Patents
Literature
773 results about "Buck–boost converter" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
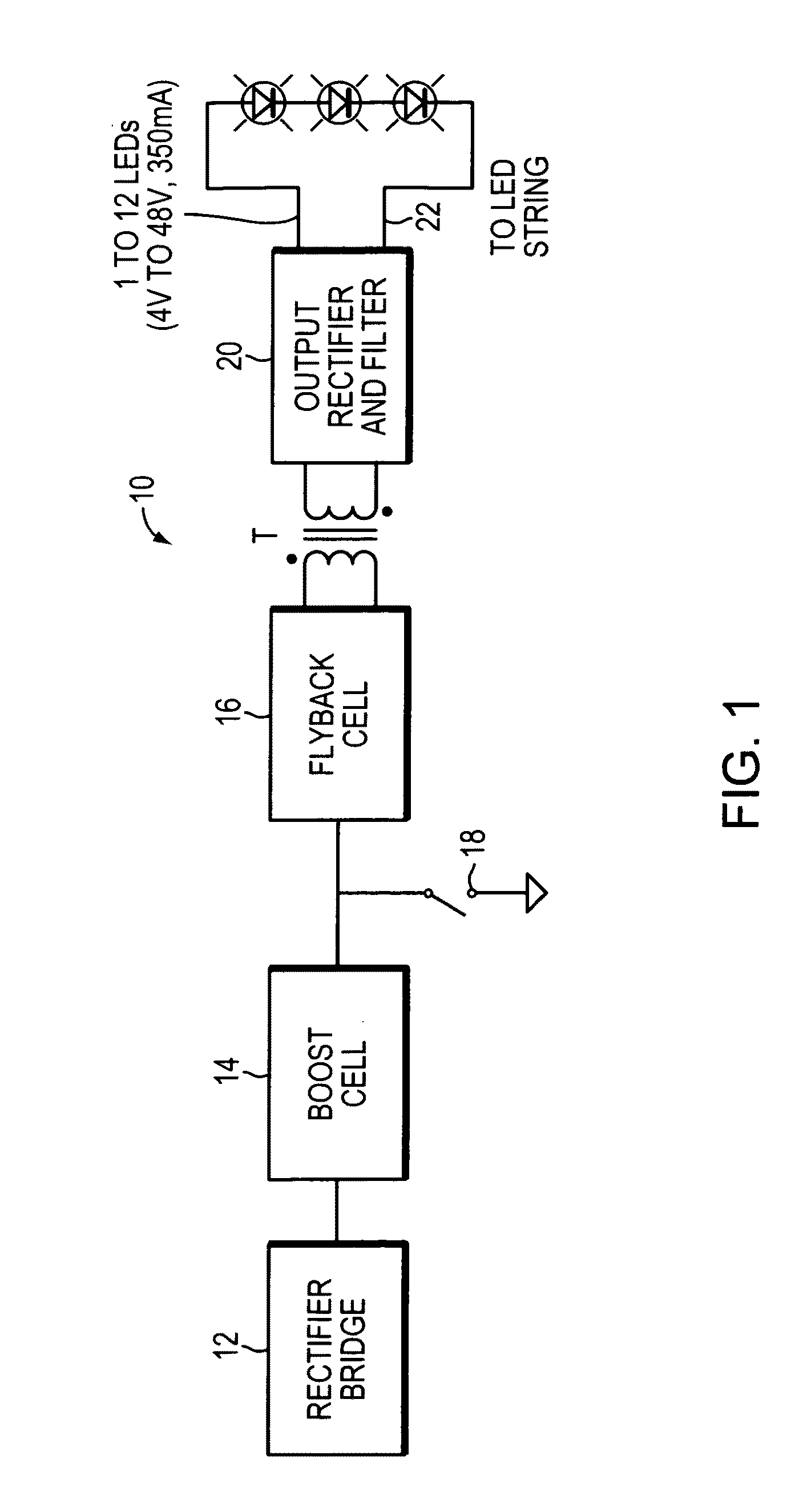
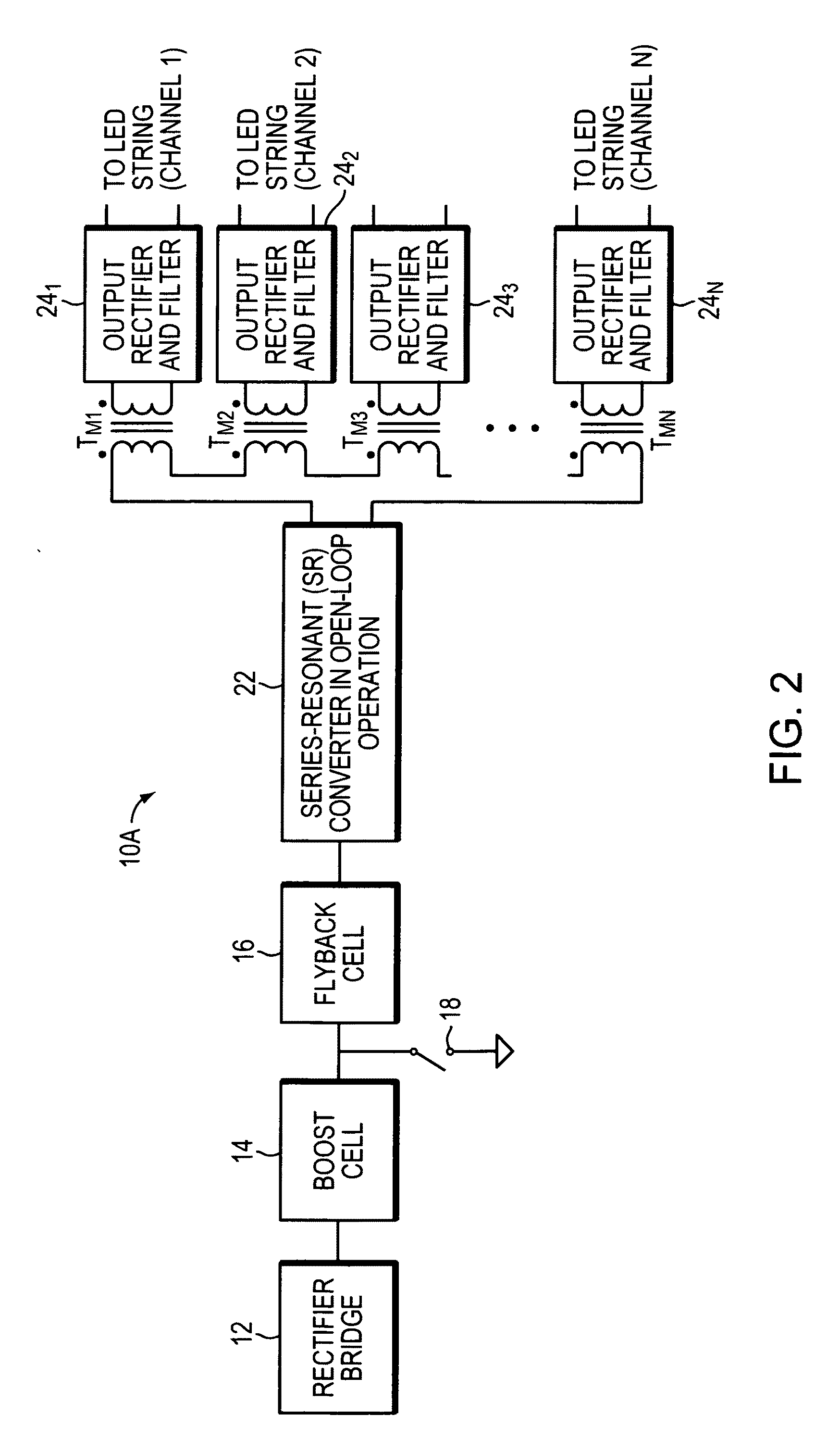
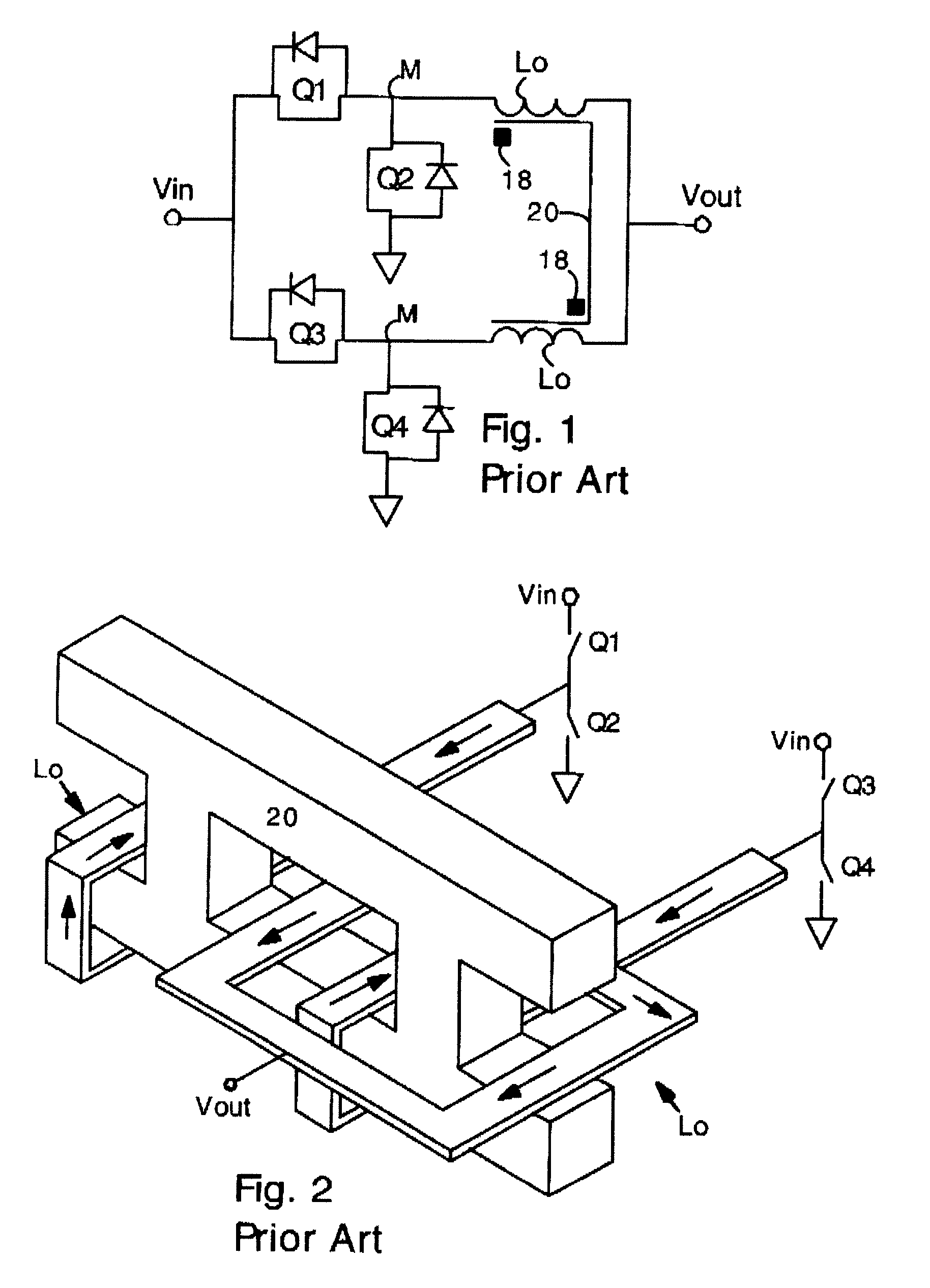
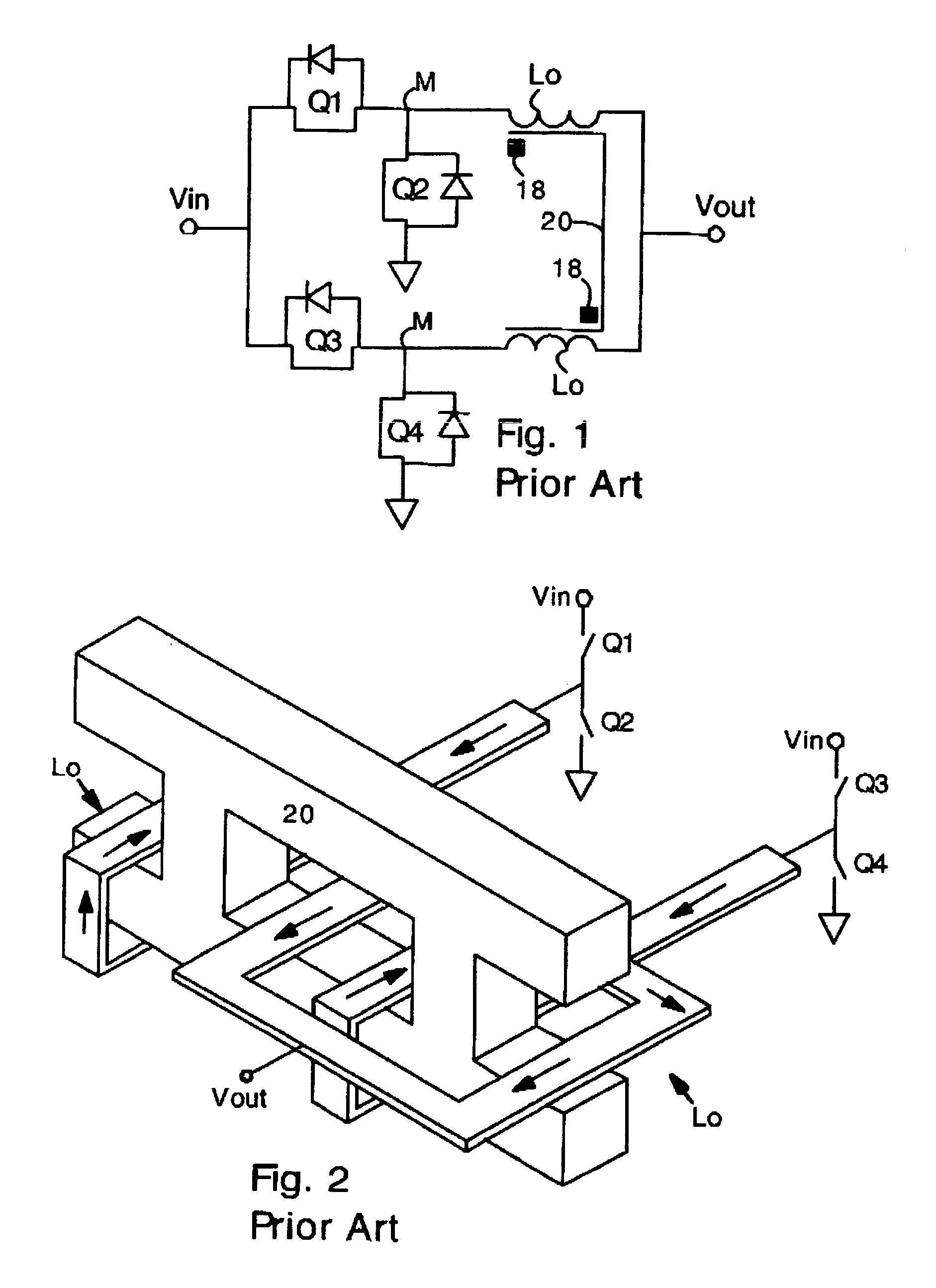
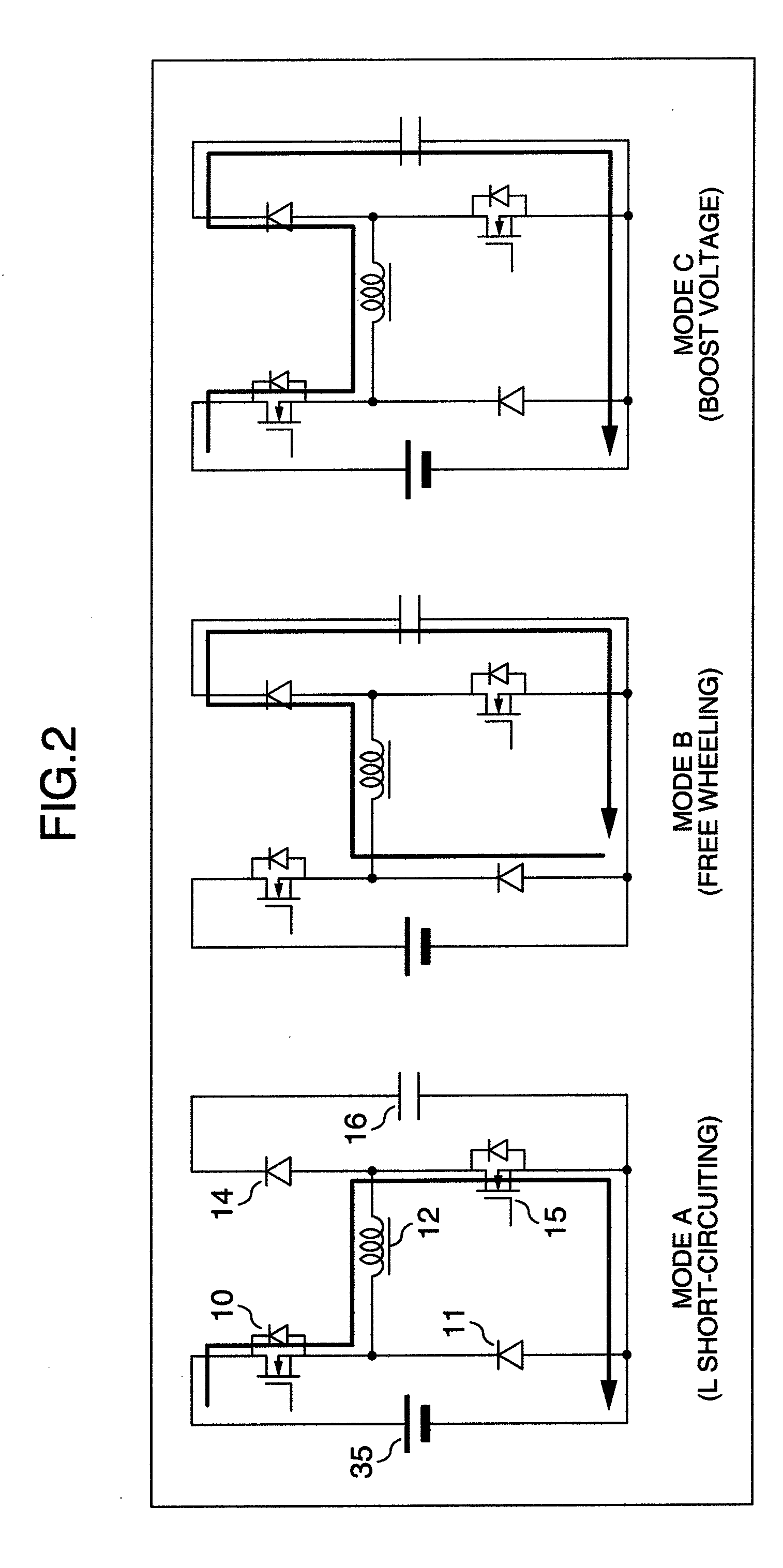
The buck–boost converter is a type of DC-to-DC converter that has an output voltage magnitude that is either greater than or less than the input voltage magnitude. It is equivalent to a flyback converter using a single inductor instead of a transformer.
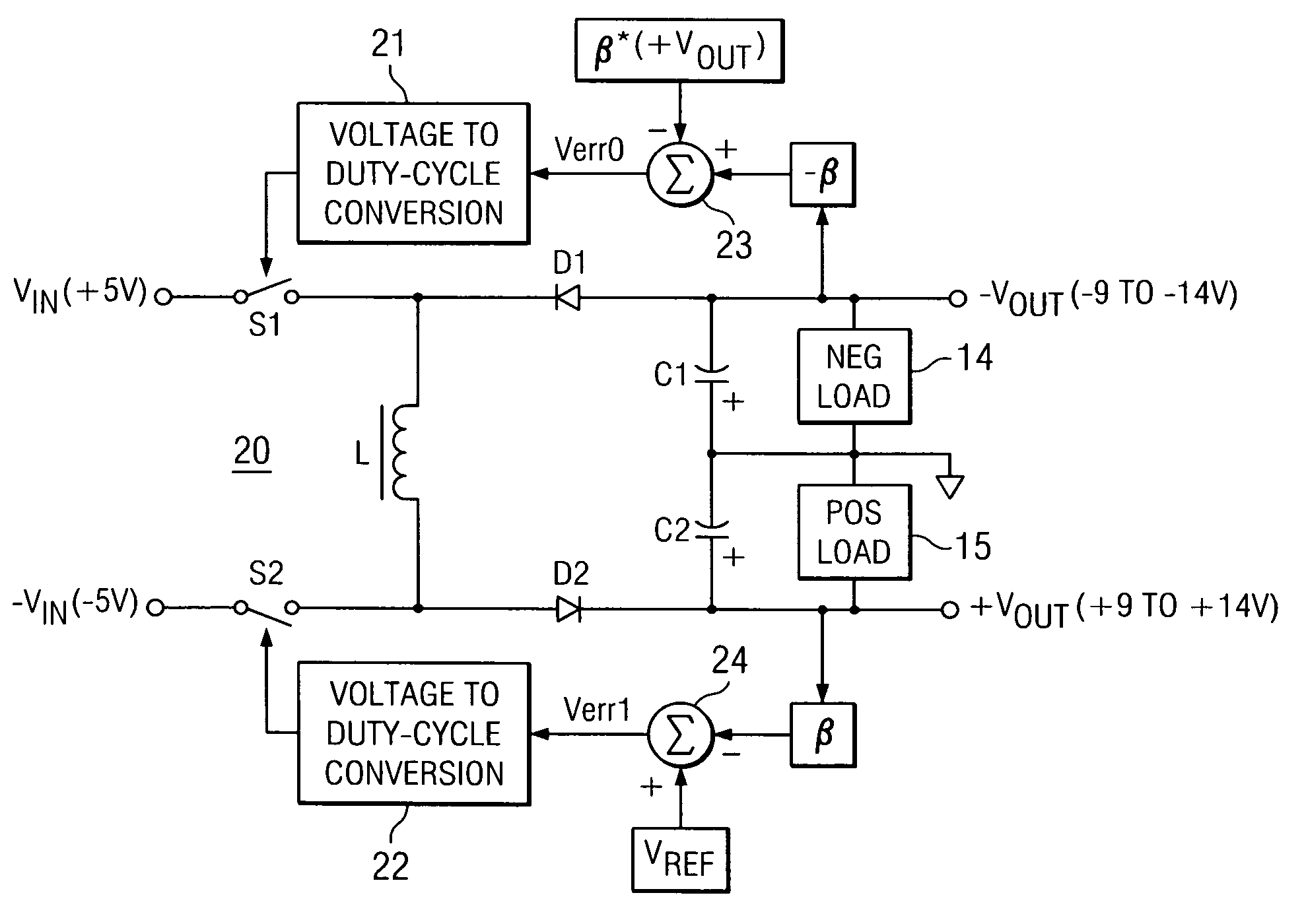
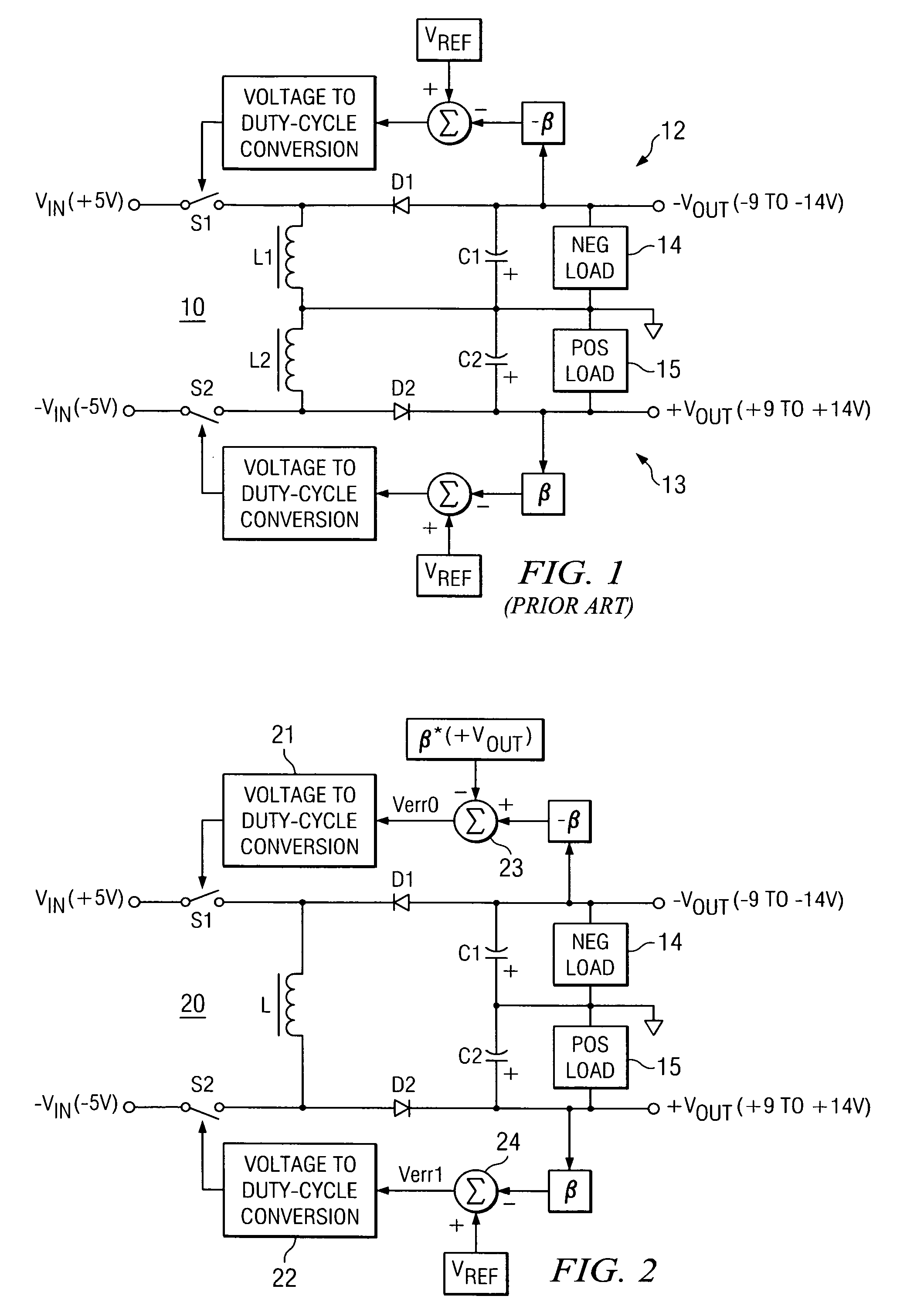
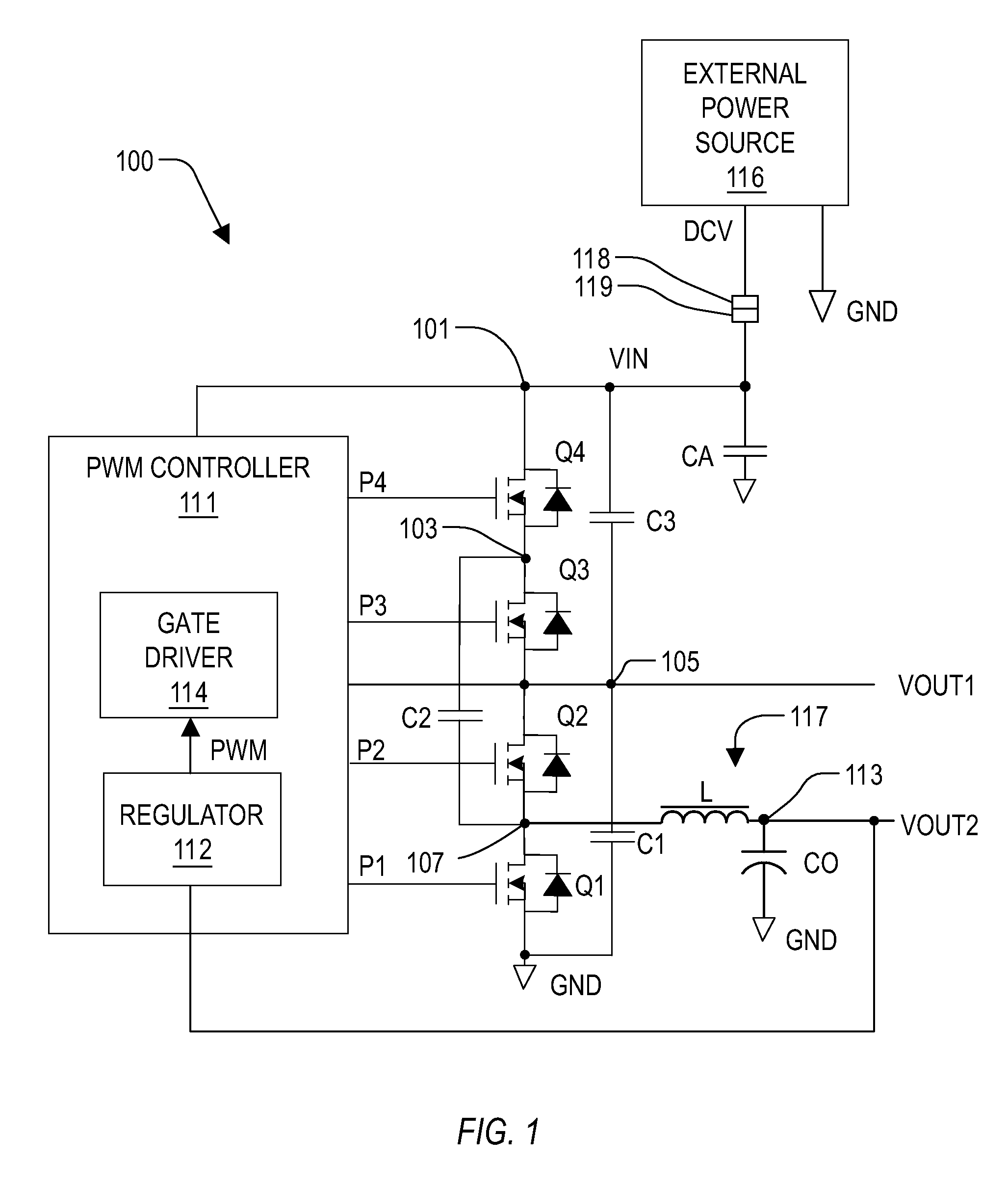
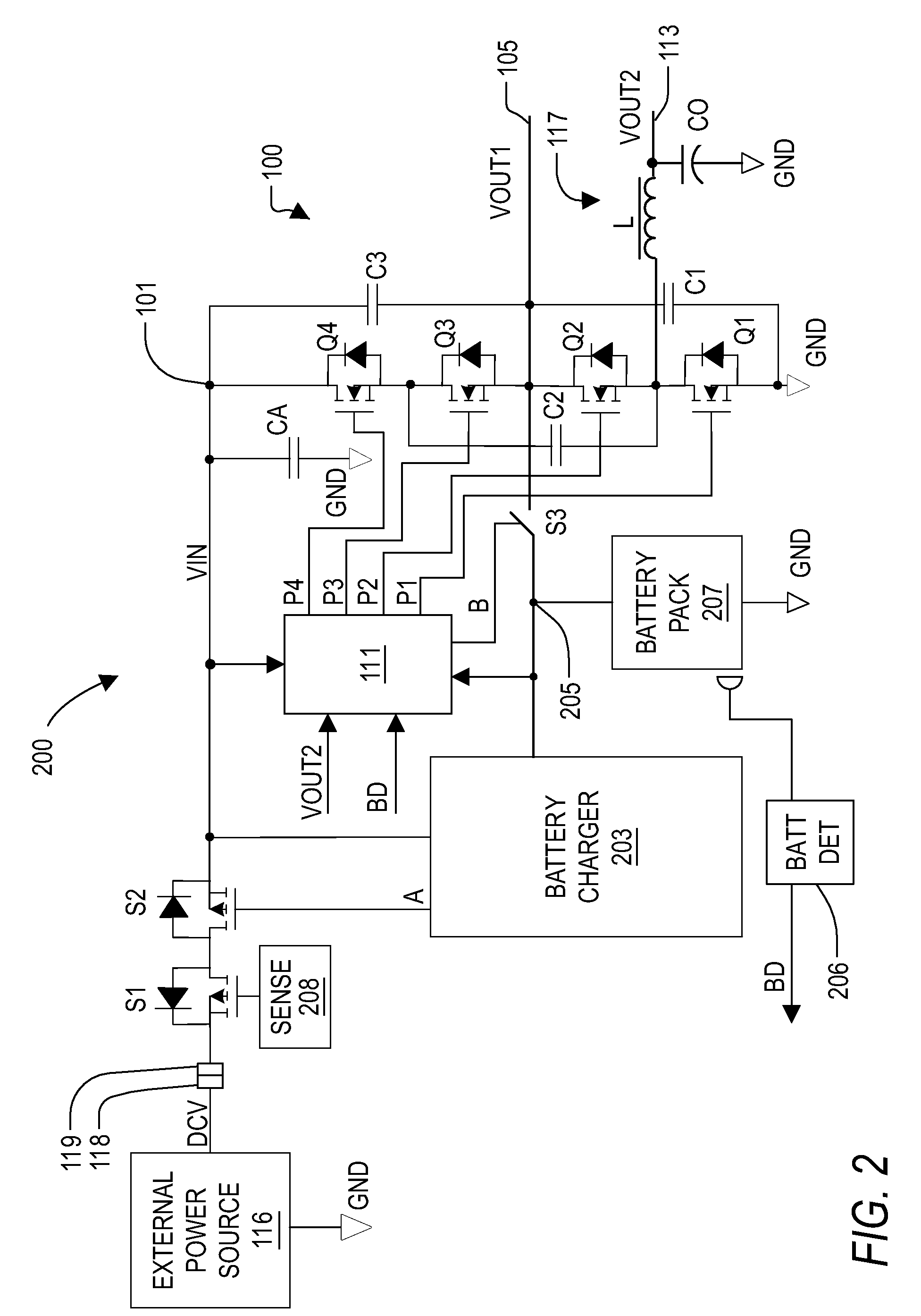
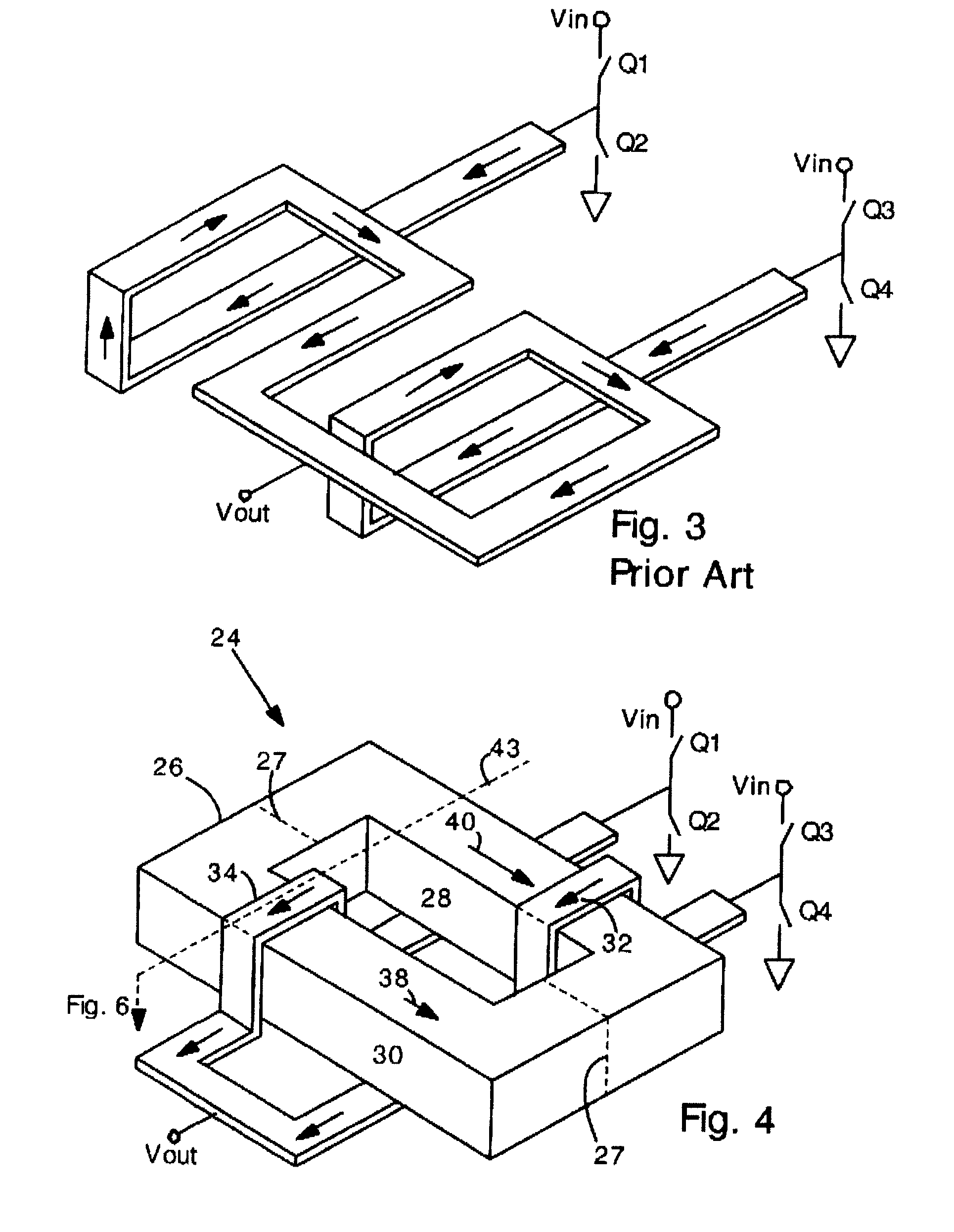
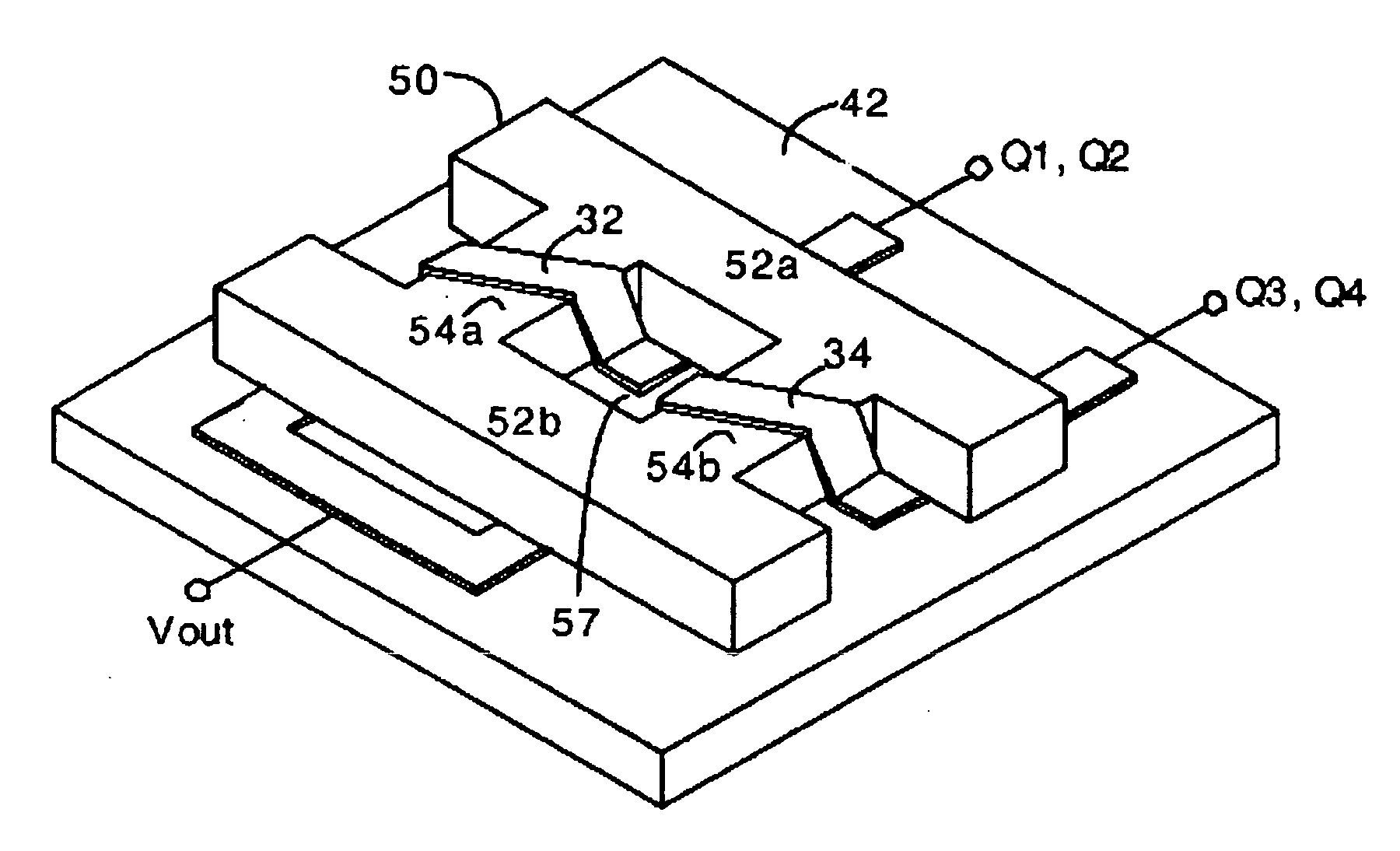
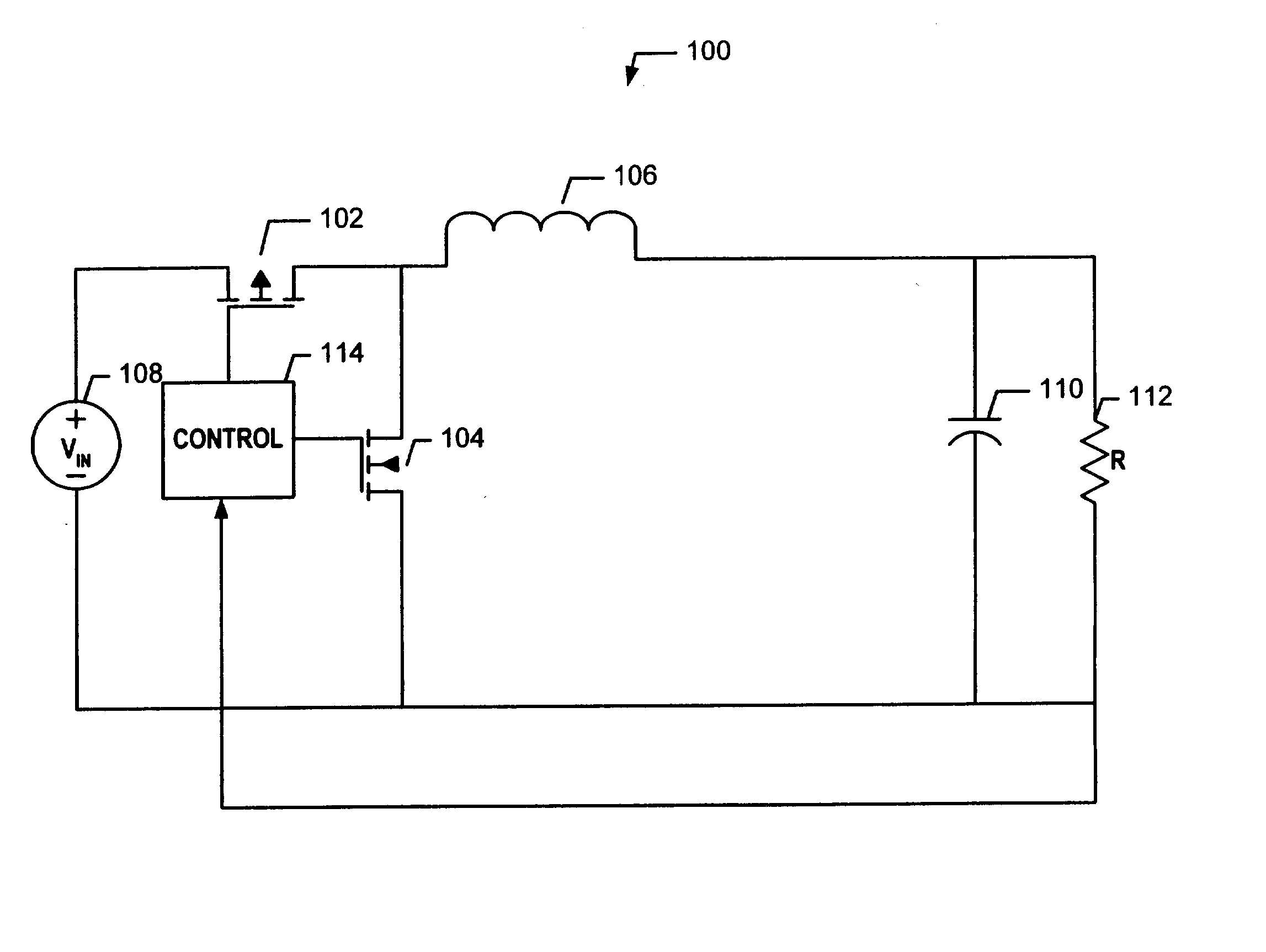
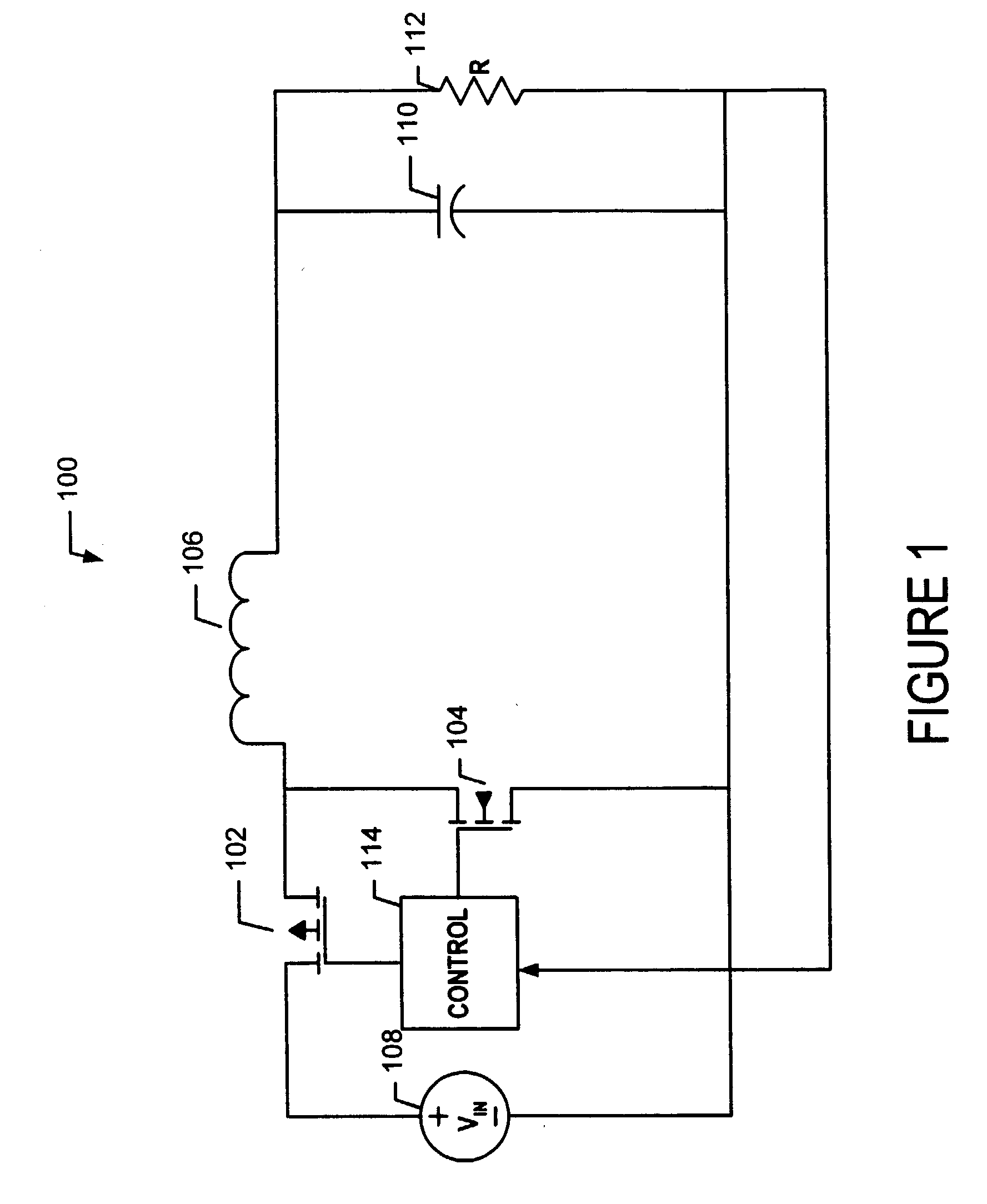
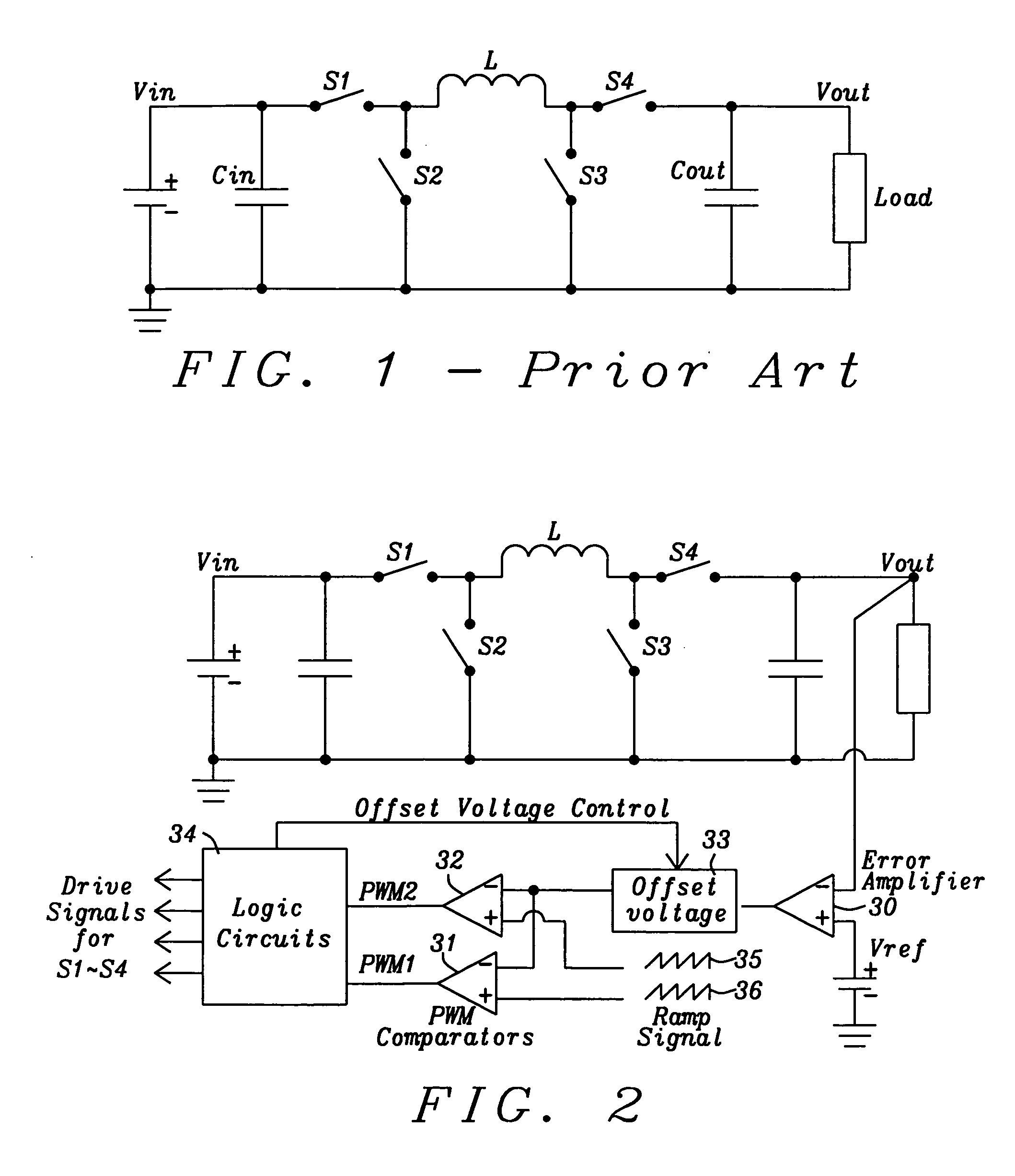
Dual buck-boost converter with single inductor
ActiveUS7276886B2Increase the pulse widthDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationSwitching cycleElectrical polarity
A dual output buck-boost power converter operates with a single inductor to achieve high efficiency with automatic or inherent load balancing. Switches associated with the opposite polarity outputs are driven based on feedback signals, with one feedback signal