures in a selected prosthesis. The remainder of the end plates are left undisrupted, to maximize bearing strength while promoting bone growth at the apertures.
Owner:SUDDABY LOUBERT
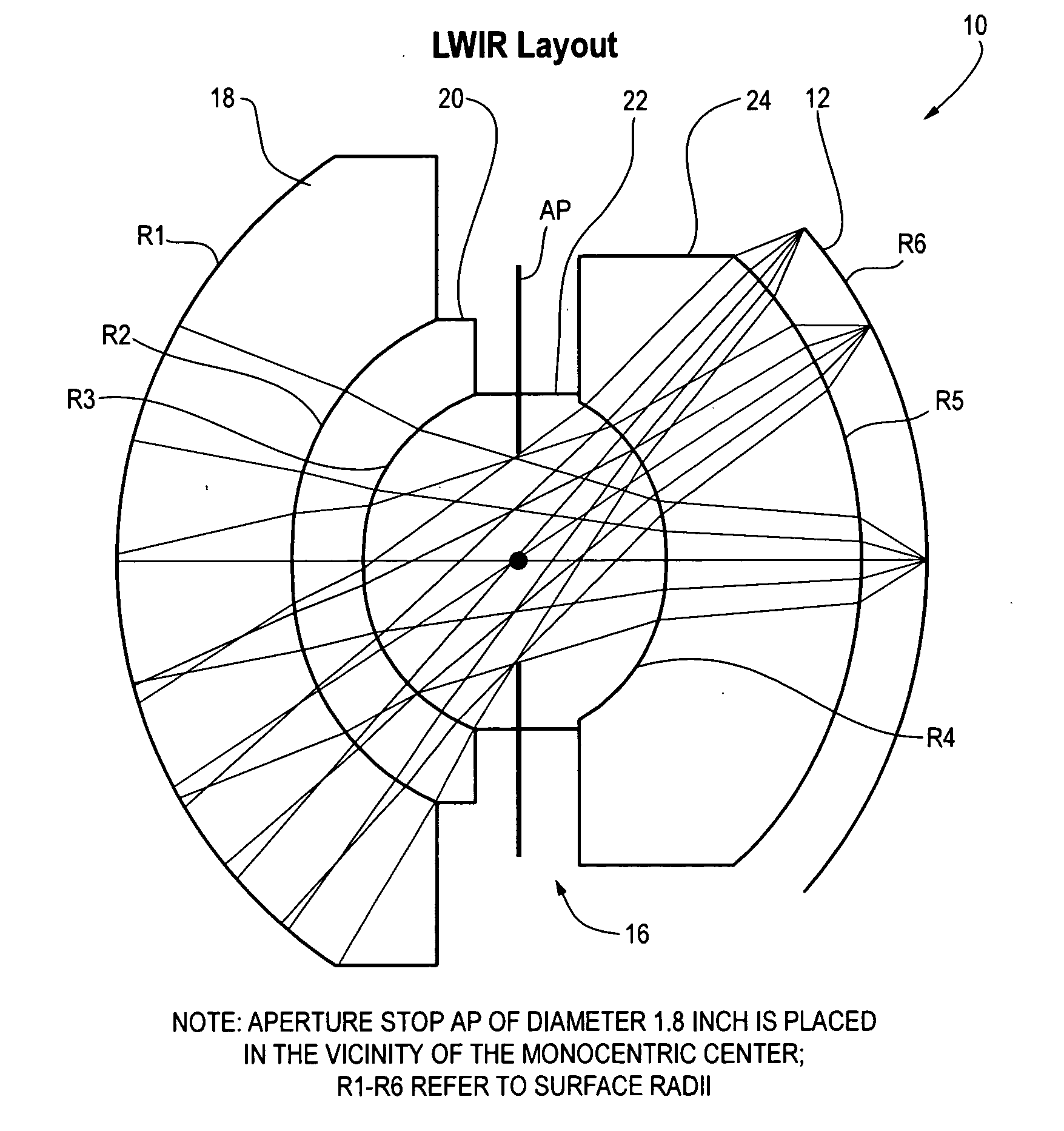
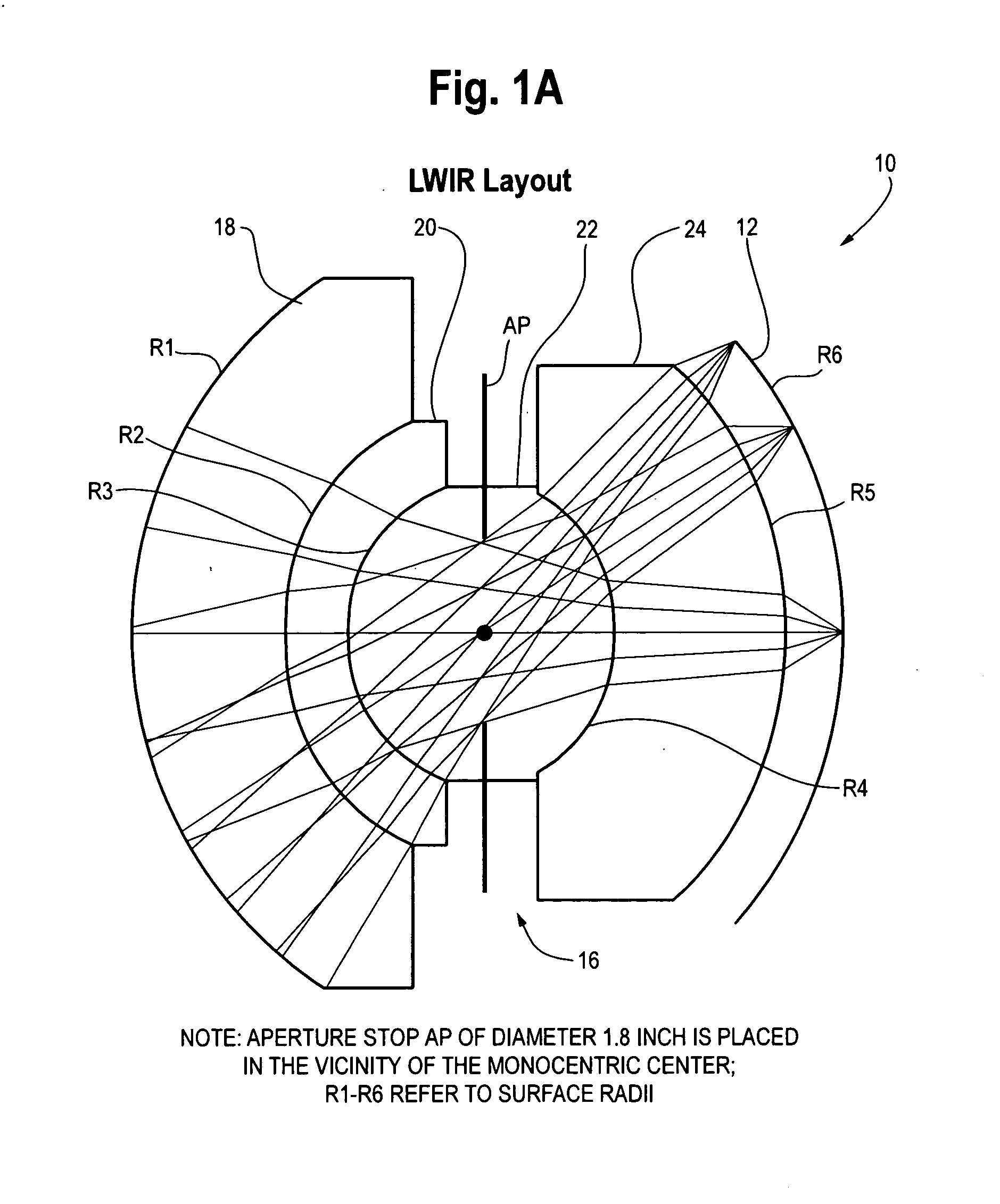
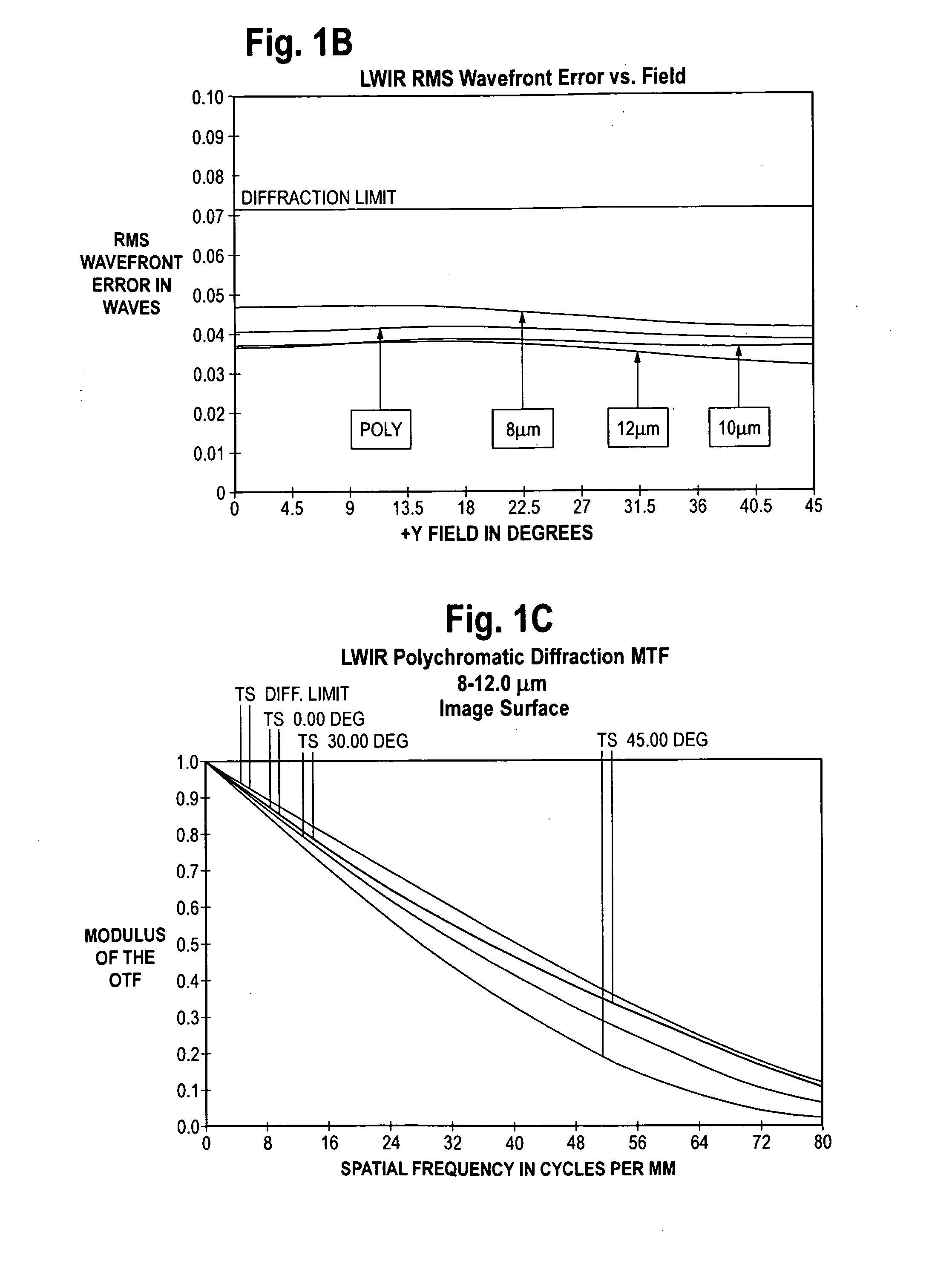
Wide field of view monocentric lens system for infrared aerial reconnaissance camera systems
ActiveUS20130076900A1Minimize chromatic aberrationMinimize spherical aberrationTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesAviationWide field
A wide field of view monocentric lens system for an infrared aerial reconnaissance camera includes front and rear lens shell elements and a core lens element, with the number of front and rear shell lens elements depending on the IR band of interest (LWIR, MWIR or SWIR). Infrared radiation entering the monocentric lens passes sequentially through the front shell lens element(s), the core lens element, and the rear shell lens element(s) and is focused onto a curved focal surface. The front shell lens element(s) and the rear shell lens element(s) are made of material having a relatively higher refractive index or a relatively higher optical dispersion, or both, in the band of interest, as compared to the core lens element.
Owner:THE BF GOODRICH CO
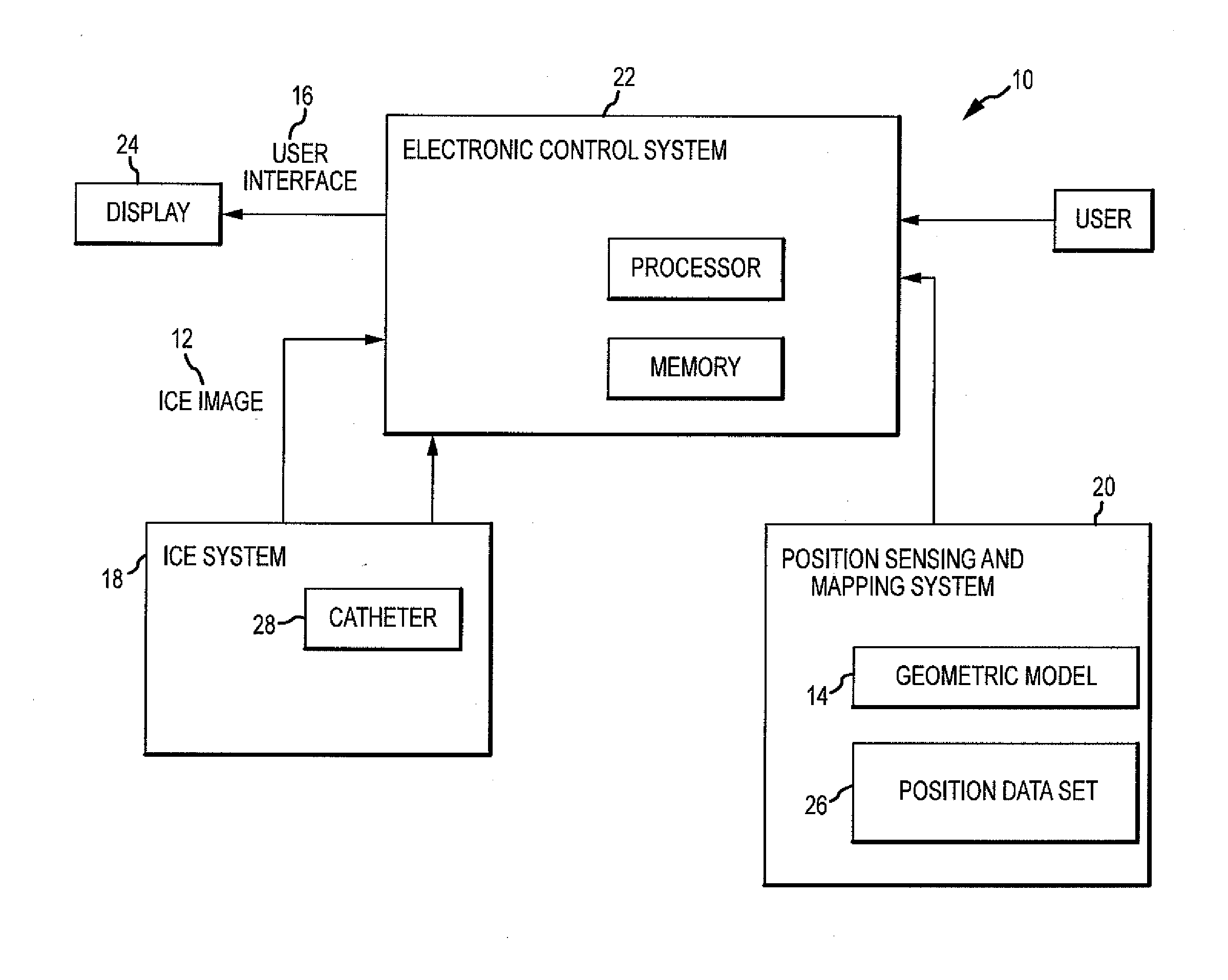
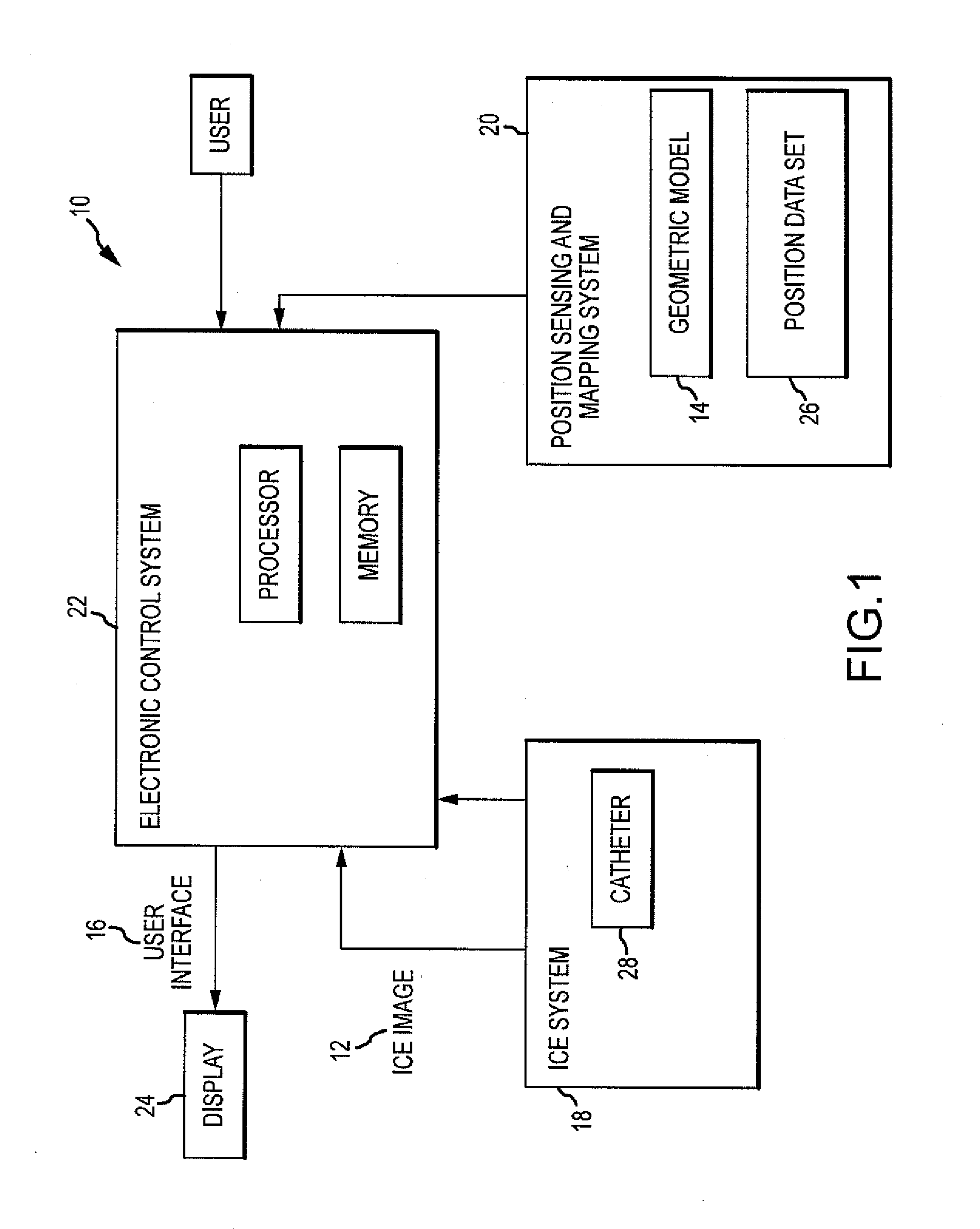
Automatic identification of intracardiac devices and structures in an intracardiac echo catheter image
InactiveUS20120172724A1Easy to browseAccurate modelingUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsCatheterIntracardiac echocardiographyIntracardiac electrode
An intracardiac imaging system configured to display electrode visualization elements within an intracardiac echocardiography image where the electrode visualization elements represent intracardiac electrodes in close proximity to the plane of the image. The system further allows cross sections of tissue structures embodied in intracardiac echocardiography images to be modeled within a visualization, navigation, or mapping system when automatically segmented to generate shell elements for modifying the modeled tissue structures.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
Waveguides having patterned, flattened modes
ActiveUS9170367B2Easy to cleanly exciteAvoid problematic hot spotGlass making apparatusMechanical apparatusFiberEngineering
Field-flattening strands may be added to and arbitrarily positioned within a field-flattening shell to create a waveguide that supports a patterned, flattened mode. Patterning does not alter the effective index or flattened nature of the mode, but does alter the characteristics of other modes. Compared to a telecom fiber, a hexagonal pattern of strands allows for a three-fold increase in the flattened mode's area without reducing the separation between its effective index and that of its bend-coupled mode. Hexagonal strand and shell elements prove to be a reasonable approximation, and, thus, to be of practical benefit vis-à-vis fabrication, to those of circular cross section. Patterned flattened modes offer a new and valuable path to power scaling.
