Estimation method of azimuth difference of digital surface model based on 3d‑zernike moment phase analysis
A technology of digital surface model and azimuth difference, applied in three-dimensional shape analysis and application of remote sensing ground objects, three-dimensional data registration of remote sensing ground objects, and change detection, to achieve excellent robustness.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
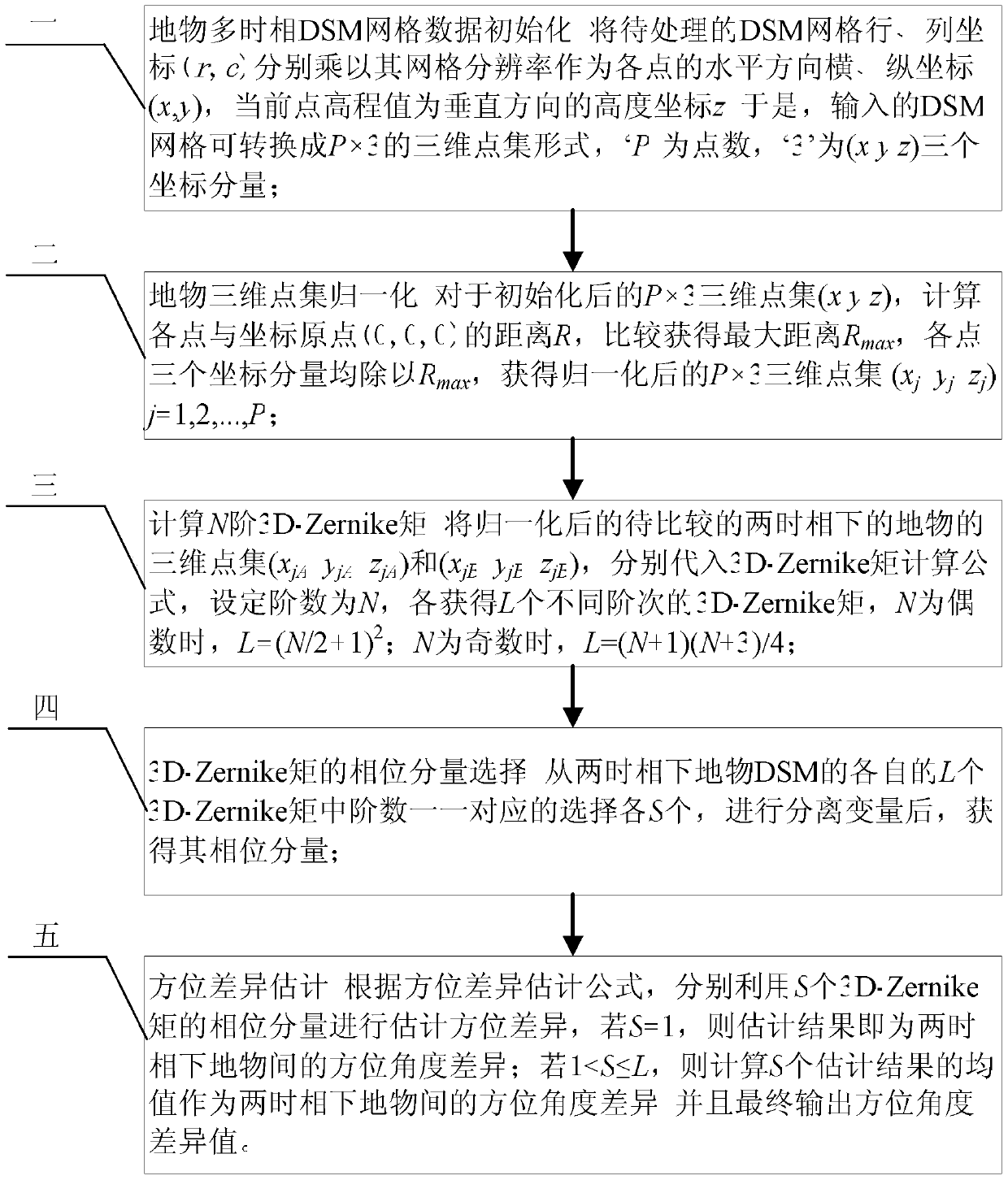
[0038] Specific implementation mode one: combine figure 1 Describe this embodiment, the implementation process of the digital surface model orientation difference estimation method based on 3D-Zernike moment phase analysis described in this embodiment is:
[0039] Step 1. Initialize the multi-temporal DSM grid data of ground objects and standardize the input data format: Multiply the row and column coordinates (r, c) of the DSM grid to be processed by their grid resolution respectively as the horizontal horizontal and horizontal directions of each point. Ordinate (x, y), the elevation value of the current point is the height coordinate z in the vertical direction; thus, the input DSM grid can be converted into a P×3 three-dimensional point set form, 'P' is the number of points, and '3' is ( x, y, z) three coordinate components;
[0040] DSM grid data initialization is as formula (1):
[0041]
[0042]Among them, r and c are the row and column coordinates of DSM, DSM(r, c)...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0048] Embodiment 2: The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that the three-dimensional data normalization method in step 2 can be a calculation method or a custom maximum distance method.
