Microfluidic Flow Regulator Based on Pneumatic Drive
A flow regulating device and pneumatic drive technology, applied in the field of microfluidics, can solve the problems of unmeasured actual flow, low flow regulation accuracy, and slow dynamic response speed, etc., and achieve good dynamic regulation characteristics, fast dynamic response speed, and flow regulation accuracy high effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
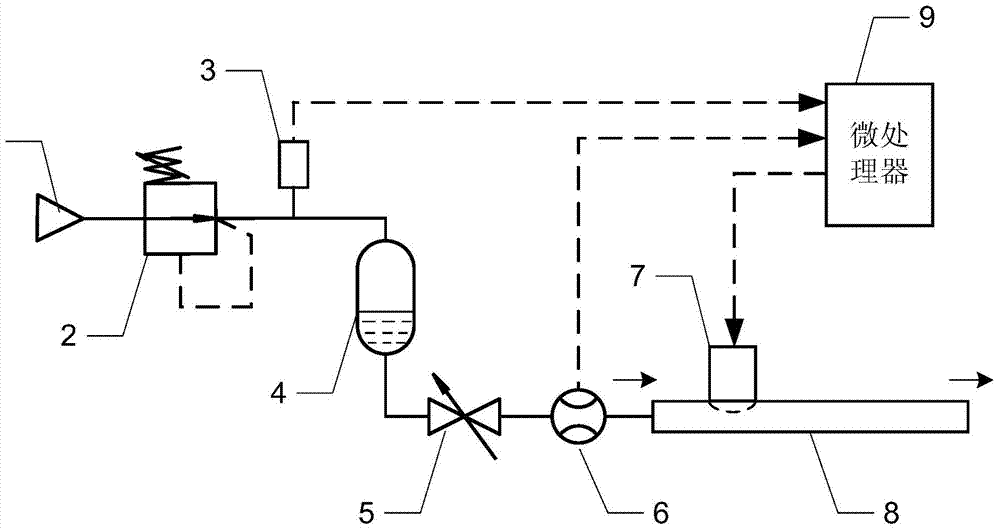
[0011] Specific implementation mode one: the following combination figure 1 with figure 2 Describe this embodiment, the air pressure-driven microfluid flow adjustment device described in this embodiment includes an air supply source 1, a pressure reducing valve 2, a pressure sensor 3, a liquid container 4, a valve 5, a flow meter 6, and a microvalve 7. The liquid microchannel 8 and the microprocessor 9; the gas inlet of the pressure reducing valve 2 communicates with the compressed air outlet of the gas supply source 1; the gas outlet of the pressure reducing valve 2 communicates with the gas inlet of the liquid container 4, and the liquid container The liquid outlet of 4 communicates with the inlet of the valve 5, and the outlet of the valve 5 communicates with the inlet of the liquid microchannel 8 through the flow meter 6; the microvalve 7 is embedded in the liquid microchannel 8;
[0012] The pressure sensor 3 detects the outlet gas pressure of the pressure reducing valv...
specific Embodiment approach 2
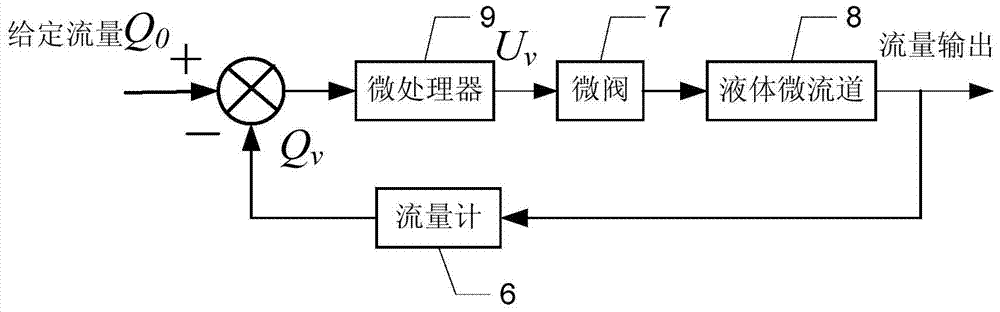
[0016] Specific implementation mode two: the following combination figure 2 Describe this embodiment, this embodiment will further explain Embodiment 1, the formation process of the flow control command signal of the microprocessor 9 is: the microprocessor 9 according to the given flow signal Q 0 and the actual liquid flow signal Q collected by flowmeter 6 v The difference forms the flow control command signal U v . The microprocessor 9 gives a flow control instruction signal to change the working state of the microvalve 7, and then change the flow cross section of the liquid microchannel 8, so that the actual liquid flow signal Q v with a given flow signal Q 0 Tend to be consistent, to achieve closed-loop control of flow.
specific Embodiment approach 3
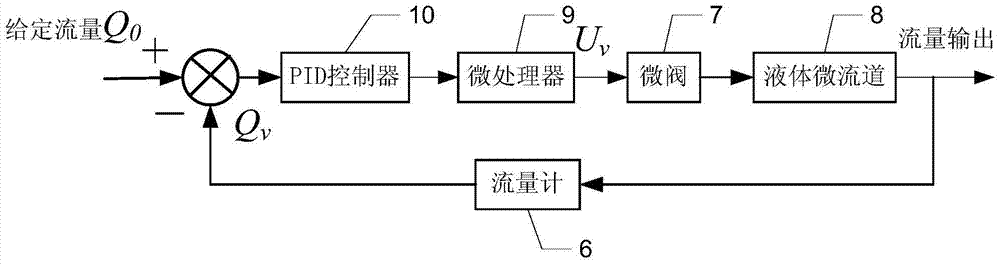
[0017] Specific implementation mode three: the following combination image 3 Describe this embodiment, this embodiment will further explain Embodiment 1 or 2, it also includes PID controller 10, given flow signal Q 0 and the actual liquid flow signal Q collected by flowmeter 6 v The difference is adjusted by the PID controller 10, and the flow control command signal U is formed by the microprocessor 9 v . The difference between the two is processed by the PID microprocessor and then the flow control command signal U is given. v , improve the flow adjustment accuracy and dynamic response speed, and meet the flow adjustment needs of different microfluidic devices.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com