Owner:LAWRENCE LIVERMORE NAT SECURITY LLC
Waveguides having patterned, flattened modes
ActiveUS20130202264A1Easy to cleanly exciteAvoid problematic hot spotGlass making apparatusLaser detailsFiberEngineering
Field-flattening strands may be added to and arbitrarily positioned within a field-flattening shell to create a waveguide that supports a patterned, flattened mode. Patterning does not alter the effective index or flattened nature of the mode, but does alter the characteristics of other modes. Compared to a telecom fiber, a hexagonal pattern of strands allows for a three-fold increase in the flattened mode's area without reducing the separation between its effective index and that of its bend-coupled mode. Hexagonal strand and shell elements prove to be a reasonable approximation, and, thus, to be of practical benefit vis-à-vis fabrication, to those of circular cross section. Patterned flattened modes offer a new and valuable path to power scaling.
Owner:LAWRENCE LIVERMORE NAT SECURITY LLC
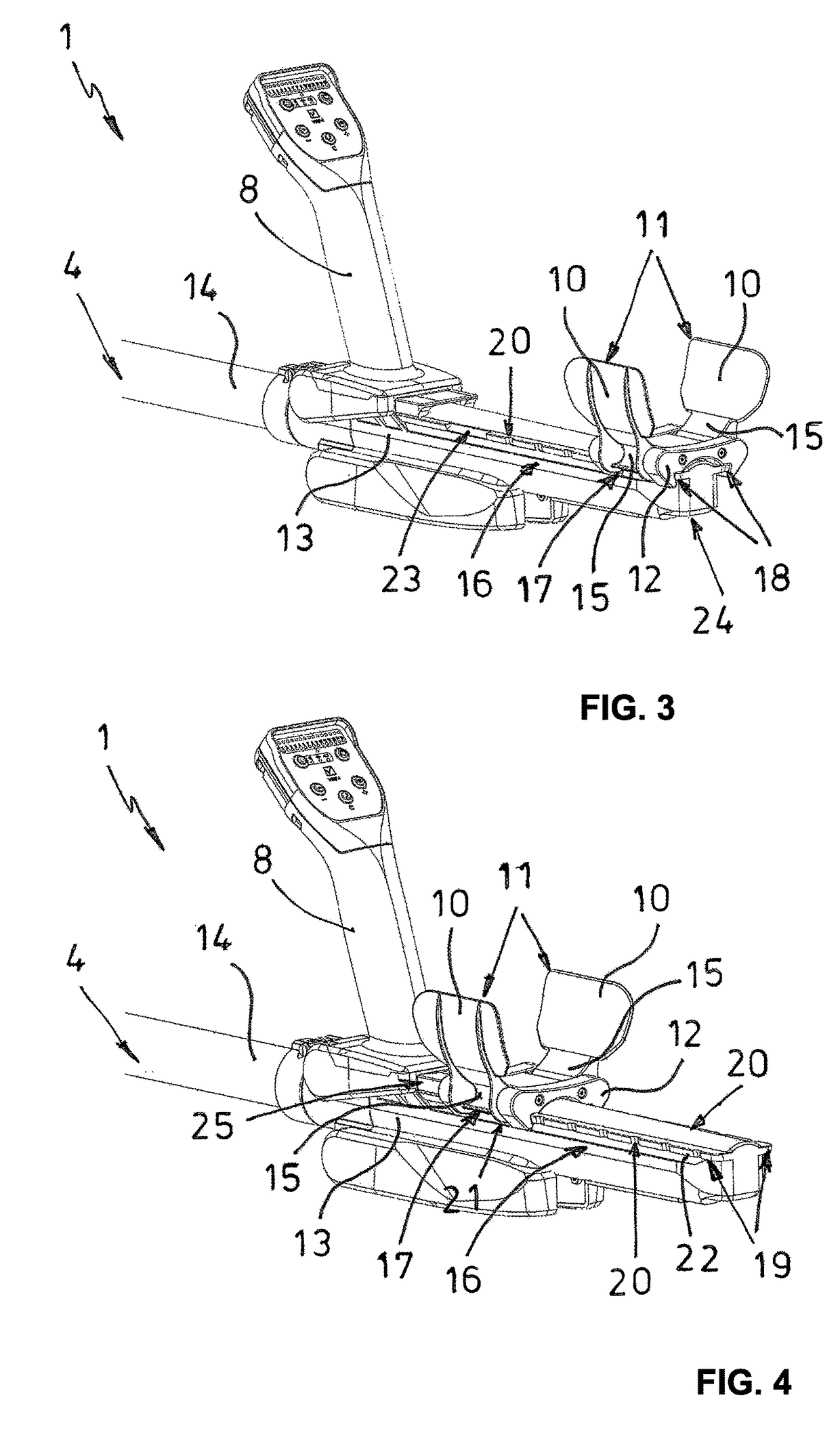
Detector with telescoping support pole and foldable arm support
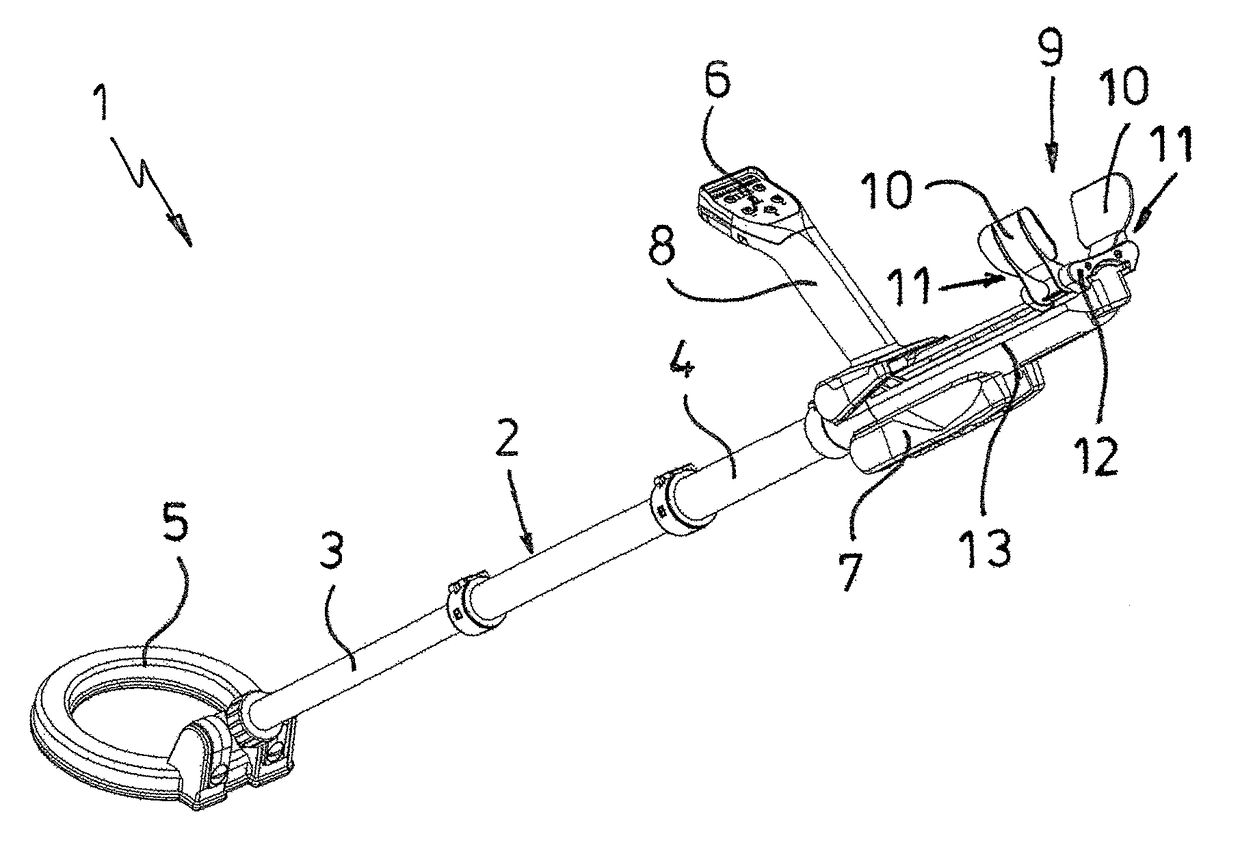
ActiveUS9864089B2Simple adaptationAdjustable distanceDefence devicesElectric/magnetic detection for transportEngineeringShell element
A detector with a telescoping support tube wherein a measuring probe is arranged at a front of a forward tube element and an electronics unit with a battery compartment, a handle element and axially offset rearward therefrom a U-shaped arm shell with two arm support bars are arranged at a rear tube element, wherein the arm support bars are pivotable relative to the rear tube element. The arm shell is axially moveable relative to the handle element and includes two arm shell elements which are laterally arranged at a support slide and pivotably moveable in a transversal direction of the support tube. The support slide is supported axially moveable by a support rail. According to the invention it is provided that the support slide is fixateable in a disengageable manner at the support rail at various locations through the arm shell elements.
Owner:VALLON 72800 ENINGEN DE
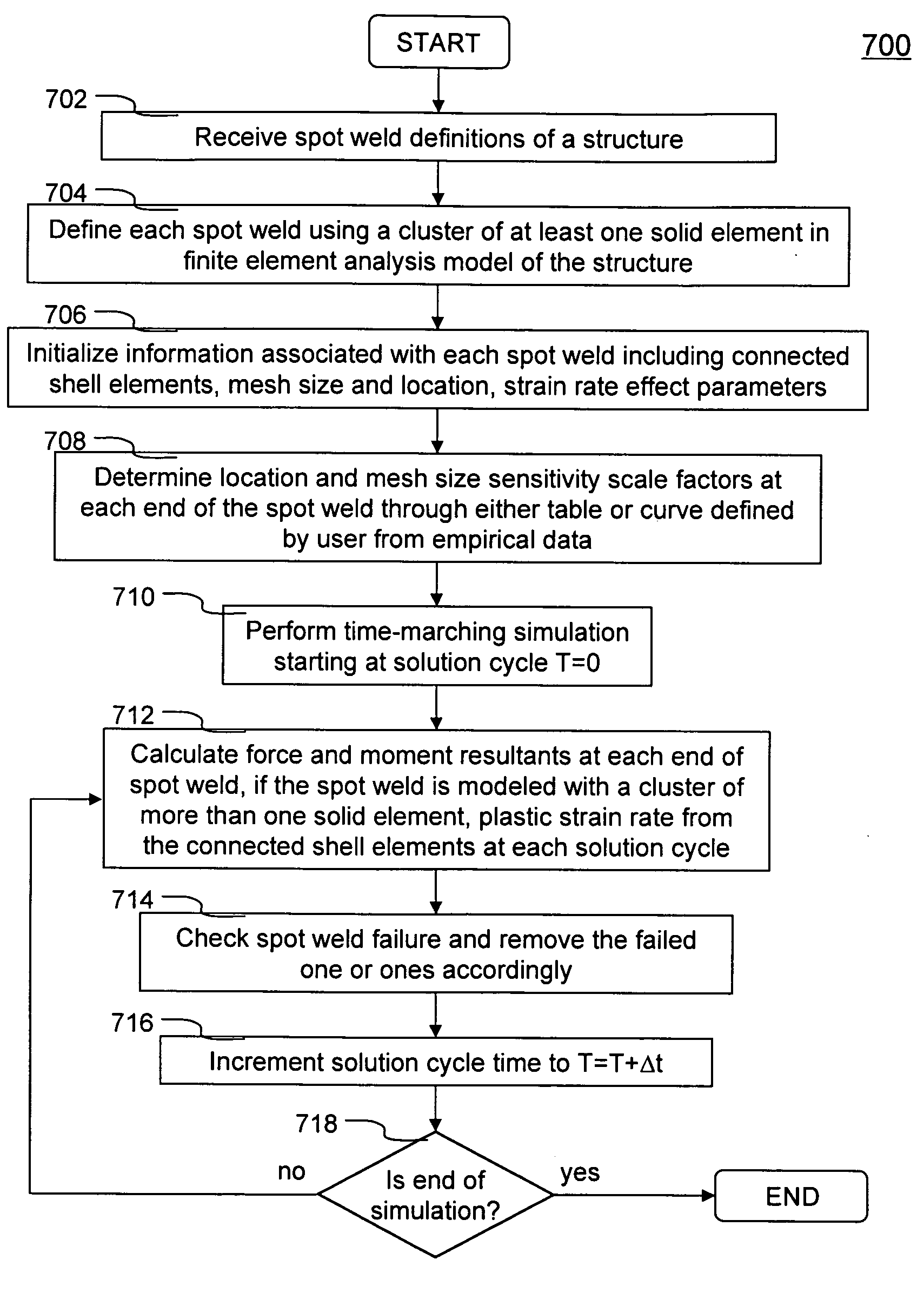
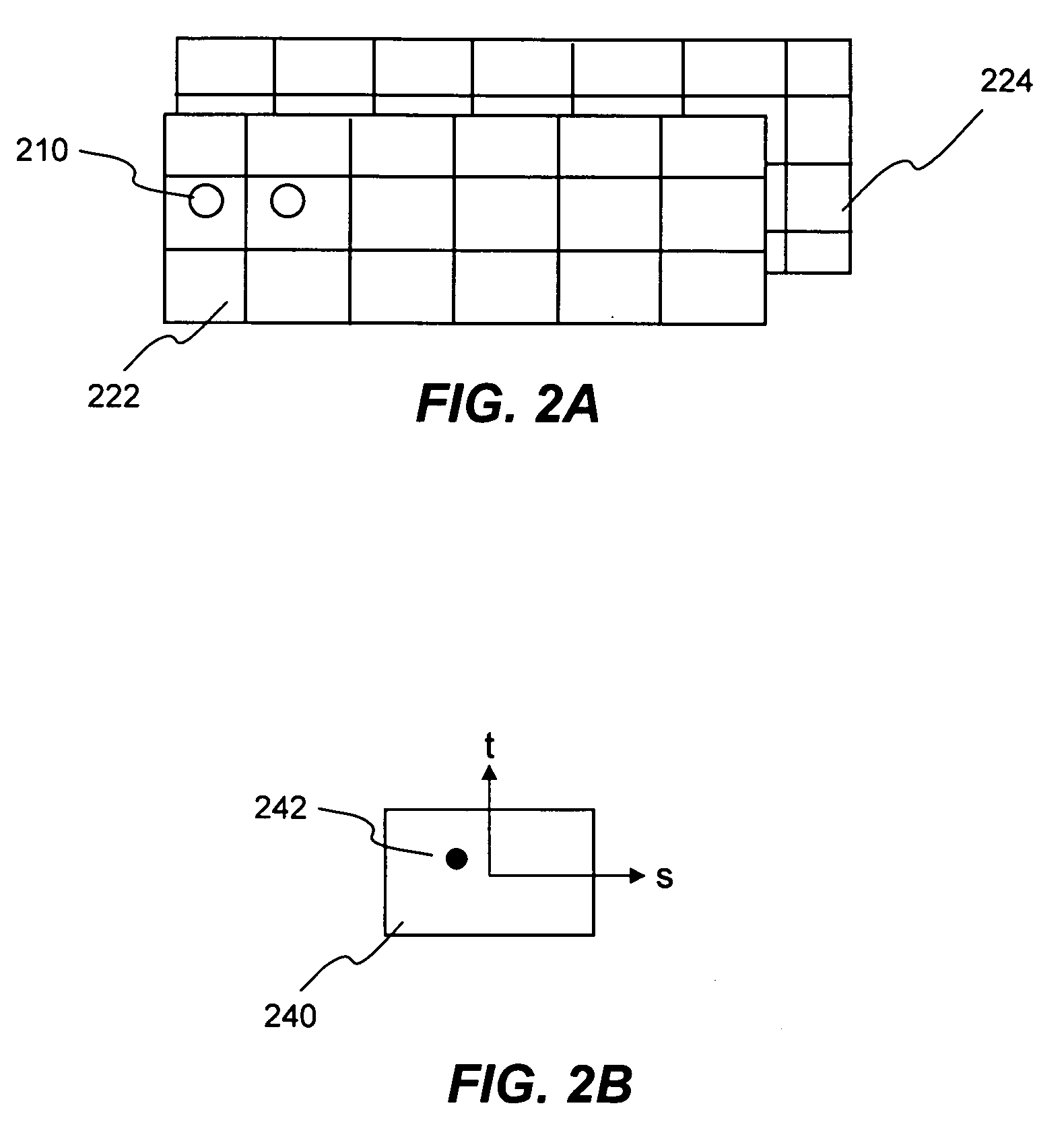
Spot Weld Failure Determination Method in a Finite Element Analysis
ActiveUS20100131256A1Cooking-vessel materialsElectrode supporting devicesElement analysisEngineering
Each spot weld in a structure is represented by a cluster of at least one solid element in a finite element analysis model of the structure. Each spot weld is used for tying together two parts. Each of the two parts are generally represented or modeled as a number of two-dimension shell elements. Since the tie-connection between the spot weld and the two parts can be located arbitrarily within the respective part, the shell elements representing the two parts do not have to be aligned in space. The only requirement is the two shell elements must be overlapped each other such that the spot weld can tie the two shell elements (i.e., one from each part) together. A spot weld failure criterion used for determining failure including shear and axial stresses acted on the spot weld, shell element size and spot weld location sensitivity scale factors and strain rate effect.
