Multi-label learning based activity prediction method for antibacterial peptide
A technology of multi-marker learning and prediction method, applied in the field of antibacterial peptide activity prediction based on multi-marker learning, which can solve the problems of time-consuming, no antibacterial peptide activity prediction, antibacterial peptide identification, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
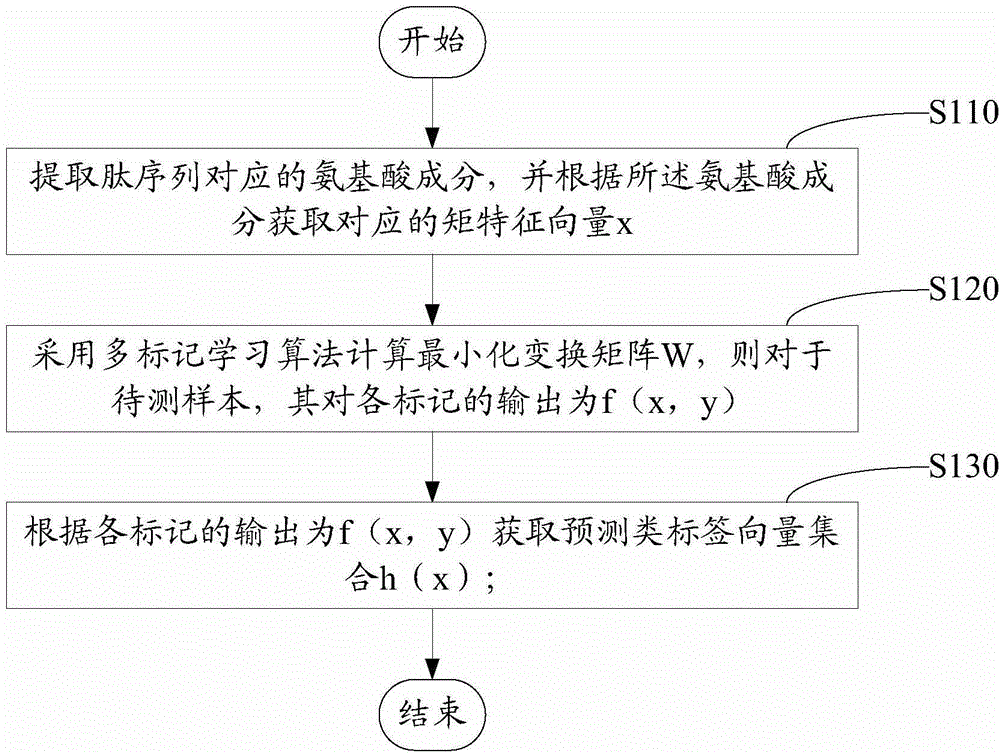
[0031] Such as figure 1 Shown is the flow chart of the antimicrobial peptide activity prediction method based on multi-label learning.
[0032] A method for predicting antimicrobial peptide activity based on multi-label learning, comprising the following steps:
[0033] Step S110, extract the amino acid composition corresponding to the peptide sequence, and obtain the corresponding moment feature vector x according to the amino acid composition, wherein the moment feature vector x is used to describe the shape characteristics of each angle of the peptide sequence.
[0034] Step S110 includes:
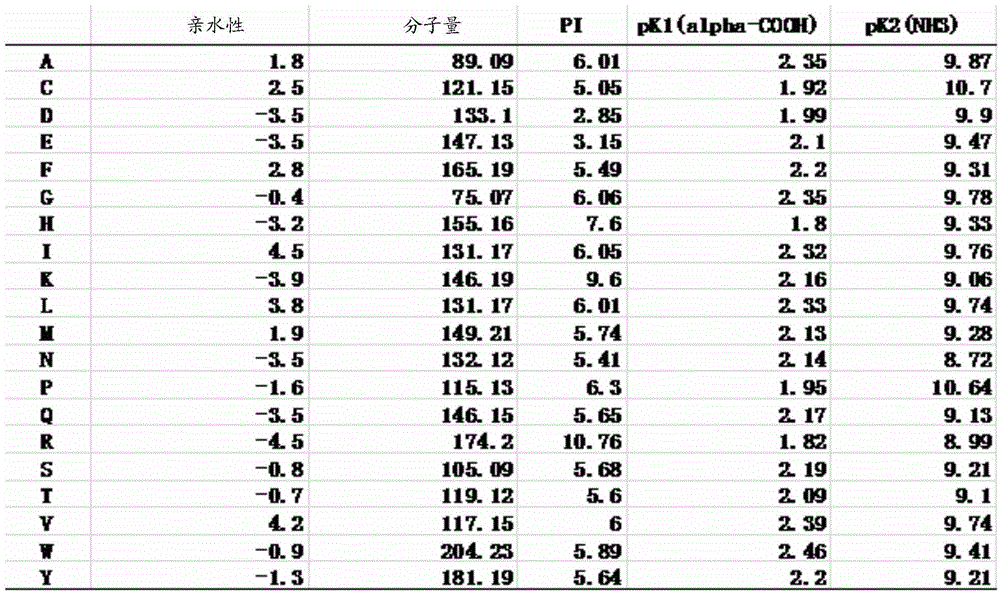
[0035] The amino acid sequence is digitally coded according to the physical and chemical property indicators of the amino acid.
[0036] The meaning of each amino acid residue in the amino acid sequence is converted into a numerical sequence.
[0037] Calculate the moment feature vector x for the whole, N-terminal and C-terminal of the peptide sequence according to the numerical sequ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com