being a reference voltage and another feedback signal being related to an opposite polarity output. The opposite polarity feedback signal is provided to a comparator with a reversed polarity to achieve a simple balanced control that maintains polarity outputs. The power converter delivers power to each output with each switching cycle and uses a single inductor to achieve high efficiency performance.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
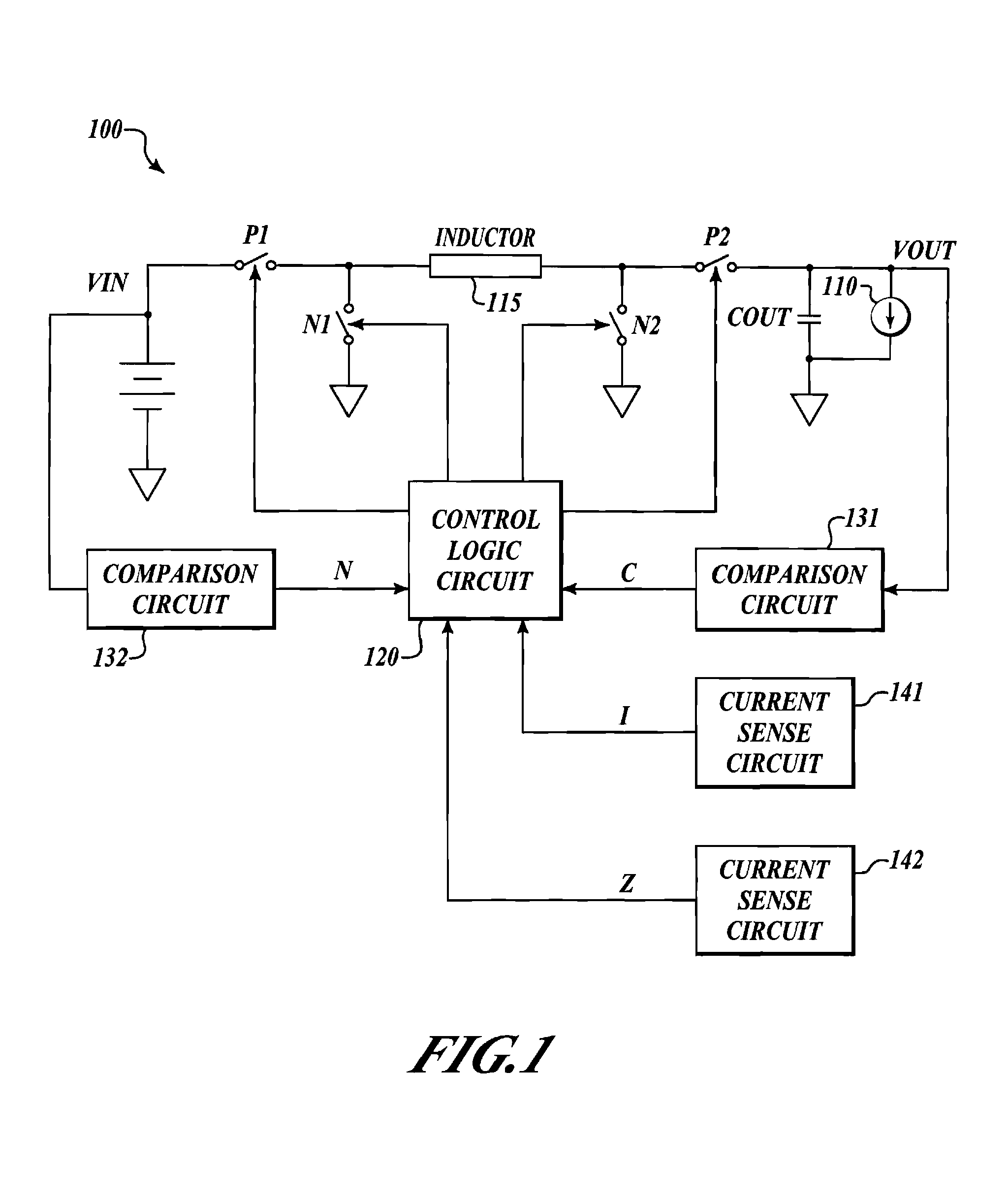
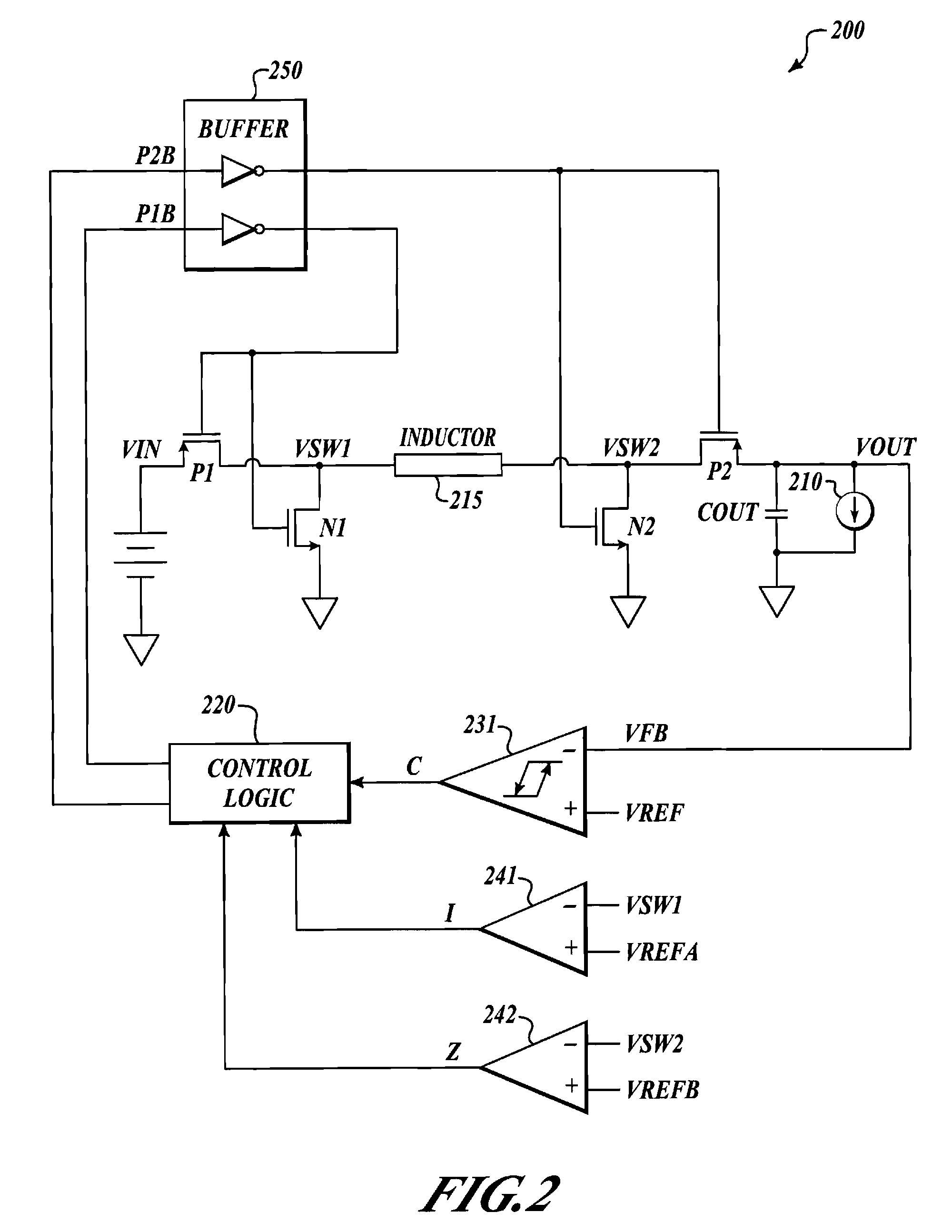
Apparatus and method for PFM buck-or-boost converter with smooth transition between modes
A PFM buck-or-boost converter is provided. The converter includes, inter alia, a hysteretic comparator, current sense circuitry, a logic circuit, drivers, current sense circuitry, a first buck switch, and a first boost switch. The current sense circuitry asserts signal Z if the current through the boost switch (from the load to the inductor) is greater than zero, and unasserts Z otherwise. Additionally, the current sense circuitry asserts signal I if the current through the buck switch is greater than a fixed current limit value, and unasserts I otherwise. The logic circuit employs the hysteretic comparator output, signal Z, and signal I to control the switches, and to determine whether to operate in buck regulation mode or boost regulation mode.