Owner:ANSYS
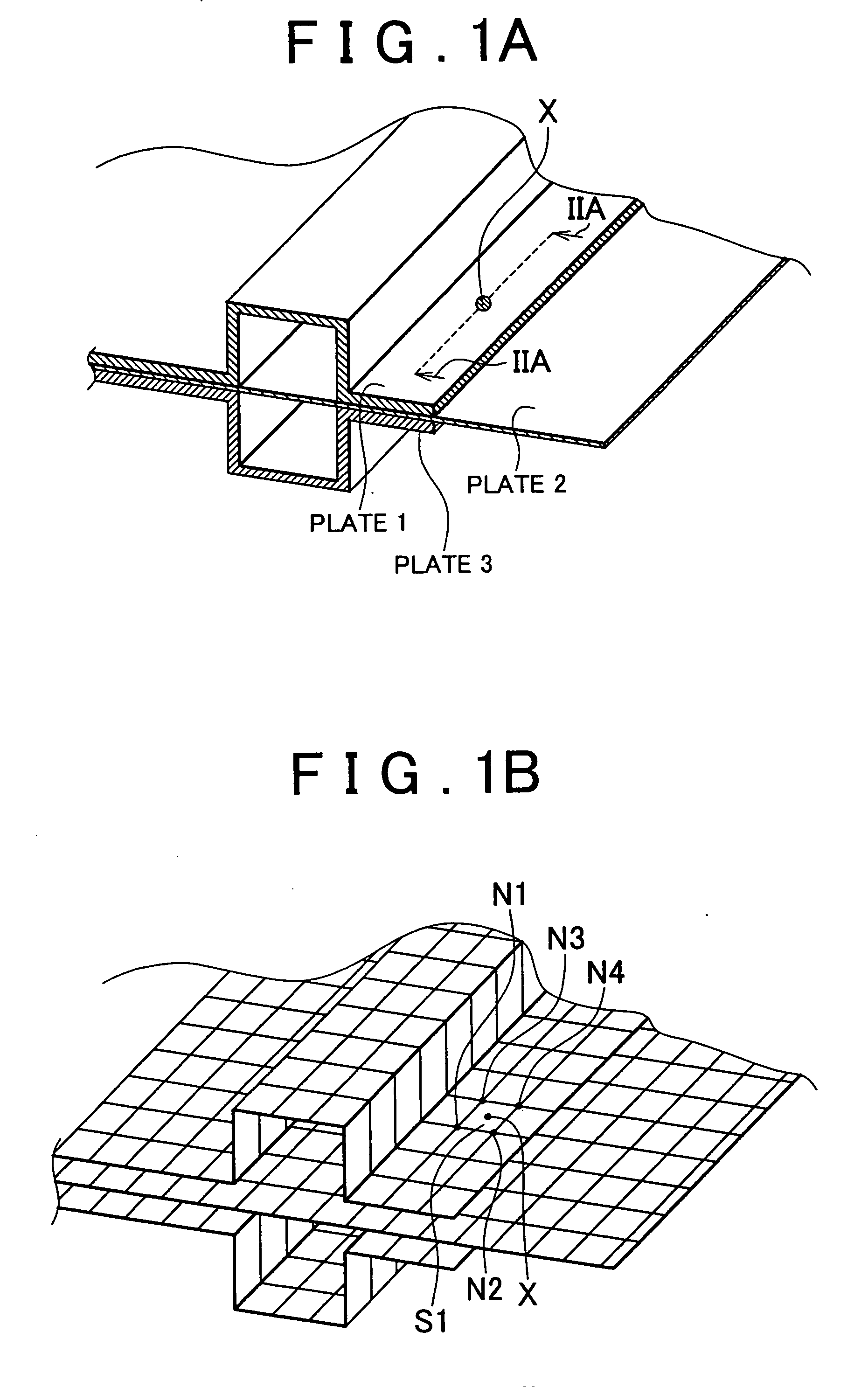
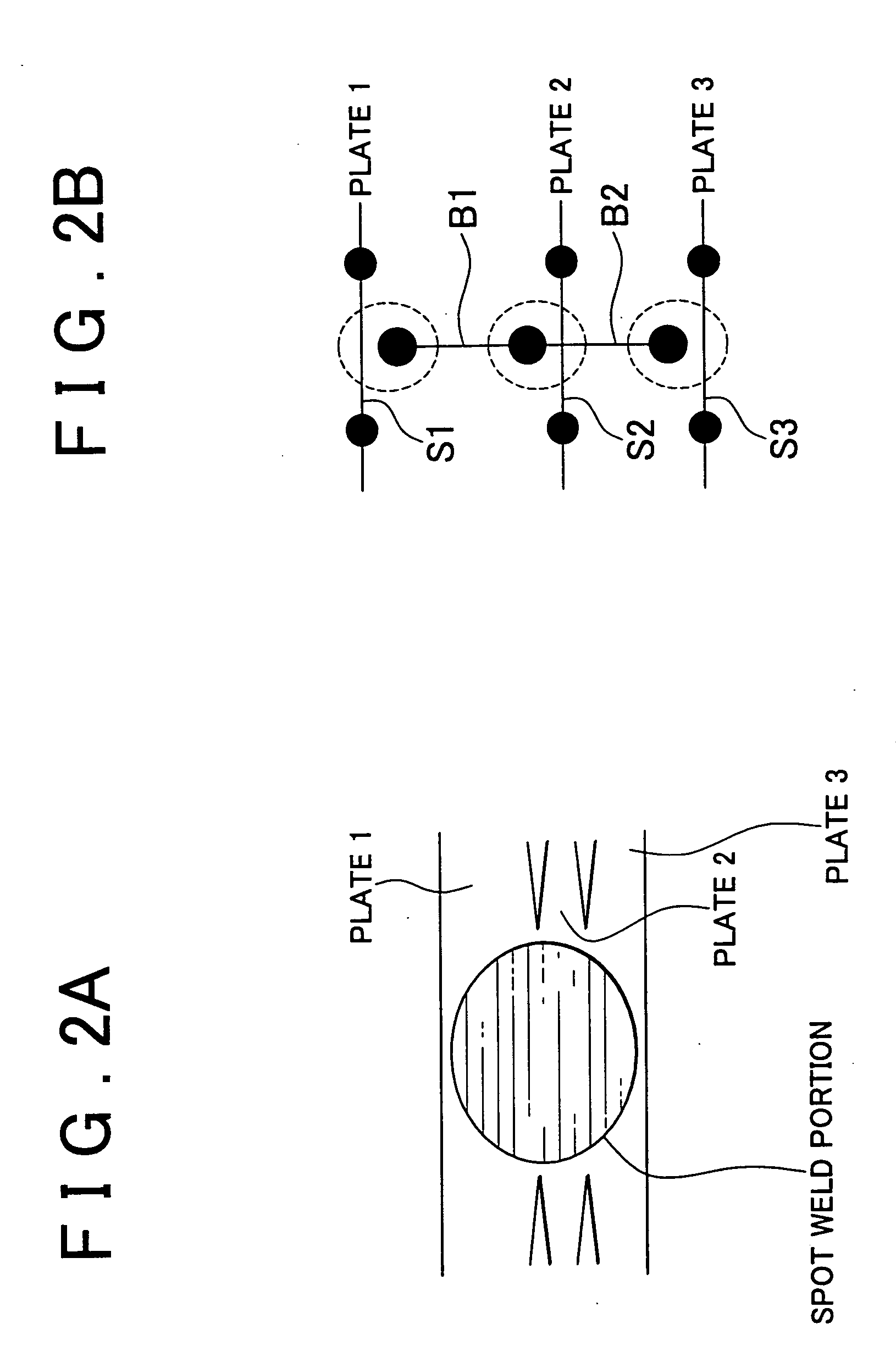
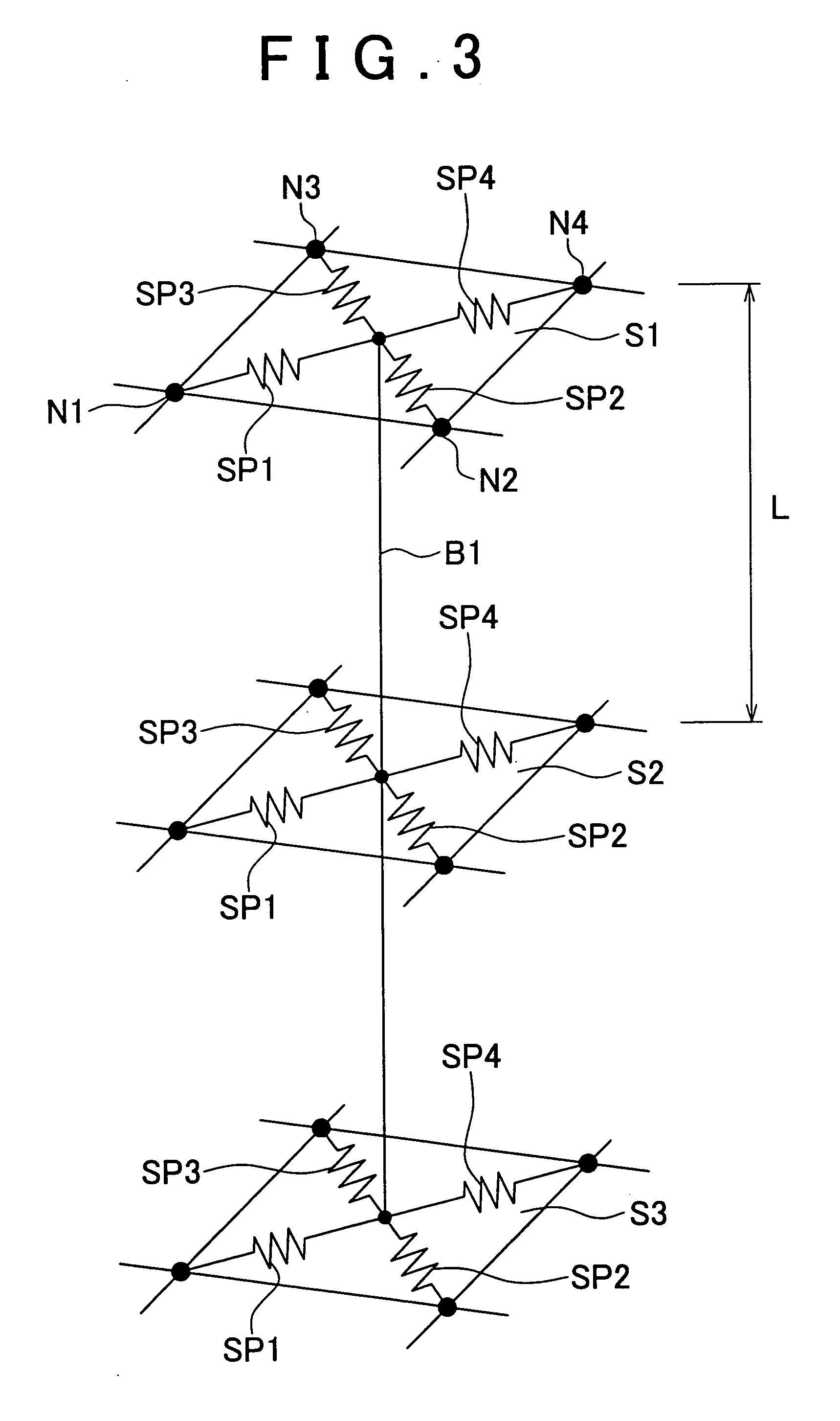
Spot weld fracture analysis method, program therefor, and analysis apparatus thereof
InactiveUS20070090165A1Improve accuracyCooking-vessel materialsDesign optimisation/simulationElement modelLight beam
A spot weld fracture analysis method for a spot weld portion of three or more mutually superimposed plates that are spot-welded at a common welding point comprises an analysis step of executing an analysis by using a finite element model in which each plate is modeled by shell elements, and the shell elements corresponding to a spot weld point position of each plate are individually interconnected via beam elements, and a prediction step of finding an element force of a beam element that acts on a shell element relevant to a middle plate from a difference between the element forces of two beam elements connected to the shell element on a basis of the analysis result, and predicting a possibility of fracture of a spot weld between the middle plate and an adjacent plate by using the difference element force found from the difference.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Time-varying Reliability Determination Method of Prestressed Concrete Box Girder Bridge
ActiveCN102286916AImprove analysis efficiencyBridgesSpecial data processing applicationsCarbonizationStress relaxation
A method for determining the time-varying reliability of prestressed concrete box girder bridges based on the stochastic finite element method. For prestressed concrete box girders that are widely used in highway bridge systems and have common early-stage diseases, by combining degenerate shell elements, material constitutive relations and The crack model simulates the nonlinear characteristics of the box girder in the cracking stage, and the embedded concrete creep, shrinkage and steel strand stress relaxation model considers the deformation, prestress loss and internal force redistribution