Wafer processing method
A processing method and chip technology, applied in stone processing equipment, fine working devices, manufacturing tools, etc., can solve problems such as deterioration of bending strength, difficulty in forming chips, chip damage, etc., and achieve the effect of deterioration of bending strength
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
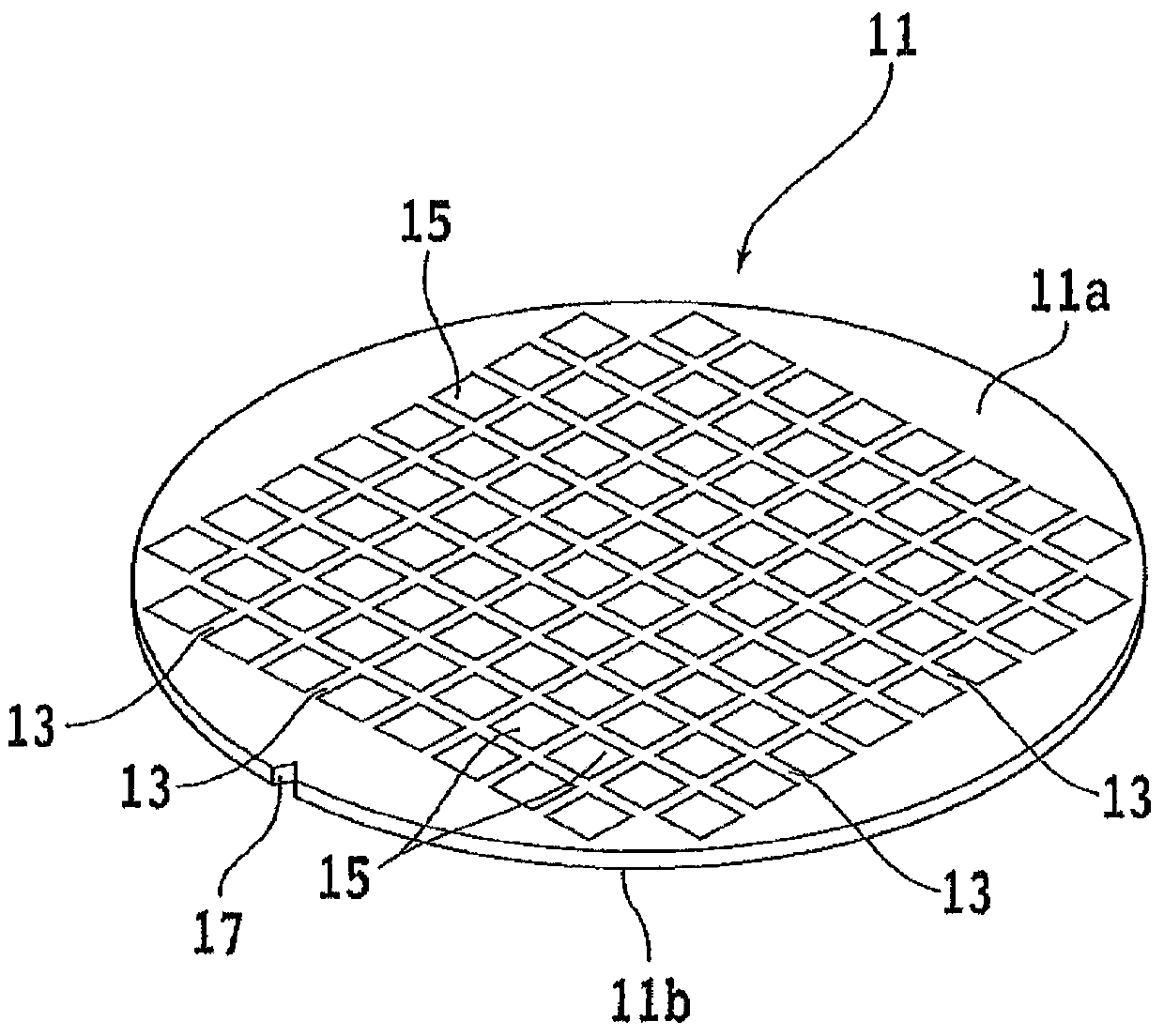
[0036] Hereinafter, embodiments of the present invention will be described in detail with reference to the drawings. refer to figure 1 , shows a front side perspective view of the semiconductor wafer 11 . Devices 15 such as ICs and LSIs are formed in regions divided by a plurality of dividing lines (streets) 13 on a front surface 11a of a semiconductor wafer (hereinafter sometimes simply referred to as a wafer) 11 . On the outer periphery of the wafer 11 is formed a notch 17 as a mark indicating the crystal orientation of the wafer.