Owner:NAT SEMICON CORP
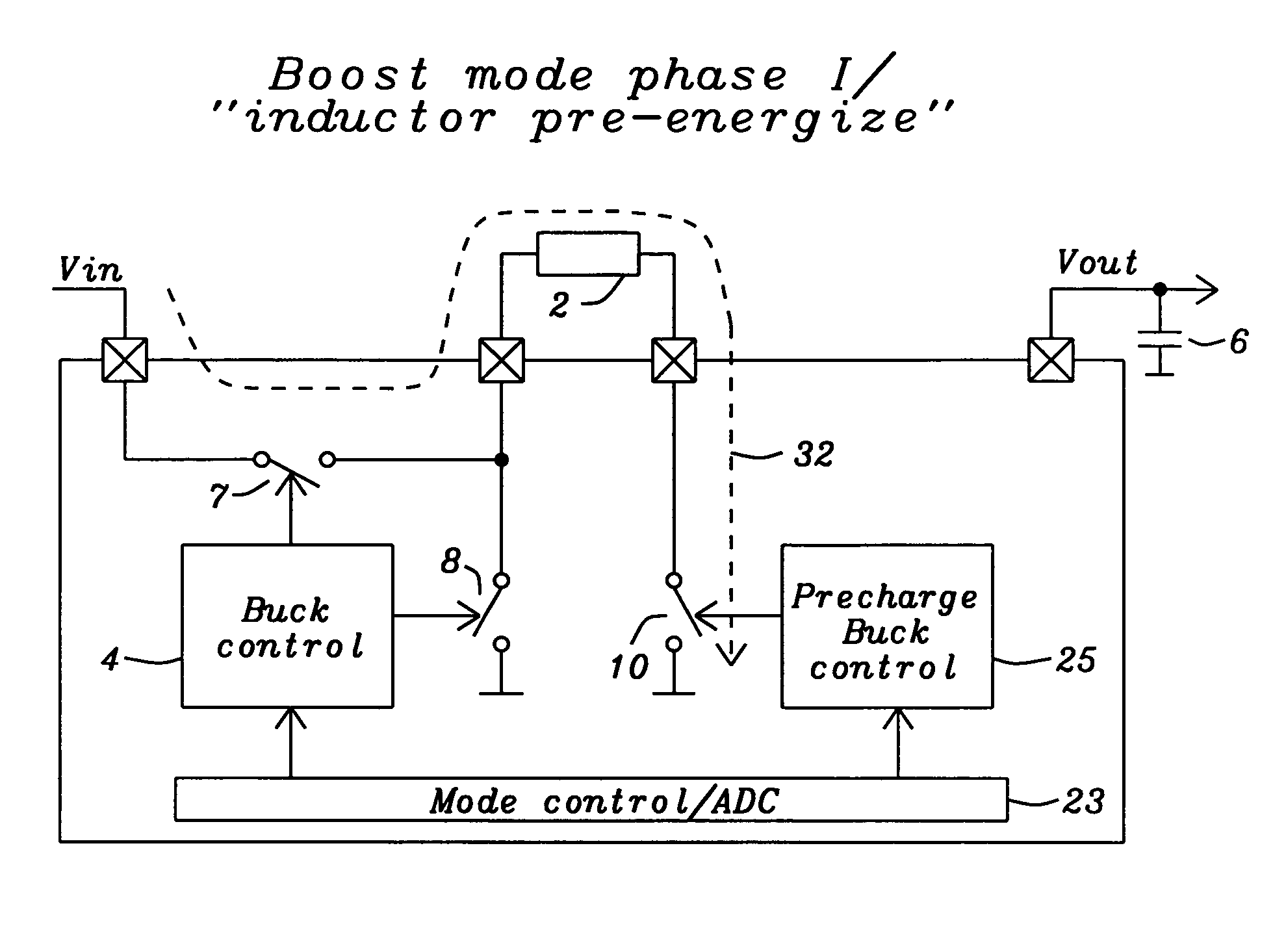
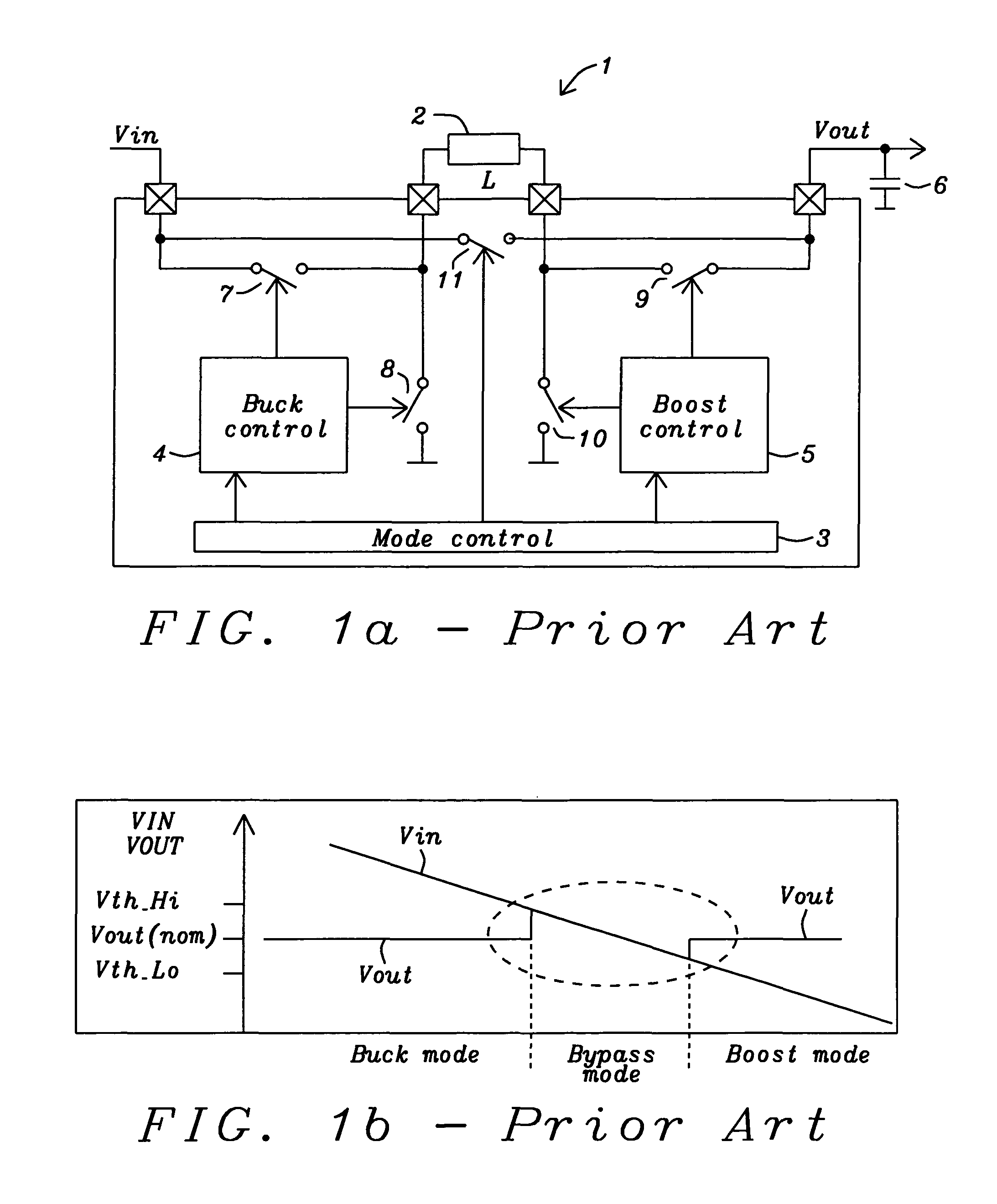
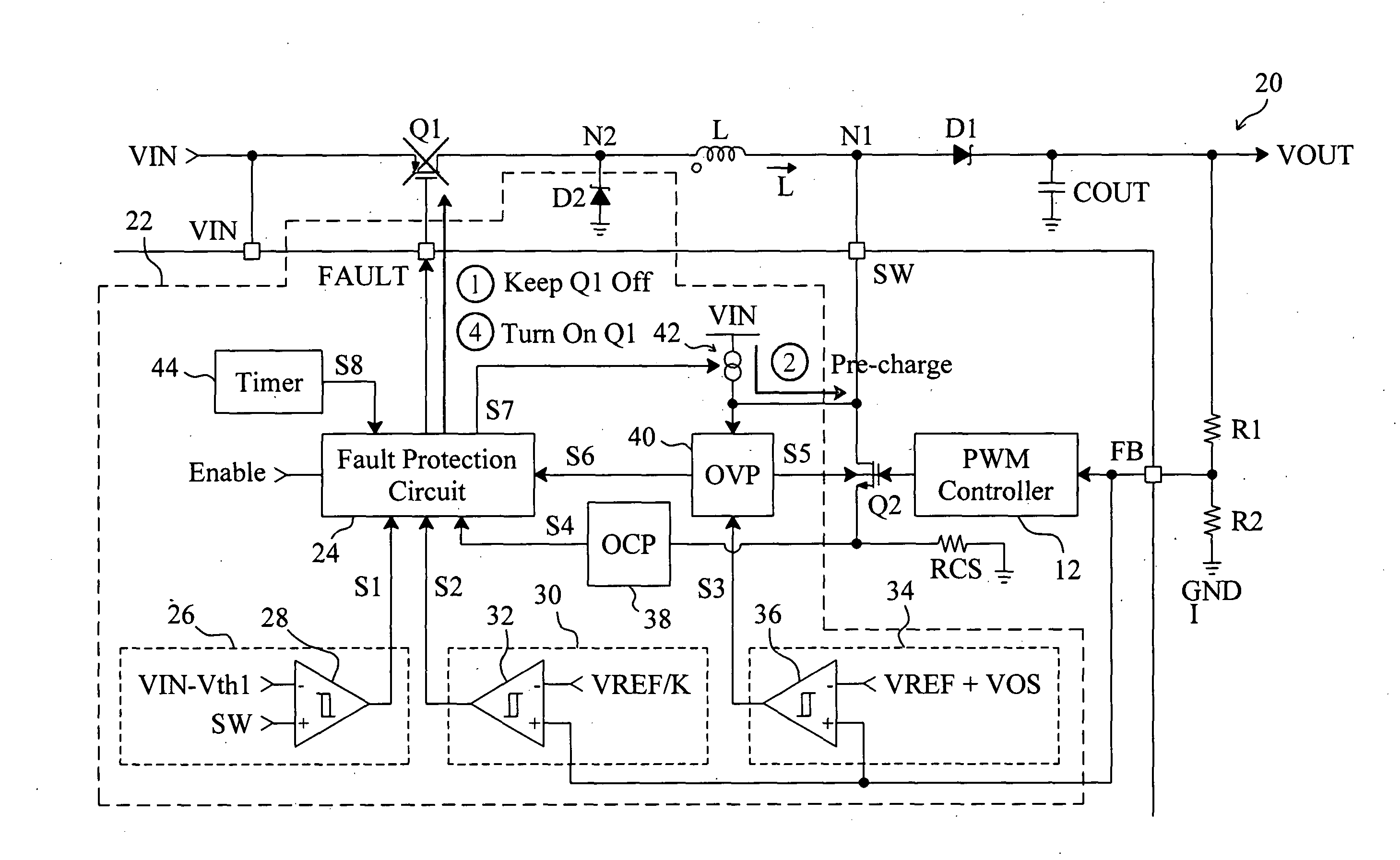
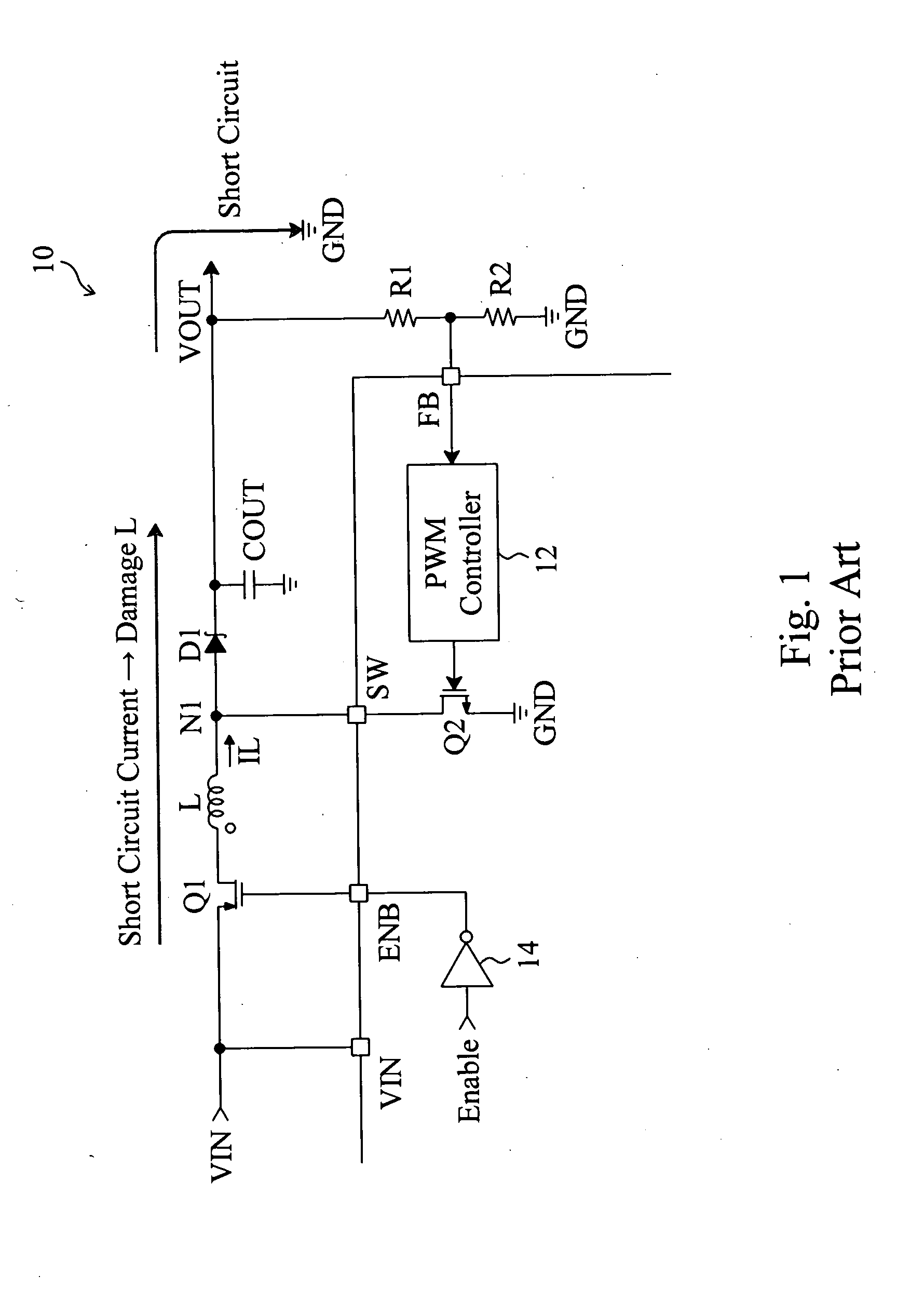
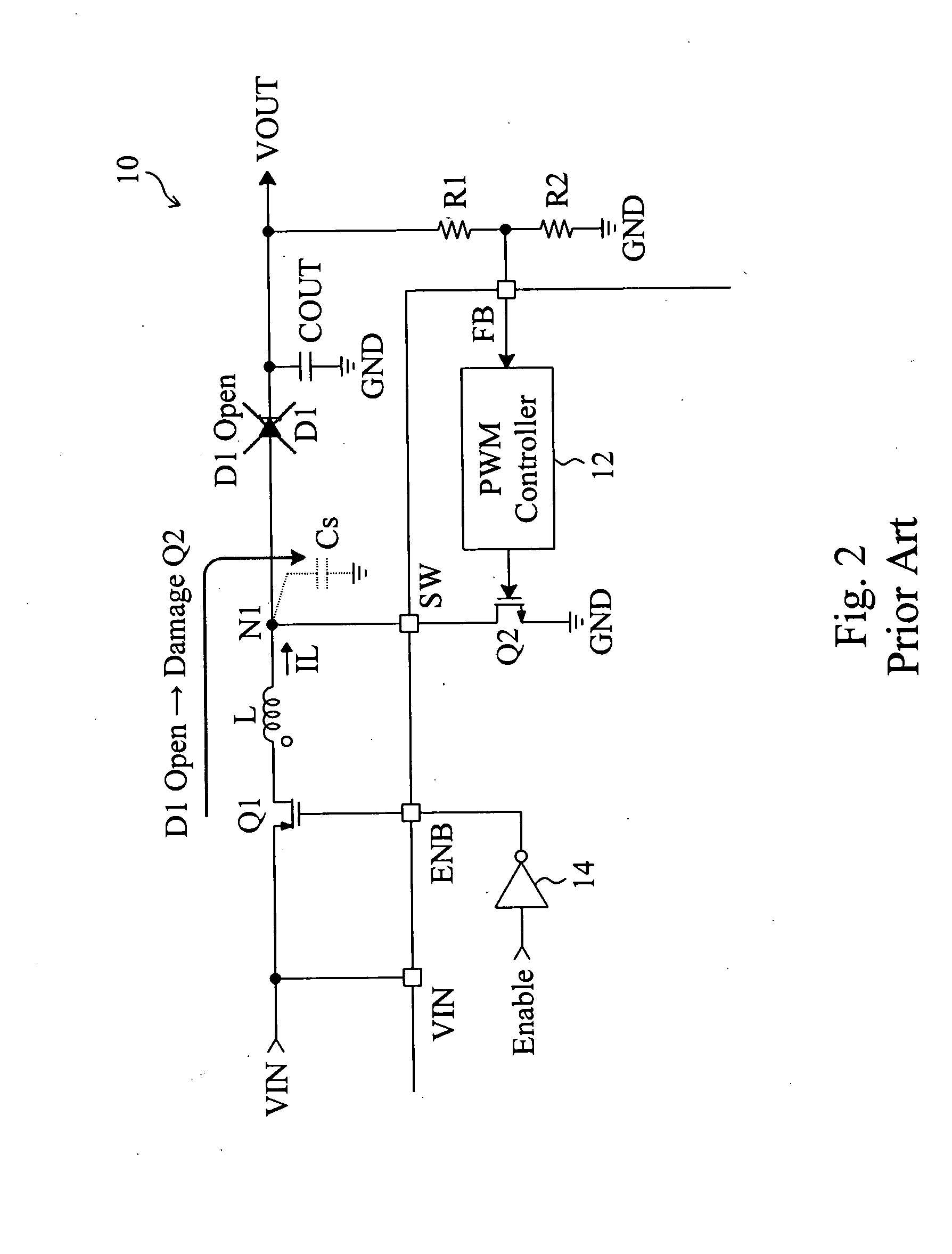
Buck converter with inductor pre-energizing
ActiveUS7804282B2Simple control circuitDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationBuck converterĆuk converter
Circuits and methods to achieve a buck-boost converter, capable to achieve a constant output voltage by pre-charging of an inductor if the input voltage is close to the output voltage has been achieved. The prior art problem of output voltage variations occurring while the input voltage is close to the output voltage is avoided. In case the input voltage is lower than a defined threshold voltage or the duty cycle exceeds a defined maximum allowable level, the inductor of the converter is pre-charged followed by boosting of the energy of the inductor to the output of the converter. In both modes the control loops of the buck converter can be used for buck duty cycle control. The duration of the pre-charge depends upon the level of the input voltage, the lower the input level is the longer is the pre-charge performed.
Owner:DIALOG SEMICONDUCTOR GMBH
Topologies for using multiple energy sources for power conversions
InactiveUS7336004B2Dc network circuit arrangementsBatteries circuit arrangementsElectric powerEnergy source
A boost converter and a buck-boost converter supply power to a load from a series connection between a first and a second power source.
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP INC
Current bypass for distributed power harvesting systems using DC power sources
ActiveUS7900361B2Improve reliabilityGuaranteed functionDc-dc conversionDc source parallel operationEngineeringElectric power
A converter circuit providing multiple current bypass routes between the output leads to provide reliability in a series connection of several converters. If the converter malfunctions due to component failure, the current bypass routes provide a path for the current that views the malfunctioning converter as substantially a short. Diodes prevent backflow into the power source connected to the converter. Redundancy is provided in the bypass portions of the converter circuit that provides alternate parallel paths in case a defective component in one of the paths opens the circuit along that path. In one example, the converter is implemented as a buck plus boost converter where either the buck or the boost portion or both are operative responsive to a controller controlling the switches of both portions. Most of the converter circuit may be implemented in an integrated circuit.