of the box girder during its entire life, through the reinforcement The uniform corrosion model and the pitting corrosion model calculate the section loss of steel bars (steel strands) in carbonization environment and chloride ion environment respectively. Finally, through the definition of random variables, sampling, calling finite element program calculation and extracting stress and strain results, the reliability calculation of the box girder bridge is realized and used to guide the subsequent maintenance and reinforcement work.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
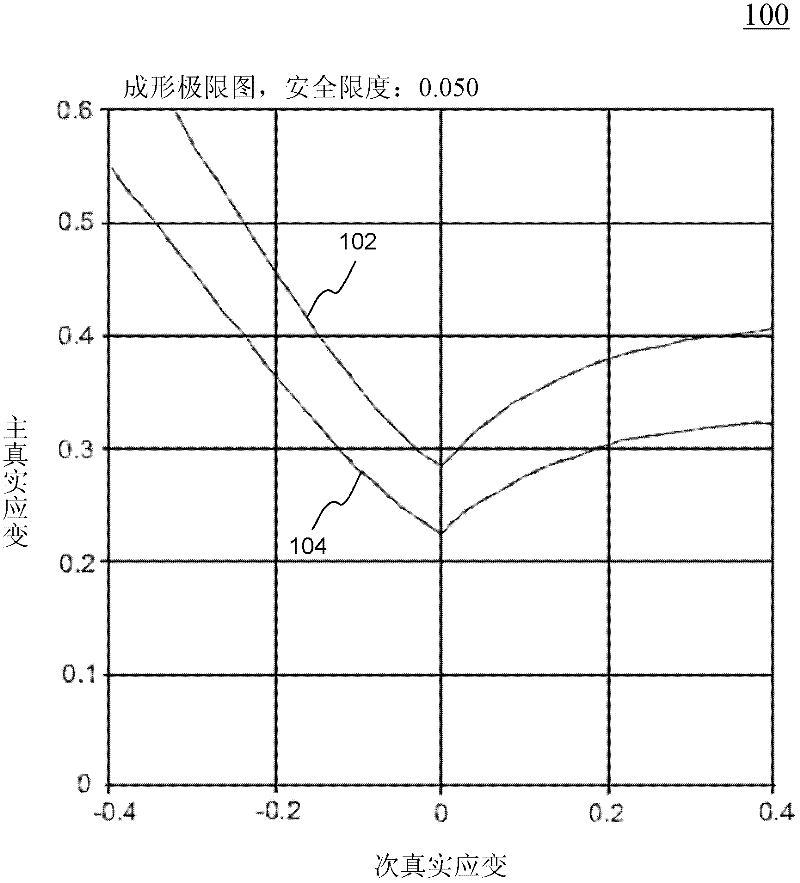
Method and system for numerically simulating and predicting necking failure in sheet metal forming
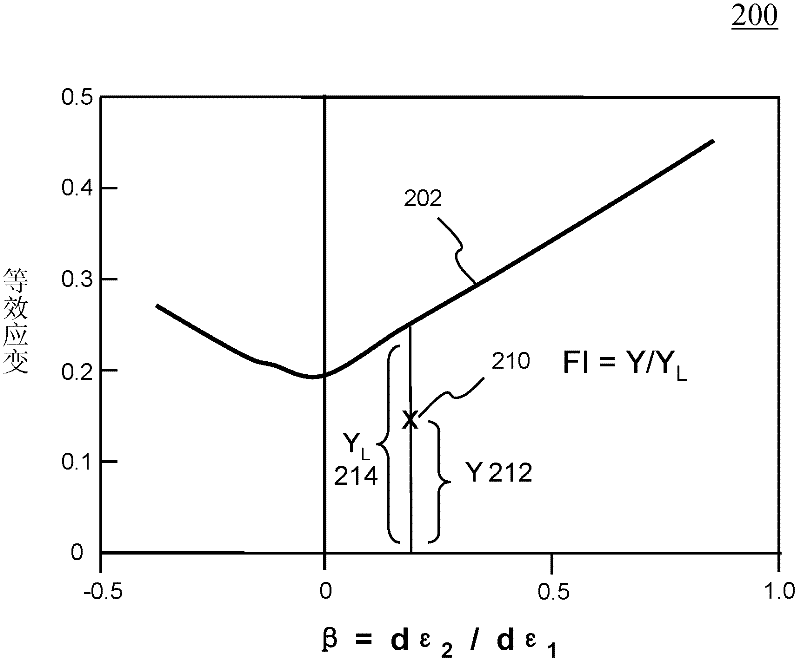
InactiveCN102262688AEasy to useEasy to observeDesign optimisation/simulationAerodynamics improvementForming limit diagramElement analysis
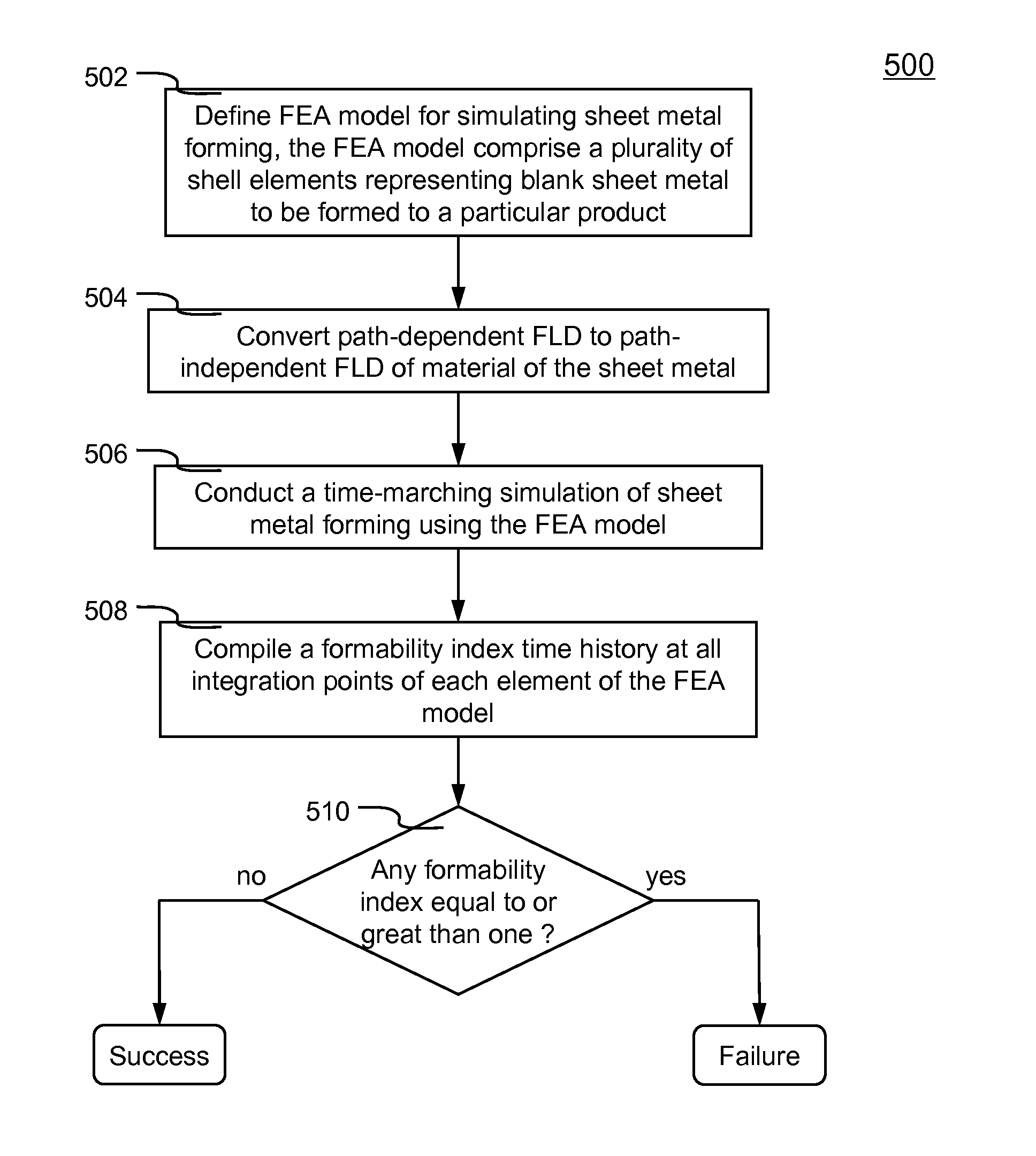
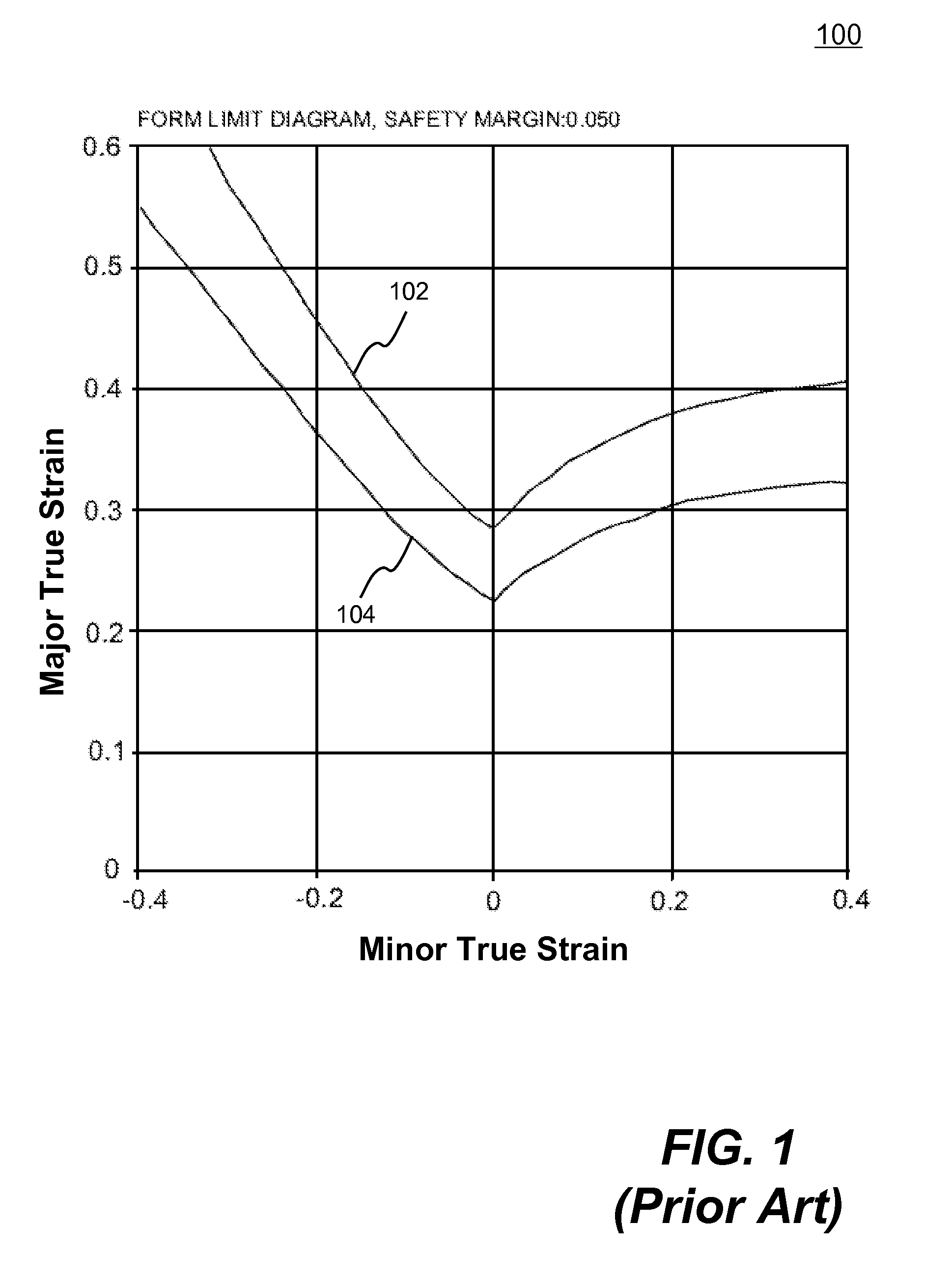
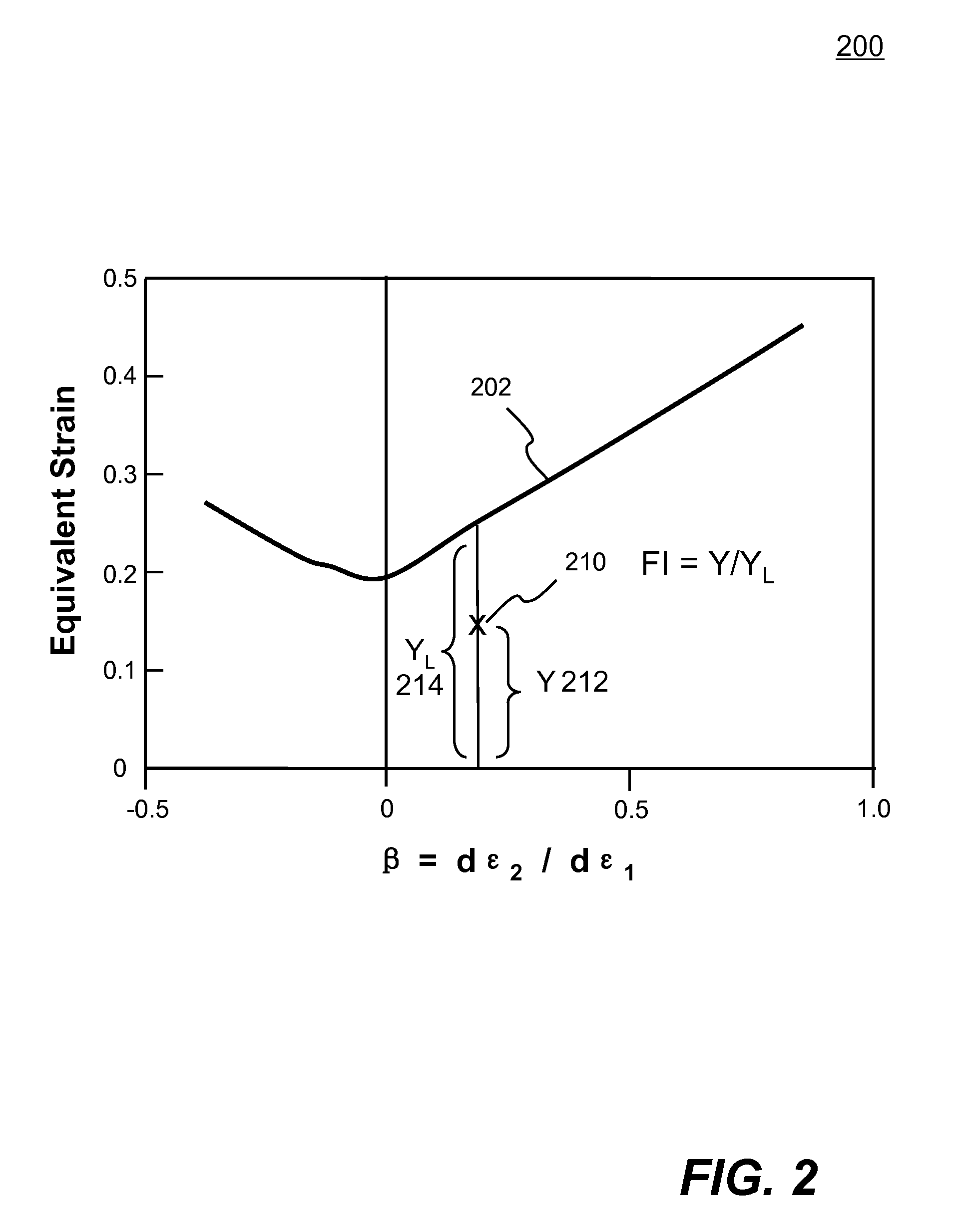
Systems and methods of predicting sheet metal forming failure using numerical simulations (e.g., finite element analysis) are disclosed. A FEA model is defined for a particular sheet metal forming process. Blank sheet metal is modeled with a plurality of shell elements. Additionally, a deformation path-dependent forming limit diagram (FLD) is converted to a path-independent FLD. A time-marching simulation of the sheet metal forming process is conducted using the FEA model. At each solution cycle, equivalent strain at each integration point of shell element is checked against the corresponding forming limit strain value of the path-independent FLD. The ratio of the equivalent strain and the forming limit strain is defined as formability index. A time history of the formability index of each shell element is saved into a file and displayed to a monitor upon user's instructions. When a particular element's formability index reaches one or higher, a localized necking is predicted.
