Non-Destructive Evaluation of Structures Using Motion Magnification Technology
A non-destructive, motion-amplifying technology that can be used in machine/structural component testing, material analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic waves, strength properties, etc., and can solve problems such as expensive
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
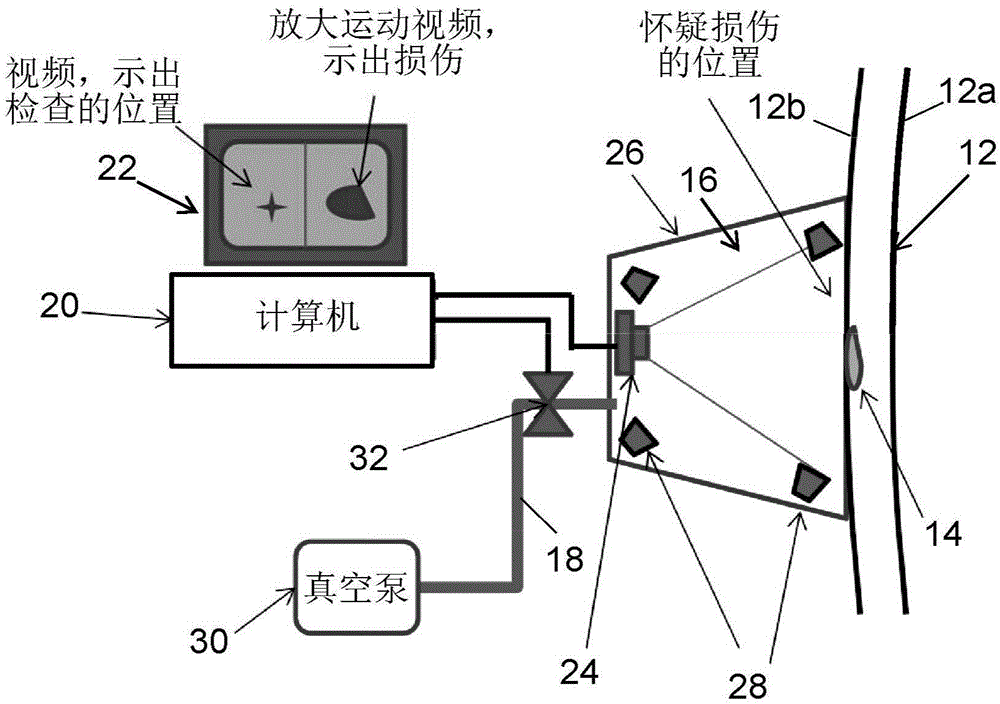
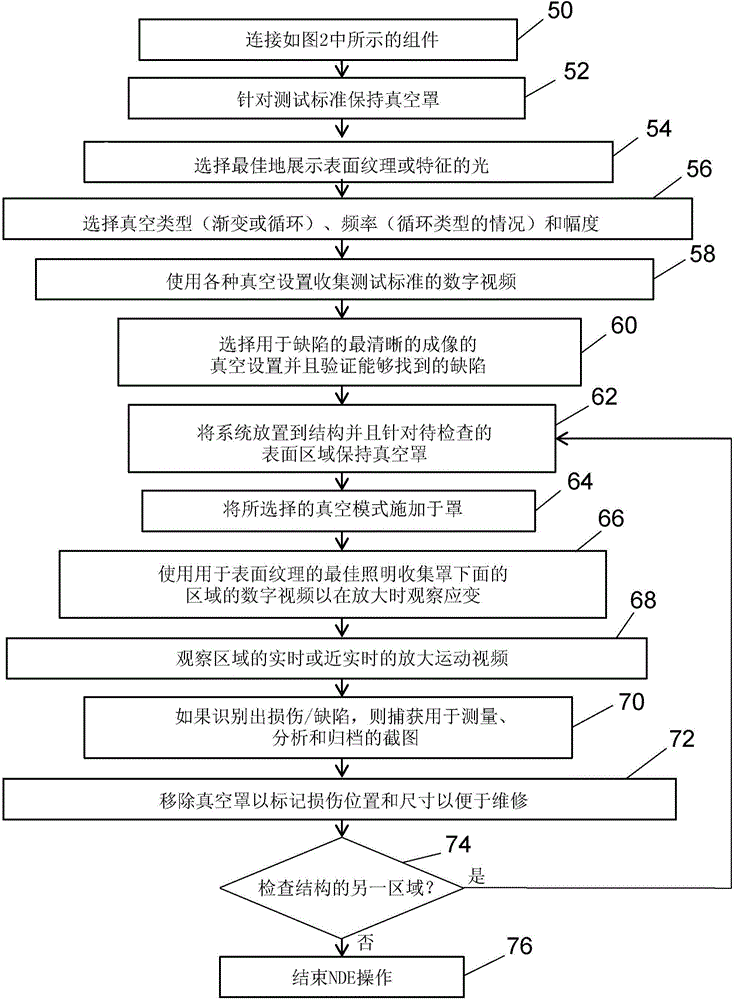
[0025] Embodiments of systems and methods for performing non-destructive assessment of structures using motion magnification techniques will now be described. The following systems and methods for monitoring structural testing using motion magnification techniques will be described.
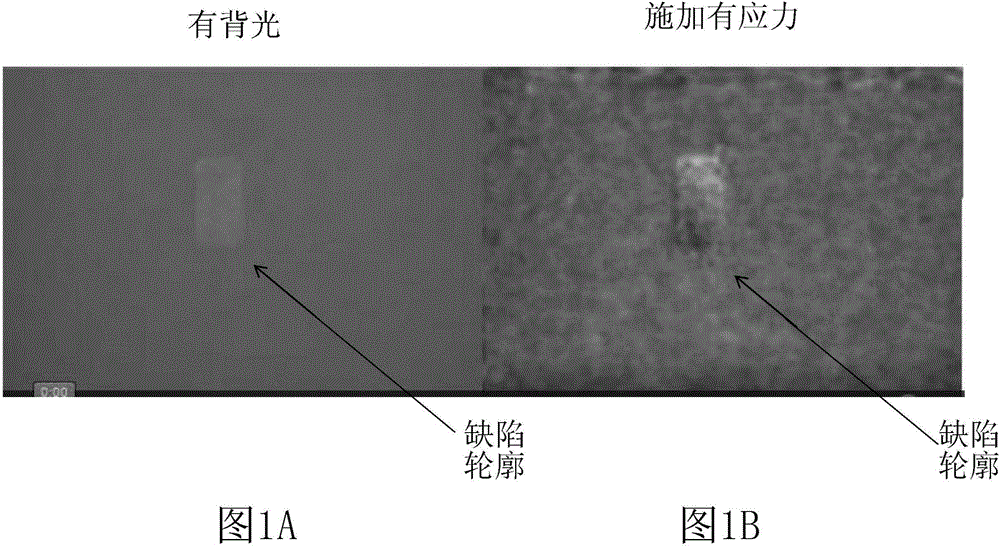
[0026] To prove the concept of using motion magnification techniques to perform non-destructive evaluation of structures, tests were performed in which a 3 / 4 inch by 1 inch defect was machined into the backside of a 1 / 8 inch thick composite layup. In the first part of the test, light was applied to the back of the stack and a video was recorded of the area on the anterior skin overlapping the machined defect. Figure 1A is a screencast video image of a backside lit stackup showing the outline of a machined defect, which would normally not be visible from the front. In the second part of the test, strain was created (ie, stress was applied) using a partial vacuum source attached to the backside of...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com