Hot-rolling method of grain-oriented electrical steel and grain-oriented electrical steel prepared by the method
A oriented electrical steel, oriented technology, applied in the manufacture of inductors/transformers/magnets, circuits, electrical components, etc., can solve problems such as inability to influence and destroy, and achieve the effects of reducing noise, high production efficiency, and improving living environment
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027] The invention of this example provides a low magnetostriction and low noise oriented electrical steel hot rolling method and the oriented electrical steel prepared by the method; the method includes:
[0028] After the oriented electrical steel continuous casting slab whose basic composition is Fe-3%Si-1%Mn-0.3%Al-0.05%C-0.002%Bi is taken out from the heating furnace, it is heated at a pass reduction rate of less than 32%. The initial rolling is carried out; when the thickness of the slab is less than 30mm and enters the hot finish rolling processing stage, the temperature of the slab should be lower than 1100°C; then the slab is sent to the hot continuous rolling mill for hot finish rolling. The reduction rate is not less than 85%, and the hot rolling is completed above 850°C; the reduction rate of each pass of the hot finish rolling is not more than 32%; 300°C rate of temperature rise.
[0029] Among them, the analog calculation formula of the noise after the low mag...
Embodiment 2
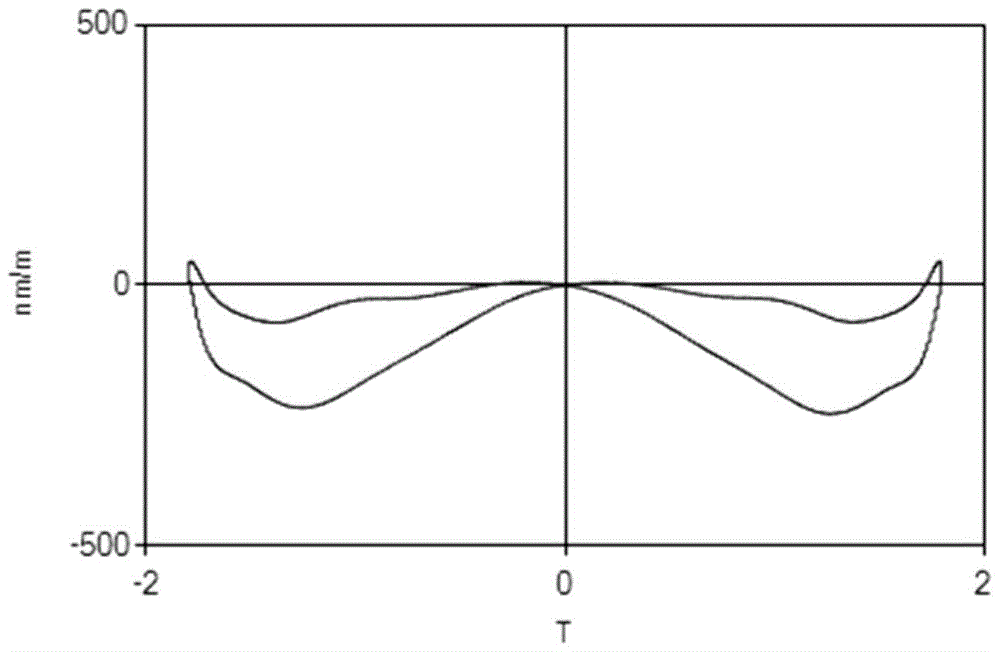
[0039] Example 2: Choose to process high-grade 27QG95 grain-oriented electrical steel. The slab with a thickness of 22.5 mm and a temperature of 990 ° C is subjected to 5 passes of hot finish rolling to a thickness of about 3 mm; the reduction rate of each pass is kept in the range of 28% to 31%, and the final rolling temperature is 860 ° C; The hot-rolled sheet is heated to 950°C at an average rate of 100°C per minute for ultra-low-speed continuous annealing. After the normalized annealed plate is subjected to subsequent conventional cold rolling and annealing, the iron loss of the finished product is: P1.5 = 0.921W / kg, and the magnetostriction coefficient is l p-p (when the magnetic flux density is 1.7T): 245nm / m ,Such as figure 2 As shown in the graph of its magnetostrictive characteristic, the noise AWV is: 48.7dB (analog A weighting).
Embodiment 3
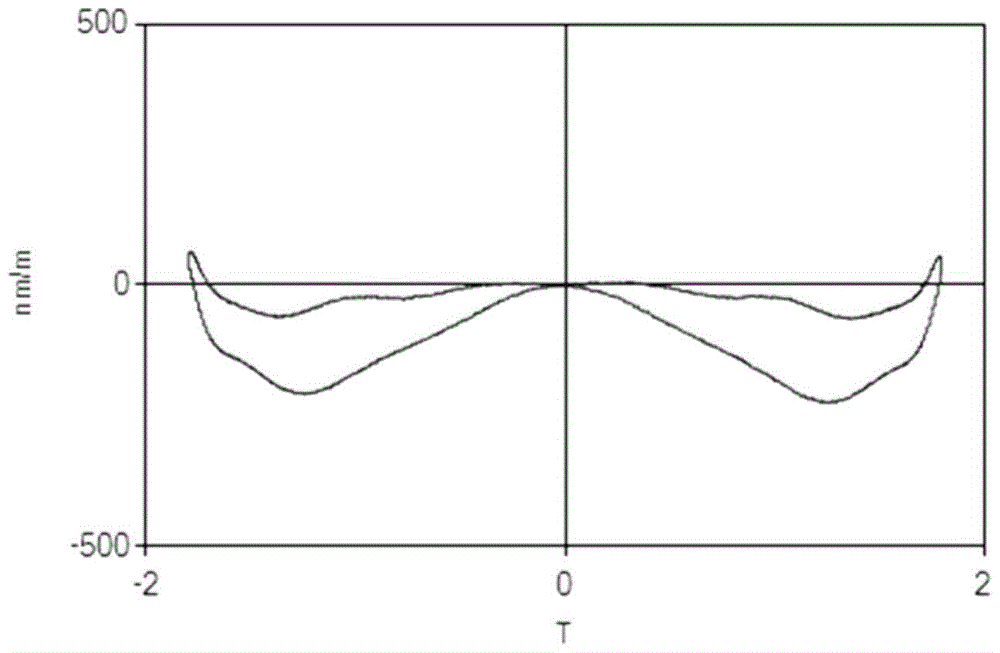
[0040] Example 3: Choose to process high-grade 27QG95 grain-oriented electrical steel. The slab with a thickness of 26.6 mm and a temperature of 960 ° C is subjected to 5 passes of hot finish rolling to a thickness of about 3 mm; the reduction rate of each pass is kept in the range of 29% to 32%, and the final rolling temperature is 850 ° C; The hot-rolled sheet is heated to 850°C at an average rate of 5°C per minute for bell furnace annealing. After the normalized annealed plate is subjected to subsequent conventional cold rolling and annealing, the iron loss of the finished product is: P1.5=0.927W / kg, and the magnetostriction coefficient is l p-p (when the magnetic flux density is 1.7T): 261nm / m ,Such as image 3 As shown in the graph of its magnetostrictive characteristic, the noise AWV is: 49.1dB (analog A weighting).
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com