Owner:LIVERMORE SOFTWARE TECH
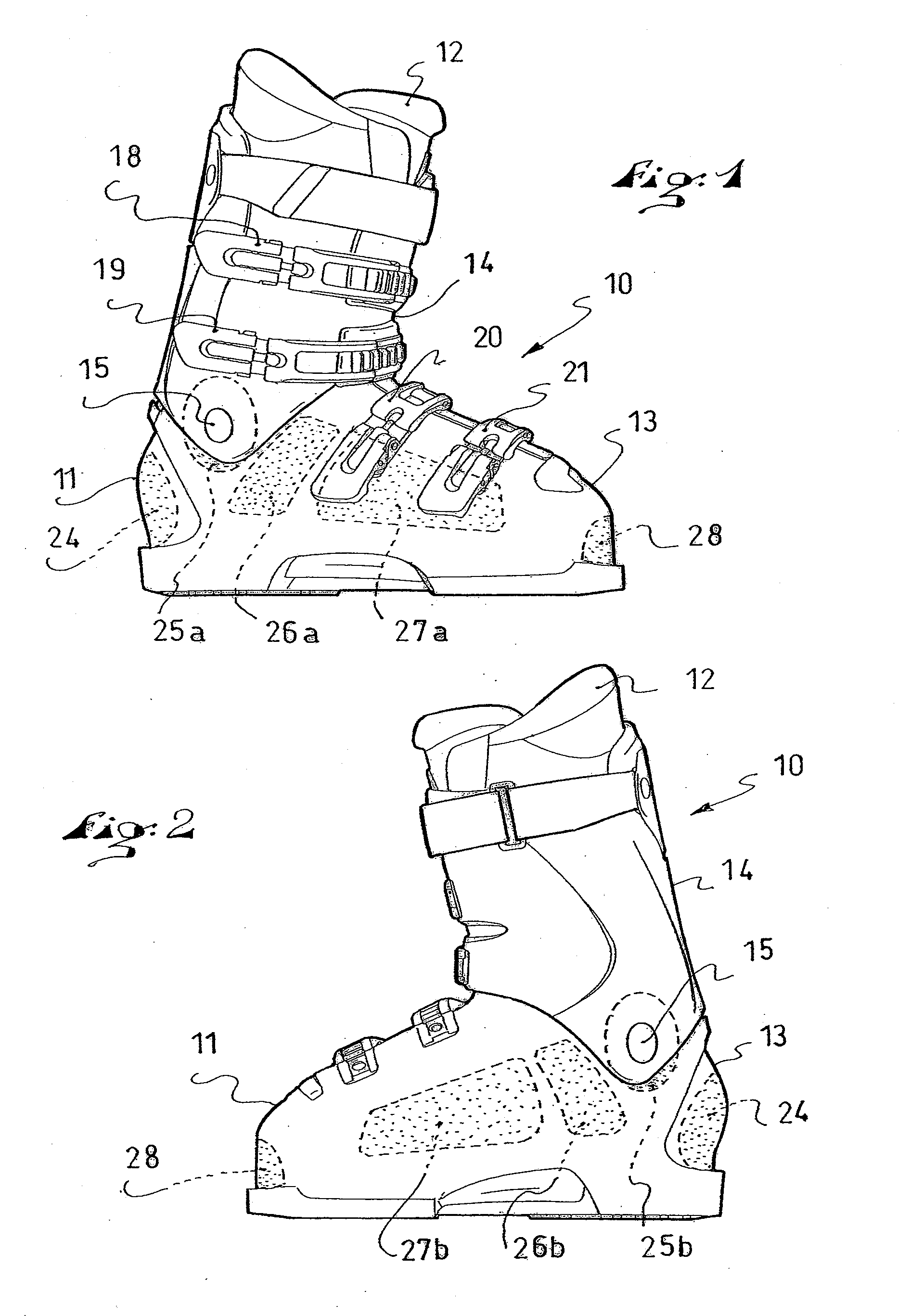
Footwear having a rigid shell
Footwear, such as a sports boot, including a shell or a shell element made of a rigid plastic base material whose softening point is greater than 170° C. and a method of manufacturing such footwear. At least in one local portion of the shell or shell element, the base material of the shell includes an additive having a melting temperature lower than 100° C., in a proportion of between 3% and 45% in a first embodiment and between 10% and 25% in a second embodiment. A heating machine includes a base provided to receive at least one boot along a longitudinal direction defined by the sole and a hot air blower. The heating machine includes at least two air blowing channels facing one another and located on each side of the longitudinal direction.
Owner:SALOMON SA
Hearing aid with exchangeable shell parts and wireless communication
Hearing aid or audio device having a behind the ear part adapted to rest behind an earlobe of a user and a speaker unit comprising a speaker, whereby the speaker unit is adapted for insertion into the ear of a user, and whereby electric leads are provided between the speaker unit and the behind the ear part, said leads having a connection part opposite the speaker unit for connection with a corresponding socket in the behind the ear part, wherein the exterior and visible parts of the behind the ear part are defined by a generally U-shaped shell element, a battery drawer and a microphone cover plate characterized in that all further inside parts of the behind the ear part are interconnected to form a single sub-assembly and in that said sub-assembly is releasably coupled to the U-shaped shell element between two upright walls thereof by latch-locks provided to interact between the microphone cover plate and the upright wall elements
Owner:OTICON
Methods and systems for creating a smooth contact-impact interface in finite element analysis
ActiveUS8180605B1Describe wellRealisticComputation using non-denominational number representationDesign optimisation/simulationComputational scienceNODAL
Improved systems and methods of creating a smooth contact-impact interface (i.e., a curve fitted surface) in finite element analysis are disclosed. According to one aspect, a smooth contact interface is created for a master segment used for simulating contacts. First, for every nodal point in the master segment, a list of elements that share at least the node is determined. Then a nodal normal vector is calculated using a weighted average of respective element normal vectors of all elements in the list. The calculated nodal normal vector is adjusted for special edge effect, which is an intersection between flat and curved geometries. A set of edge control points are created using a pair of adjacent corner nodes. A mid-element control point is further created for quadrilateral shell elements. The smooth contact interface is configured to encompass all corner nodes and all of the control points.
Owner:ANSYS
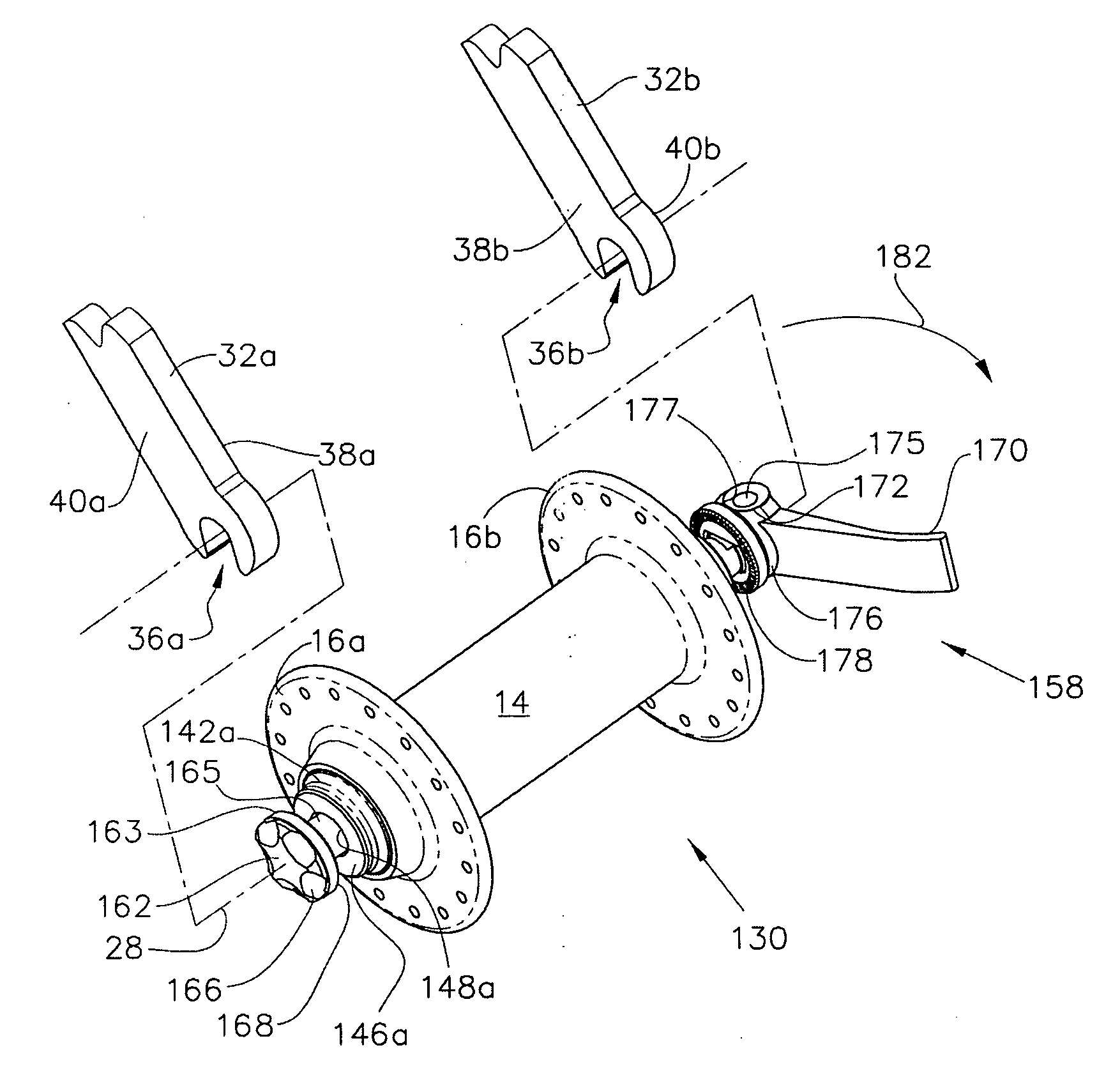
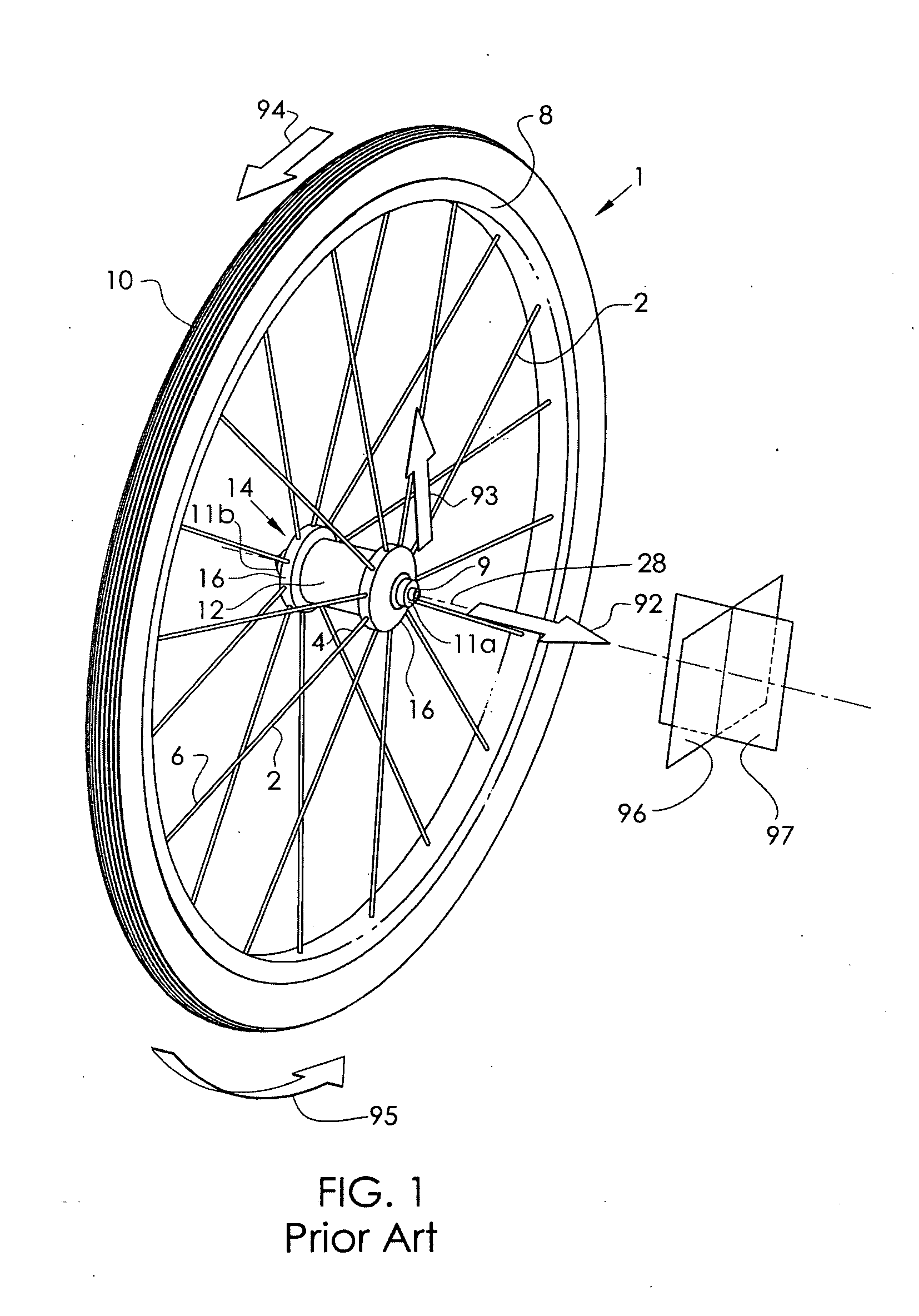
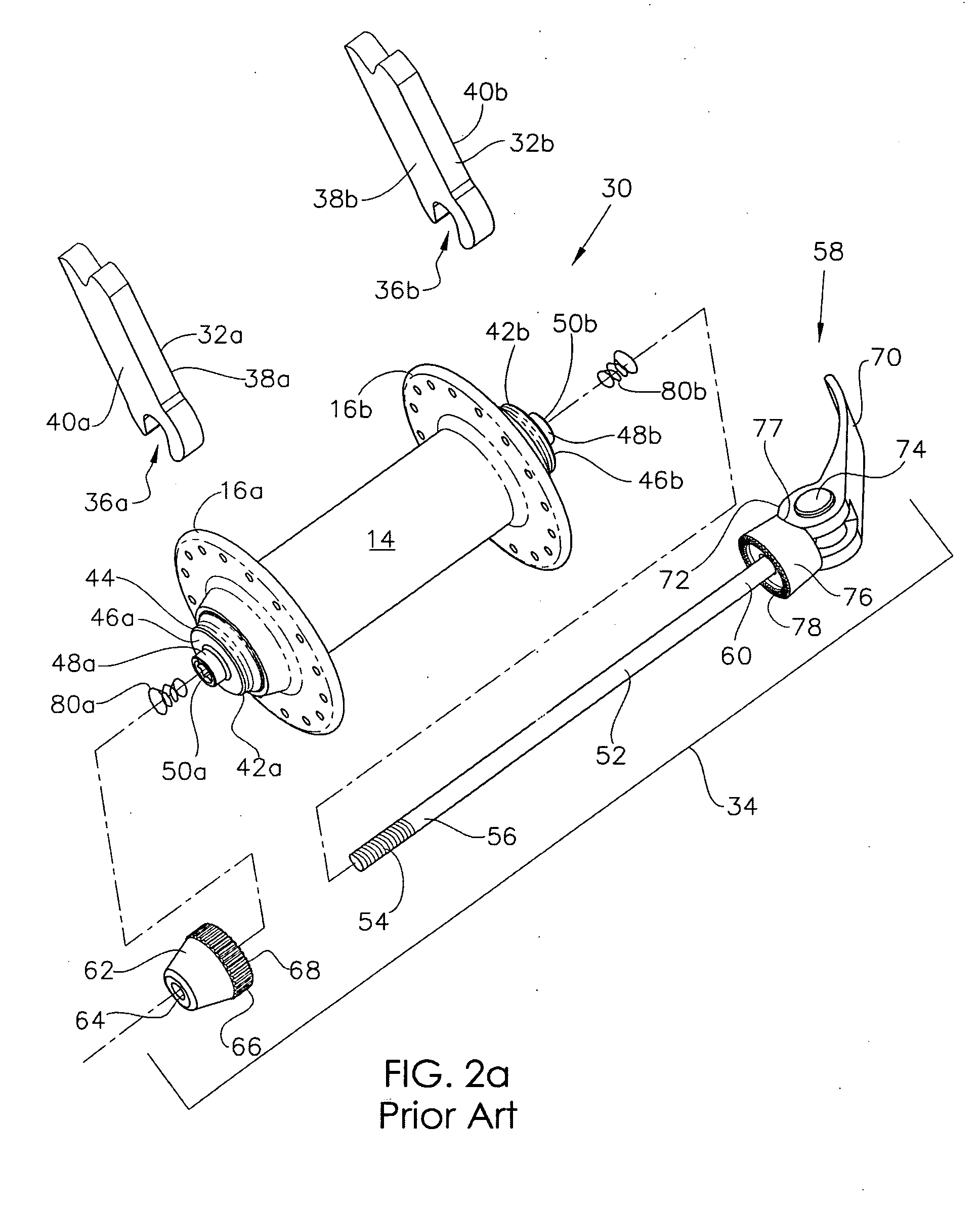
Quick release hub assembly
A quick release hub assembly, comprising a stationary axle element with a first outer face and an axially opposed second outer face and an opening that extends axially between the first outer face and the second outer face, a rotatable hub shell element that is rotatable about the axle element and a quick release skewer assembly that includes a first skewer element with a first gripping face and a first collar portion extending axially inboard of the gripping face and a second skewer element with a second gripping face and a skewer shaft connecting the first skewer element and the second skewer element. The first gripping face is axially opposed and facing the second gripping face and the axial distance between the first gripping face and the second gripping face is selectively variable. The first gripping face is axially outboard the first outer face and the second gripping face is axially outboard the second outer face and the quick release skewer assembly extends through the opening. The first skewer element is connected to the skewer shaft by means of a connection at a location that is axially inboard of the first gripping face. Preferably including a frame with a frame element with first and second mounting portions, where the first collar portion includes locating geometry to provide radially positioning alignment with the first mounting portion.
