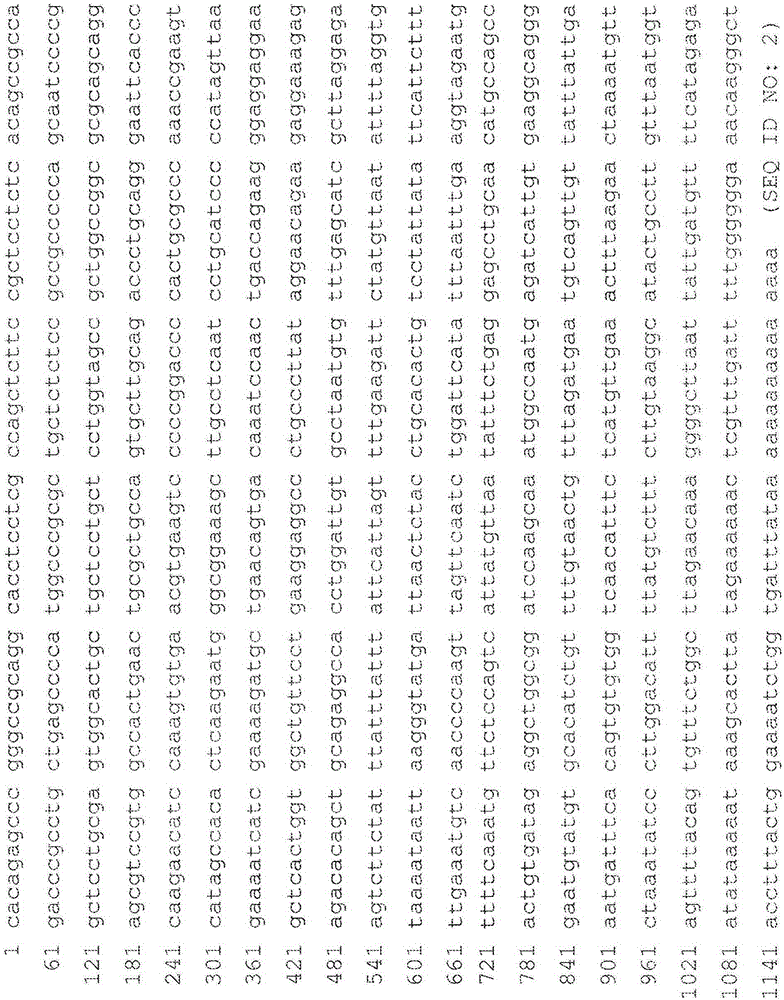
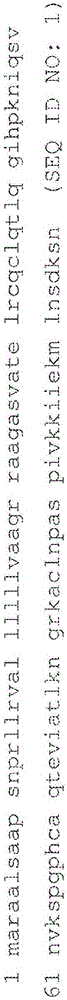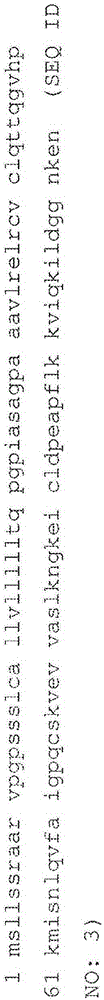Anti-TNF and anti-IL17 combination therapy biomarkers for inflammatory disease
A combined therapy and technology for inflammatory diseases, applied in allergic diseases, biological tests, bone diseases, etc., can solve the problem that the treatment plan is not completely effective
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0164] Example 1 - Efficacy of Anti-TNF and Anti-IL17 Alone and Combined in a Mouse Collagen-Induced Arthritis Model
[0165] In this example, the efficacy of anti-TNF or anti-IL17 or a combination thereof was evaluated in a collagen-induced arthritis model in mice, and the results are shown in image 3middle. Male DBA / 1J mice were injected i.d. at the base of the tail with 100 μl of an emulsion containing 100 μg type II bovine collagen dissolved in 0.1 N acetic acid and 100 μl of complete Freund's adjuvant containing 100 μg Mycobacterium Tuberculois H37Ra. Mice were boosted i.p. with 1.0 mg zymosanA in 200 μL phosphate buffered saline (PBS) 21 days later. Disease onset occurred within 3 days of the boost. Mice were monitored for arthritis daily for the first week and three times weekly thereafter. Each paw was scored by the following criteria: 0=normal; 1=swelling at one site (foot or ankle); 2=swollen foot and ankle; 3=stiffness of the joint. Scores were summed for all f...
Embodiment 2
[0166] Example 2: Comparison of bone protection of anti-TNF and anti-IL17 alone and in combination in a mouse collagen-induced arthritis model
[0167] In this example, the higher efficacy of combined blockade of TNF and IL17 to prevent bone loss was demonstrated and shown in Figure 4 middle. Arthritis was induced in DBS / 1J mice as described in Example 1. At the end of the study, three weeks after the onset of arthritic signs, the level of bone loss was assessed. The protective efficacy against bone loss is measured in animals that have received the therapeutic treatment regimen. Hind paws were removed in the middle of the tibia / fibula and stored in 10% neutral buffered formalin. The paw was imaged using a Scanco μCT40 (ScancoMedical AG) at 55 kVp and 145 μA using high-resolution settings (1000 projections / 180° at 2048 × 2048 pixel reconstruction) and Isotropic Voxels with an integration time of 180 μs to obtain a 18 μm × 18 μm × 18 μm Final isotropic voxel size. A cylin...
Embodiment 3
[0168] Example 3: Interaction of TNF and IL-17 in CIA and RA
[0169] In this example, gene expression profiling was used as a tool to study biomarkers reflecting the synergy of anti-TNF and anti-IL17 treatments. In this case, the 8C11 antibody was used as the anti-TNF treatment, and the rat anti-mouse anti-IL17 antibody MAB421 was used as the anti-IL17 treatment unless otherwise indicated. Using methods known in the art, characterize responses to disease-associated RNAs and identify cohorts that are sensitive to combined anti-TNF and anti-IL17 therapy but significantly less sensitive to anti-TNF or anti-IL17 monotherapy. CXCL1 and CXCL5 were identified as biomarkers because they are stable over time in readily available biological fluids that require minimal preparation or manipulation in the clinical setting. Using the collagen-induced arthritis (CIA) model in mice, measurements of CXCL1 and CXCL5 biomarkers in whole paw homogenates indicated that changes in RNA levels are ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com