Deformation-preventing solid-wood floor-heating-resistant floor base material, manufacturing method of deformation-preventing solid-wood floor-heating-resistant floor base material and floor manufactured with deformation-preventing solid-wood floor-heating-resistant floor base material
An anti-deformation, solid wood technology, applied in wood processing equipment, manufacturing tools, floors, etc., can solve the problems of non-environmental protection, high cost, and easy deformation of solid wood composite floors, and achieve the goal of increasing density, increasing costs, and eliminating internal stress Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
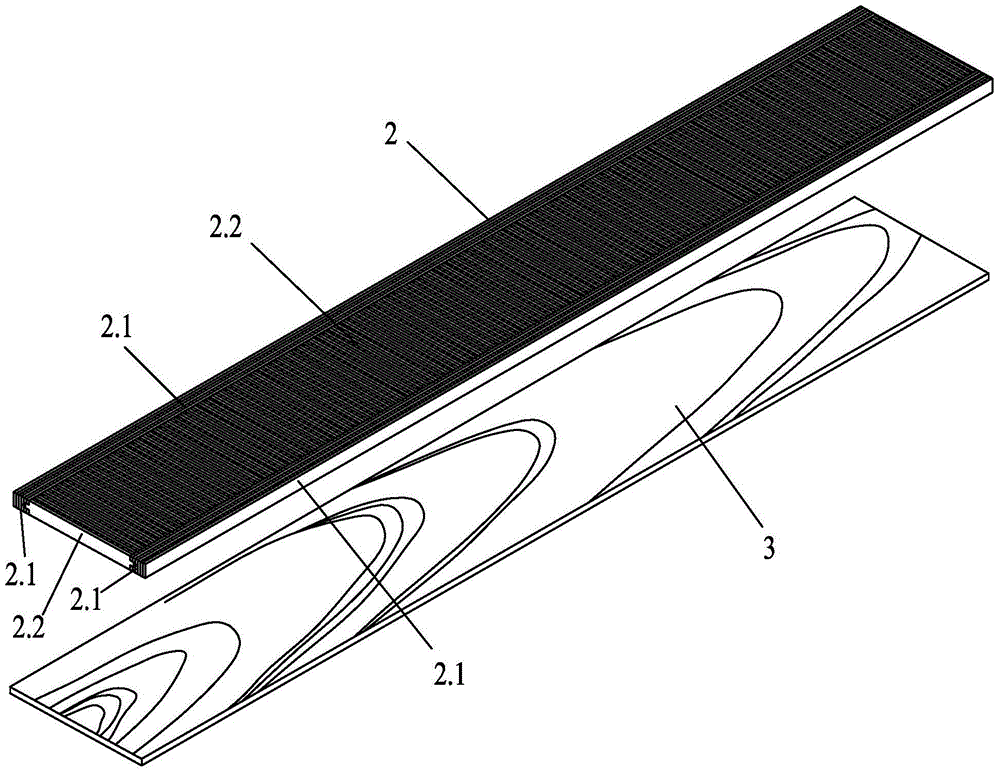
[0020] Specific implementation mode one: combine figure 1 To illustrate this embodiment, the anti-deformation solid wood heat-resistant floor substrate includes two parts: the middle layer 2 and the bottom plate 3 . The bottom of the middle layer 2 is bonded with a base plate 3; the base plate 2 is made of artificial accelerated forest veneer, and the grain direction of the base plate 2 is longitudinal; the middle layer 2 is made of artificial accelerated forest veneer, mainly composed of two side strips 2. The core material 2.2 is formed, and the side strips 2.1 are composed of long thin wood strips A arranged along the length direction of the floor (it can also be made of solid wood "leftover material" or "three leftovers of forest wood" solid wood slats), and the two side strips are arranged on the core material 2.2 On both sides, the side strip 2.1 is composed of several long veneer boards A bonded, and the core material 2.2 is composed of several short veneer boards B arr...