Owner:SCHLANGER RAPHAEL
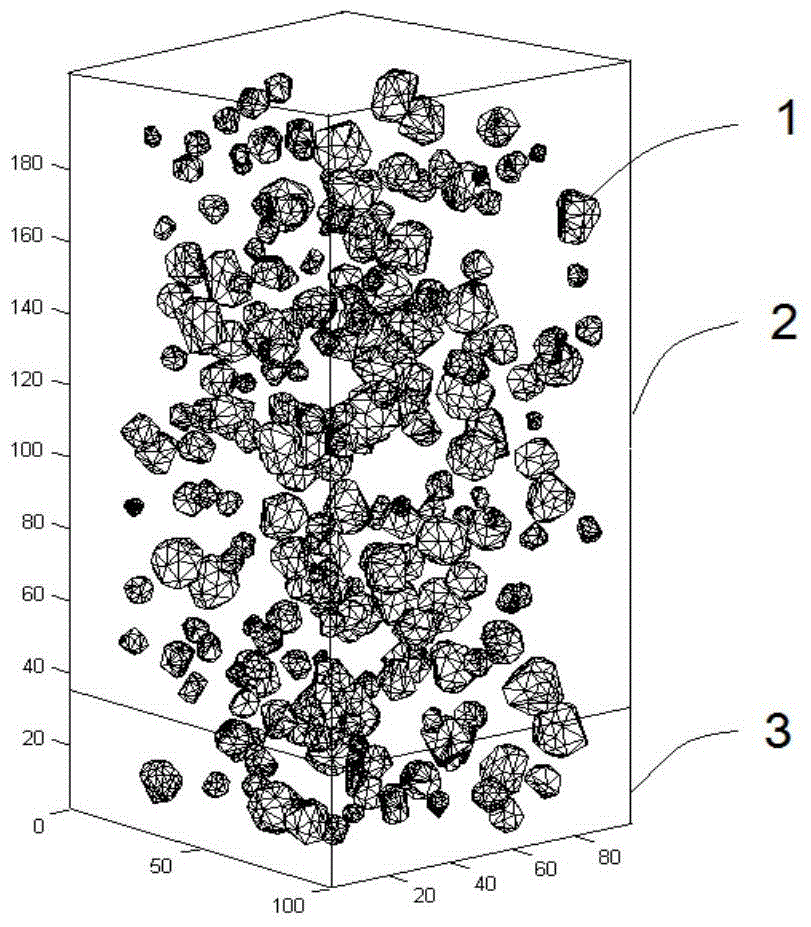
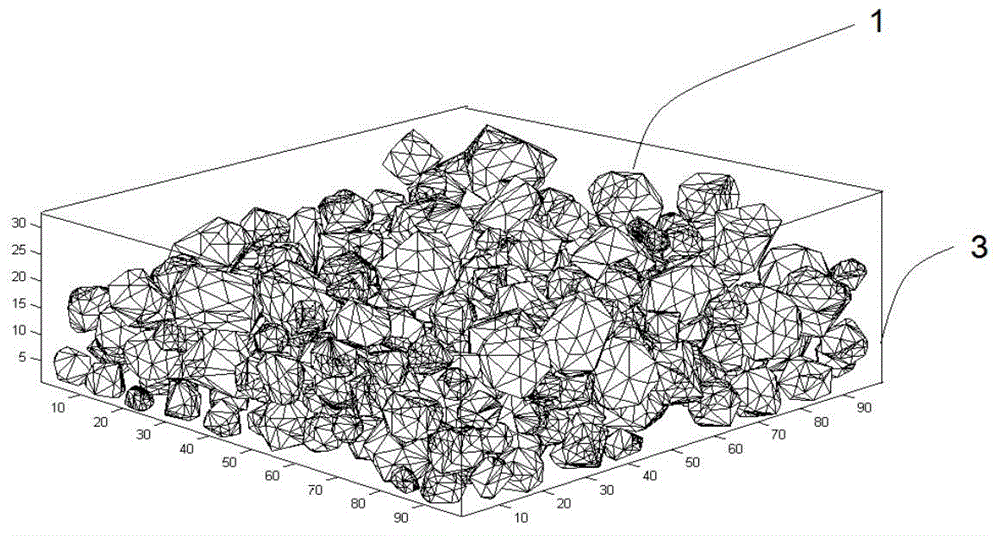
Modeling method of dispersed-phase reinforced composite material meso-structure
ActiveCN104899393AGuaranteed uniformityImprove production efficiencySpecial data processing applicationsElement modelModel method
The invention relates to a modeling method of a dispersed-phase reinforced composite material meso-structure. The modeling method comprises the following steps that the shape and the size of a model of a composite material are prepared, and the boundary of the model is determined; the sum of the volumes of particle reinforced phases in different size ranges in the model is prepared; particle models in all the size ranges are generated; the surface of each particle model is divided into finite element grids, and the prepared boundary of the model is divided into finite element grids; shell element attributes are given to the finite element grids; the mode of contact between the particle models and the mode of contact between the particle models and the boundary of the model are defined, and the descending process of particles in the space is simulated through a finite element method; the internal space of the model can be exactly filled with the particle models in all the size ranges; finite element models of the particle models and a finite element model of a substrate are obtained; modeling of the particle reinforced composite material structure is accomplished through the definition of the mode of constraint between the substrate and the particles and the material attributes of the substrate and the particles.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Integrated poolscape comprised of pre-fabricated elements and related methods
InactiveUS20080134426A1Satisfies restrictionSure easyGymnasiumSwimming poolsEngineeringShell element
A poolscape is disclosed that comprises at least two of a plurality of pre-fabricated shell elements, each of said shell elements having a wall that conforms to a wall of one or more other shell elements comprising said plurality, wherein said at least two shell elements are conformably combined, and where the shell elements may be one of a swimming pool, a tanning ledge, a hot tub or spa, a fountain, a sun shelf, and a thermal ledge or variants thereof. The poolscape may include in-pool features, such as a pre-fabricated bench or pre-fabricated stairs.
Owner:TRILOGY POOLS LLC
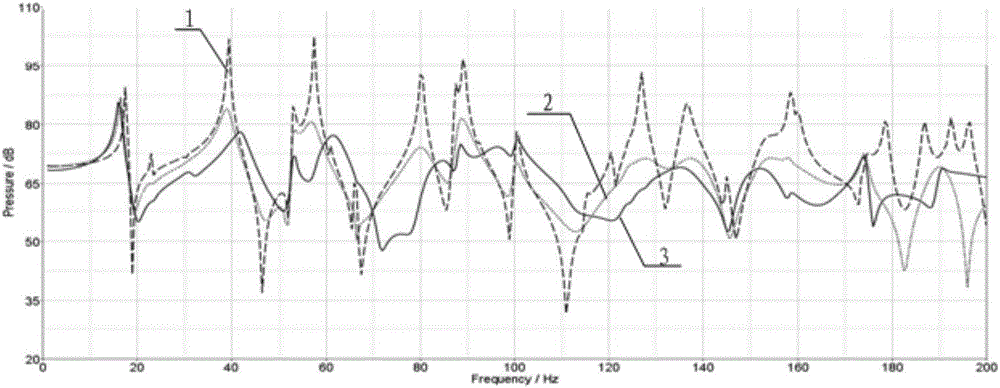
Method and system for optimizing automobile body damping distribution
ActiveCN106202653AGuaranteed noiseGuaranteed normal vibrationInternal combustion piston enginesDesign optimisation/simulationElement modelTopology optimization
The invention provides a method for optimizing automobile body damping distribution. The method comprises the following steps: a finite element model of a composite damping plate is constructed, an automobile body is taken as a flexible panel of the composite damping plate, and a layer of conode bias shell elements for simulating a damping material is arranged on the flexible panel; values of assigned frequencies in a noise transfer function are solved in a preset frequency range, sound pressure amplitudes of the assigned frequencies are obtained, and corresponding target sound pressure values are set for the assigned frequencies; a target function is determined, and a topological optimization model is established with the relative thickness of a damping unit as a design variable and the mass of the damping unit as a constraint condition; modal analysis is performed on all the shell elements on the composite damping plate according to the finite element model, the topological optimization model of each shell element is solved, and an automobile body damping distribution nephogram and a noise transfer function curve are obtained. With implementation of the method, damping distribution is designed, global optimization processing of all modals in a certain frequency range is realized, and the inhibition action of damping distribution on noise radiation can be improved obviously.
Owner:GUANGZHOU AUTOMOBILE GROUP CO LTD
Quasi self-destructive core for investment casting
A composite core for forming a passage in an investment casting mold is provided including a generally hollow structural element. The structural element is configured to deform when a force is applied to an end thereof. A rigid shell element is formed about the structural element. The shell element extends beyond both an interior surface and an exterior surface of the structural element. The shell element is configured to shatter when the structural element deforms.
Owner:SIKORSKY AIRCRAFT CORP
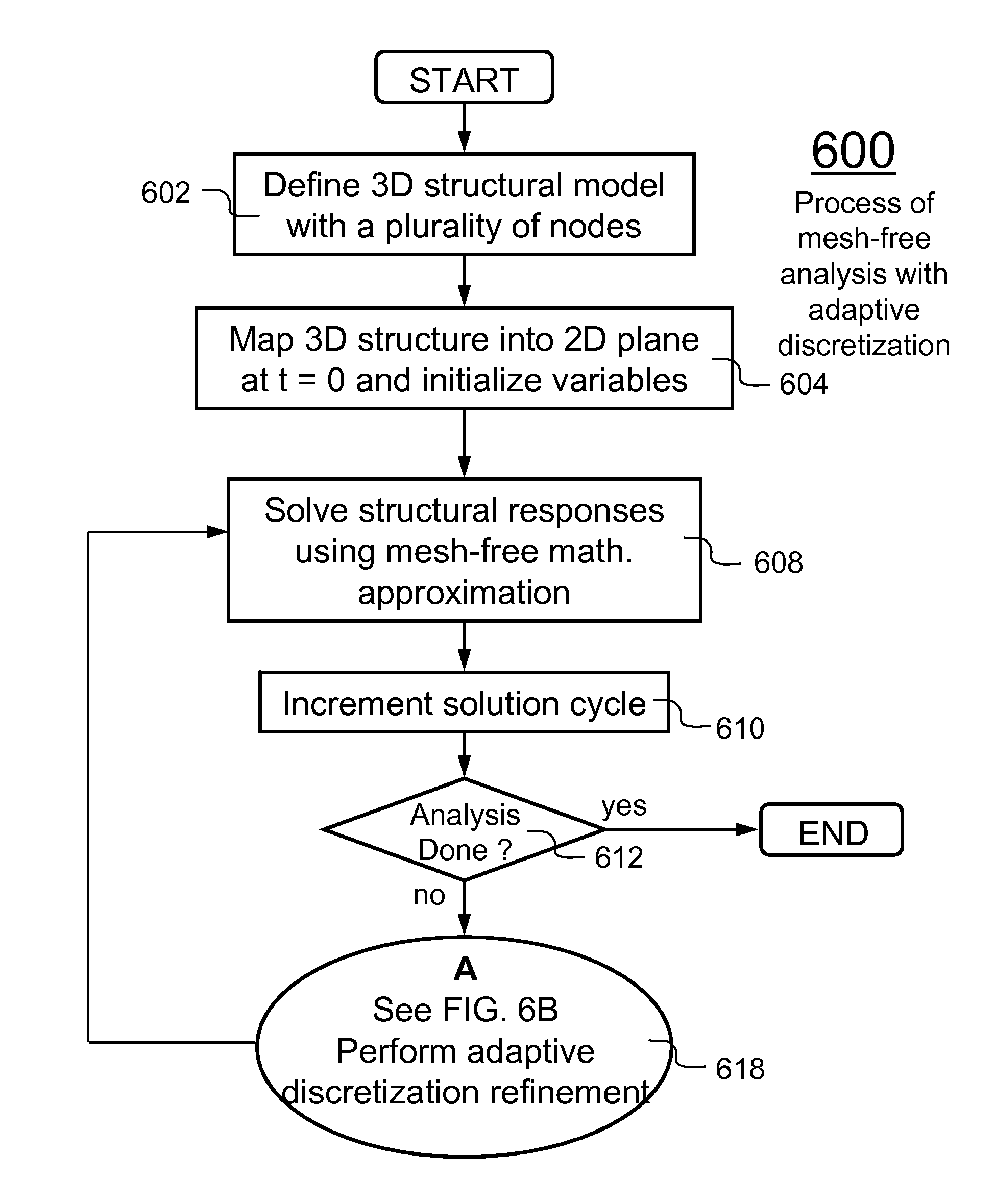
Method and system for adaptive mesh-free shell structures
ActiveUS7702490B1Efficient analysisRealistic analytical resultComputation using non-denominational number representationDesign optimisation/simulationComputational scienceTime domain
A method, system and computer program product pertained to adaptive discretization refinement of shell structure is disclosed. The adaptive mesh-free model is based on a technique for dividing the critical area into a finer model. The present invention is a method for enabling adaptive mesh-free shell structure in a time-domain analysis, the method comprises: defining the mesh-free shell structure by a structural geometry description file including a plurality of nodes and a reference 3-D mesh, which includes a plurality of shell elements, mapping the 3-D reference mesh into a 2-D parametric plane, wherein the 2-D parametric mesh includes a plurality of integration cells corresponding to the plurality of shell elements, solving structural responses at current solution cycle using mesh-free mathematical approximations pertaining to each of the plurality of integration cells, performing adaptive discretization refinement for the plurality of the integration cells.
Owner:ANSYS
Sheet Metal Forming Failure Prediction Using Numerical Simulations
InactiveUS20110295570A1Computation using non-denominational number representationDesign optimisation/simulationForming limit diagramElement analysis
Systems and methods of predicting sheet metal forming failure using numerical simulations (e.g., finite element analysis) are disclosed. A FEA model is defined for a particular sheet metal forming process. Blank sheet metal is modeled with a plurality of shell elements. Additionally, a deformation path-dependent forming limit diagram (FLD) is converted to a path-independent FLD. A time-marching simulation of the sheet metal forming process is conducted using the FEA model. At each solution cycle, equivalent strain at each integration point of shell element is checked against the corresponding forming limit strain value of the path-independent FLD. The ratio of the equivalent strain and the forming limit strain is defined as formability index. A time history of the formability index of each shell element is saved into a file and displayed to a monitor upon user's instructions. When a particular element's formability index reaches one or higher, a localized necking is predicted.
Owner:LIVERMORE SOFTWARE TECH
Thermal Fluid-Structure Interaction Simulation in Finite Element Analysis
ActiveUS20100204963A1Design optimisation/simulationChemical/physical/physico-chemical processesElement analysisEngineering
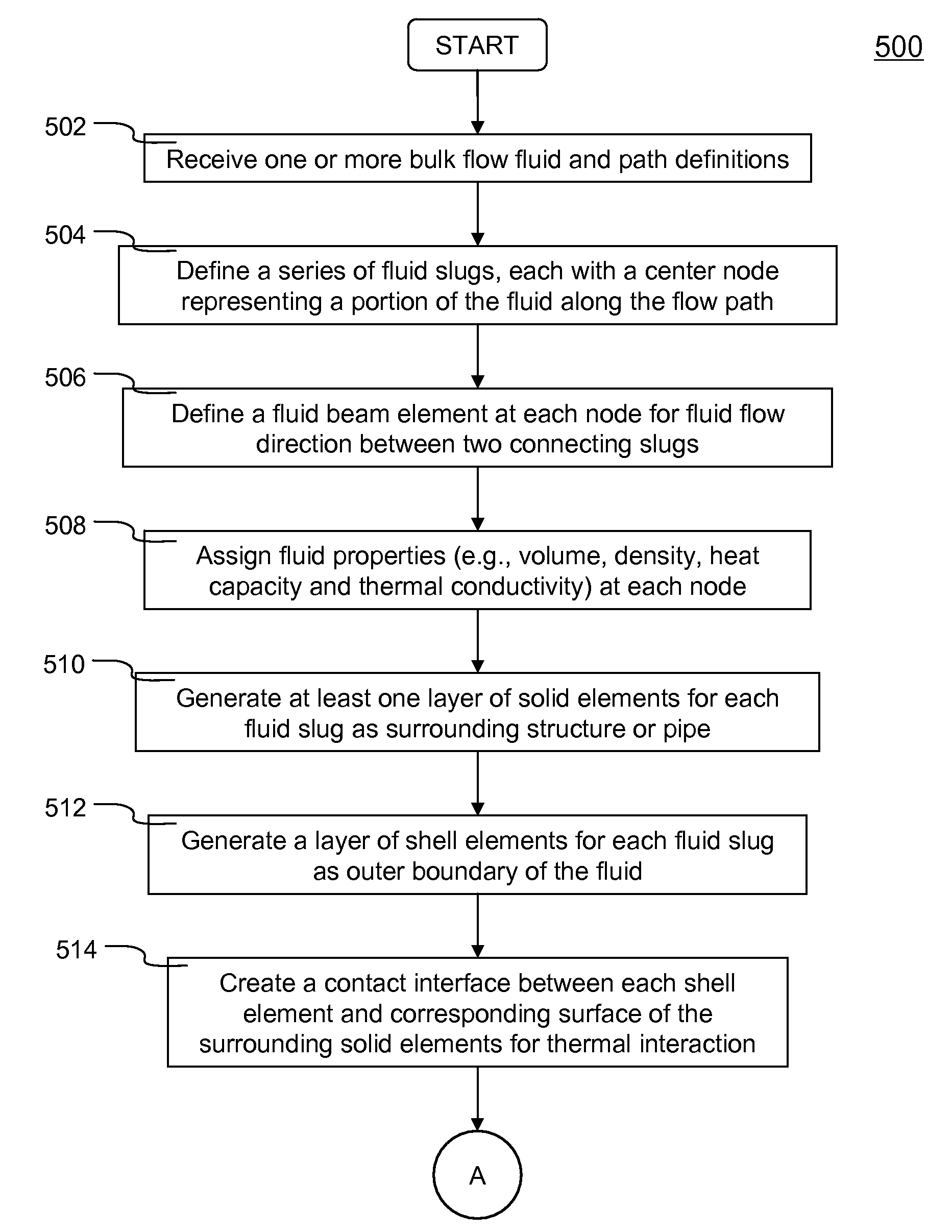
Simulation of thermal fluid-structure interaction using bulk flow fluid elements (BFFEs) is described. Each BFFE is configured to include the following characteristics: 1) at least one surrounding layer of solid elements representing either the surrounding structure or the pipe wall; 2) a layer of shell elements or Bulk Node Segments representing the outer boundary of the fluid; 3) a Bulk Node at the center of the BFFE for defining fluid properties (e.g., density, specific heat) and volume (i.e., fluid volume is calculated as the enclosed volume between the Bulk Node and all of the Bulk Node Segments that surround it); 4) a fluid flow beam element or Bulk Node Element for defining fluid flow path to another BFFE; and 5) a contact interface between the solid elements and the shell elements for conducting fluid-structure thermal interaction.