Owner:SOLAREDGE TECH LTD
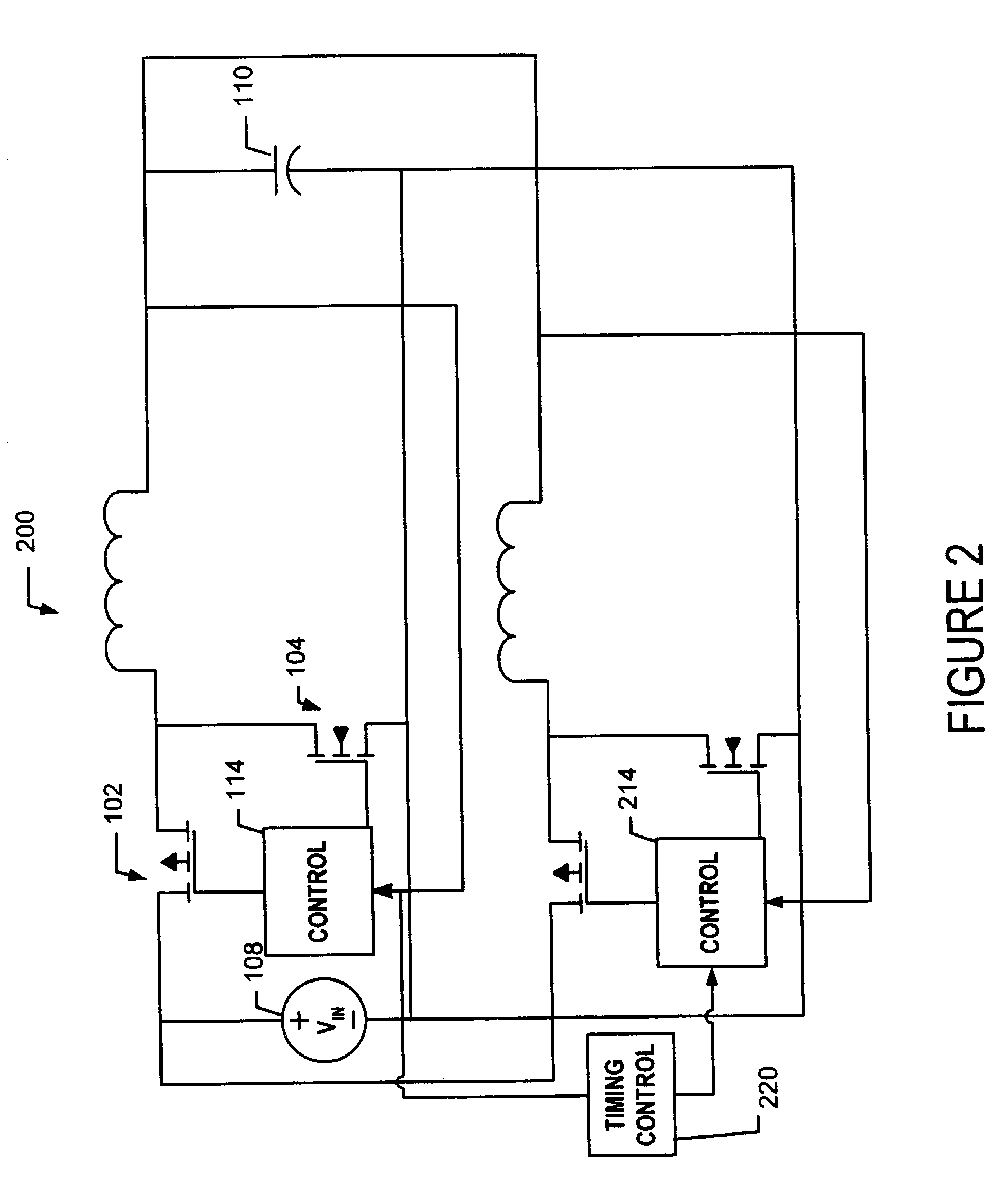
Dual buck-boost converter with single inductor
ActiveUS20070075689A1Increase the pulse widthIncrease the output voltageDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationSwitching cycleElectrical polarity
A dual output buck-boost power converter operates with a single inductor to achieve high efficiency with automatic or inherent load balancing. Switches associated with the opposite polarity outputs are driven based on feedback signals, with one feedback signal being a reference voltage and another feedback signal being related to an opposite polarity output. The opposite polarity feedback signal is provided to a comparator with a reversed polarity to achieve a simple balanced control that maintains polarity outputs. The power converter delivers power to each output with each switching cycle and uses a single inductor to achieve high efficiency performance.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
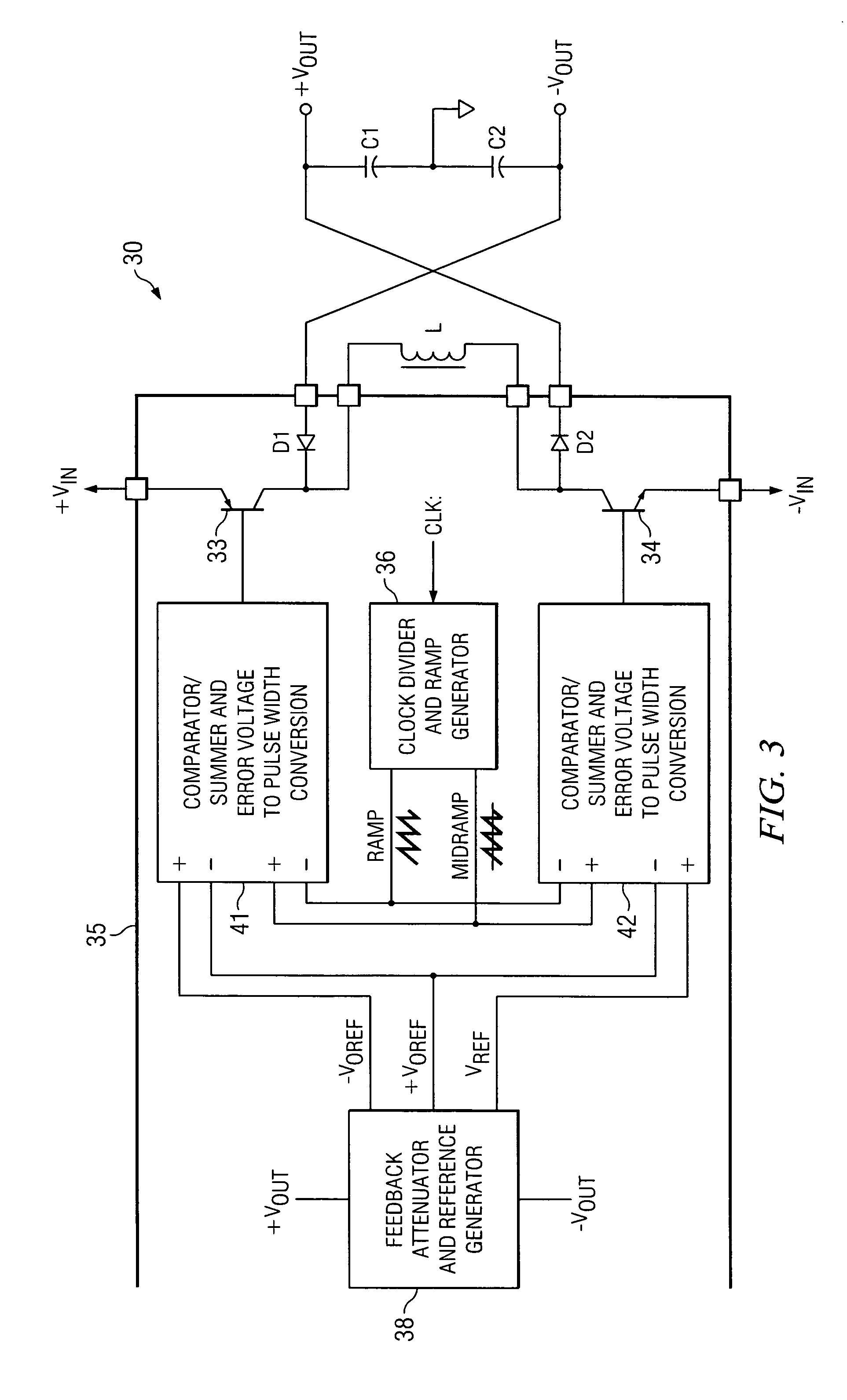
Multiphase clamp coupled-buck converter and magnetic integration
InactiveUS6784644B2Emergency protective circuit arrangementsApparatus without intermediate ac conversionVoltage regulator modulePush pull
Voltage regulation, transient response and efficiency of a voltage regulator module (VRM) is improved where short duty cycles are necessitated by large differentials of input and output voltage by including at least one clamping of a tap of an inductance in series with an output of each of a plurality of parallel branches or phases which are switched in a complementary fashion or providing coupling between inductors of respective phases. Such coupling between inductors is achieved in a small module with an integrated magnetic structure. Reduced component counts are achieved while deriving built-in input and output filters. Principals of the invention can be extended to isolation applications and push-pull forward converts, in particular. A lossless clamping circuit is also provided allowing spike currents to be suppressed while returning power to the output of the VRM.
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP INC
Multiphase voltage regulator having coupled inductors with reduced winding resistance
InactiveUS7649434B2Transformers/inductances coils/windings/connectionsDc-dc conversionBuck converterCoupling
A multiple phase buck converter or boost converter, or buck-boost converter has an inductor in each phase. The inductors are inversely coupled. In a first embodiment, the converter includes a toroidal magnetic core with inductors extending under and over opposite sides of the toroidal magnetic core. The coupled inductors are thereby inversely coupled and have a relatively low ohmic resistance. In a second embodiment, the converter comprises a ladder-shaped magnetic core (i.e. having parallel sides, and connecting rungs). In this case, the inductors extend under the sides, and over the rungs. Each inductor is disposed over a separate rung. The ladder-shaped magnetic core is preferably disposed flat on a circuit board. Inverse coupling and low ohmic resistance are also provided in the second embodiment having the ladder structure.
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP INC
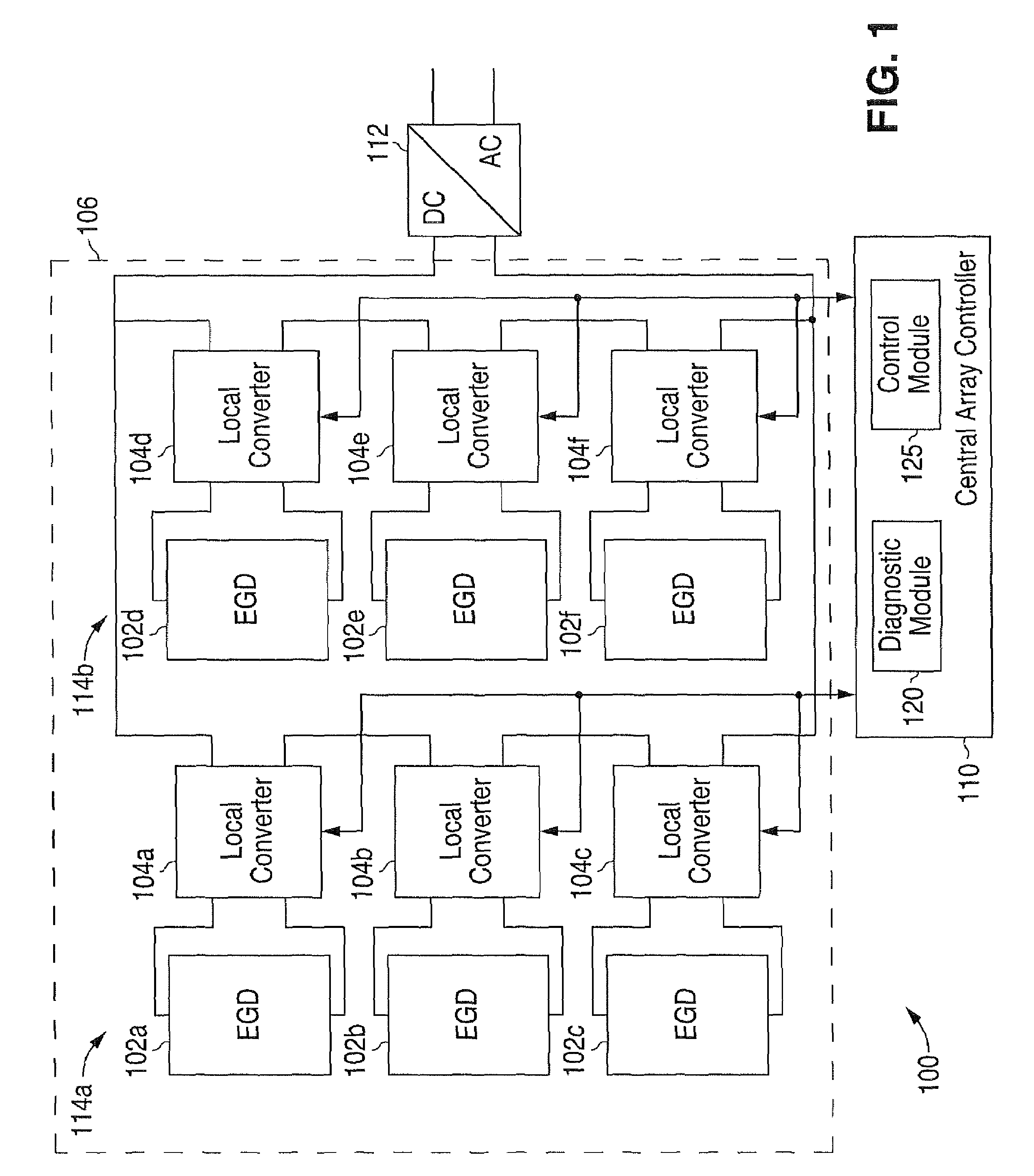
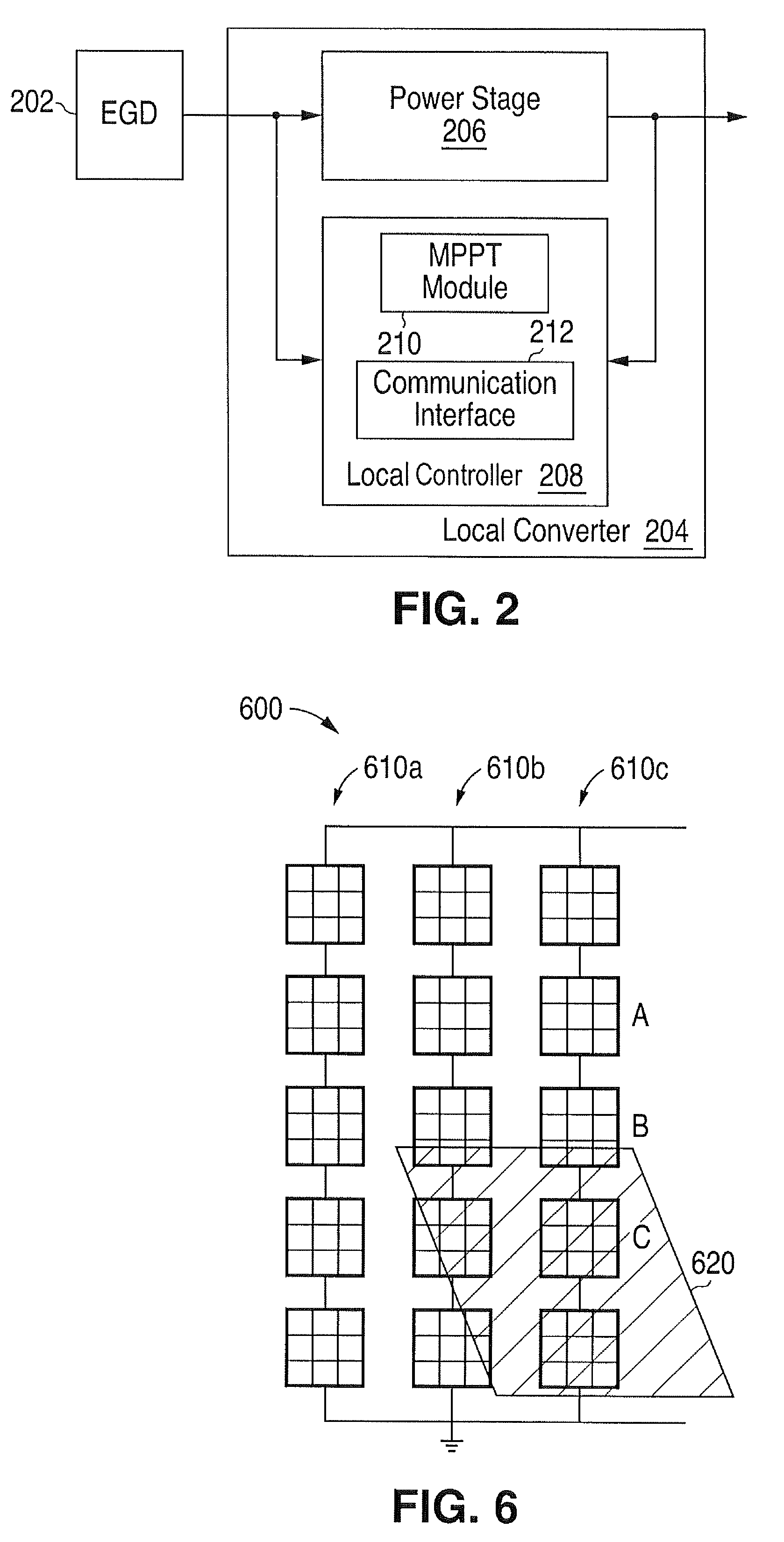
Method and system for providing local converters to provide maximum power point tracking in an energy generating system
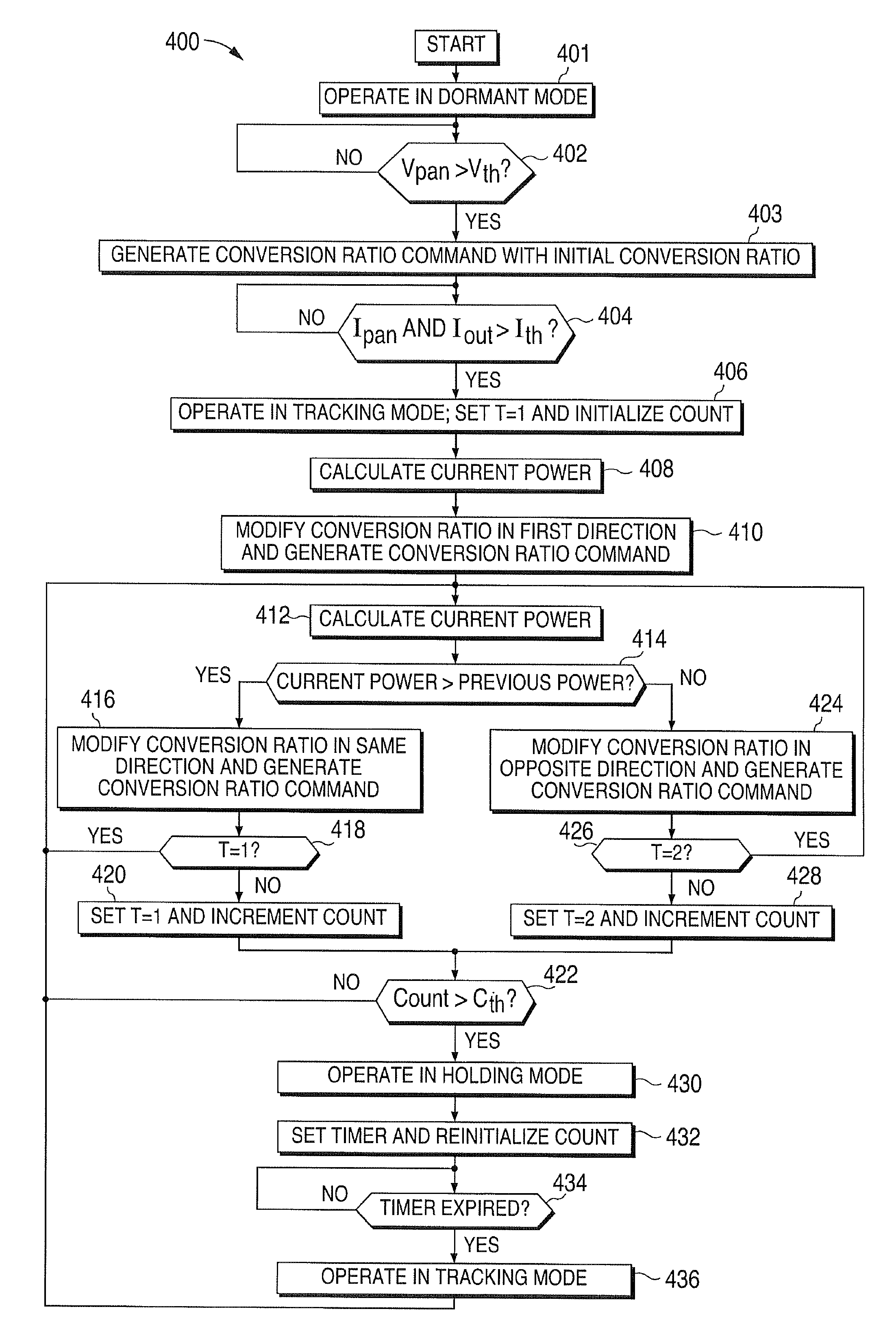
A method for providing maximum power point tracking for an energy generating device using a local buck-boost converter coupled to the device is provided. The method includes operating in a tracking mode, which includes initializing a conversion ratio for the buck-boost converter based on a previous optimum conversion ratio. A device power associated with the initialized conversion ratio is calculated. The conversion ratio is repeatedly modified and a device power associated with each of the modified conversion ratios is calculated. A current optimum conversion ratio for the buck-boost converter is identified based on the calculated device powers. The current optimum conversion ratio corresponds to one of a buck mode, a boost mode and a buck-boost mode for the buck-boost converter.
Owner:NAT SEMICON CORP
Voltage converter with combined capacitive voltage divider, buck converter and battery charger
InactiveUS20090033293A1Batteries circuit arrangementsEfficient power electronics conversionĆuk converterCapacitive voltage divider
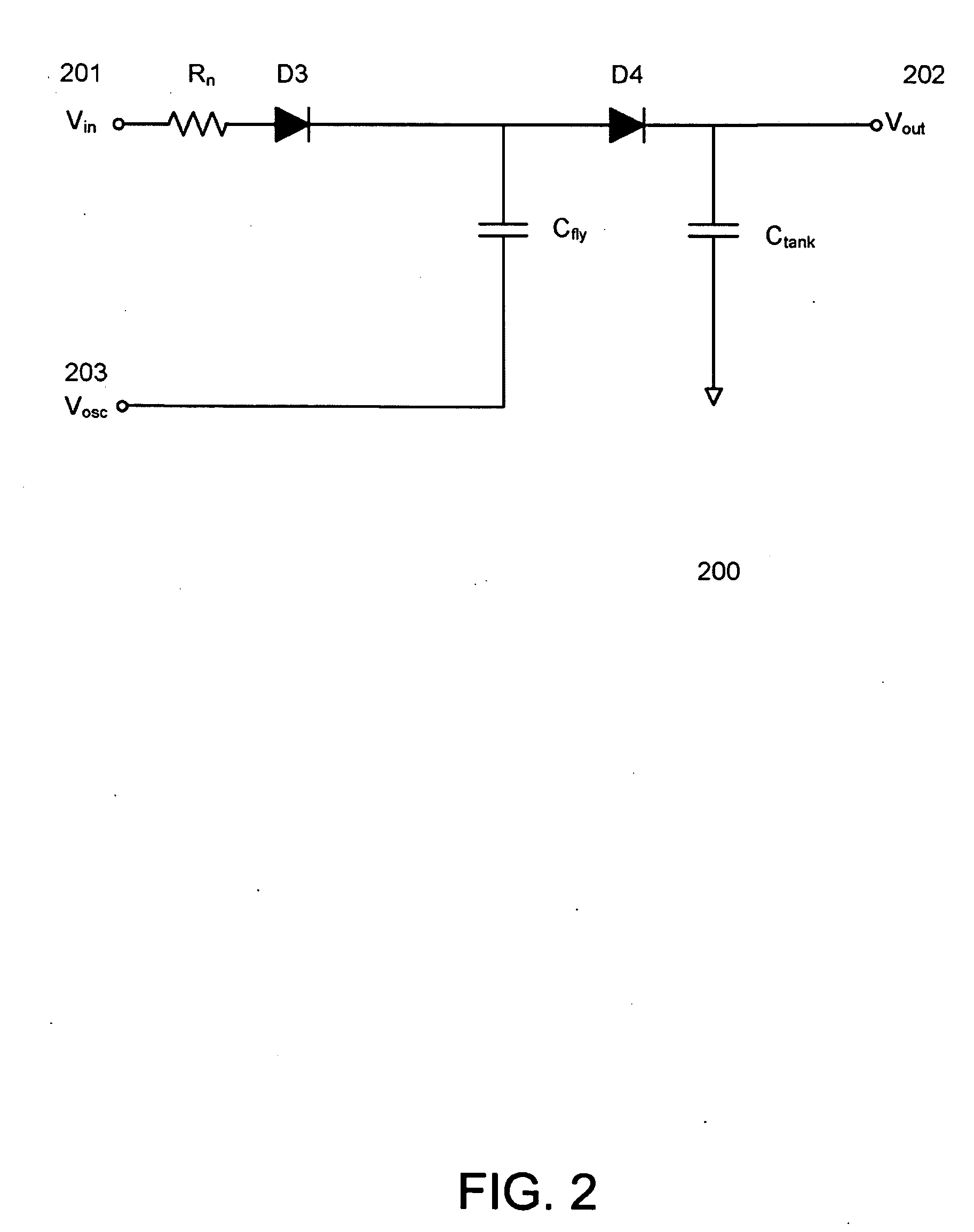
A voltage converter including a capacitive voltage divider combined with a buck converter and battery charger. The converter includes four capacitors, a switch circuit, an inductor and a controller. The capacitors form a capacitor loop between an input node and a reference node and include a fly capacitor controlled by the switch circuit, which is controlled by a PWM signal to half the input voltage to provide a first output voltage on a first output node, and to convert the first output voltage to the second output voltage via the inductor. The controller controls the PWM signal to regulate the second output voltage, and provides a voltage control signal to control the input voltage to maintain the first output node between a predetermined minimum and maximum battery voltage levels. A battery charge path is coupled to the reference node and battery charge mode depends upon the battery voltage.
Owner:INTERSIL INC
Hysteretic CL power converter
ActiveUS20120170334A1Reduce the valueSmall sizeEfficient power electronics conversionAc-dc conversionĆuk converterSwitching frequency
A novel switching hysteretic power converter is presented. The power converter combines the function of a capacitive charge pump with the function of an inductive step down converter to obtain a switching boost converter with a much simpler control method with respect to conventional inductive boost power converters. The hysteretic control provides stable operation in all conditions with excellent load transient response. Furthermore the hysteretic control allows high frequency switching reducing the size and cost of the passive components. The Discontinuous Conduction Mode of operation provides very high efficiency even at light loads. The presented power converter can be operated as a boost converter or as a buck converter simply by changing the switching phase of one switch. In both types of operation the efficiency of the hysteretic power converter can be quite high even at high switching frequencies.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
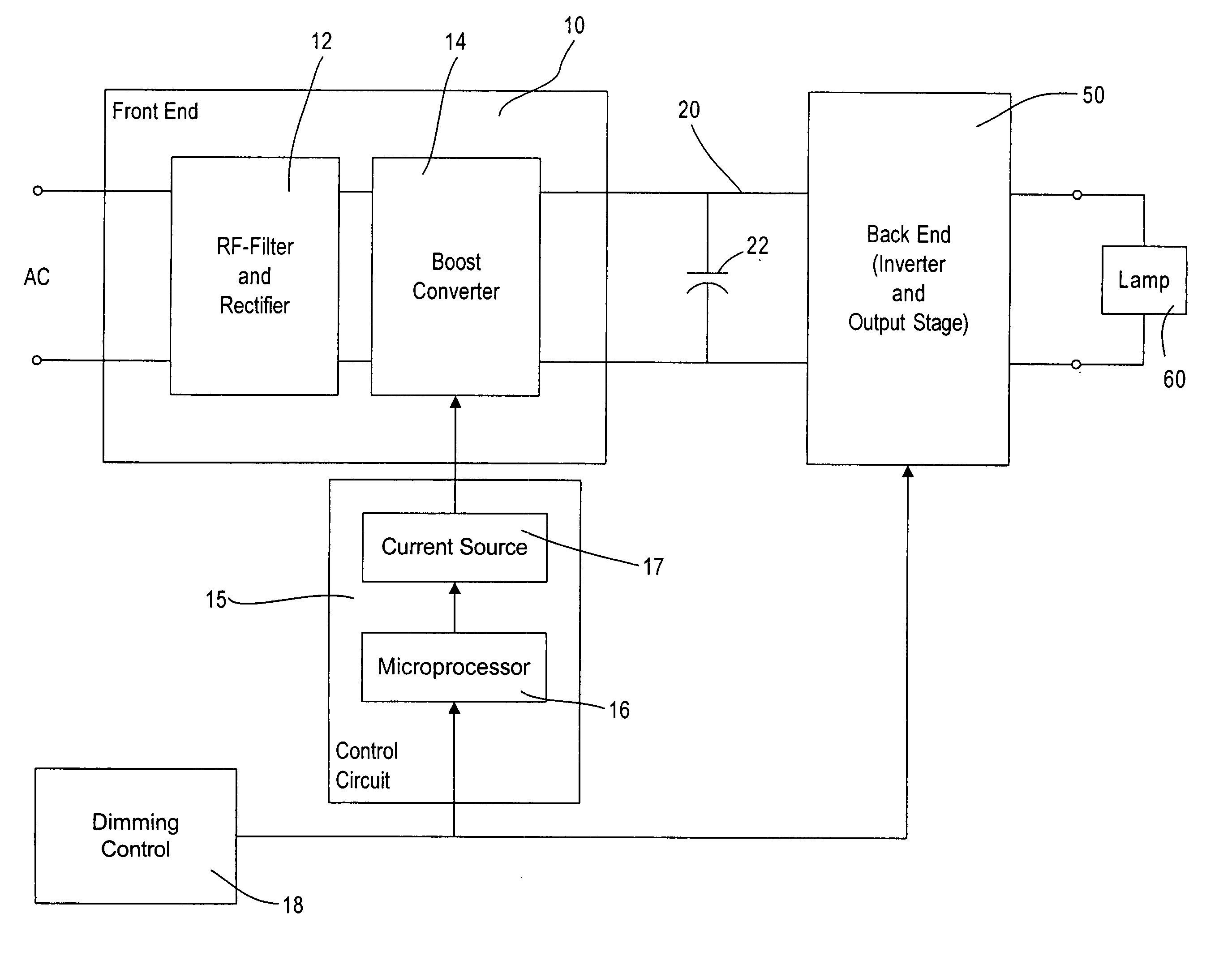
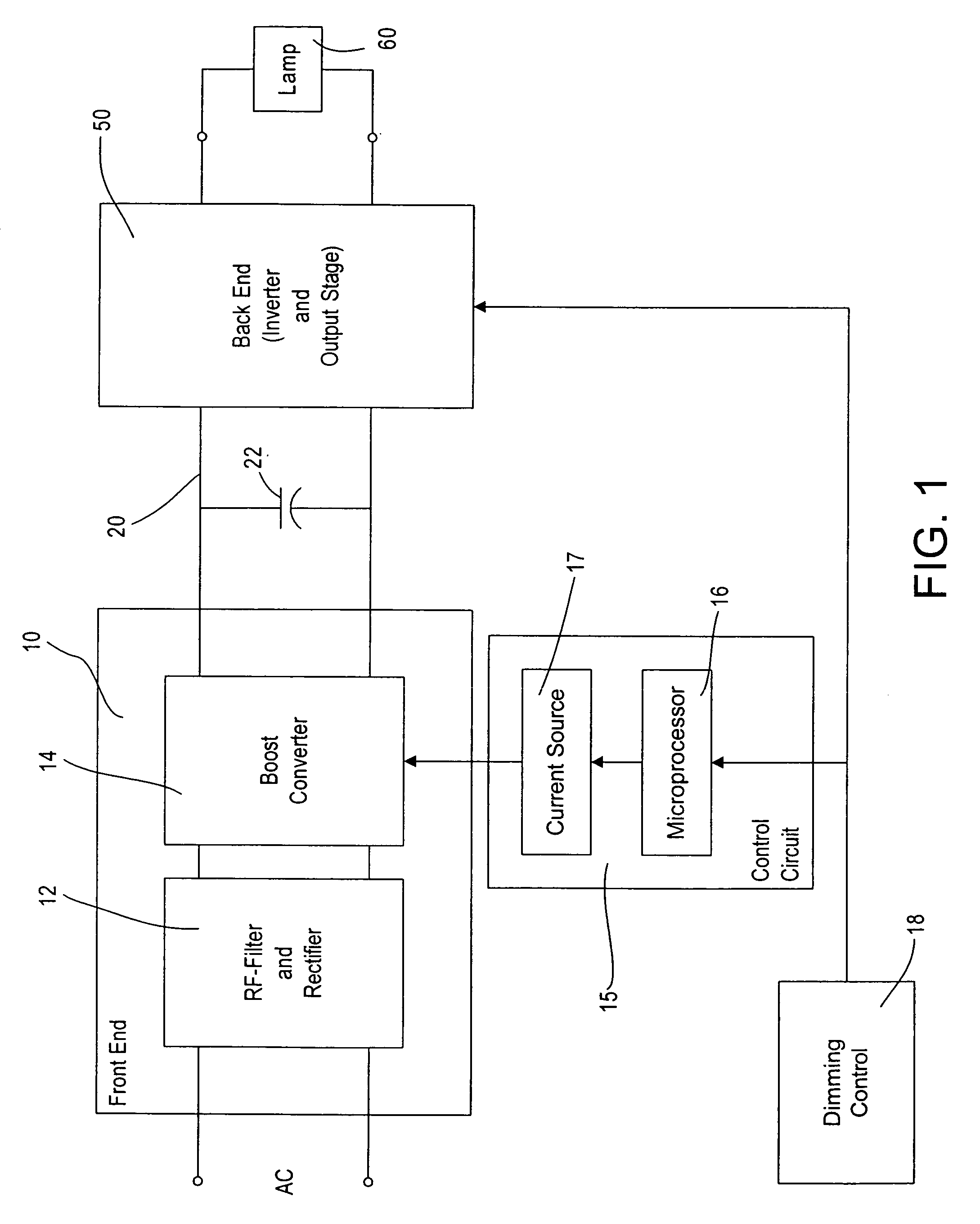
Ballast circuit for high intensity discharge lamps
InactiveUS6181084B1Eliminate flickeringMinimises levelAc-dc conversion without reversalConversion with intermediate conversion to dcBuck converterBoost controller
A ballast circuit for a high intensity discharge lamp includes a boost converter, responsive to a dc input voltage, for providing a boosted dc output voltage; a boost controller, responsive to the boosted dc output voltage, for driving the boost converter to maintain the boosted output voltage at a predetermined level; a buck converter, responsive to the boosted dc output voltage, for providing a reduced dc output voltage; and a buck controller, responsive to the reduced output voltage, for driving the buck converter to operate the discharge lamp in a transition mode and maintaining the reduced dc output voltage at a preselected level for operating the discharge lamp in a steady state mode.
