Foot adsorption wall-climbing robot movement mechanism and movement method
A wall-climbing robot and robot movement technology, applied in the field of robotics, can solve problems such as inability to move forward and turn at a uniform speed, complex structure of the wall-climbing robot, and inability to control the height of the wall smoothly.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
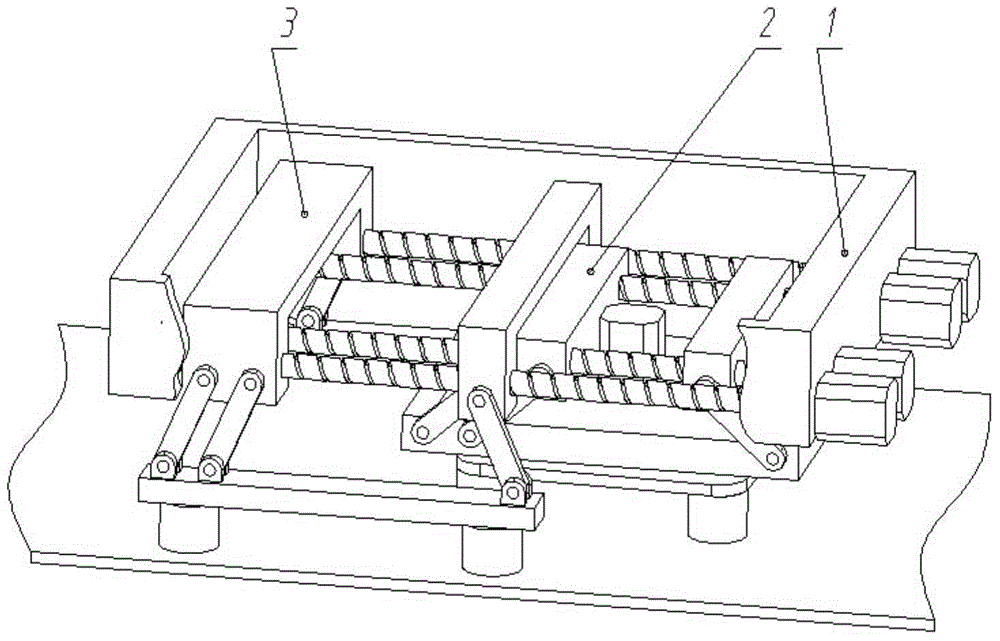
[0026] Embodiment 1, a schematic diagram of the motion mechanism of a foot-type adsorption wall-climbing robot, as shown in figure 1 as shown,
[0027] A motion mechanism of a foot-type adsorption wall-climbing robot, comprising: a body, an inner foot assembly, and an outer foot assembly; the inner foot assembly and the outer foot assembly are respectively installed on the body, and have symmetrical structures on the left and right sides of the body.
[0028] Specifically, it includes: a body 1, an inner foot assembly 2 and an outer foot assembly 3, the inner foot assembly 2 and the outer foot assembly 3 are installed on the body 1 respectively, and the inner foot assembly 2 and the outer foot assembly 3 are installed on the two sides of the screw guide rod. The lateral direction is symmetrical. Due to the symmetrical structure, the robot moves smoothly.
Embodiment 2
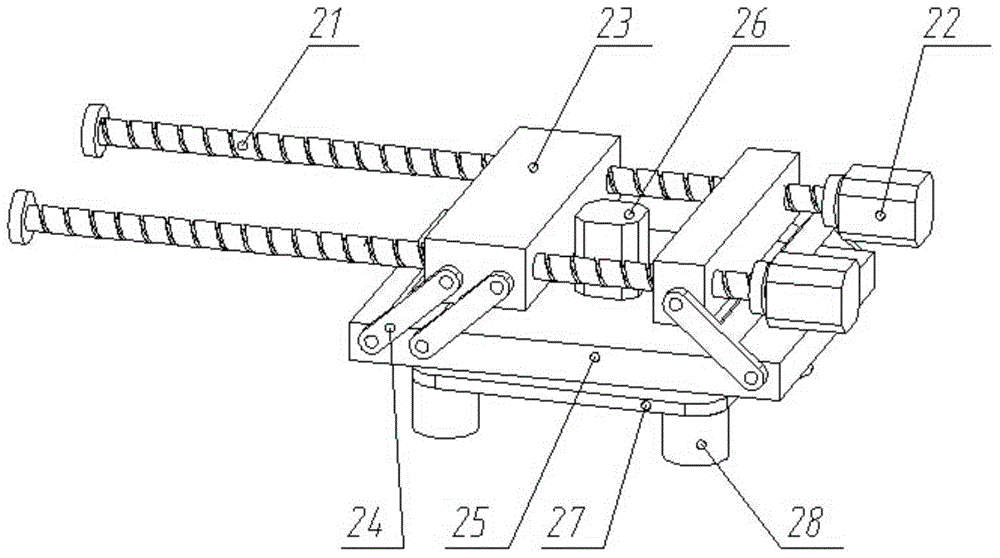
[0029] Embodiment 2, a schematic diagram of the motion mechanism of a foot-type adsorption wall-climbing robot, as shown in figure 2 as shown,
[0030] On the basis of embodiment one, further include:
[0031] The inner foot assembly 2 includes an inner screw guide rod 21, an inner screw guide rod driving motor 22, and two inner sliders 23 respectively, wherein the two inner screw guide rods 21 are distributed in parallel, and there are bearings and bearings at both ends respectively. The body 1 is connected, and two inner screw guide rod driving motors 22 are fixedly installed on the body 1, and one end of each inner screw guide rod 21 is coaxially connected with an inner screw guide rod driving motor 22 respectively.
