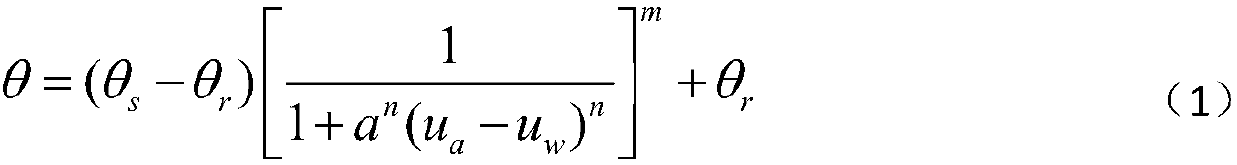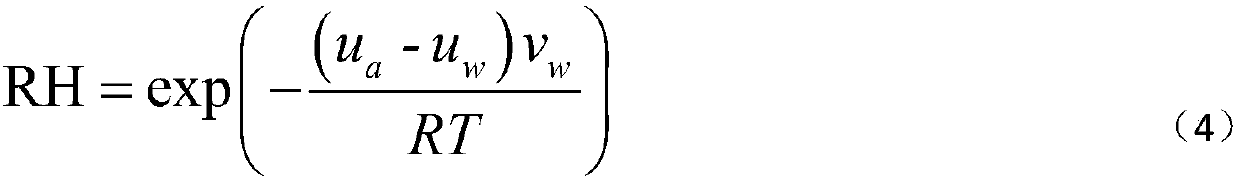Derivation Method of Equivalent Pore Size of Pores Between Clay Particles
A technology of pore radius and particle, applied in the field of practical application of geotechnical engineering, can solve the problem of not given quantitative method, limitation and so on
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0059] A method for deriving the equivalent pore size of pores between clay particles, specifically according to the following steps:
[0060] step 1,
[0061] Firstly, clay-containing soil samples were prepared for soil-water characteristic test, and a complete soil-water characteristic curve was obtained by fitting the formula (1) through MATLAB, expressed in terms of mass water content. The fitting formula is as follows:
[0062]
[0063] In the formula: θ is mass water content;
[0064] u a -u w is the matrix suction;
[0065] θ r is the residual moisture content;
[0066] θ s is the saturation moisture content;
[0067] a, m and n are fitting parameters. The parameter n is related to the soil pore size distribution, and the parameter m is related to the overall symmetry of the soil-water characteristic curve.
[0068] The pore structure of soil determines the vapor pressure in equilibrium. The Kelvin (Kelvin) formula, on the premise of not violating the orig...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com