Owner:EXCELITAS TECH
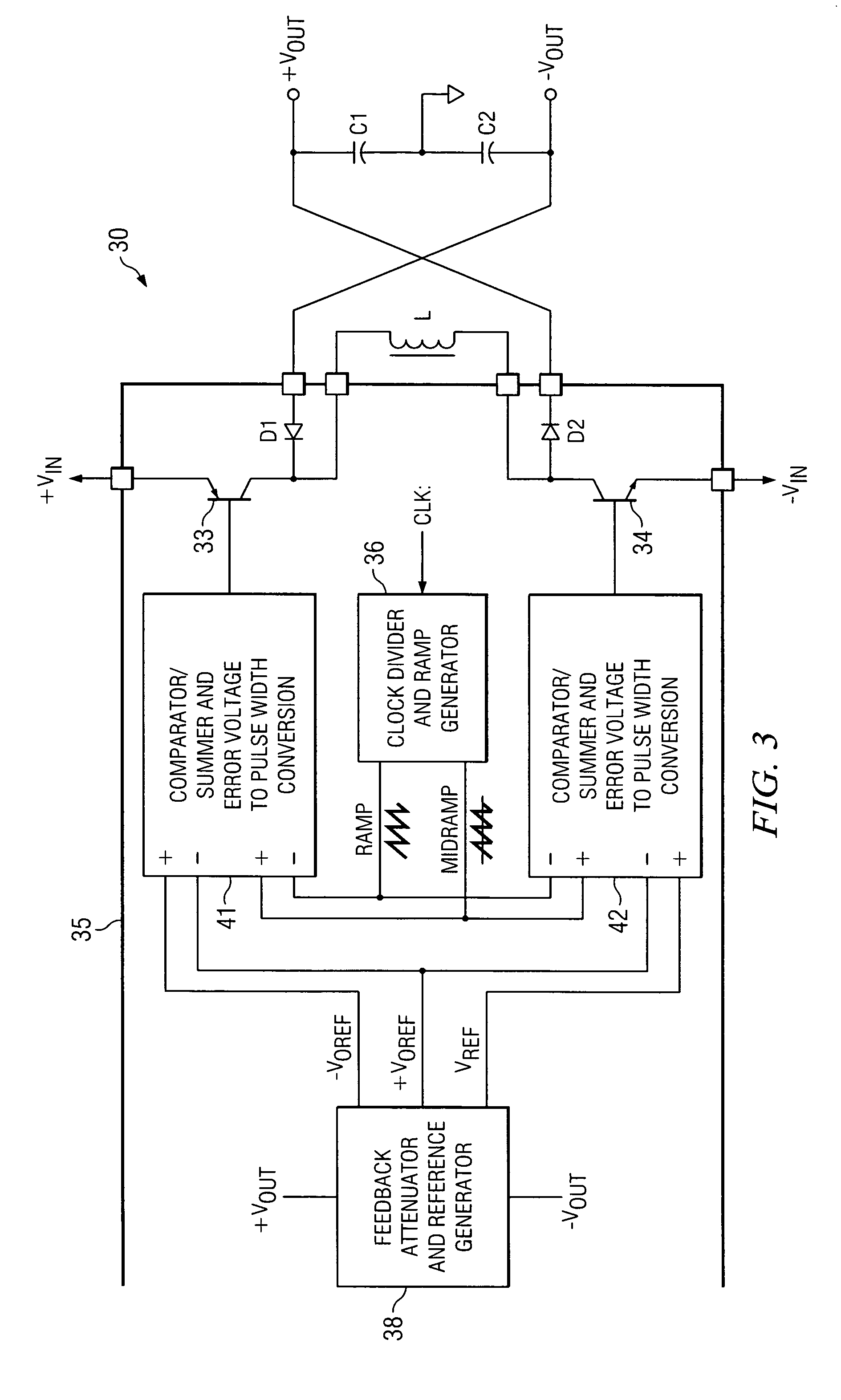
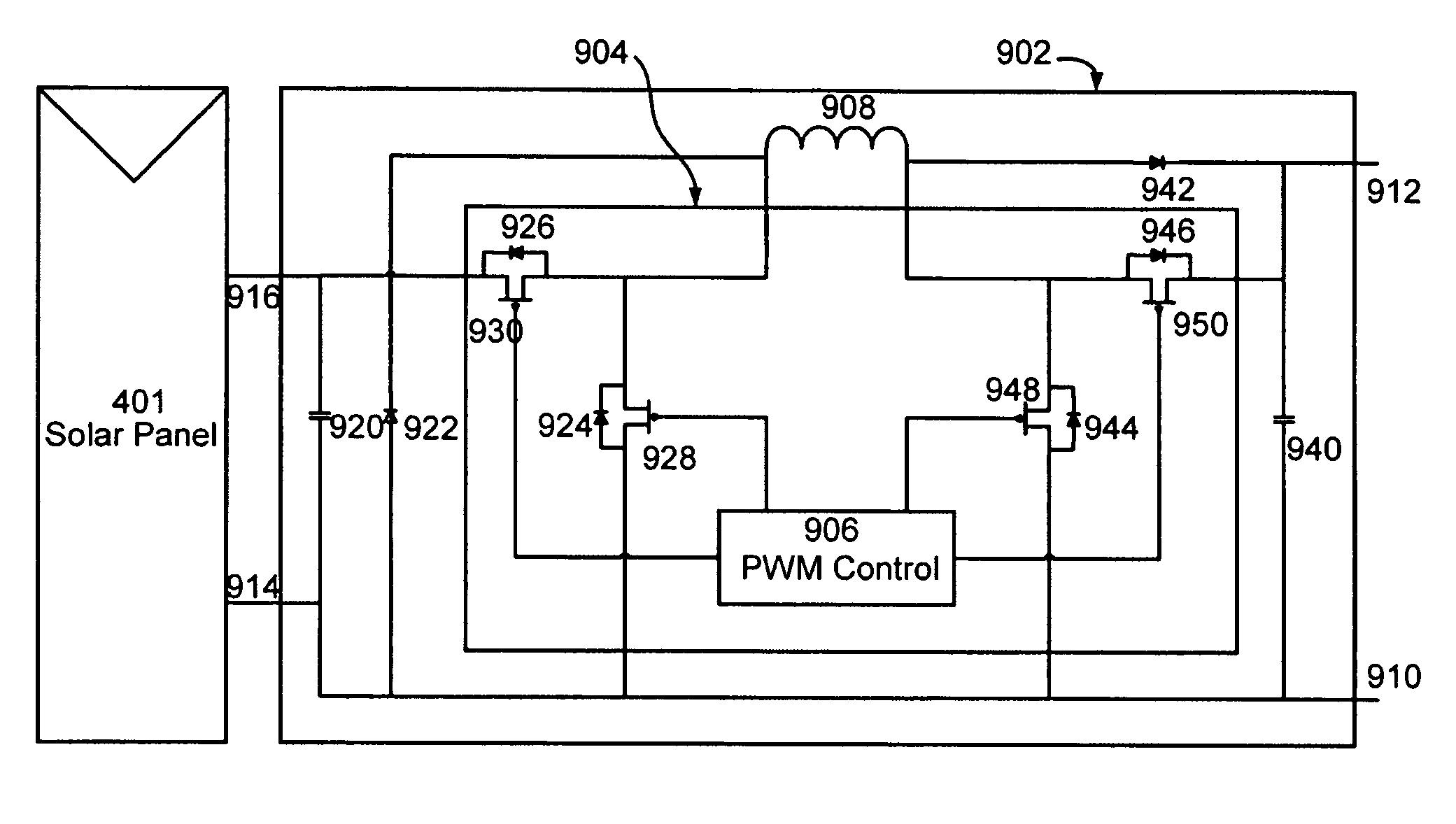
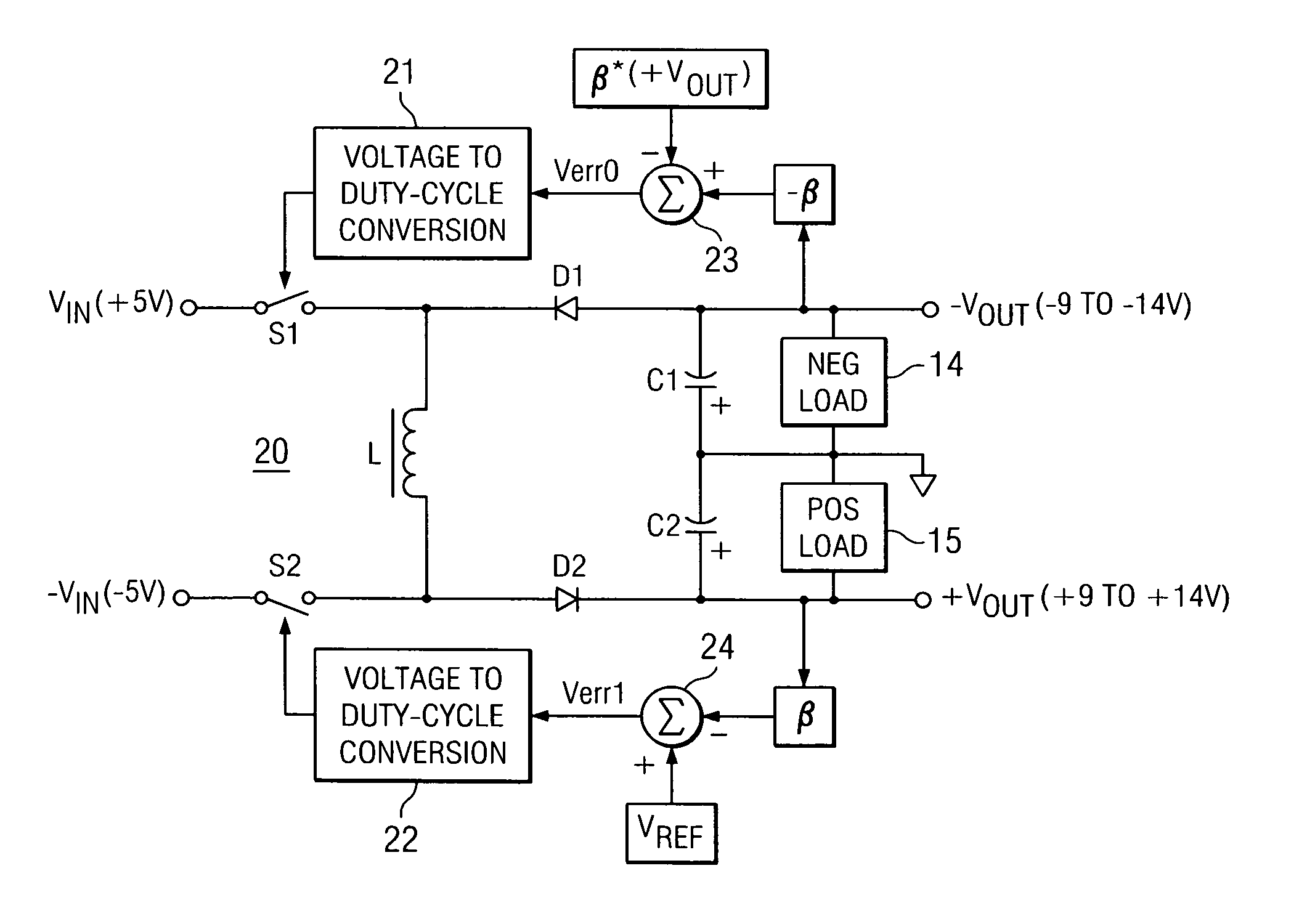
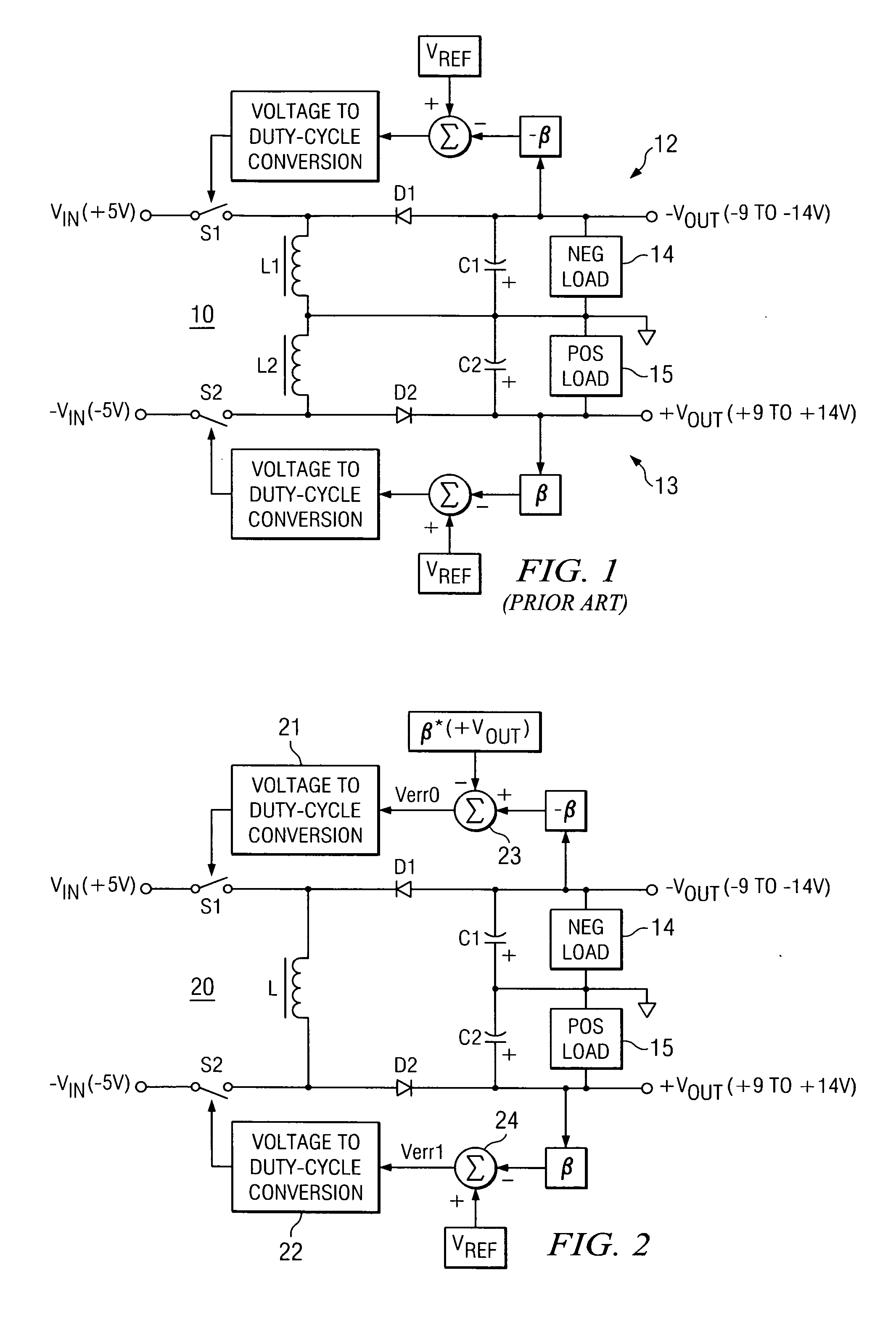
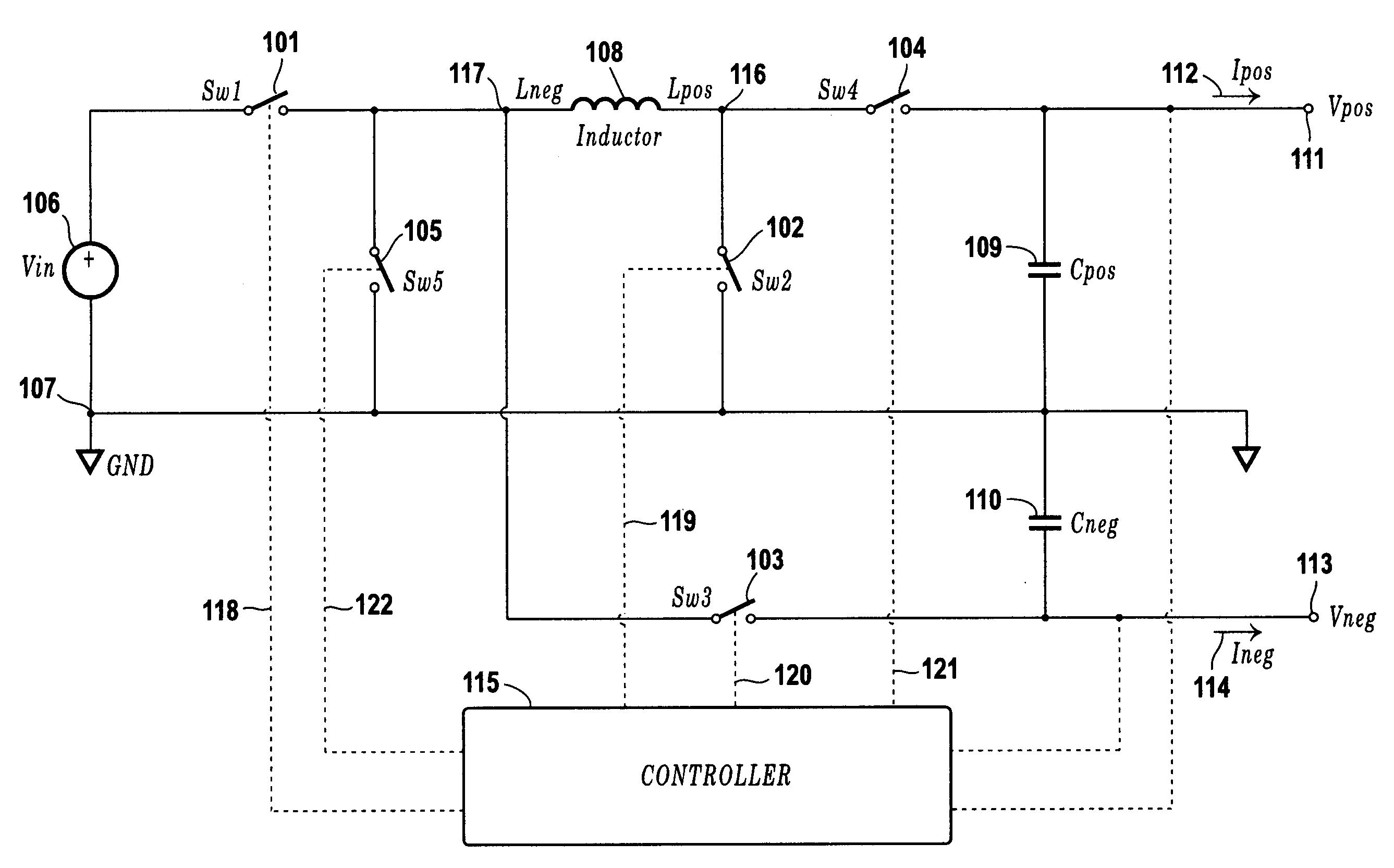
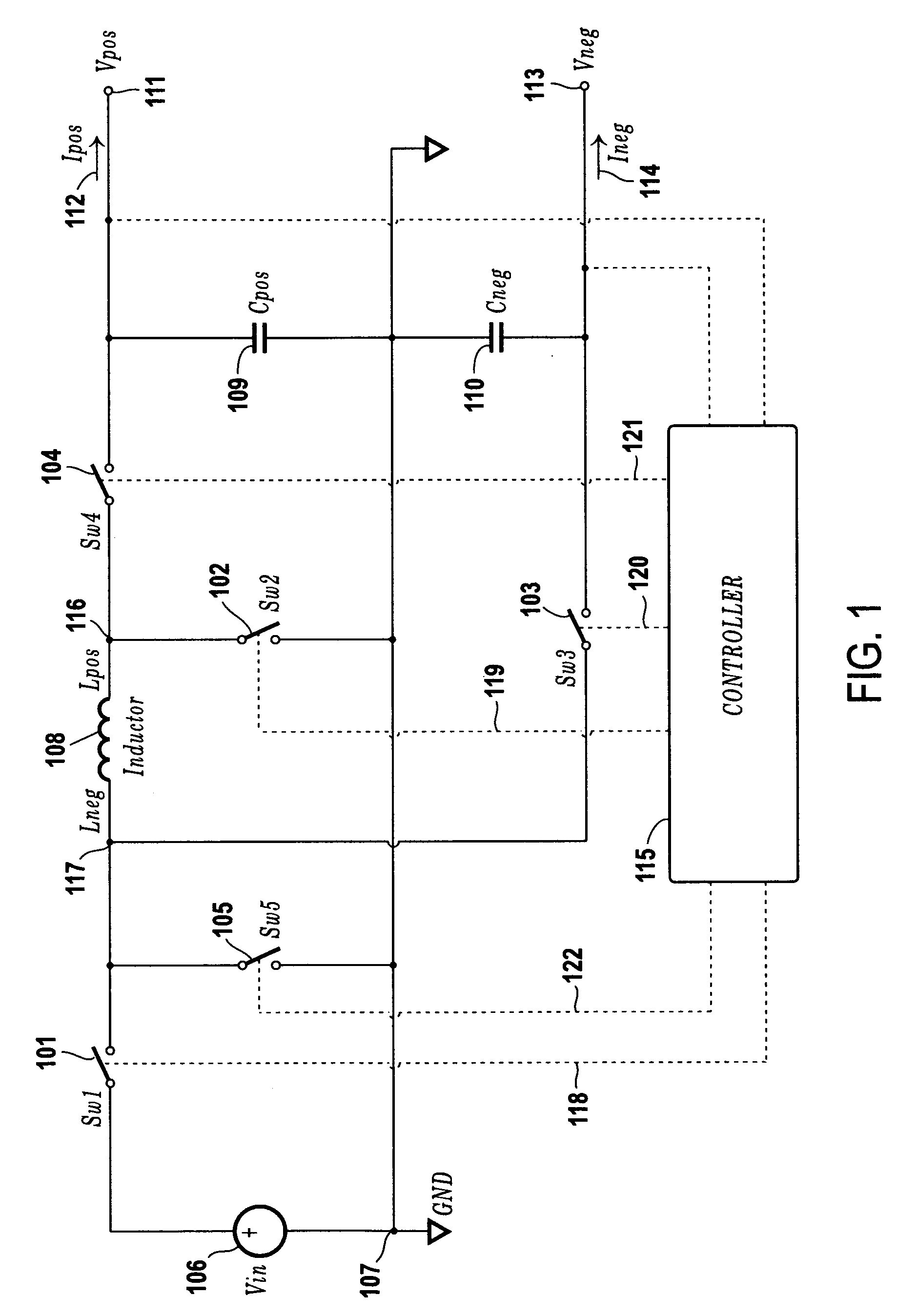
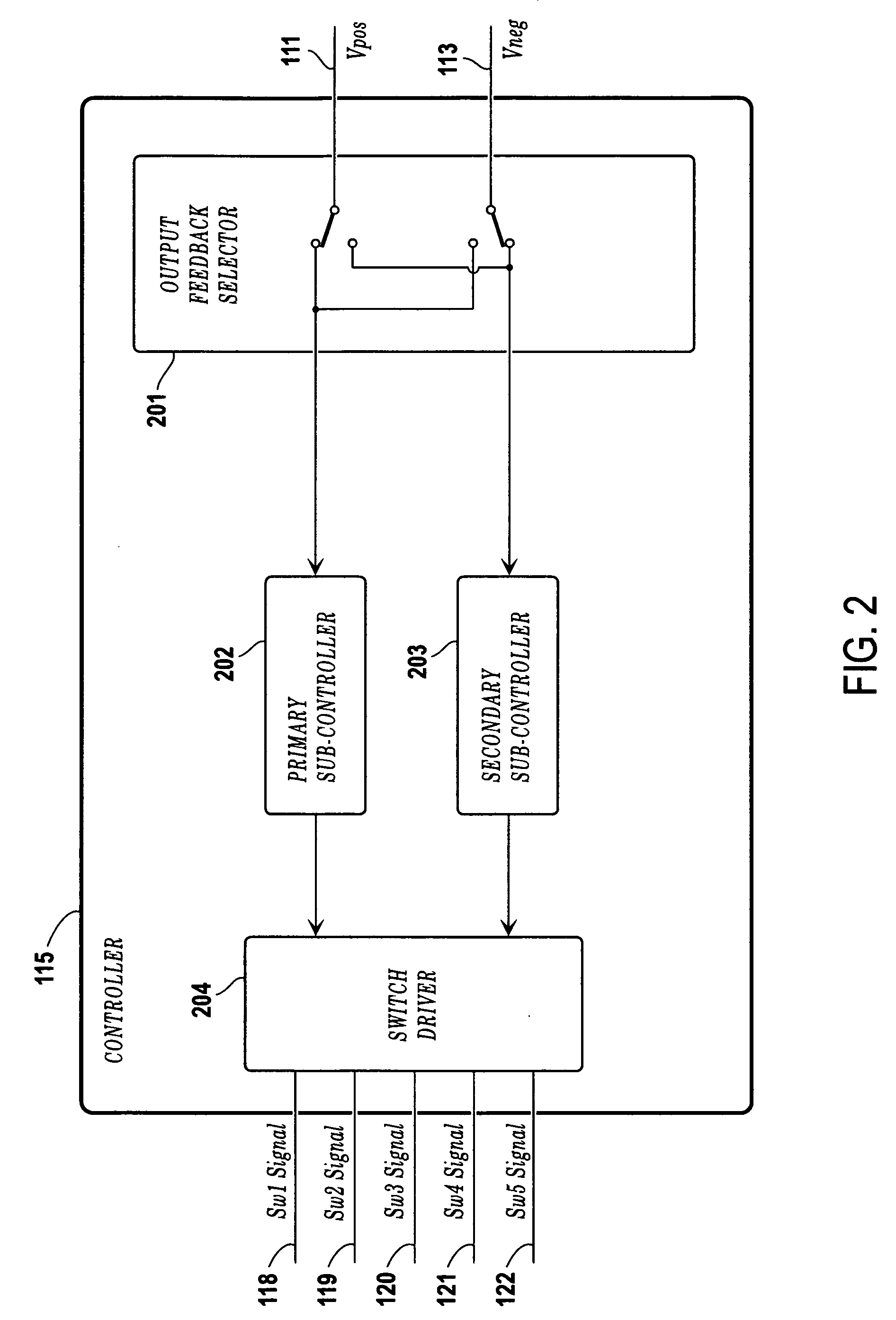
Single-inductor buck-boost converter with positive and negative outputs
InactiveUS20100039080A1Increase costLow output voltage rippleDc-dc conversionAc network voltage adjustmentVoltage regulationInductor
A single-inductor power converter with buck-boost capability provides regulated bipolar output voltage to a positive and a negative load. A five-switch bridge topology allows a controller to direct the inductor current to the appropriate outputs or circuit ground as needed to maintain regulation. The controller also adjusts the inductor current level for proper output voltage regulation. The five-switch bridge topology makes possible a wide range of ratios between the positive and negative output currents of the converter.