[0032] Two inner sliders 23 are distributed forward and backward along the direction of the inner screw guide rod 21; the connection between each inner slider 23 and the two inner screw guide rods 21, one is a thread pair connection, and the other is a movin...
Embodiment 3
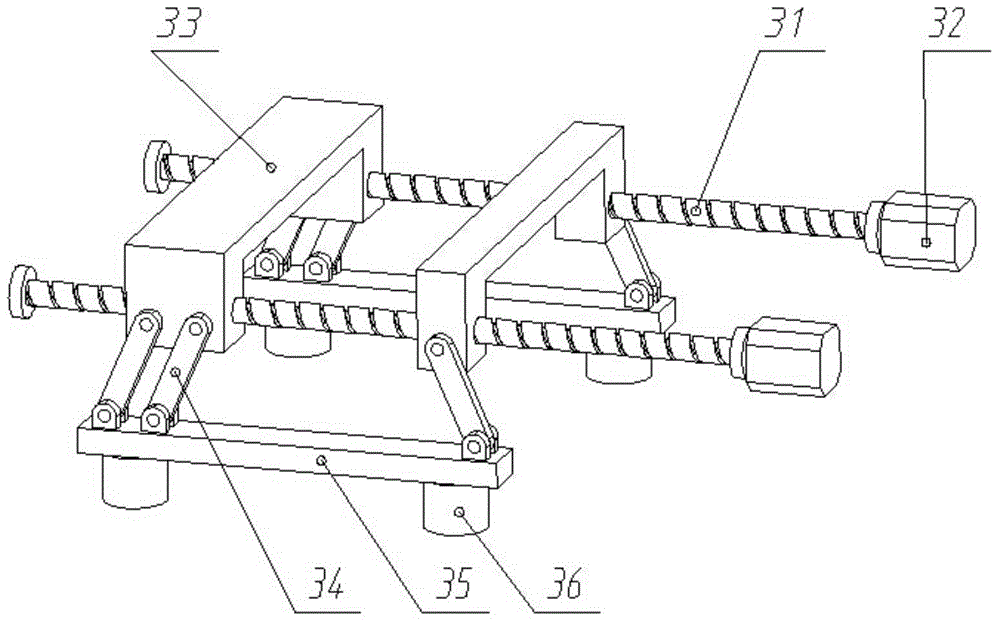
[0036] Embodiment 3, a schematic diagram of the motion mechanism of a foot-type adsorption wall-climbing robot, as shown in image 3 as shown,
[0037] On the basis of embodiment one and two, further include:
[0038]The outer foot assembly 3 includes an outer screw guide rod 31, an outer screw guide rod drive motor 32, and two outer sliders 33 respectively, wherein the two outer screw guide rods 31 are distributed in parallel, and there are bearings and bearings at both ends respectively. The body 1 is connected, and two outer screw guide rod driving motors 32 are fixedly installed on the body 1, and one end of each outer screw guide rod 31 is coaxially connected with an outer screw guide rod driving motor 32 respectively.
[0039] Two outer slide blocks 33 are distributed forward and backward along the direction of the outer lead screw guide rod 31; the connection between each outer slide block 33 and the two outer lead screw guide rods 31, one is a thread pair connection, ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com