[0049] Calculation method: the distance R formula in step 2 can be calculated as formula (2):
[0050]
[0051] The calculated distance R can be compared and sorted to obtain R max value;
[0052] The normalization formula is as formula (3):
[0053]
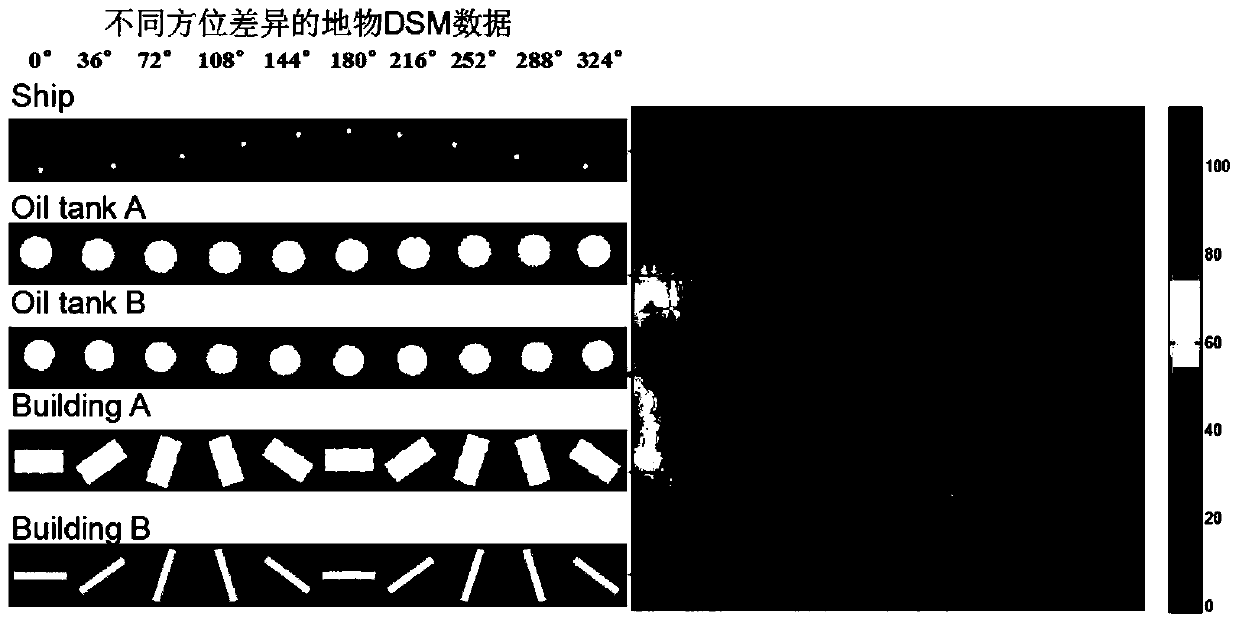
[0054] Custom maximum distance method: according to the input DSM data, a uniform maximum distance value R can be set for the DSM data of all ground objects max Carry out the normalization processing of each object DSM, but R max It is necessary to make the three-dimensional point set (x j ,y j ,z j )j=1,2,...,P data are in the unit sphere to meet the calculation requirements of 3D-Zernike moments.
[0055] Other steps are the same as in the first embodiment.
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0056] Specific embodiment three: the digital surface model orientation difference estimation method based on 3D-Zernike moment phase analysis described in the present embodiment, the 3D-Zernike moment numerical calculation formula in step 3 is as formula (4):
[0057]
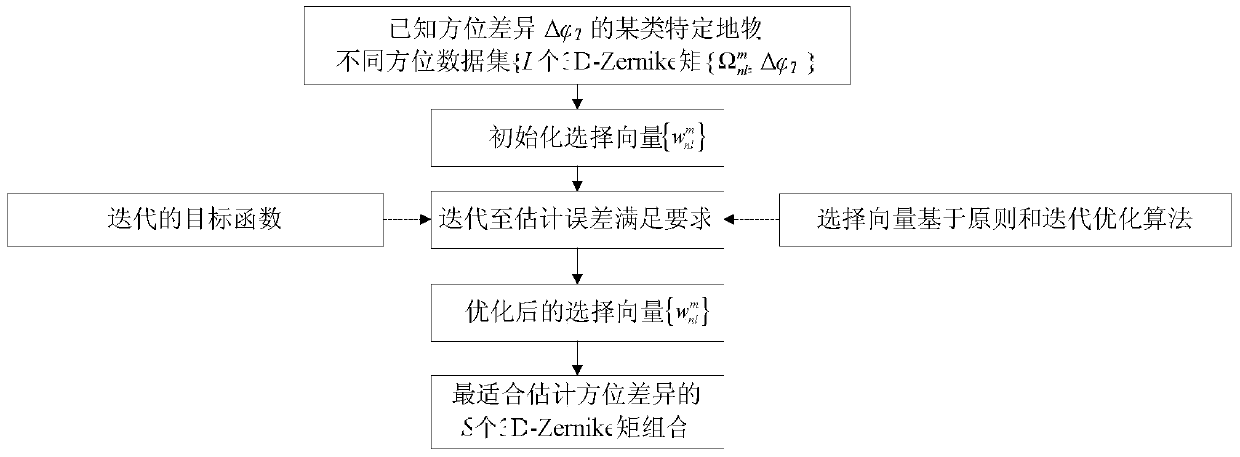
[0058] Formula (4) is a simplified numerical calculation method derived from the original definition of 3D-Zernike moments, where n∈[0,N],l∈[0,n],m∈[-l,l],k=( n-l) / 2 and must be an integer, this is the order condition of the N-order 3D-Zernike moment, each {n,l,m} combination that satisfies the order condition corresponds to a specific order 3D-Zernike moment j=1,2,...,P, is the serial number of P three-dimensional points; for DSM data, usually set N<5;
[0059] In formula (4), the orthogonalization coefficient The calculation formula is as formula (5):
[0060]
[0061] In formula (4), the harmonic function part The calculation formula is as formula (6):
[0062]
[0063] Where i is the imagin...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com