Owner:ASAHI KASEI TOKO POWER DEVICE
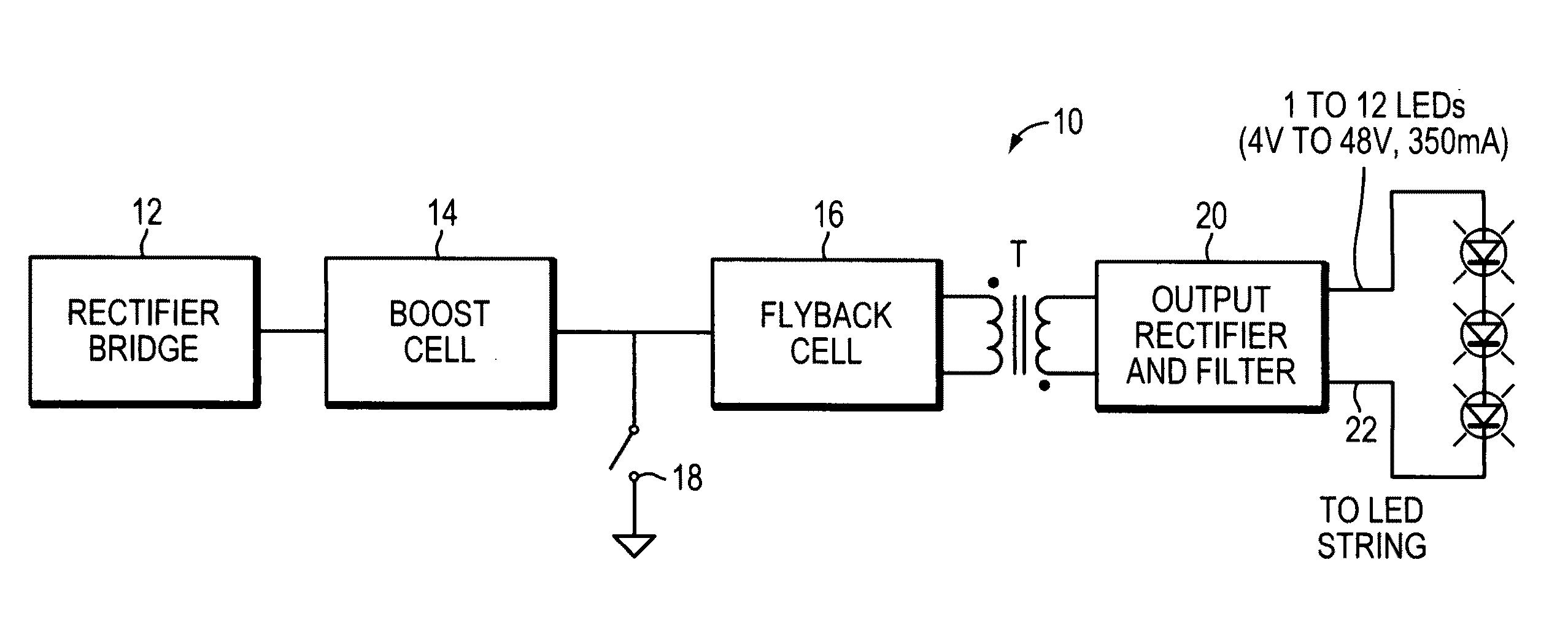
LED Illumination systems
InactiveUS20110309760A1Improve reliabilityLow costEfficient power electronics conversionElectroluminescent light sourcesBuck converterFlyback diode
An illumination system includes a power supply having a boost converter operating in the discontinuous conduction mode, a flyback converter operating in the critical conduction mode, and a switch coupled to the flyback converter. Several light emitting diodes receive power from the power supply. The boost converter may include a boost inductor (LB) and a boost diode (DB), constructed to perform the boost power factor correction (PFC) function. The flyback converter may includes a flyback inductor (LFB) and a flyback diode (DFB) and the power supply may be constructed to turn on the switch around the point where the current flowing in the flyback inductor reaches zero value.
Owner:EMD TECH
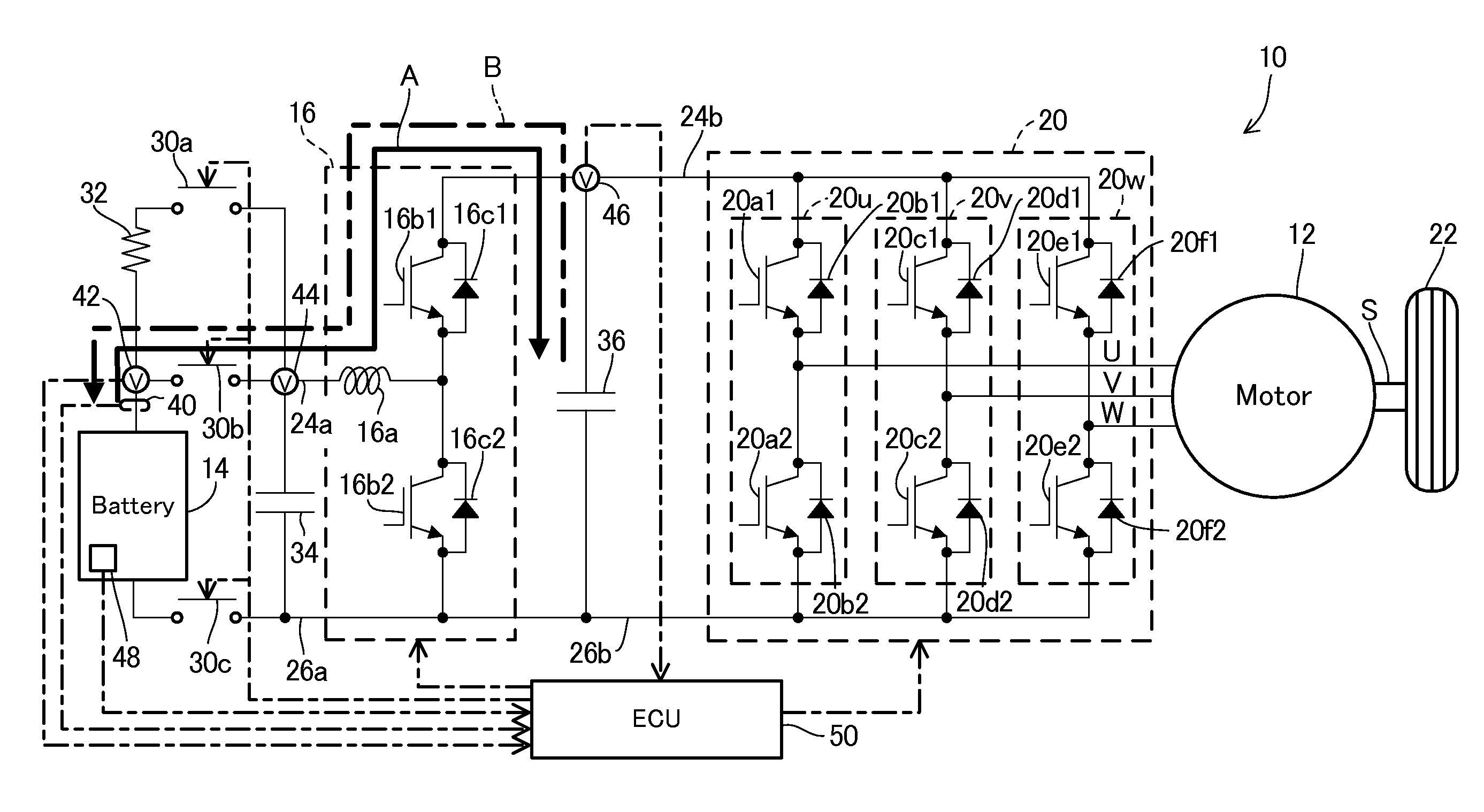
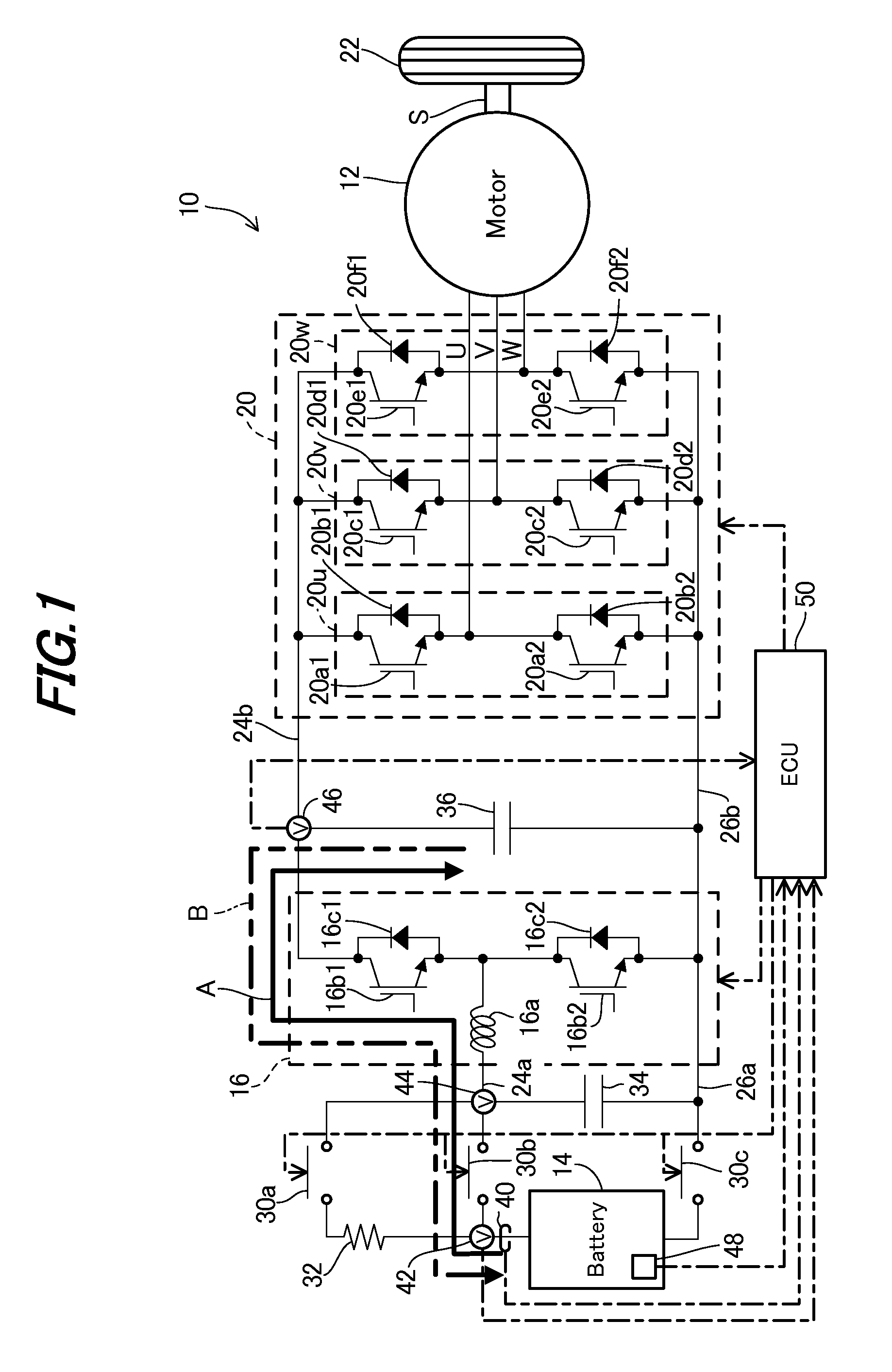
Battery heating apparatus for vehicle
InactiveUS20110298427A1Efficient heatingAffecting size of apparatusBatteries circuit arrangementsElectric devicesPower flowElectrical battery
In an apparatus for heating a battery of a vehicle, having an electric rotating machine and buck-boost converter between the battery and rotating machine to step up / down voltage outputted from the battery to be supplied to the rotating machine and step up / down voltage generated by the rotating machine to be supplied to the battery, it is configured to have a first capacitor interposed between wires connecting the battery to the converter, a second capacitor interposed between wires connecting the converter to the rotating machine, and a heating controller to control operation of the converter to generate current similar to rectangular wave current and input / output the current between the battery and the second capacitor through the first capacitor so as to heat the battery. With this, it becomes possible to efficiently heat the battery so that the battery can output expected power, without adversely affecting the size of the apparatus.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Hysteretic buck converter having dynamic thresholds
ActiveUS20090322300A1Improved ripple controlEfficient power electronics conversionEmergency protective circuit arrangementsBuck converterĆuk converter
A hysteretic buck converter provides improved regulation control, in particular for buck converter standby operation. A comparison circuit compares the output voltage of the buck converter to a waveform that is generated from an indication of the output current of the converter, so that the turn-on time of the converter is advanced as the output current demand increases. The resulting action anticipates a reduction in output voltage due to the increased current, preventing an excursion of the output voltage below the ripple voltage minimum. The turn-off time of the converter is controlled by an upper threshold that limits the ripple voltage maximum. The output current indication may be a measurement of output current, or may be a dynamic value calculated from the input voltage and the output voltage waveform.
Owner:CIRRUS LOGIC INC
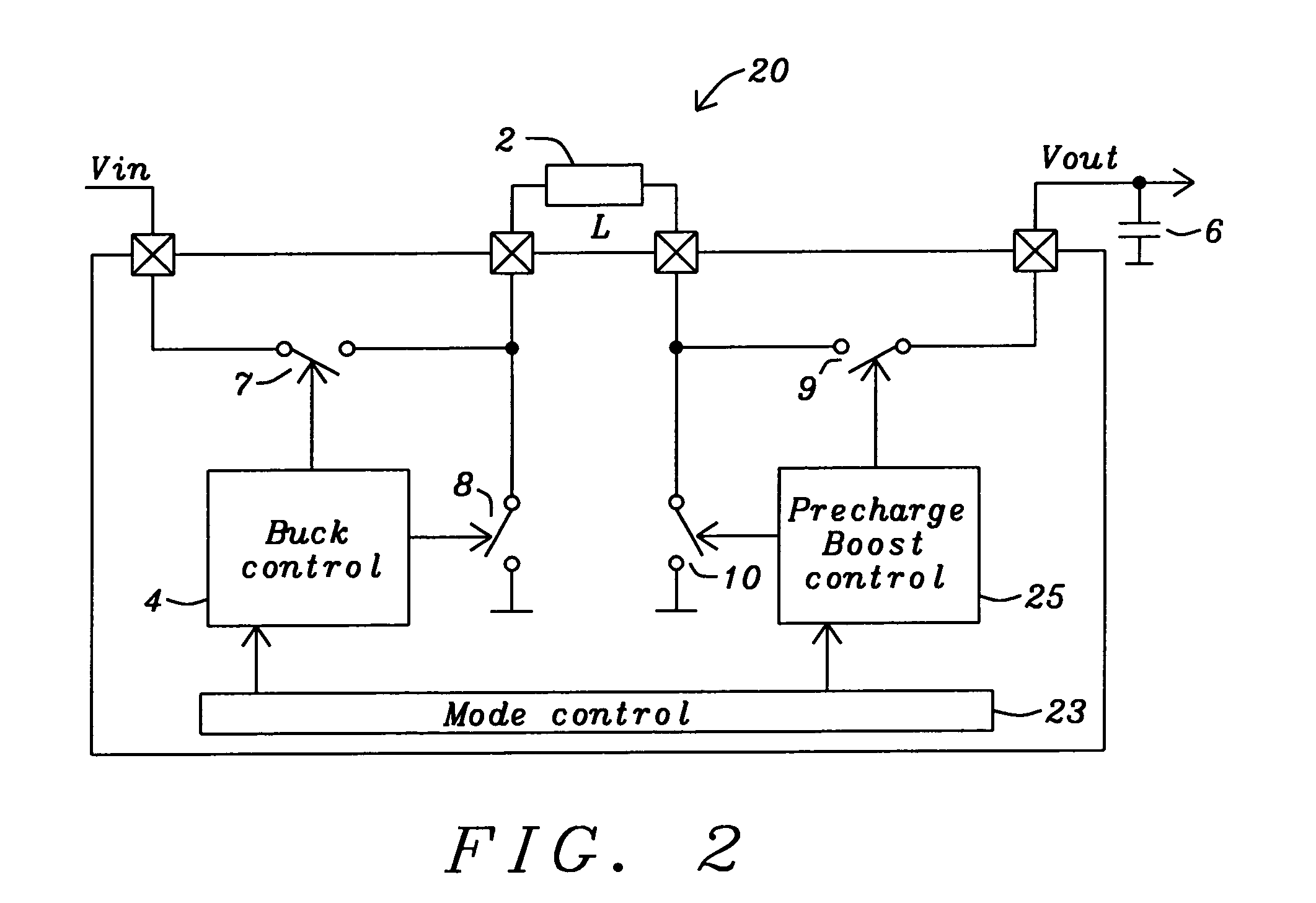
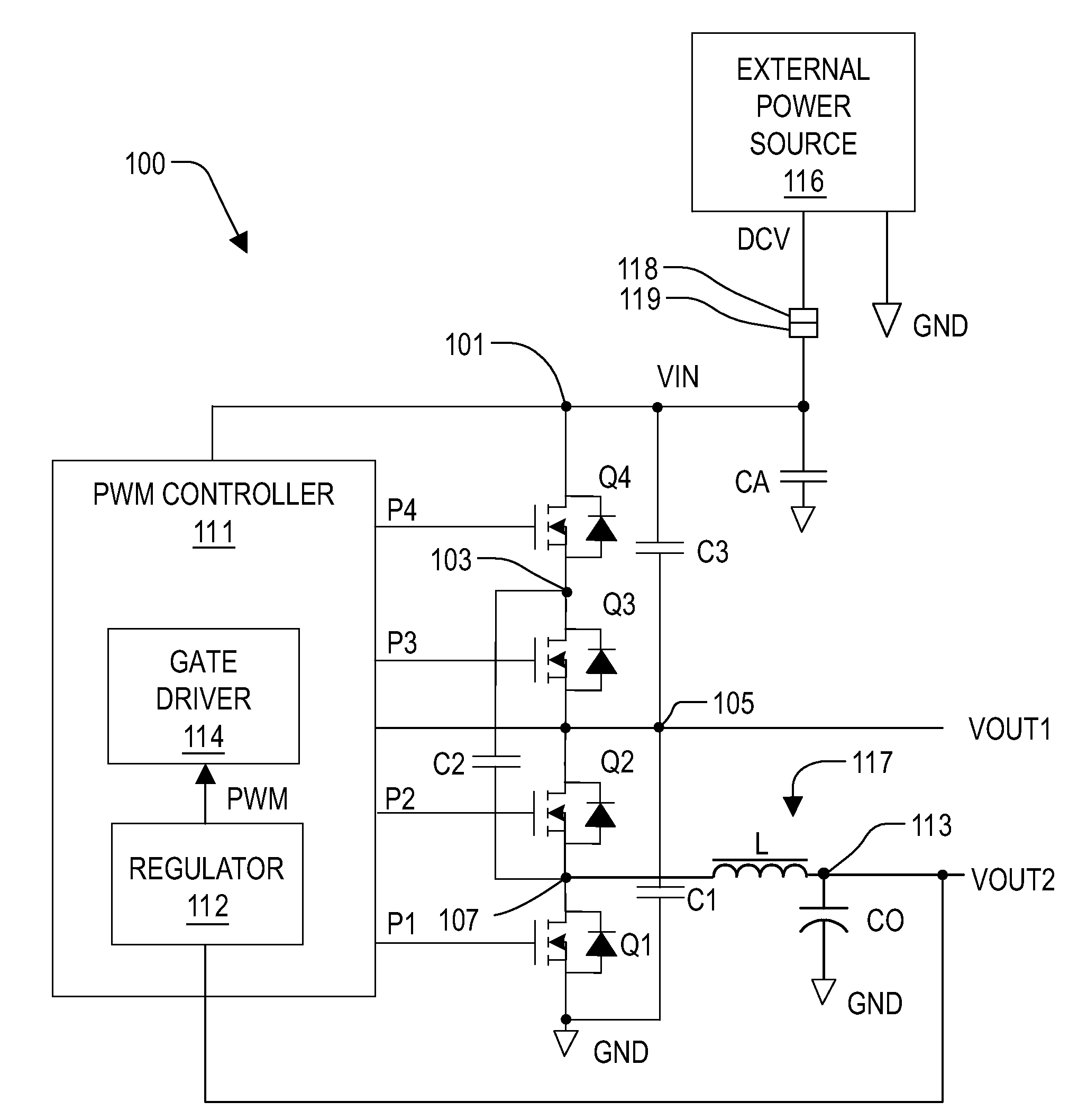
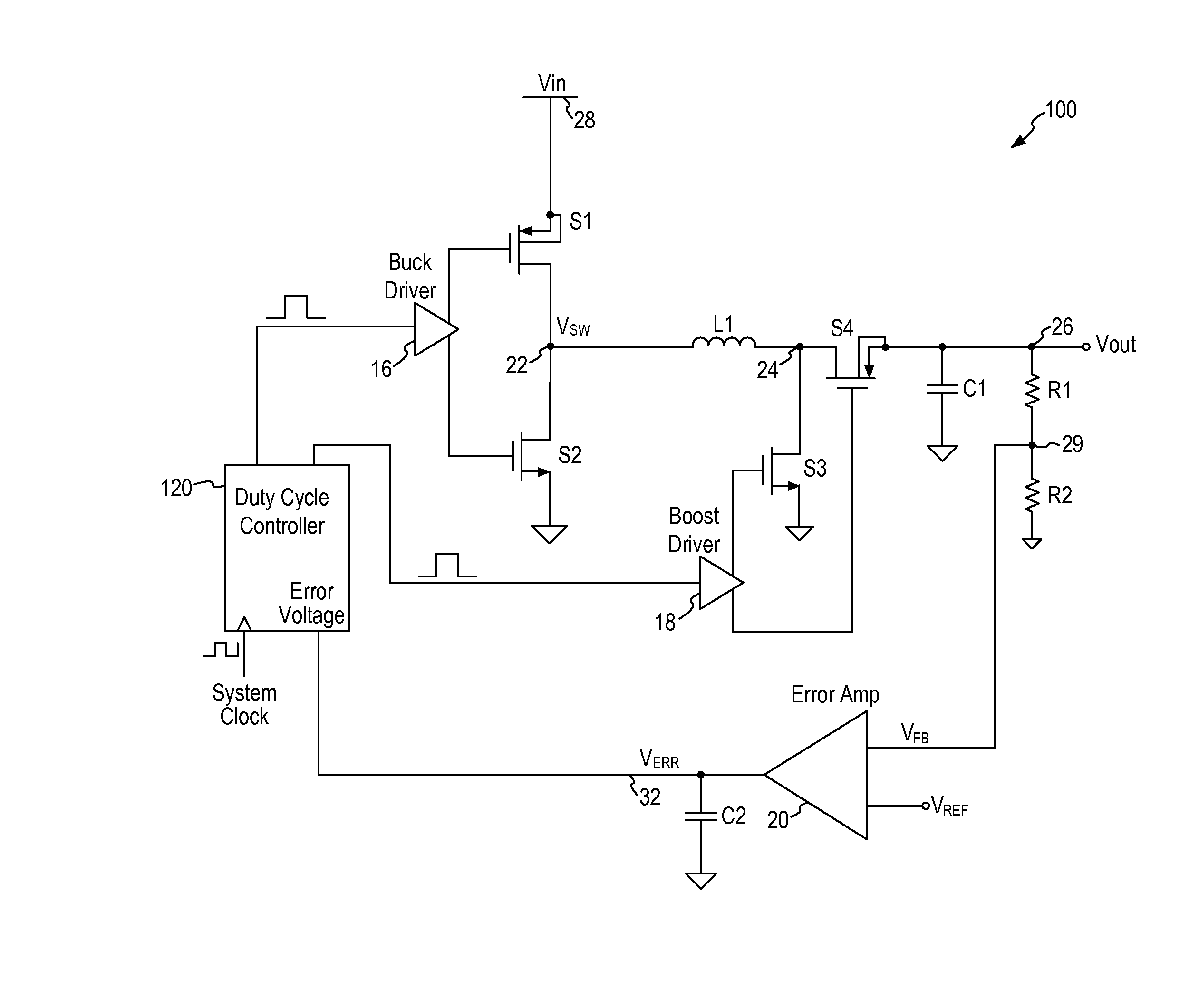
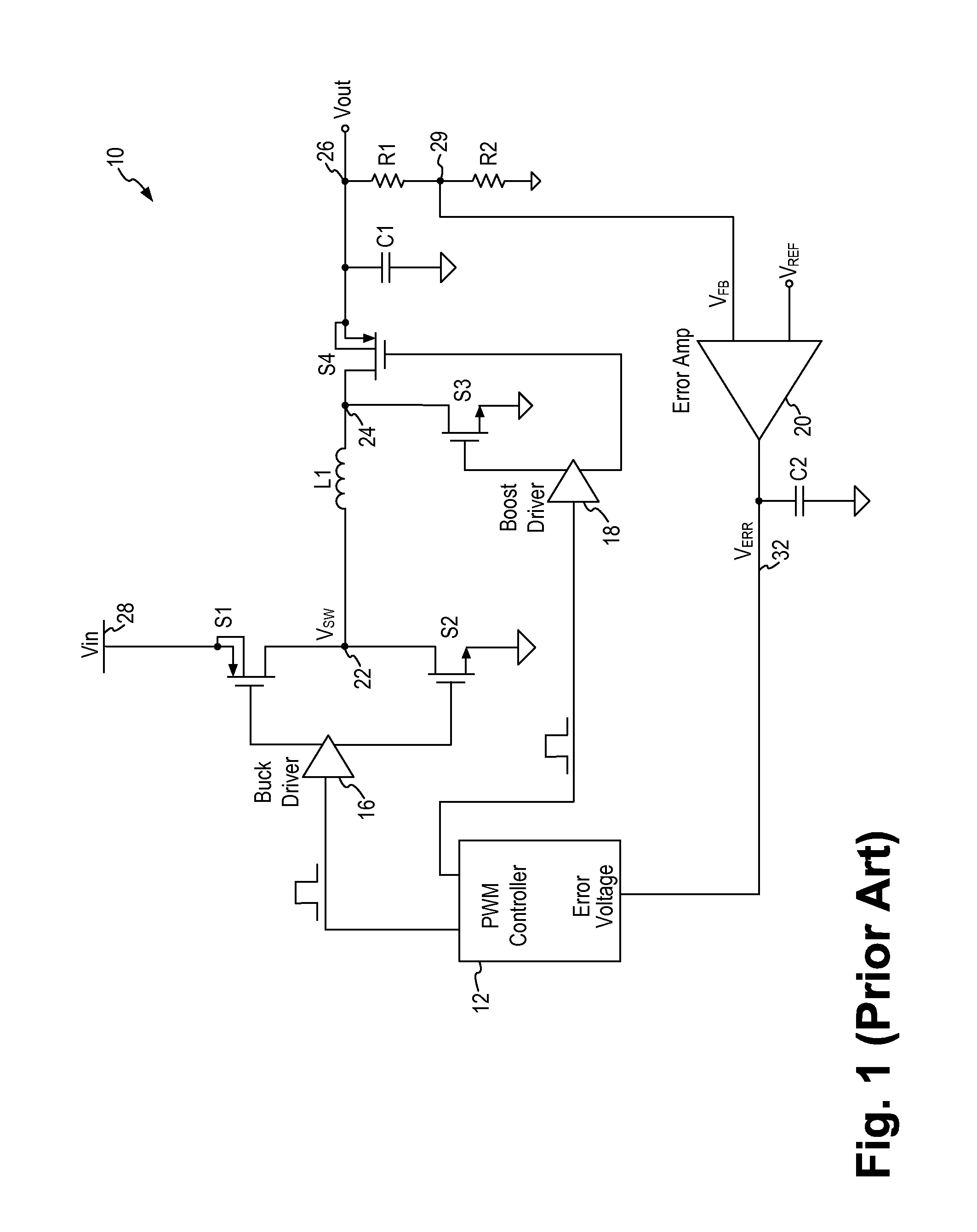
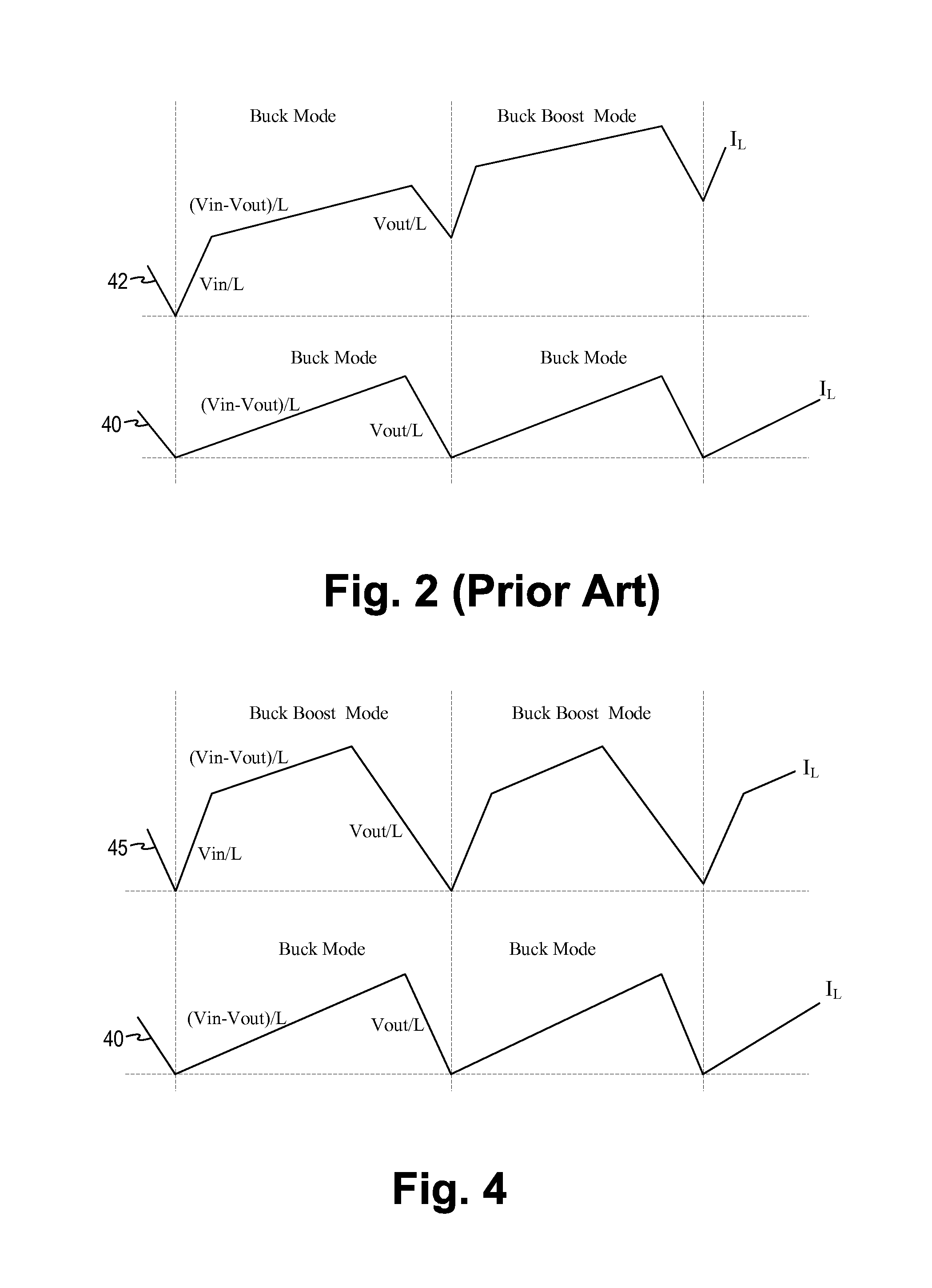
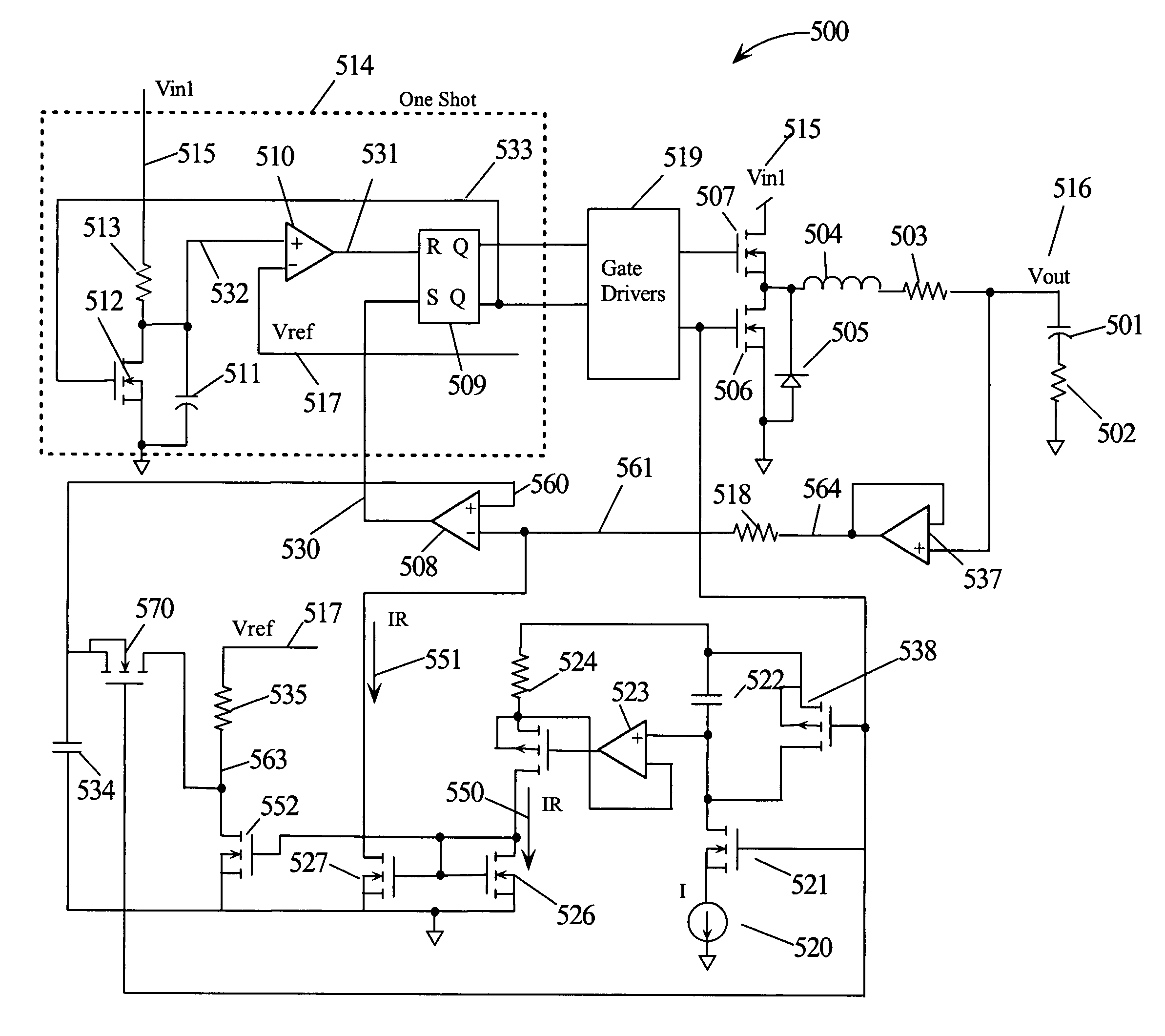
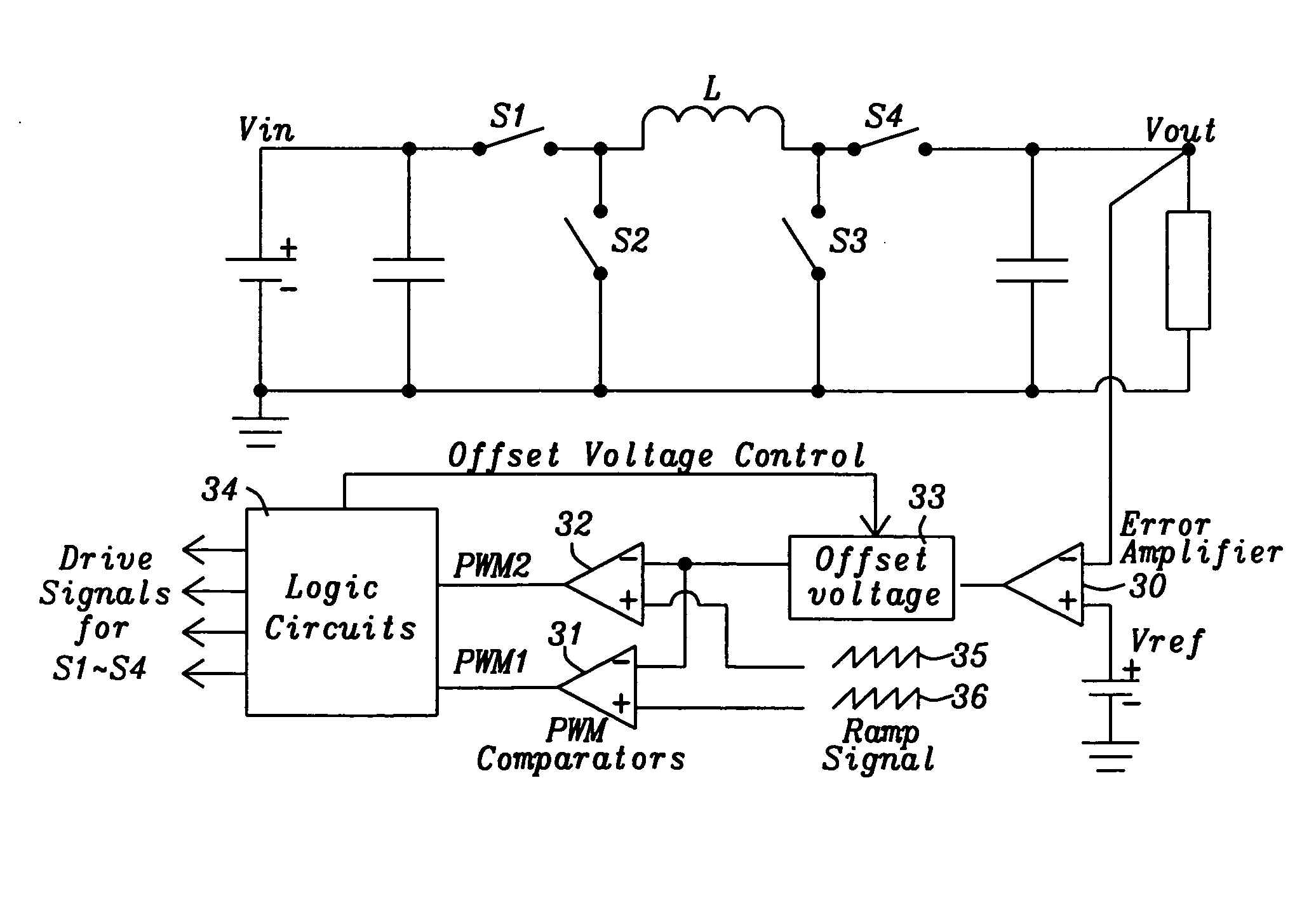
Buck-Boost Converter Using Timers for Mode Transition Control
A DC-to-DC, buck-boost voltage converter includes a duty cycle controller configured to generate control signals for a buck driver configured to drive first and second buck switching transistors at a buck duty cycle and to generate control signals for a boost driver configured to drive first and second boost switching transistors at a boost duty cycle. The duty cycle controller includes at least a duty cycle timer and an offset timer where the duty cycle controller applies the duty cycle timer and the offset timer to control transitions between the buck, the buck-boost and the boost operation modes of the voltage converter.