Owner:ANSYS
Electronic device shell
ActiveCN102202477AImprove overall senseNot easy to fall offCasings with display/control unitsShell elementElectrical and Electronics engineering
The invention provides an electronic device shell, which comprises a shell element and a window element. A window part is arranged on the shell element; the window element covers the window part; a gap is formed between the window element and the shell element; a plurality of open pores are formed at the position, adjacent to the window part, of the shell element; an adhesive layer is arranged in the gap; the adhesive layer is respectively combined with the shell element and the window element closely to fixedly connect the window element to the shell element; and the adhesive layer is formed by injecting viscose into the open pores and filling the viscose into the gap.
Owner:JIANGSU WUWEI POLICE EQUIP MFG
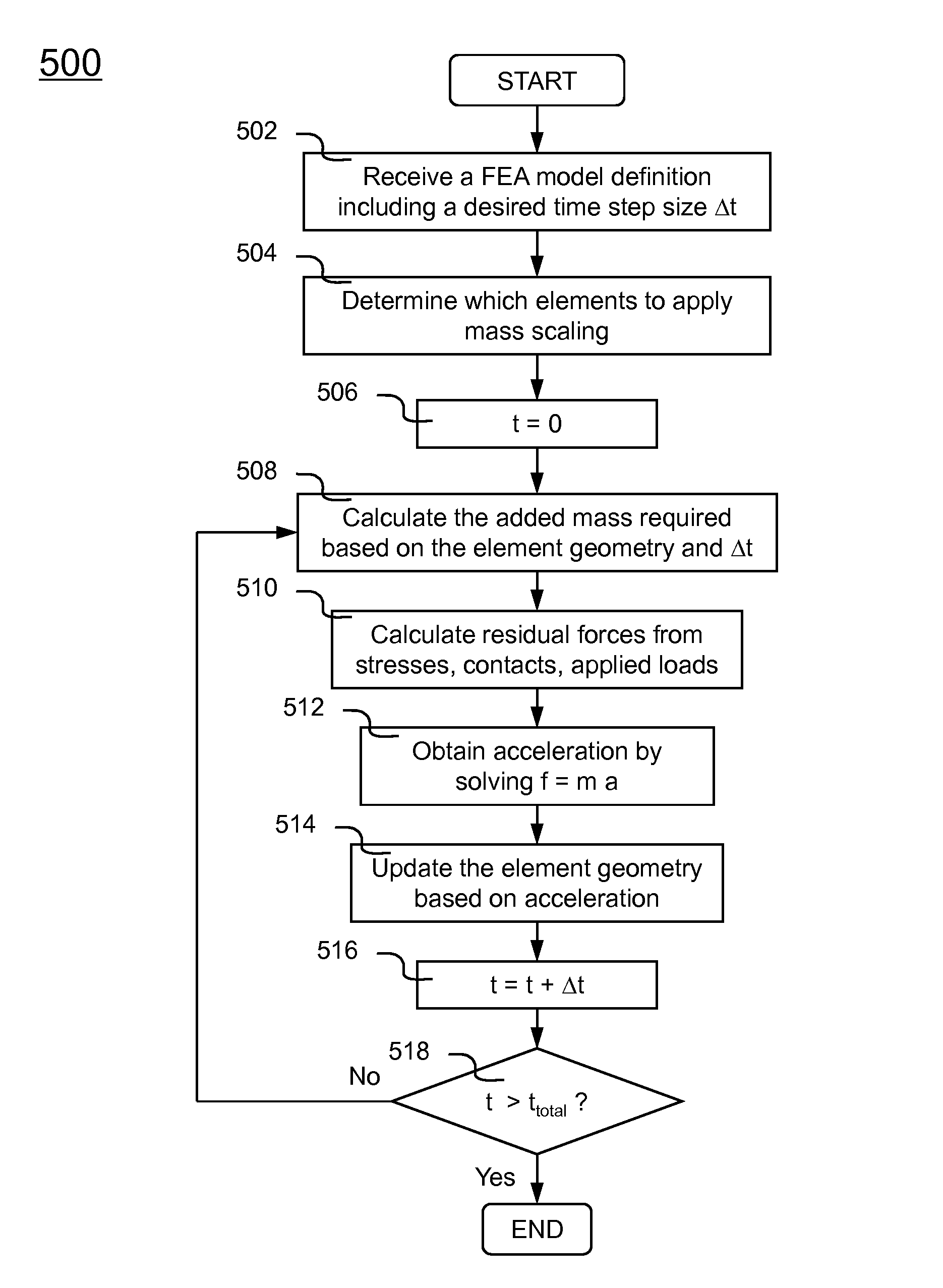
Methods and systems for applying mass scaling in finite element analysis
InactiveUS20120323536A1Reduce the impactIncrease mass densityDesign optimisation/simulationCAD numerical modellingComputational scienceElement analysis
Methods and systems for applying mass scaling in finite element analysis is described. Elements with a critical time step smaller than a user desired time step are identified. Out of these elements, elements located in a particular region requiring realistic simulated dynamic responses are processed with selective mass scaling and the rest are processed with regular mass scaling. Selective mass scaling requires more computation but can better preserve dynamic structural characteristics. The aforementioned method is referred to as a mixed mode mass scaling. Mixed mode mass scaling allows engineering simulation to be conducted within a reasonable turnaround time, because only a portion of the FEA model is subjected to more computation intensive selective mass scaling. Selective mass scaling technique includes reducing effects caused in three translational and three rotational rigid body modes of shell element.
Owner:LIVERMORE SOFTWARE TECH
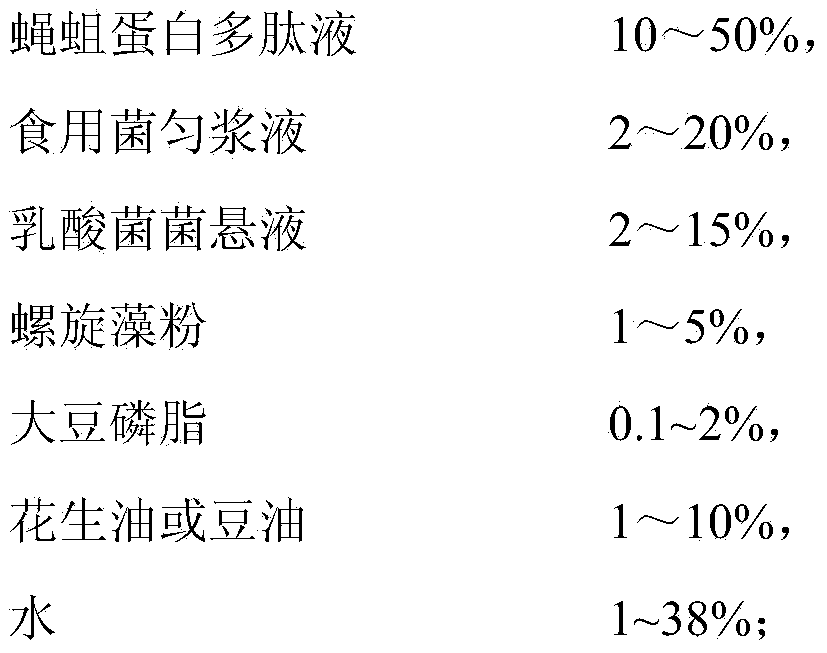
Compound aquatic microcapsule initial baits, preparation method and application of initial baits
The invention discloses a compound aquatic microcapsule initial baits, a preparation and application of the initial baits. The initial baits are prepared by mixing the following main materials mixed in different proportion: maggot protein polypeptide, edible fungus fermentation liquid, lactobacillus, spirulina powder, soya lecithin and vegetable oil with sodium alga acid according to proportion, carrying out high-speed homogenizing, pressurizing, and spraying the mixture into CaCl2 liquid form micro capsules, and filtrating. The diameters of the initial baits are from micrometers to millimeters and the initial baits can suspend in water in a certain time. The initial baits are suitable for newly hatched aquatic seedlings in different growth stages, can strengthen body immunity, regulate ecological balance of intestinal and promote the growth and development. The initial baits meet the requirements on Green feed and feed addictives due to no antibiotics and shell element and no chemical residue, also have the advantages of low cost, convenience in usage and can be widely adopted in aquatic breeding and aquaculture fields.
Owner:JINLING INST OF TECH
Analogue simulation method for automobile windshield collision
ActiveCN111046602AImprove stabilityAvoid the problem of calculation suspensionDesign optimisation/simulationElement analysisSimulation
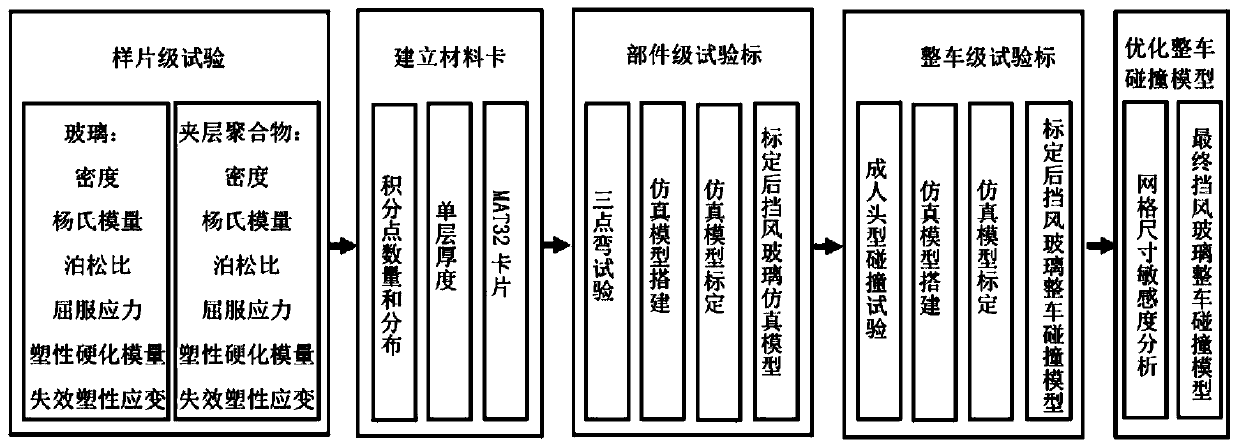
The invention relates to the technical field of finite element analysis, and discloses an analogue simulation method for automobile windshield collision. According to the method, an MAT32 # material card in LS-DYNA software is utilized; a windshield is defined by adopting a single-layer shell unit; simulation of an interlayer polymer entity shell unit is cancelled, the problem of calculation suspension caused by entity unit distortion or negative volume in collision simulation analysis can be avoided, the calculation stability of a simulation model is improved, multi-layer grid contact connection is cancelled, and meanwhile, the simulation calculation time can be obviously shortened by utilizing single-layer shell unit setting; besides, parameters used by the method are obtained from a sample-level test, a component-level test, a whole-vehicle-level test and analogue simulation. The method is high in practicability, collision simulation of different automobile windshields can be easilyachieved, the process that pedestrians collide with the windshields can be accurately simulated, accurate HIC damage values and damage curves are obtained, and therefore development of automobile andpedestrian protection performance can be guided.
Owner:CHINA FIRST AUTOMOBILE
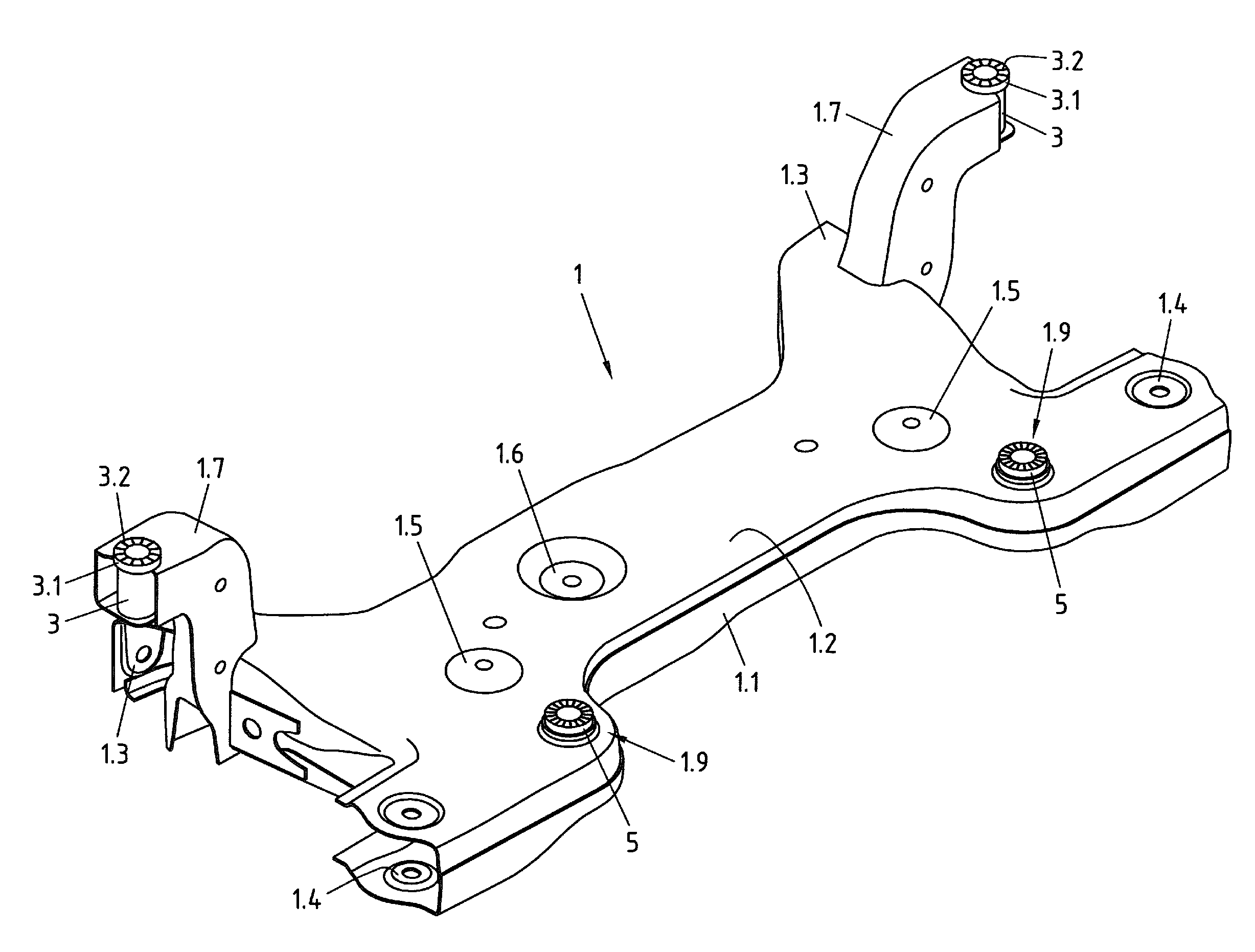
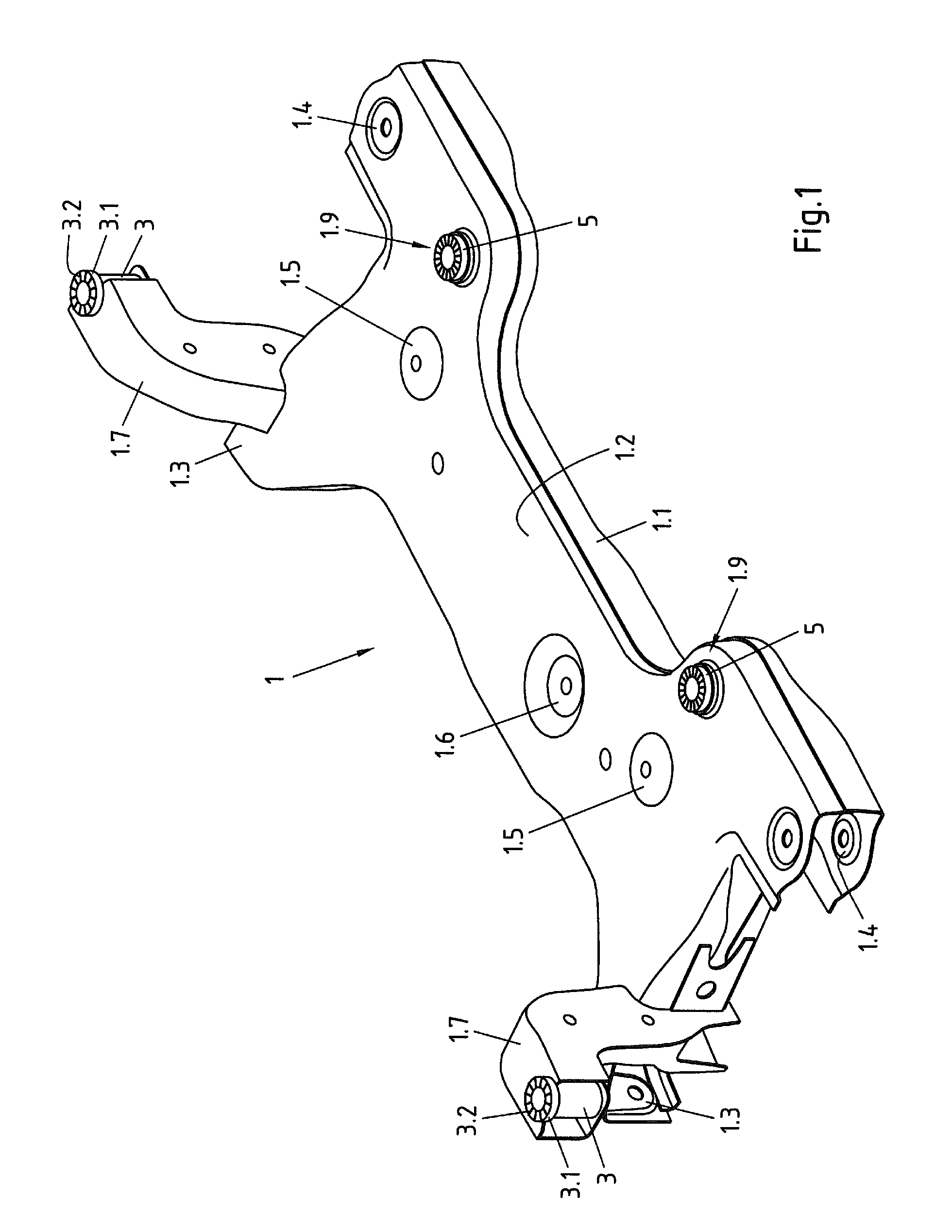
Subframe For a Motor Vehicle, In Particular a Front Axle Subframe, and Bodywork Comprising such a Subframe
ActiveUS20150217808A1Easy to installImprove security levelUnderstructuresMobile vehicleVehicle frame
The invention relates to a subframe for a motor vehicle, in particular a front axle subframe, including a first shell element and a second shell element which is rigidly connected to the first shell element and defines a cavity therewith, and at least one bodywork connection sleeve for inserting a screw therethrough. The bodywork connection sleeve is attached at one of its ends to a through-hole in the first shell element and extends within the cavity towards a through-hole in the second shell element. So that such a subframe can be easily mounted and can provide a high level of security against slipping relative to the bodywork, the invention provides that an annular disc is allocated to the attached end of the bodywork connection sleeve, which disc projects radially relative to the outer surface of the sleeve, is arranged on the outside of the first shell element and is integrally bonded thereto, and that a toothed disc produced separately from the bodywork connection sleeve is arranged on the outside on the through-hole in the second shell element, which the other end of the bodywork connection sleeve faces, which toothed disc has an external diameter which is greater than the internal diameter of the through-hole in the second shell element, and is integrally bonded to the second shell element.
