A Prediction Method of Gravity Deformation of Beam of Heavy Gantry Milling Machine Based on Finite Difference Method
A finite difference method and gravity deformation technology, which is applied in special data processing applications, instruments, electrical digital data processing, etc., can solve problems such as accurate calculation of beam gravity deformation curves and large differences in actual deformation values
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
[0035] Specific Embodiment 1: A method for predicting the gravitational deformation of a beam of a heavy-duty gantry milling machine based on the finite difference method in this embodiment is specifically prepared according to the following steps:
[0036] Step 1. By placing shim iron at the assembly place of the beam and the column, simulating the actual assembly conditions to design the self-weight deformation experiment of the heavy-duty machine tool beam, and obtain the self-weight deformation curve of the beam considering the material inhomogeneity;
[0037] Step 2. Using the theory of material mechanics, the beam is simplified into a beam self-weight deformation model and a beam torsional deformation model according to the stress of the beam under its own weight;
[0038]Step 3. Discretize the beam into a group of discrete micro-segments. After discretizing the self-weight deformation model of the beam obtained in Step 2, combine the finite difference method to establish...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0047] Specific embodiment 2: The difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment 1 is that in step 1, by placing pad iron at the assembly place of the beam and the column, simulating the actual assembly conditions to design the self-weight deformation experiment of the beam of the heavy-duty machine tool, and obtaining the material inhomogeneity The specific process of the self-weight deformation curve of the beam is as follows:
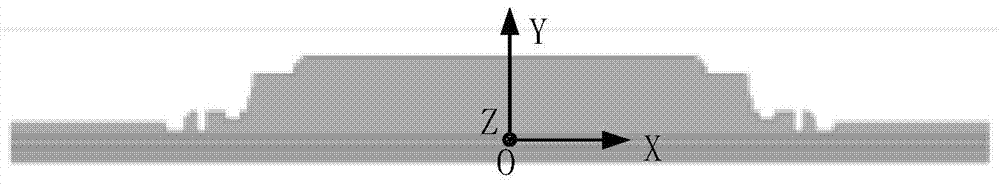
[0048] (1) According to the top view of the beam of the heavy-duty gantry milling machine, the midpoint of the beam in the horizontal plane where the lower guide rail of the beam is located is taken as the origin O of the coordinate system, and the Cartesian coordinate system is established. The X-axis direction is along the direction of the beam guide rail, and the positive and Y axes are to the right Perpendicular to the X-axis, and upward is positive and the positive direction of the Z-axis conforms to the right-hand rule as image 3 s...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0053] Embodiment 3: The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 or 2 is that in step 2, the theory of material mechanics is used to simplify the beam into a deformation model of the weight of the beam and a torsional deformation model of the beam according to the force of the beam under its own weight. The process is:
[0054] (1) According to figure 2 The shape of the beam is simplified by using the calculation method of material mechanics to simplify the calculation model, and according to the working environment and assembly constraints of the machine tool beam, the bending deformation part of the beam is simplified as a simply supported beam;
[0055] (2) Gravity is applied to the simply supported beam as a uniformly distributed load, and the uniformly distributed load is expressed by the gravity on the unit length of the beam, that is, the concentration of gravity load; Figure 6 The mechanical model of simply supported beam;
[0056] (3) According to the s...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com