specific Embodiment approach 2
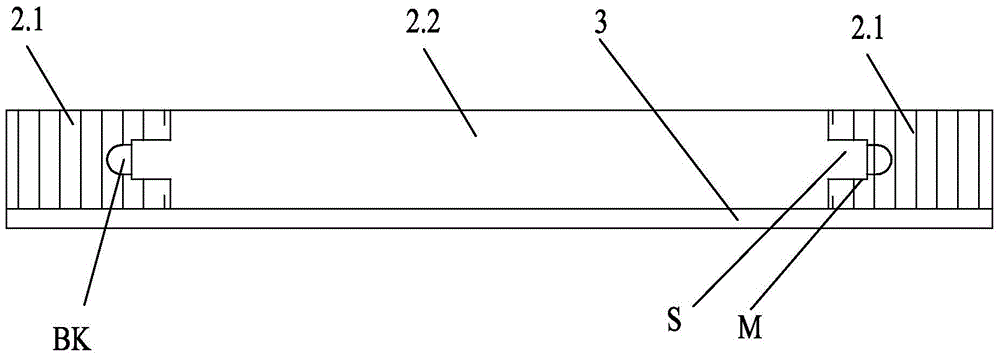
[0026] Specific implementation mode two: combination figure 2 To illustrate this embodiment, the difference from Embodiment 1 is that the joint between the side strip 2.1 and the middle core material 2.2 is a combination of male and female concave-convex structures, and the side strip 2.1 is milled with concave and convex grooves M and ventilation grooves BK, The middle core material 2.2 is milled with a tenon S. Other structures and connection methods are the same as those in the first embodiment.
specific Embodiment approach 3
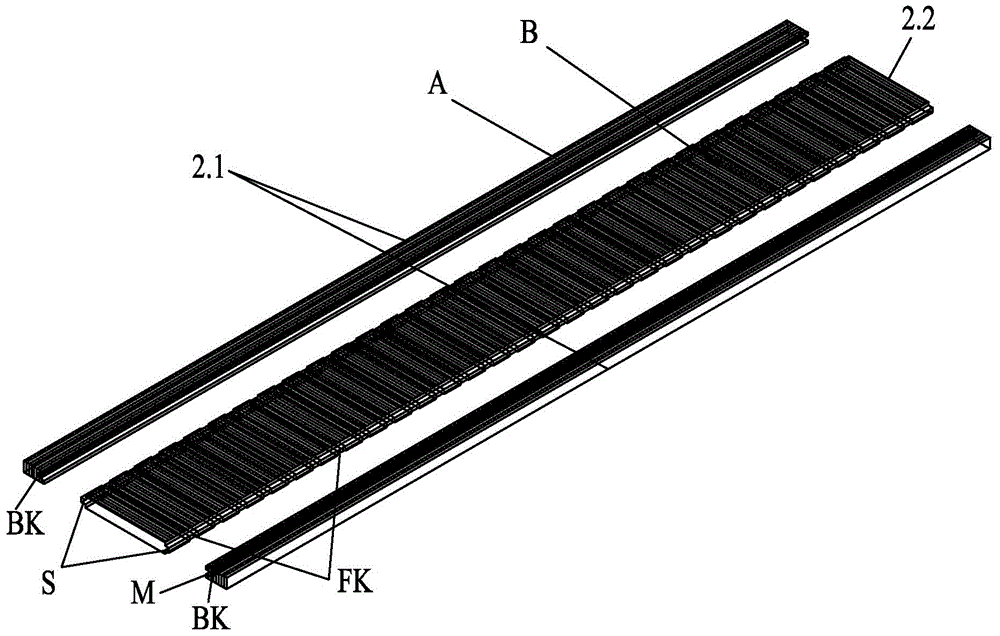
[0027] Specific implementation mode three: combination image 3This embodiment is different from Embodiment 1 in that: rectangular hollow grooves FK are evenly arranged at intervals of 30-50 mm on the intermediate core material 2.2, and the central axis of the rectangular hollow grooves FK is consistent with the width direction of the floor. Other structures and connection methods are the same as those in the first embodiment.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com