Owner:AUTOTECH ENG DEUT
Derotational brace for treatment of idiopathic scoliosis
A brace for correction of scoliosis is disclosed, comprising at least one thoracic shell element and a pelvic shell element and at least one working element having a main longitudinal axle to be oriented parallel to the trunk to be treated, anchored on one of its opposite ends to the thoracic shell element and on the other to the pelvic shell element, and having spring characteristics adapted to apply continuous de-rotational force about said longitudinal axle.
Owner:HADASIT MEDICAL RES SERVICES & DEVMENT
Vertical form inculcating technology of lathy hard surface component of bamboo compound material windmill leaf blade
InactiveCN101229689ASolve the problem of indoctrinationGlue evenlyDomestic articlesEngineeringShell element
The invention relates to a process for erectly instilling a slender shell element in a blade of a wind turbine with bamboo compound material, which includes a cleaning die, an assembling die, a fixed die, wrapped glass cloth, wrapped demoulding cloth, wrapped diversion net, a winding spiral pipe, instilling substrate glue material, hardener and demoulding. The erect instilling method solves the instilling problems of one-time forming of the slender shell element in the blade of the wind turbine; at the same time, by using gravity, the glue is uniformly pasted, thus, avoiding glue accumulation caused by horizontal placement of the instillation, deflection due to male die as well as difficult cloth wrapping and avoids the glue accumulation; the produces has relatively high coaxiality; besides, the inner surface of the products has high precision and the invention is in particular applied to the inner surface of the products with high requirements.
Owner:无锡天奇竹风科技有限公司
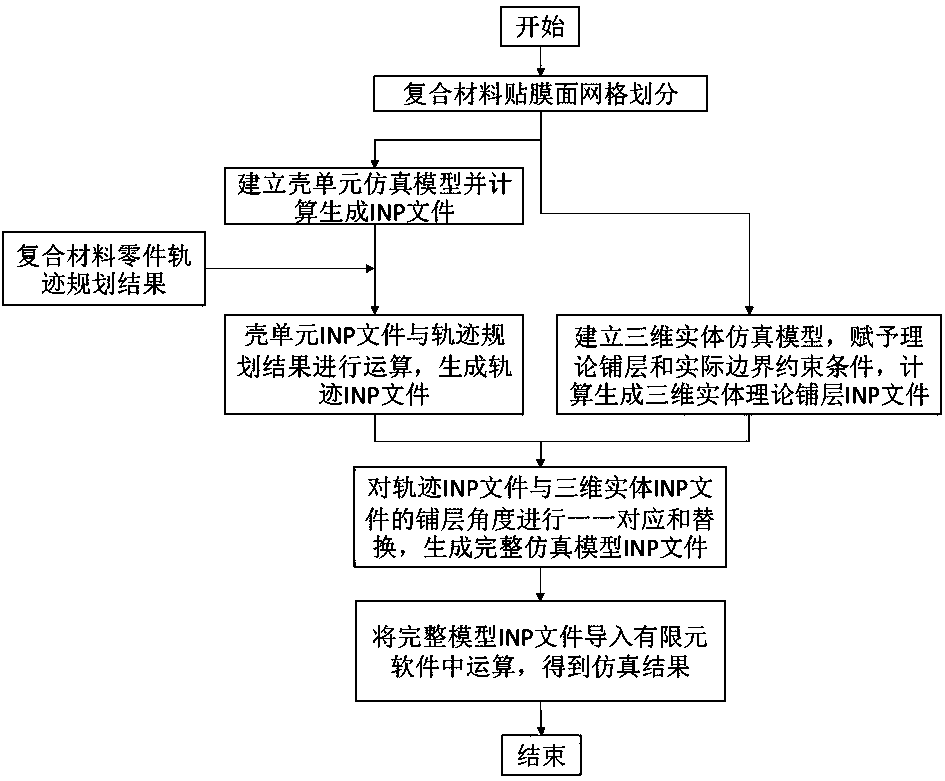
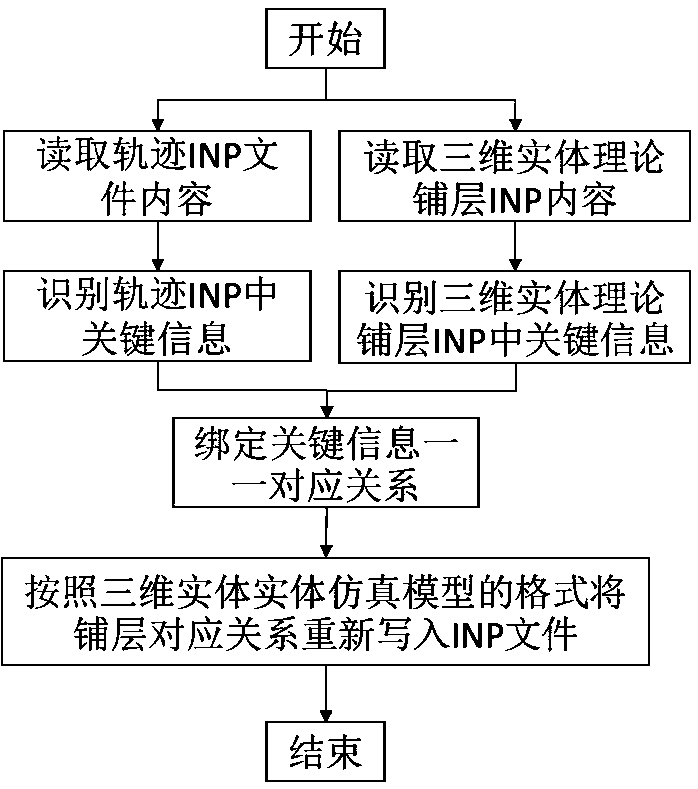
Composite material curing deformation simulation modeling method based on fiber placement track
The invention discloses a composite material solidification deformation simulation modeling method based on a fiber placement track, and the method comprises the steps: meshing a film pasting surfaceof a composite material part into a shell unit grid model, and generating an INP file through simulation operation; performing operation on the INP file of the shell element grid model and an automatic fiber placement trajectory planning result to generate a trajectory INP file; establishing a complete composite material simulation model, and generating a three-dimensional entity theoretical layupINP file; replacing the actual angle in the track INP file with the theoretical angle in the three-dimensional entity theoretical layup INP file to form a complete simulation model INP file; and calculating the complete INP file to obtain a deformation simulation result. When curing deformation simulation analysis is carried out on a composite material part manufactured by adopting an automatic fiber placement technology, modeling can be carried out on the basis of a real track of fiber placement, and the curing deformation condition of a composite material part can be analyzed more truly andaccurately.
Owner:CHENGDU AIRCRAFT INDUSTRY GROUP
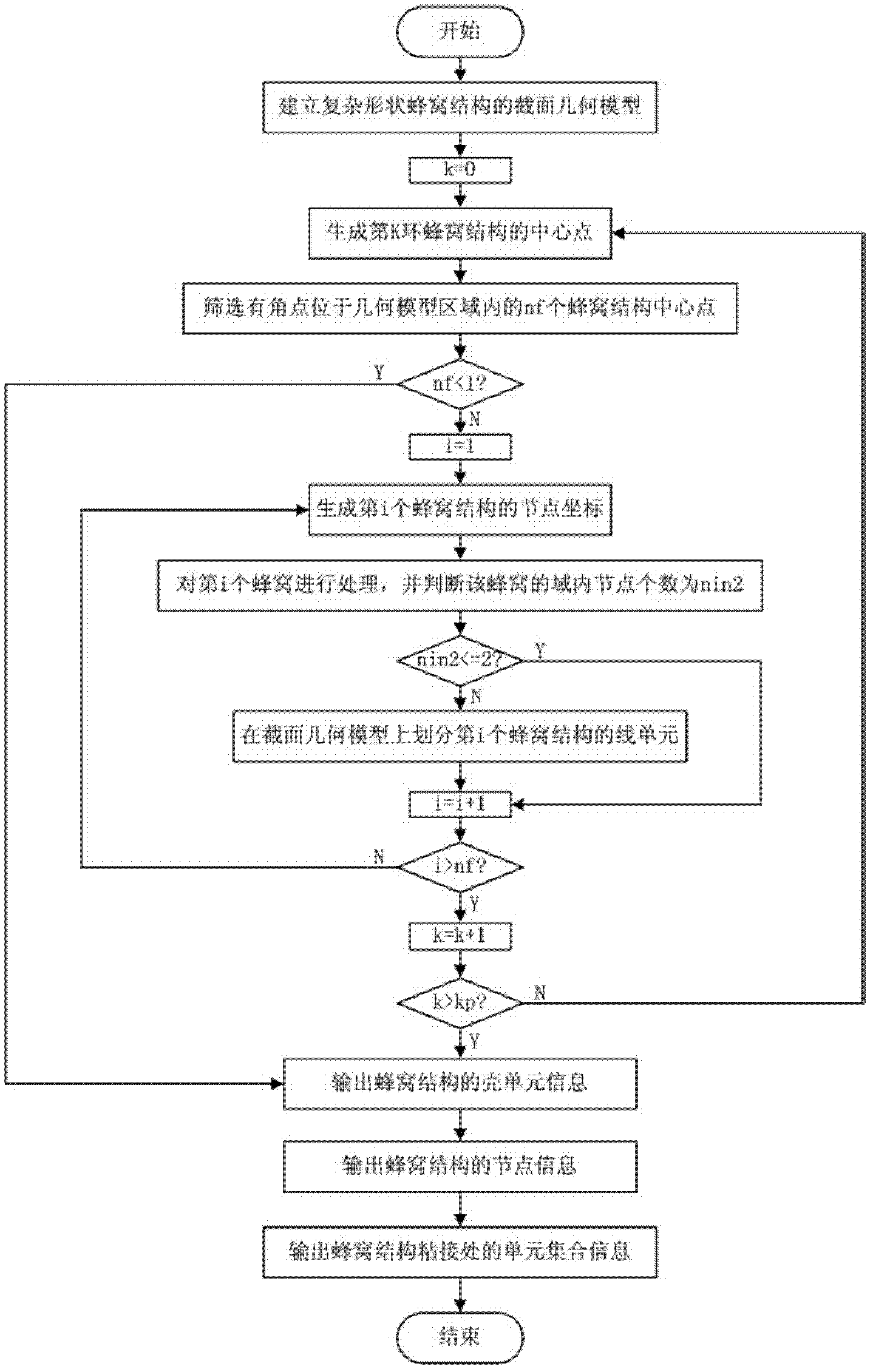
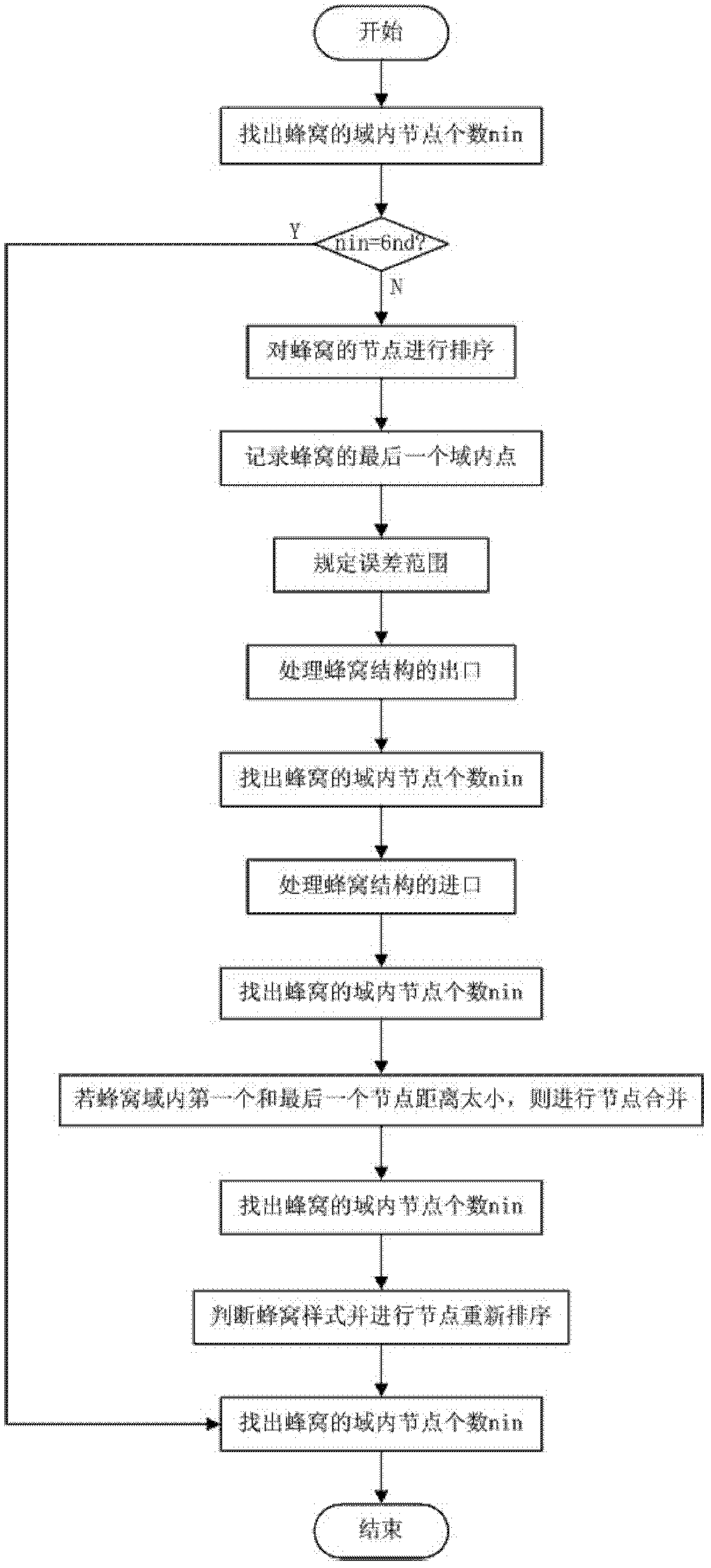
Finite element modeling method for heterotype honeycomb structure
InactiveCN102663153AAvoid the modeling processImprove modeling efficiencySpecial data processing applicationsElement modelLinear element
The invention provides a finite element modeling method for a heterotype honeycomb structure, comprising thirteen steps: 1. establishing a cross section geometry model of the heterotype honeycomb structure; 2. generating a central point of the Kth ring honeycomb structure; 3. screening out an intra-domain honeycomb of the Kth ring honeycomb structure; 4. carrying out a step 11 if there is nonexistence of the intra-domain honeycomb in the Kth ring, otherwise carrying out a step 5; 5. generating nodes of each intra-domain honeycomb in the honeycomb structure on the Kth ring; 6. dealing with the nodes of the intra-domain honeycomb; 7. carrying out a step 8 if number of the nodes in the intra-domain honeycomb exceeds 2, otherwise carrying out a step 9; 8. dividing linear elements of the intra-domain honeycomb; 9. returning to carry out the step 5. if the finite element model of the intra-domain honeycomb on the Kth ring honeycomb structure is not completely generated, otherwise carrying out a step 10;10. returning to carry out the step 2, if the finite element model of the intra-domain honeycomb of thehoneycomb structures on all rings is not completely generated, otherwise carrying out a step 11; 11. outputting shell element information; 12.outputting node information; and 13.outputting element set information of the honeycomb structure sticking-joint.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com