Buck-boost converter with buck-boost transition switching control
一种升压切换、控制器的技术,应用在输出功率的转换装置、控制/调节系统、仪器等方向,能够解决低效率等问题
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
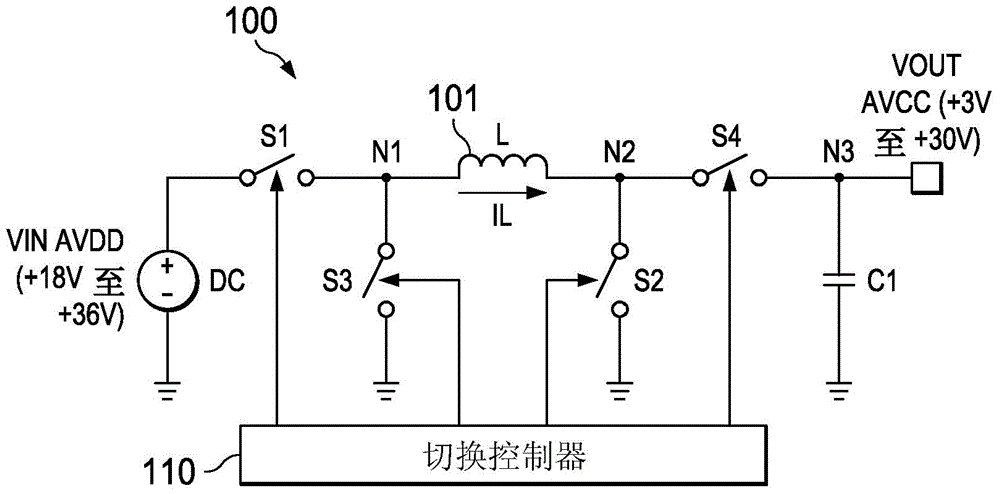
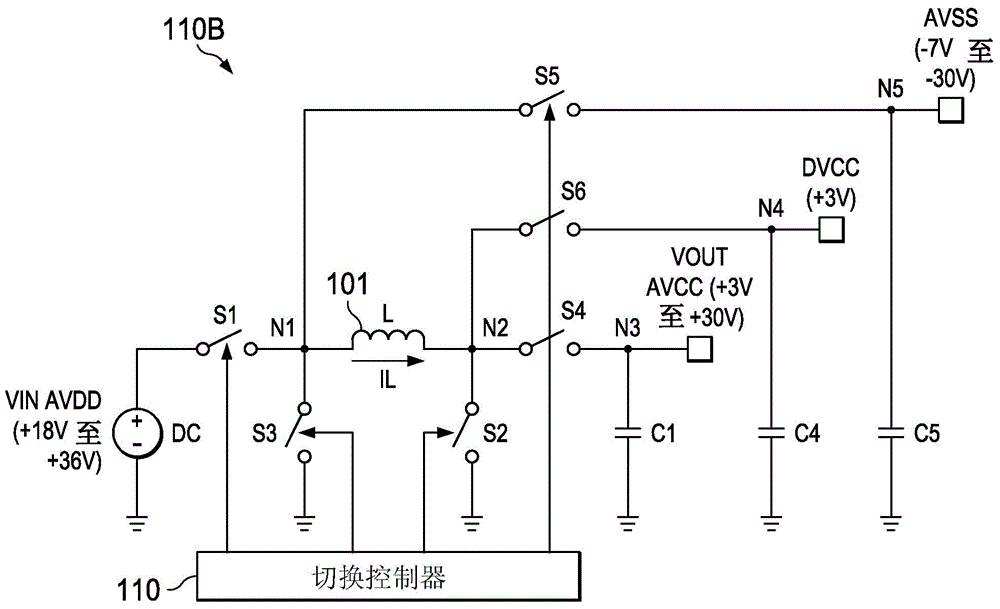
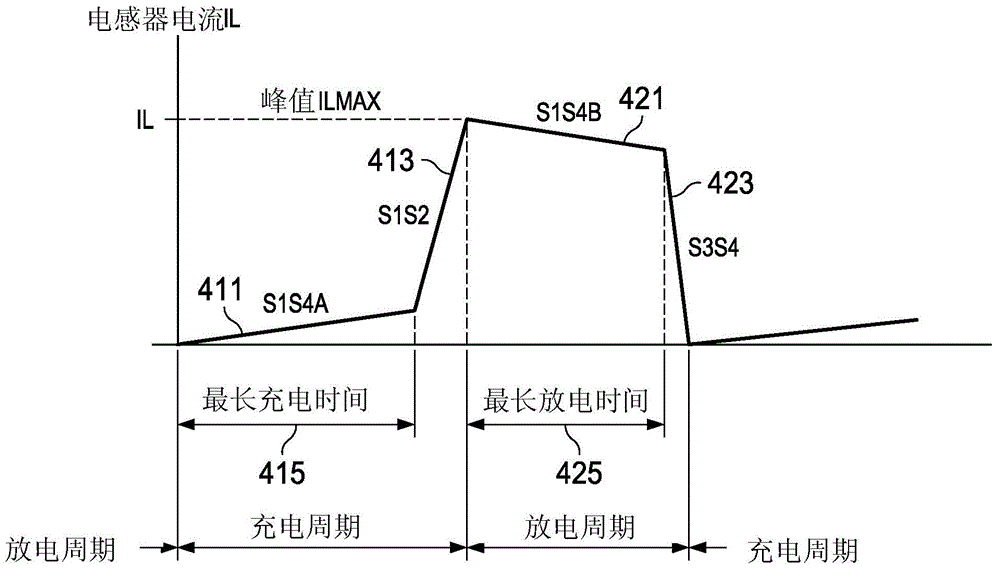
[0022] Buck-boost regulation (switching control) method including buck-boost transition switching control according to the present invention can be adapted for single inductor buck-boost switching conversion operating in DCM (Discontinuous Conduction Mode) regulator / regulator architecture. Converter and regulator are used interchangeably, although in general a regulator includes a converter circuit with appropriate inductors and output capacitors (ie, for typical applications, the inductor and output capacitor will not be integrated with the converter circuit). The converter circuit includes a switching network coupled to the inductor and an associated switching controller, which can be integrated or can be implemented separately from the switching controller, for example implemented as an integrated circuit. To simplify, with Figure 1A / Figure 1B , image 3 and Figure 5A / Figure 5B The accompanying description refers to the illustrated example embodiment as a regula...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com