Electrode device and method for lowering arsenic and lead concentrations in rice
An electrode device and a technology of lead concentration, applied in the field of reducing the concentration of arsenic and lead in rice, can solve the problems of increasing cadmium, and achieve the effect of controlling transfer and reducing accumulation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
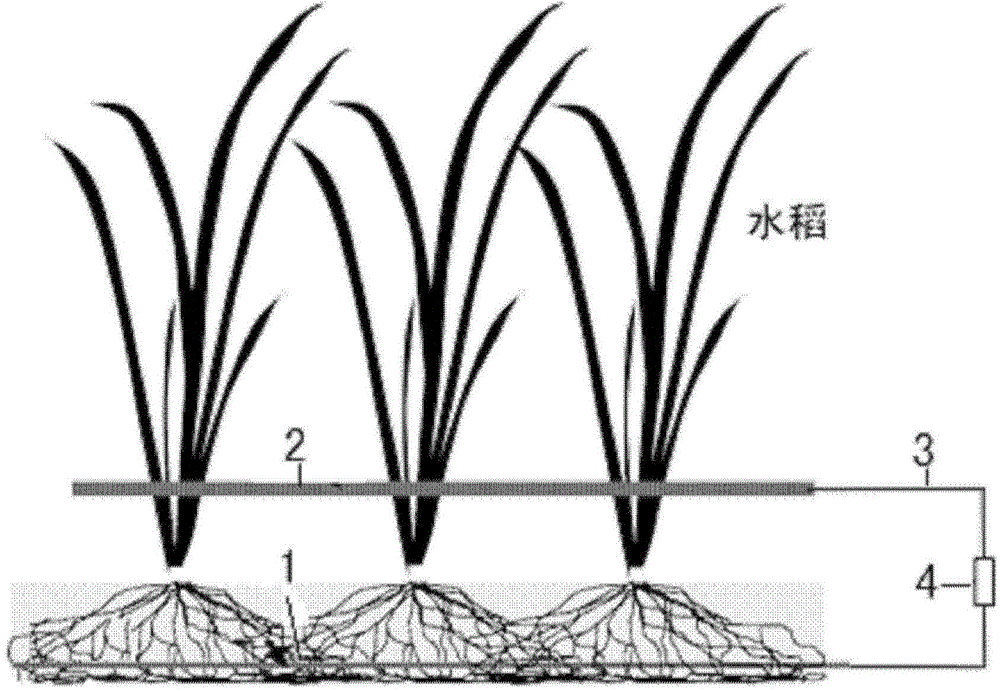
[0032] The paddy soil is Jiaxing paddy soil with arsenic added to 120ppm, and the rice variety is Xiushui 128. The soil was placed in a plastic pot with a diameter of 9 cm and a depth of 15 cm. After flooding for 11 days, the rice seedlings were moved into them. After 7 days of growth, samples were taken to analyze the concentrations of heavy metals arsenic, copper, cadmium, and lead in the roots and leaves.
[0033] The anode electrode area is divided into three gradients: 15, 21 and 27cm 2 . The electrode thickness is: 0.5cm, the electrode burial depth is 6cm: the external resistance is 500 ohms. Three replicates per gradient.
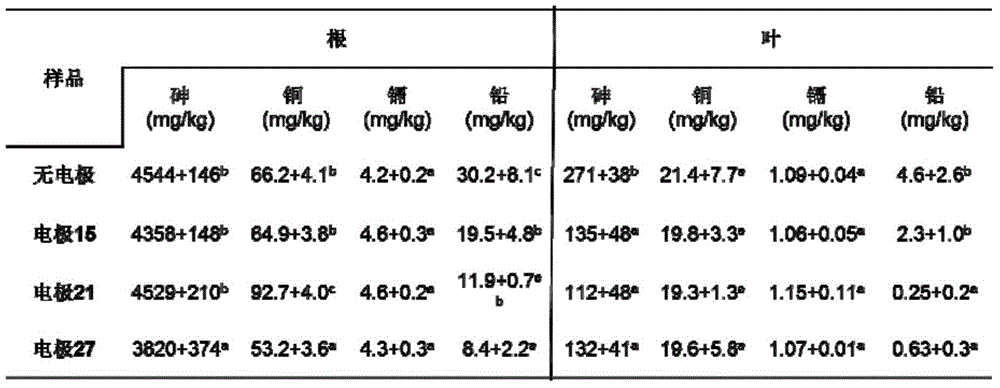
[0034] In the system with or without electrodes, the content of heavy metals in rice is shown in the table below:
[0035]
[0036] The results show that after adding electrodes, the arsenic in rice roots dropped from 4544mg / kg to 3820mg / kg, and the arsenic in rice leaves dropped from 271mg / kg to 112mg / kg; lead dropped from 30.2mg / kg in roots t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com