Owner:MICREL
Multiphase clamp coupled-buck converter and magnetic integration
InactiveUS20020118000A1Emergency protective circuit arrangementsDc-dc conversionVoltage regulator modulePush pull
Voltage regulation, transient response and efficiency of a voltage regulator module (VRM) is improved where short duty cycles are necessitated by large differentials of input and output voltage by including at least one clamping of a tap of an inductance in series with an output of each of a plurality of parallel branches or phases which are switched in a complementary fashion or providing coupling between inductors of respective phases. Such coupling between inductors is achieved in a small module with an integrated magnetic structure. Reduced component counts are achieved while deriving built-in input and output filters. Principals of the invention can be extended to isolation applications and push-pull forward converts, in particular. A lossless clamping circuit is also provided allowing spike currents to be suppressed while returning power to the output of the VRM.
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP INC
Power efficient charge pump with controlled peak currents
InactiveUS20100013548A1Apparatus without intermediate ac conversionElectric variable regulationElectrical resistance and conductancePower efficient
A charge pump which uses a current limit resistor to limit in-rush current and peak currents. An additional advantage of such a charge pump is that, when being coupled to a boost converter or other switching converter utilizing an inductive energy storage element, it may avoid unnecessary power dissipation caused by the current limit resistor.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
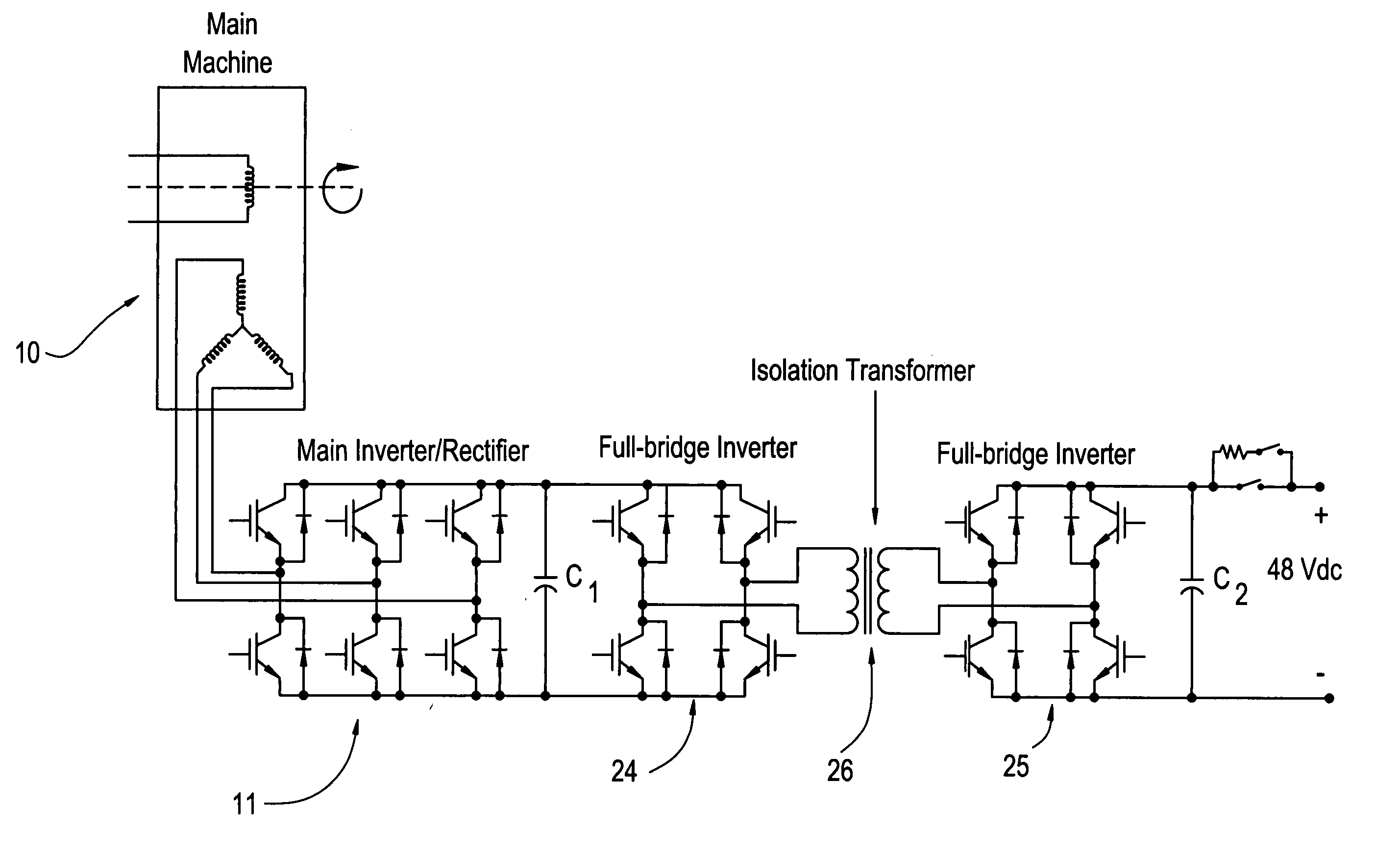
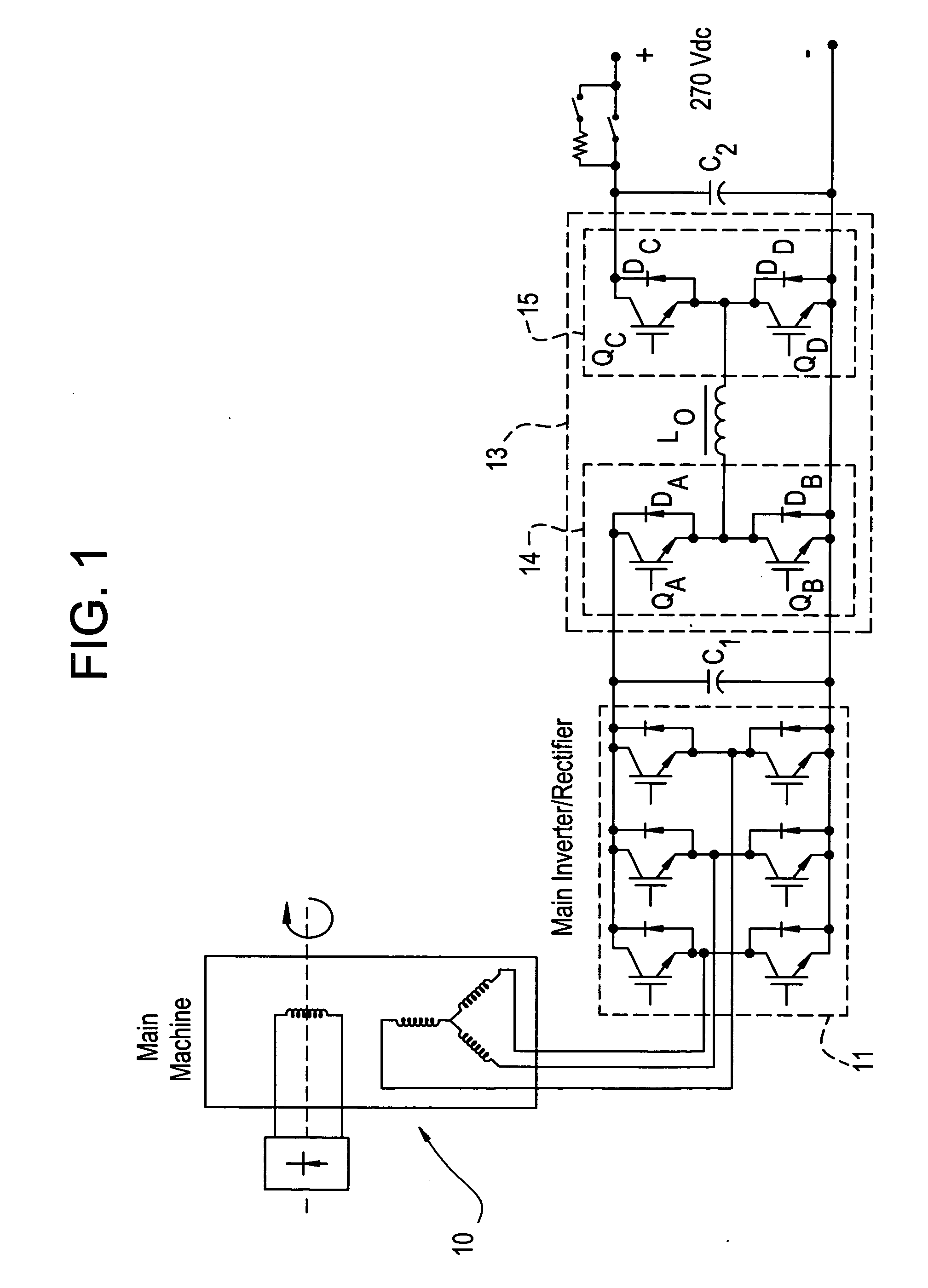
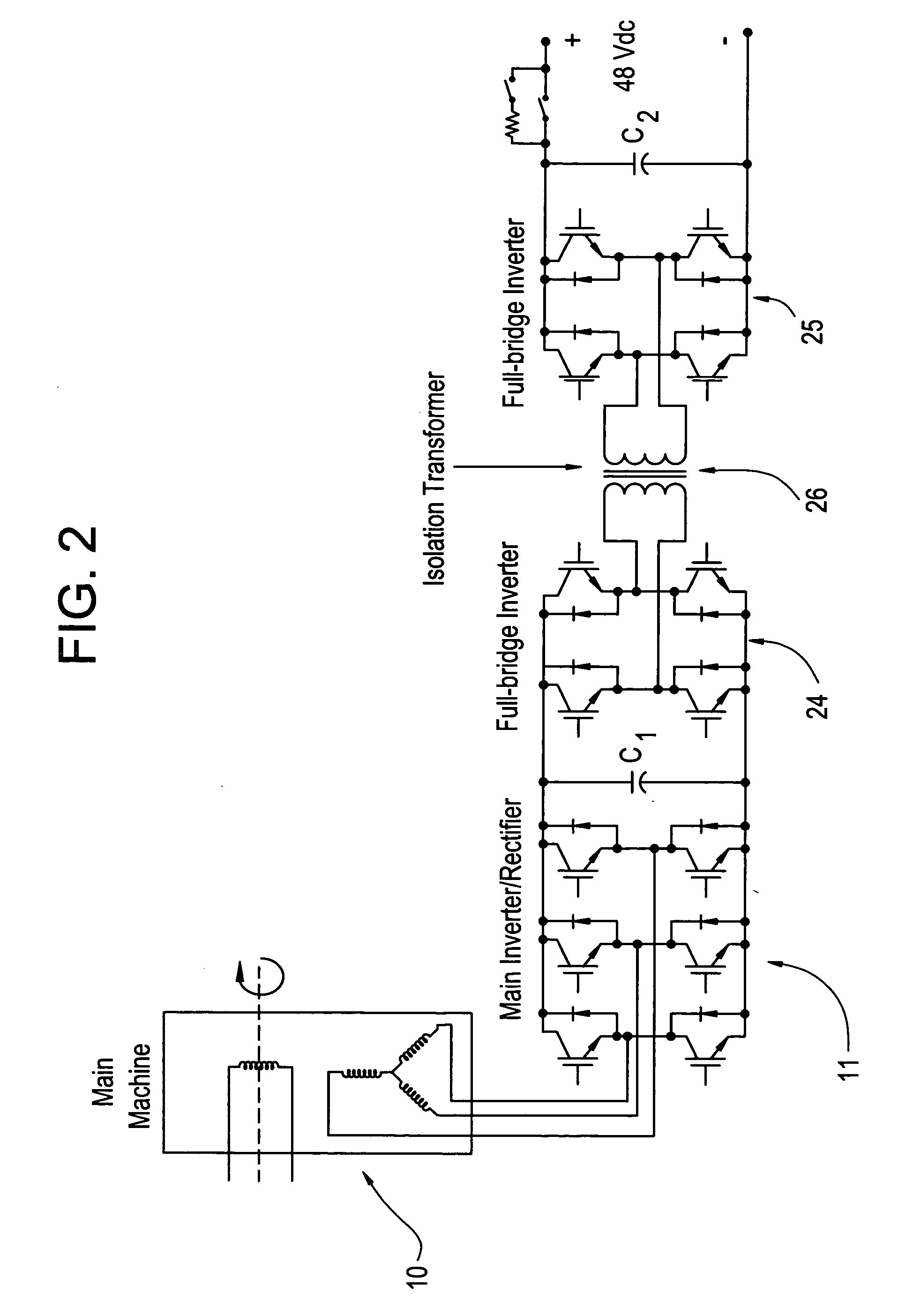
Bidirectional buck-boost power converters, electric starter generator system employing bidirectional buck-boost power converters, and methods therefor
ActiveUS20060103341A1Single-phase induction motor startersElectronic commutation motor controlStarter generatorBoost power converter
A bidirectional buck-boost power converter 13 including a pair of inverter modules 14, 15 disposed at an output of a machine, and an inductor Lo connected between the pair of inverter modules 14, 15. A method for controlling a voltage output of a machine starter generator having an inverter rectifier and bidirectional buck-boost converter, includes outputting a dc voltage controlled by bidirectional buck-boost pulse width modulation (PWM) switching control, when the starter generator is in a generator mode.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
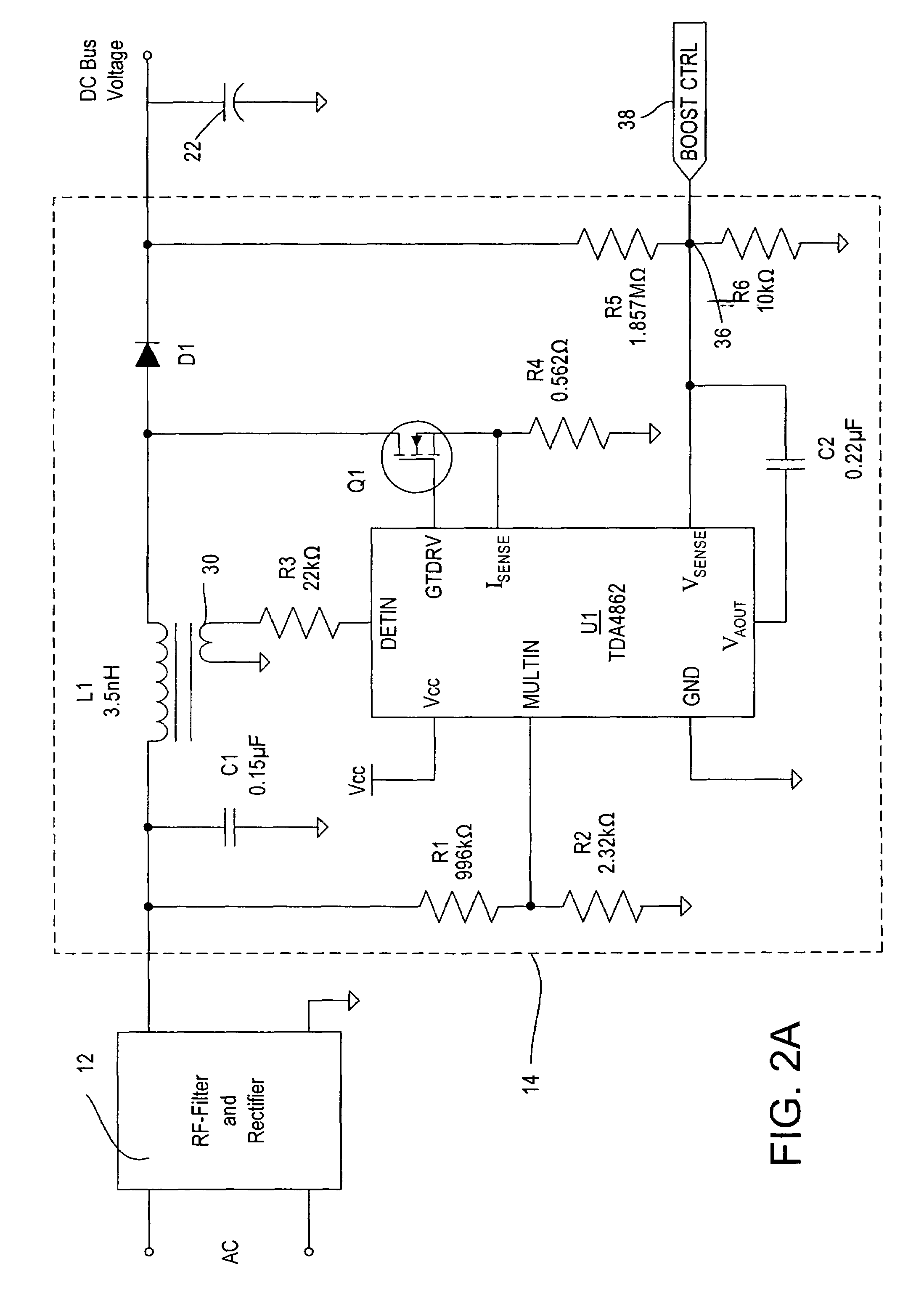
Lighting ballast having boost converter with on/off control and method of ballast operation
ActiveUS7075254B2Save energyLess powerElectric light circuit arrangementGas discharge lamp usageControl signalAlternating current
A ballast for driving a gas discharge lamp comprising a rectifier stage having an alternating current (AC) input and providing a rectified output voltage, a boost converter stage receiving the rectified output voltage as an input and providing a boosted direct current (DC) output voltage across a DC bus, an inverter output stage for converting the DC bus voltage to a high-frequency AC output voltage to drive the lamp, further comprising a control stage receiving a desired light level signal controlling the desired light level of the lamp and providing an output control signal for turning the boost converter stage on or off in dependency on the desired light level signal. The ballast thereby has reduced power consumption at low light levels for greater energy efficiency.
