In-vivo implanted ossiphone vibrating device
A vibration device and implant technology, applied in the field of medical equipment, can solve the problems of large vibration contact area of vibrating plate or vibrating plate, low vibration frequency of vibrating plate or vibrating plate, unsuitable for high-frequency vibration, etc., and achieve useful work output Large, high vibration efficiency, large amplitude effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
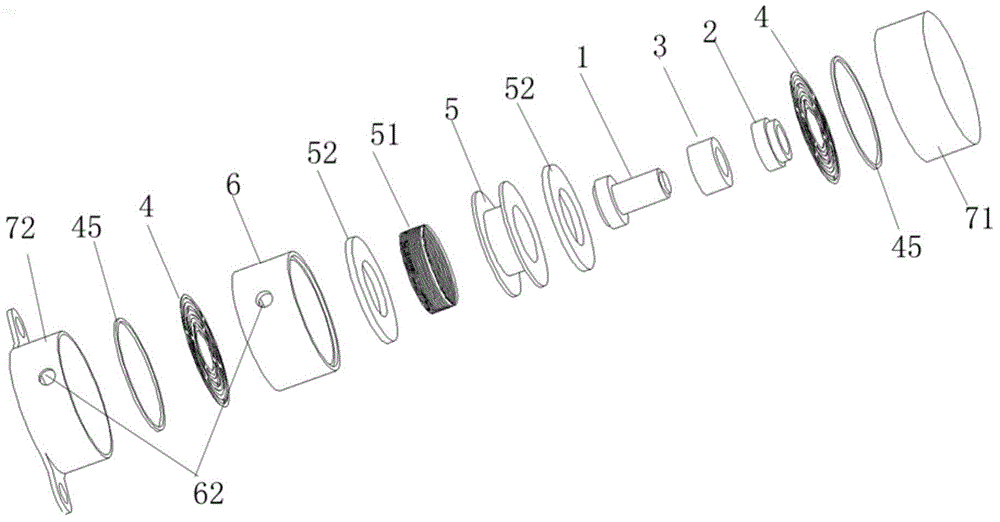
[0062] Please refer to figure 1 , figure 1 It is a schematic diagram of the explosive structure of a bone conduction hearing aid vibration device implanted in the body of the present invention. A bone conduction hearing aid vibration device implanted in the body, the vibration device includes a first vibrator 1, a second vibrator 2, a reed 4, a reed pressure plate 45, a magnetic conductive sheet 52, a coil frame 5, a coil 51, a magnet 3, Fixed frame 6, shell 7.
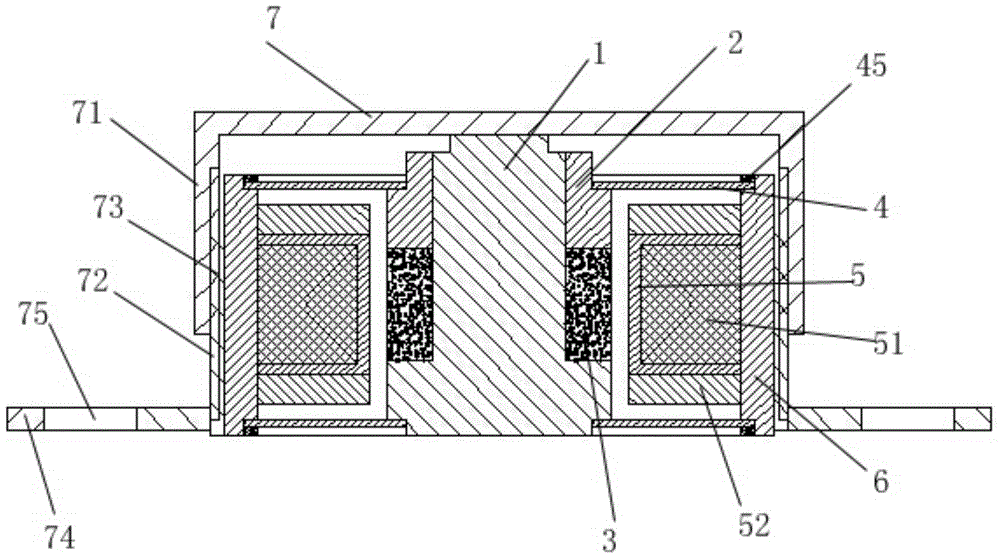
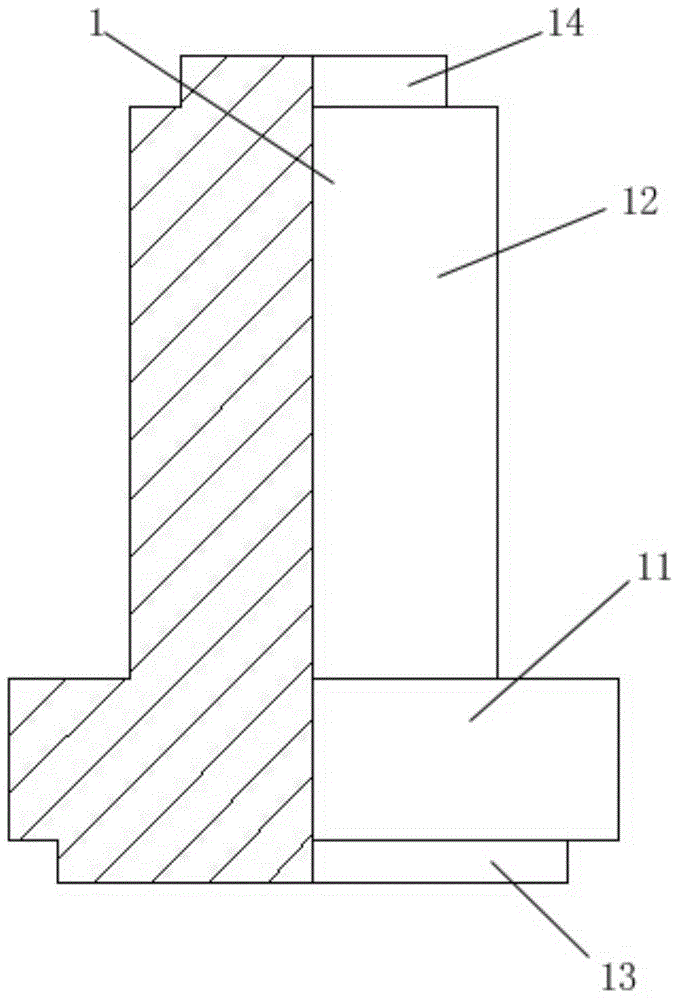
[0063] Please refer to figure 2 , figure 2 It is a schematic diagram of the assembly of a bone conduction hearing aid vibration device implanted in the body of the present invention. The first vibrator 1 has a stepped structure, and the first vibrator 1 includes a bottom cylinder 13, a first boss 11, a second boss 12, and a top cylinder 14; the bottom cylinder 13, the first boss The platform 11, the second boss 12, and the top cylinder 14 are integrally formed at one time; the bottom cylinder 13, the first boss...