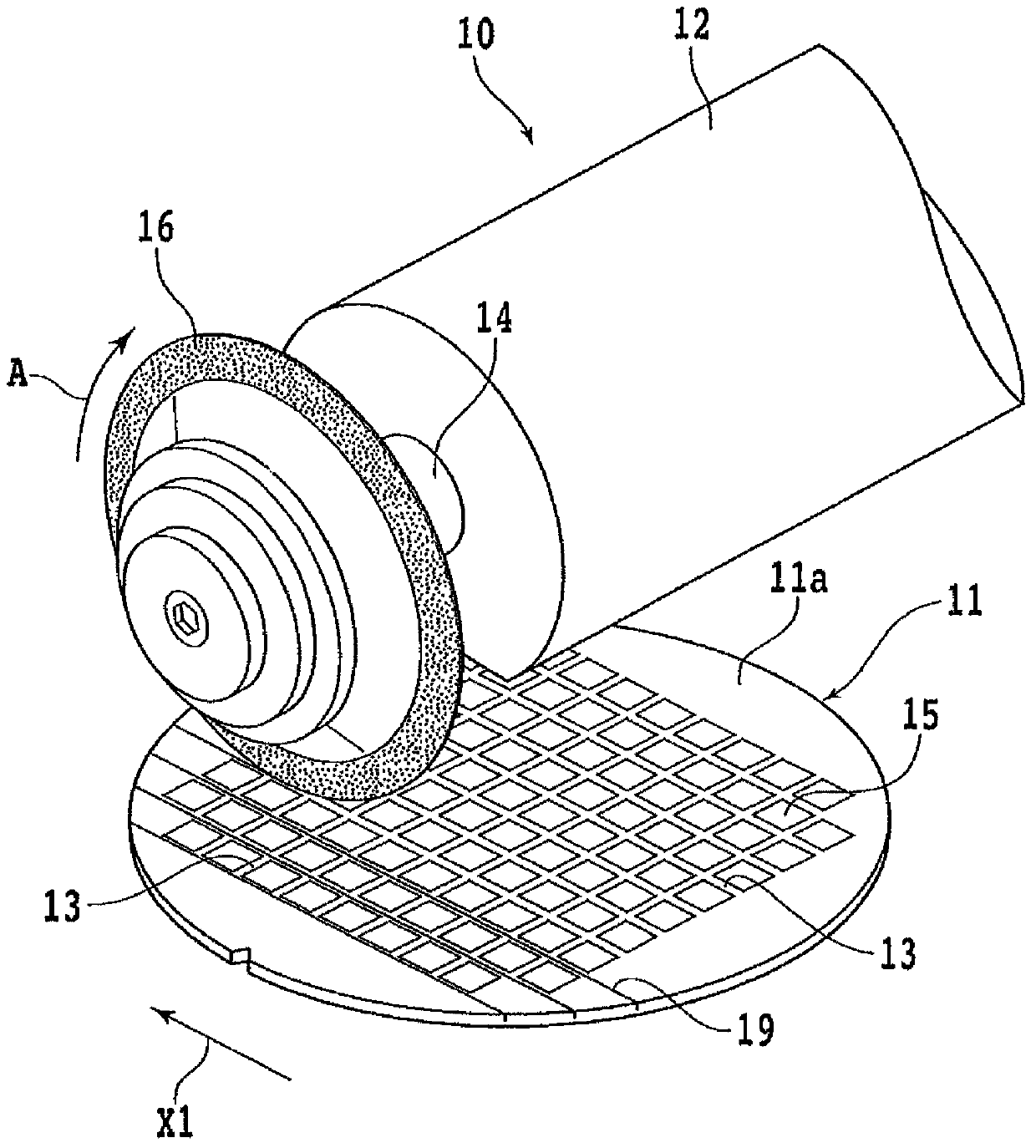
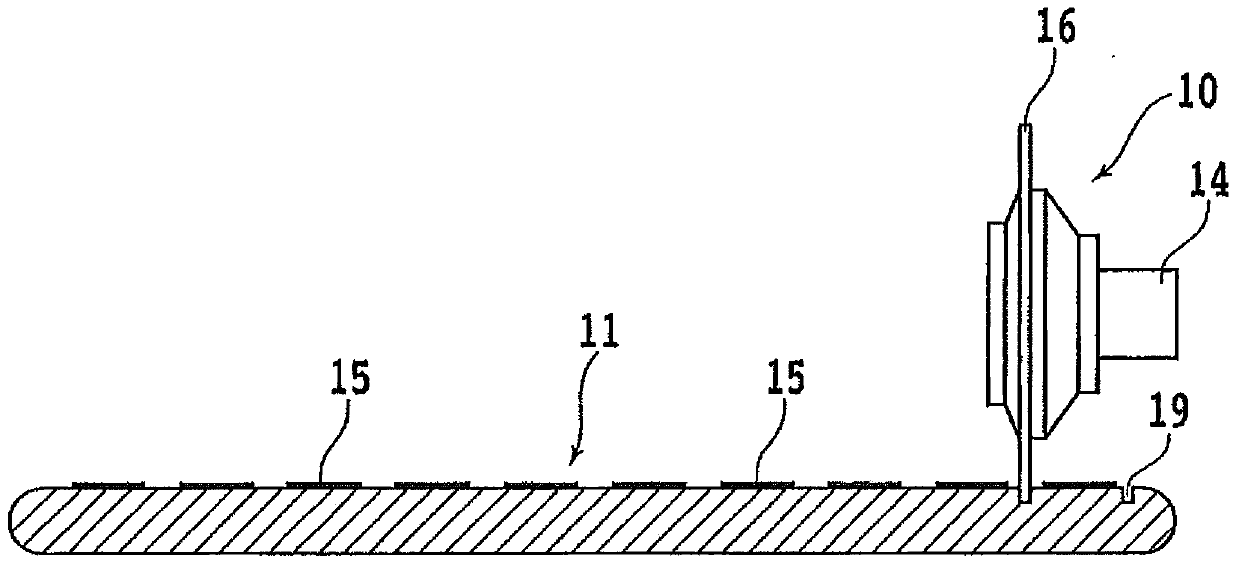
[0037] In the wafer processing method of the present invention, first, a groove forming step is performed in which a plurality of grooves are formed from the front surface 11a of the wafer 11 along the planned dividing line 13 to a depth not reaching the finished thickness. figure 2 is a perspective view showing a groove forming step, image 3 is its cross-sectional view. exist figure 2 and image 3 In , the chuck table for holding the wa...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com