Owner:LUTRON TECH CO LLC
Multiphase voltage regulator having coupled inductors with reduced winding resistance
InactiveUS20070175701A1Prevent magnetic saturationTransformers/inductances coils/windings/connectionsDc-dc conversionElectrical resistance and conductanceBuck converter
A multiple phase buck converter or boost converter, or buck-boost converter has an inductor in each phase. The inductors are inversely coupled. In a first embodiment, the converter includes a toroidal magnetic core with inductors extending under and over opposite sides of the toroidal magnetic core. The coupled inductors are thereby inversely coupled and have a relatively low ohmic resistance. In a second embodiment, the converter comprises a ladder-shaped magnetic core (i.e. having parallel sides, and connecting rungs). In this case, the inductors extend under the sides, and over the rungs. Each inductor is disposed over a separate rung. The ladder-shaped magnetic core is preferably disposed flat on a circuit board. Inverse coupling and low ohmic resistance are also provided in the second embodiment having the ladder structure.
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP INC
Multiphase voltage regulator having coupled inductors with reduced winding resistance
InactiveUS20070176726A1Prevent magnetic saturationTransformers/inductances coils/windings/connectionsDc-dc conversionBuck converterCoupling
A multiple phase buck converter or boost converter, or buck-boost converter has an inductor in each phase. The inductors are inversely coupled. In a first embodiment, the converter includes a toroidal magnetic core with inductors extending under and over opposite sides of the toroidal magnetic core. The coupled inductors are thereby inversely coupled and have a relatively low ohmic resistance. In a second embodiment, the converter comprises a ladder-shaped magnetic core (i.e. having parallel sides, and connecting rungs). In this case, the inductors extend under the sides, and over the rungs. Each inductor is disposed over a separate rung. The ladder-shaped magnetic core is preferably disposed flat on a circuit board. Inverse coupling and low ohmic resistance are also provided in the second embodiment having the ladder structure.
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP INC
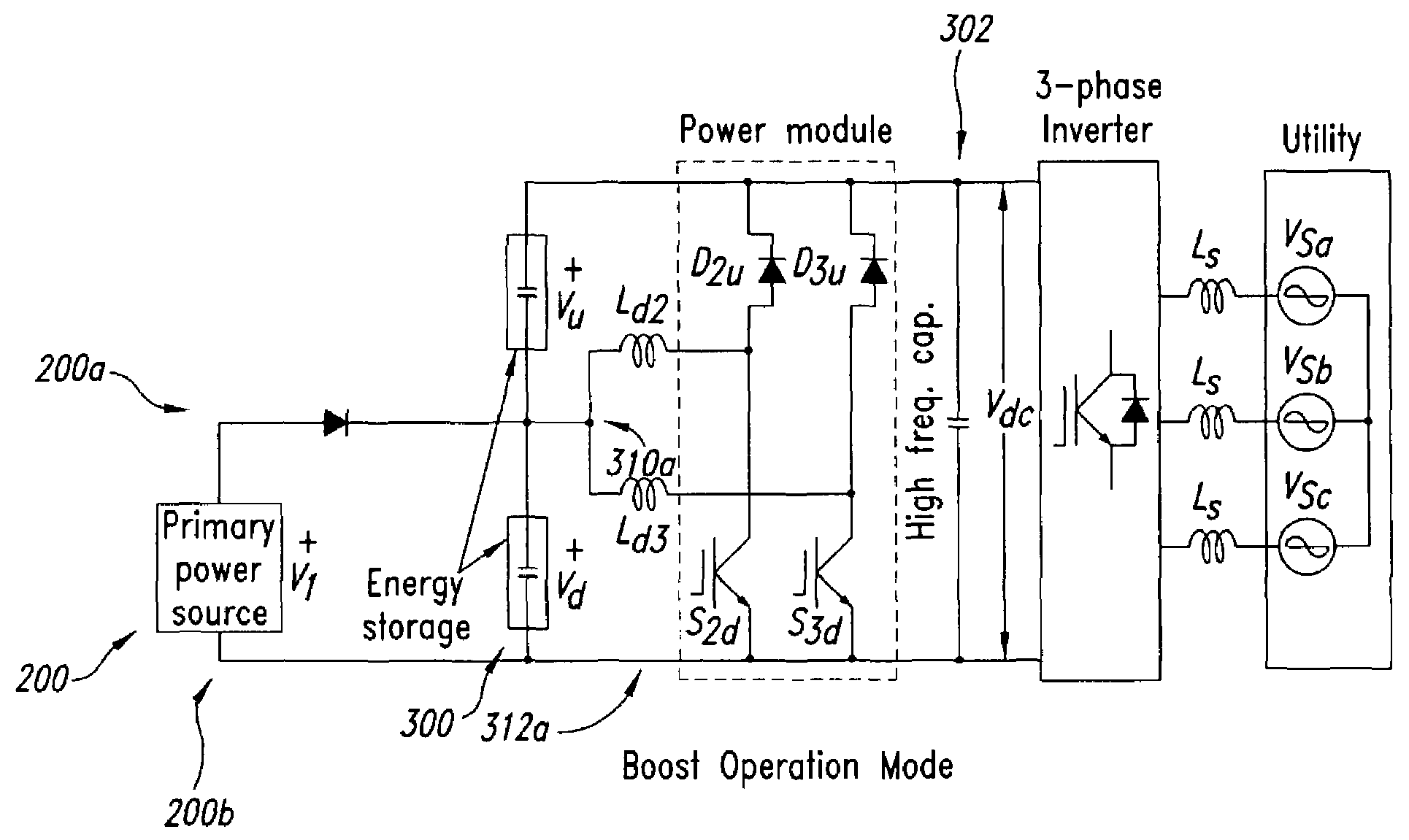
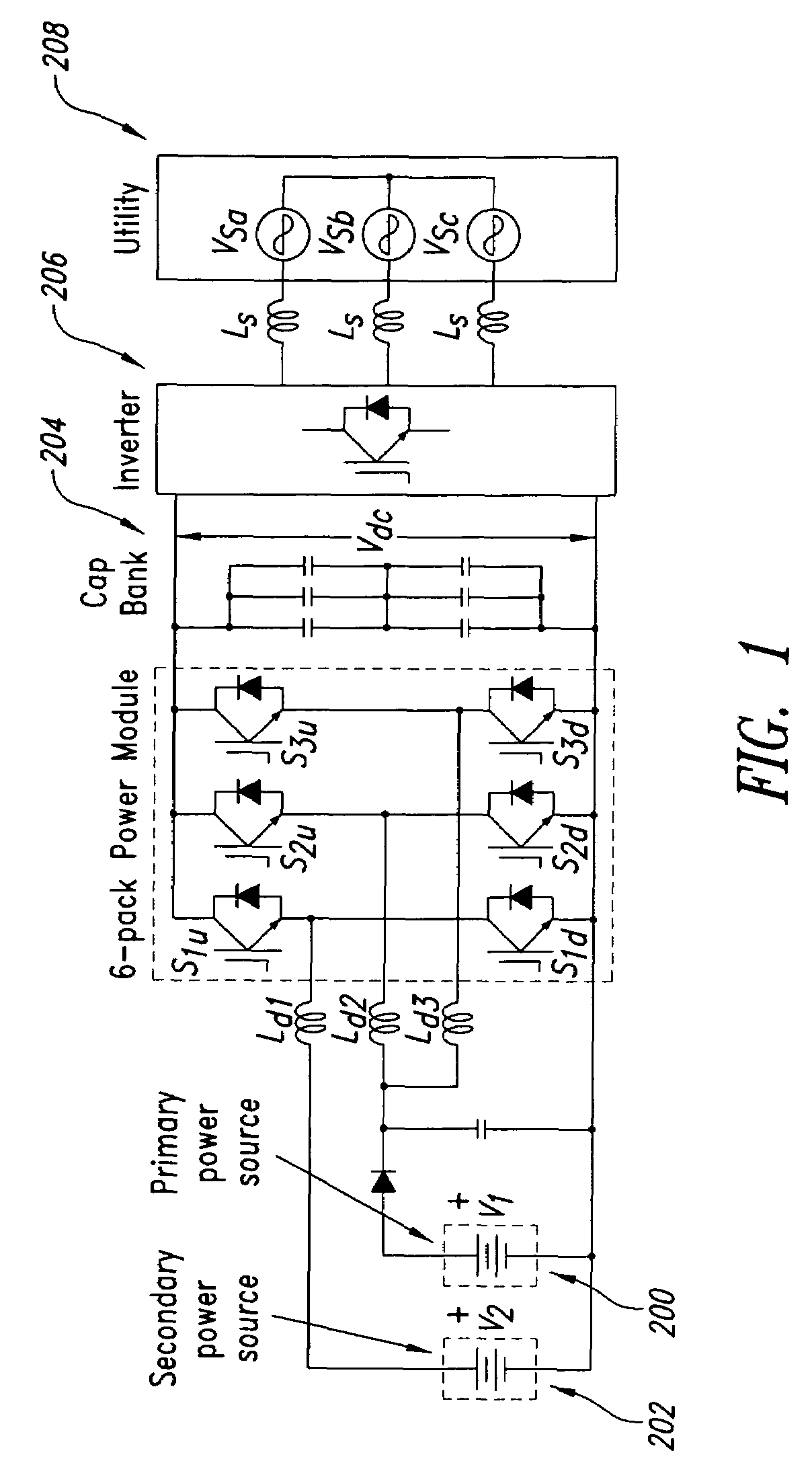
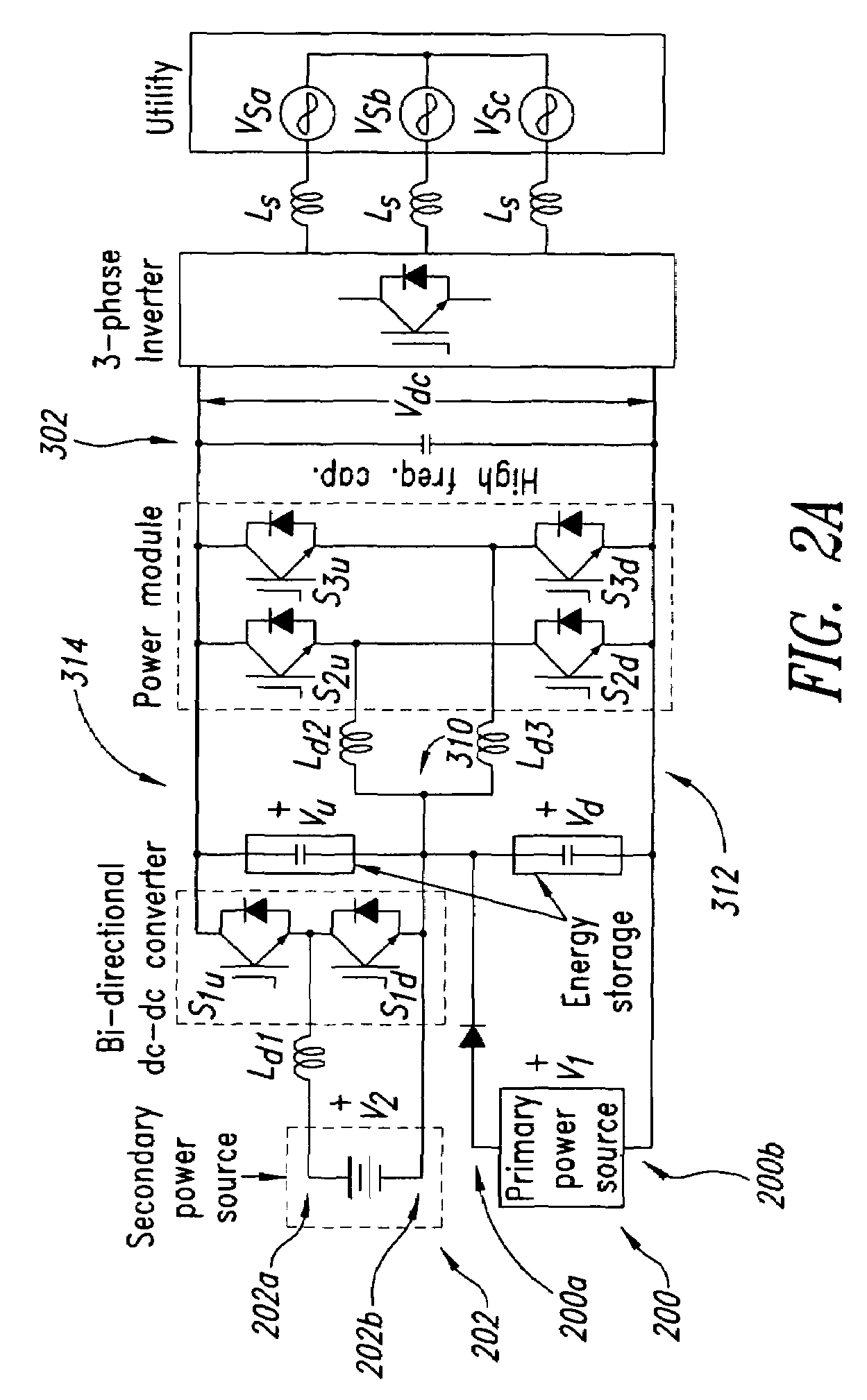
Topologies for multiple energy sources
A system and method for converting power are disclosed. Briefly described, one embodiment comprises a first power source having a first-source positive terminal and a first-source negative terminal; a second power source having a second-source positive terminal and a second-source negative terminal; an output capacitor having an output-capacitor positive terminal operably coupled with the second-source positive terminal and an output-capacitor negative terminal operably coupled with the first-source negative terminal; a series electrical connection between the first-source positive terminal and the second-source negative terminal; a boost converter having a boost-converter input operably coupled with the series electrical connection and the first-source negative terminal, and a boost-converter output operably coupled with the output-capacitor positive and negative terminals; and a buck-boost converter having a buck-boost-converter input operably coupled with the series electrical connection and the second-source positive terminal, and a buck-boost-converter output operably coupled with the output-capacitor positive and negative terminals.
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP INC
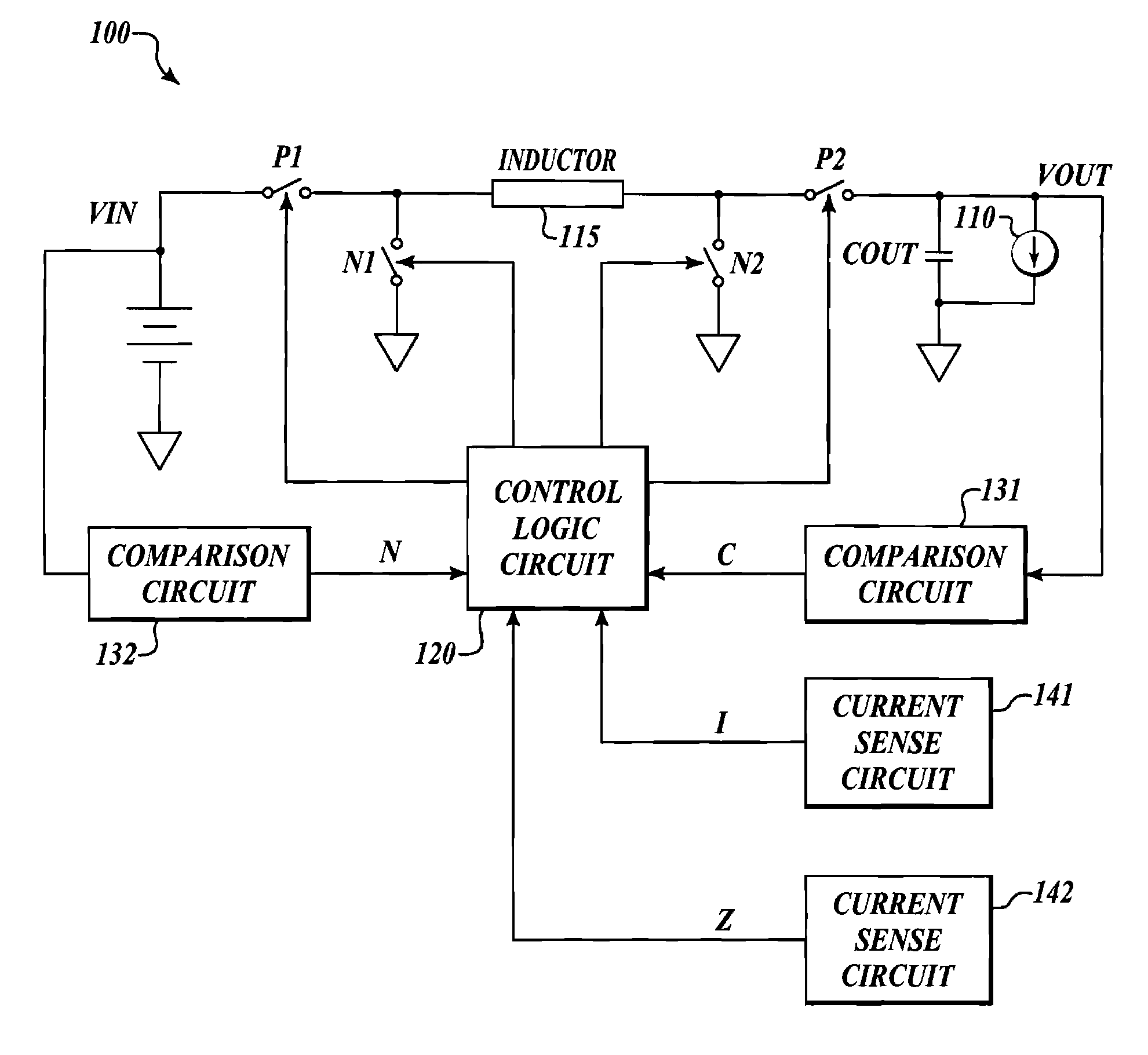
Short circuit and open circuit protection for a boost converter
ActiveUS20100123978A1Preventing a boost converter from short circuit and open circuit damagesInrush of the inductor current at start-up is reduced or eliminatedDc-dc conversionEmergency protective arrangements for limiting excess voltage/currentPower switchingShort circuit protection
A boost converter includes a load disconnect switch connected between a voltage input terminal and an inductor, a power switch connected to the inductor by a switching node, a diode connected between the switching node and a voltage output terminal, and an output capacitor connected to the voltage output terminal to provide an output voltage. A protection apparatus is connected to the load disconnect switch, switching node and power switch to monitor the voltage at the switching node and the output voltage to provide open circuit and short circuit protection for the boost converter.
Owner:RICHTEK TECH
Constant ON-time controller for a buck converter
ActiveUS7019504B2Reduce Noise SensitivityDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationElectrical resistance and conductanceTransverter
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
Switching power supply
InactiveUS20090027925A1High voltageImprove efficiencyEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionEngineeringCapacitor
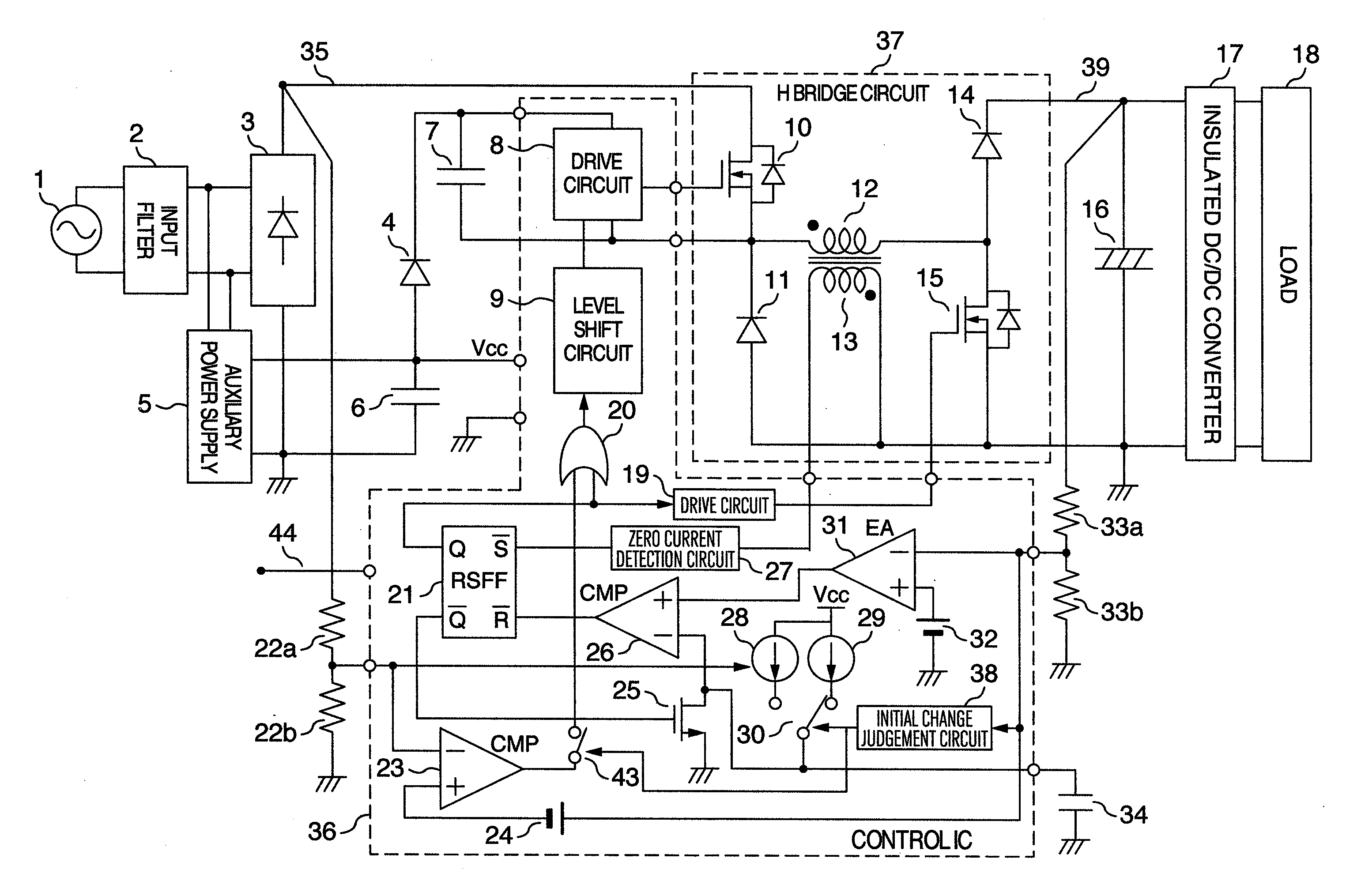
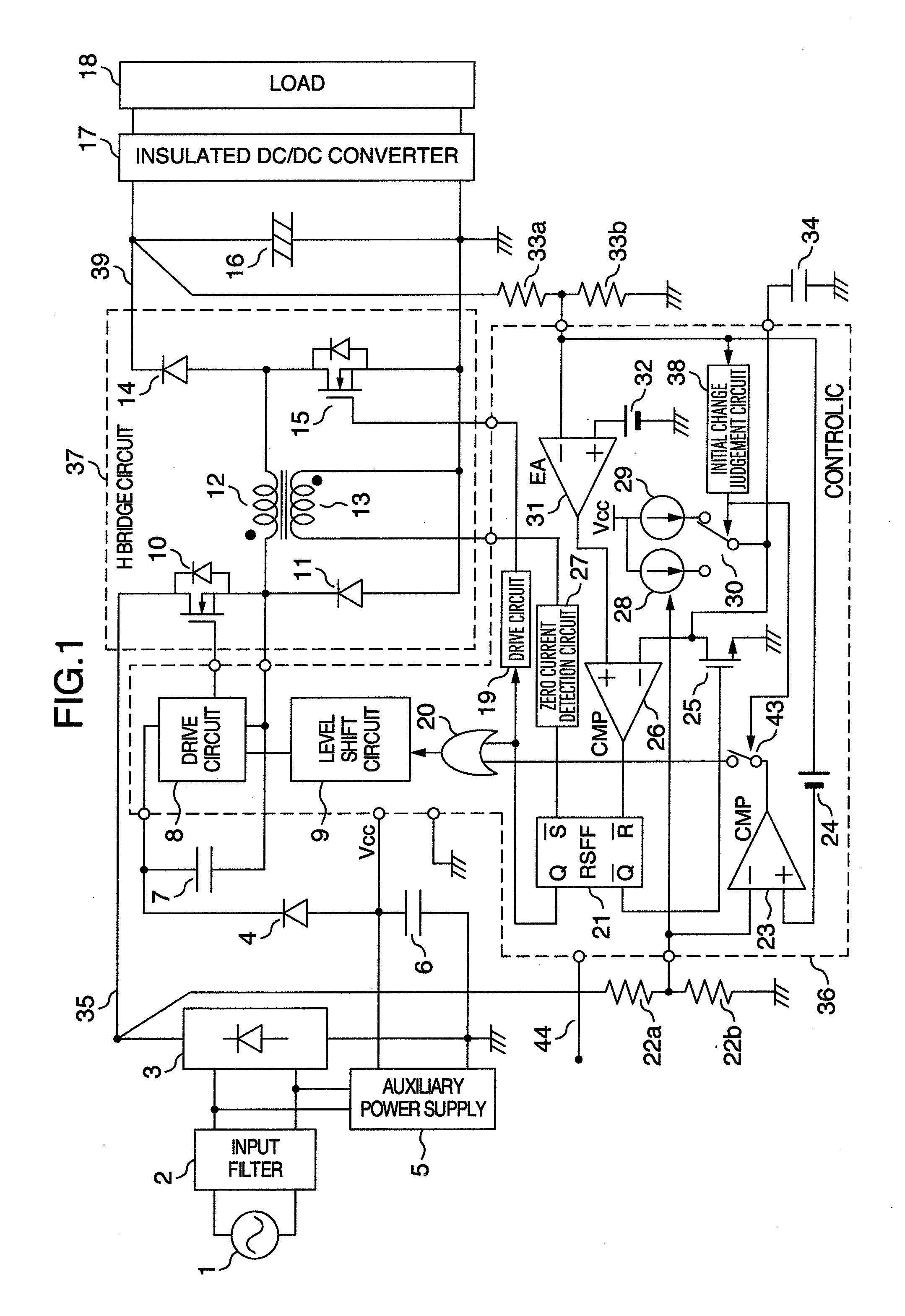
A buck-boost converter of an H bridge type having a function for initially charging a smoothing output capacitor without a relay and a rush current preventing resistance. A compact and flat power supply is attained by employing a current critical mode H bridge system for a PFC converter and providing a function of initially charging a smoothing output capacitor to a converter circuit.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Power factor correction rectifier that operates efficiently over a range of input voltage conditions
ActiveUS20090303762A1Ac-dc conversion without reversalEfficient power electronics conversionBuck converterCapacitor
A PFC rectifier comprises a first converter having a first output capacitor and a second converter having a second output capacitor. The he first and second capacitors are coupled to each other to increase the output voltage of the PFC rectifier. Fore example the first or second output capacitors can be serially coupled to each other. At least one or both of the first or second converters comprise buck or buck-boost converters, including inverting or non-inverter buck converters. The first and second converters can also form a bi-directional ac-ac inverter.
Owner:DELTA ELECTRONICS INC
Multislice DC-DC converter
InactiveUS20030090244A1Energy efficient ICTEfficient power electronics conversionCapacitanceDead time
A novel monolithic step-down dc-dc buck converter that uses two or more ("n") parallel slices to achieve a high output current with a small filter capacitor is provided. Each of the n slices may be operated with a phase difference of 360° / n. Each of the converter slices may be based on a synchronous rectifier topology to avoid the excessive power losses introduced by the diode component of conventional step-down buck converters. Hysteretic control may be used (with or without pulse-width modulation and pulse-frequency modulation) to provide an internal gate-drive waveform without the need to provide a dedicated clock signal or oscillator circuit. The hysteretic control is further refined using digital control techniques to enforce a brief dead time between the activation of each slice such that undesirable circulating currents are prevented. A significant advantage of the proposed multi-slice step-down dc-dc buck converter and its associated control is that the semiconductor switches, filter inductors and capacitor, and the control circuit may be fabricated as part of a single monolithic integrated circuit.
Owner:SHAKTI SYST
Circuit of high efficient buck-boost switching regulator and control method thereof
ActiveUS20120146594A1Improve efficiencyDc-dc conversionAc network voltage adjustmentSwitching frequencyEngineering
Owner:DIALOG SEMICONDUCTOR GMBH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com