Embodiment 2
[0076] Please refer to Figure 7 , Figure 7 It is an assembly schematic diagram of another implanted bone conduction hearing aid vibration device of the present invention. This embodiment is basically the same as Embodiment 1, except that the end face of the fixing plate 74 is flush with the end face of the lower cover 72. Compared with Embodiment 1, this embodiment is easy to operate during installation.
Embodiment 3
[0078] Please refer to Figure 8 , Figure 8 It is a schematic diagram of the explosive structure of another implanted bone conduction hearing aid vibration device of the present invention. A bone conduction hearing aid vibration device implanted in the body, the vibration device includes a first vibrator 1, a second vibrator 2, a reed 4, a reed pressure plate 45, a magnetic conductive sheet 52, a coil frame 5, a coil 51, a magnet 3, Fixed frame 6, shell 7;
[0079] Please refer to Figure 9 , Figure 9It is an assembly schematic diagram of another implanted bone conduction hearing aid vibration device of the present invention. The first vibrator 1 is assembled on the upper end surface of the magnet 3; the outer periphery of the magnet 3 is provided with a coil bobbin 5; the coil bobbin 5 is wound with a coil 51; the two ends of the coil bobbin 5 are provided with magnetic conductive sheets 52; The magnetically conductive sheet 52 is a stepped structure, and the end face ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com