Manufacturing method of metal circuit micro-structures
A metal circuit and microstructure technology, which is applied in the input/output process of data processing, instruments, electrical digital data processing, etc., can solve the problems of increasing the cost of manufacturing metal circuits, difficult accuracy control, and increasing process difficulty and cost. Achieve the effect of improving light transmittance and invisible rate, easier control of fineness, and improving product yield
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0044] Some typical embodiments embodying the features and advantages of the present application will be described in detail in the description in the following paragraphs. It should be understood that the present case can be varied in various ways without departing from the scope of the present case, and that the description and drawings therein are illustrative in nature and not intended to limit the present case.
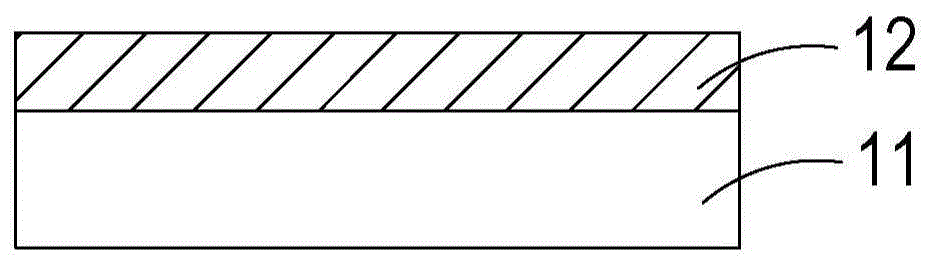
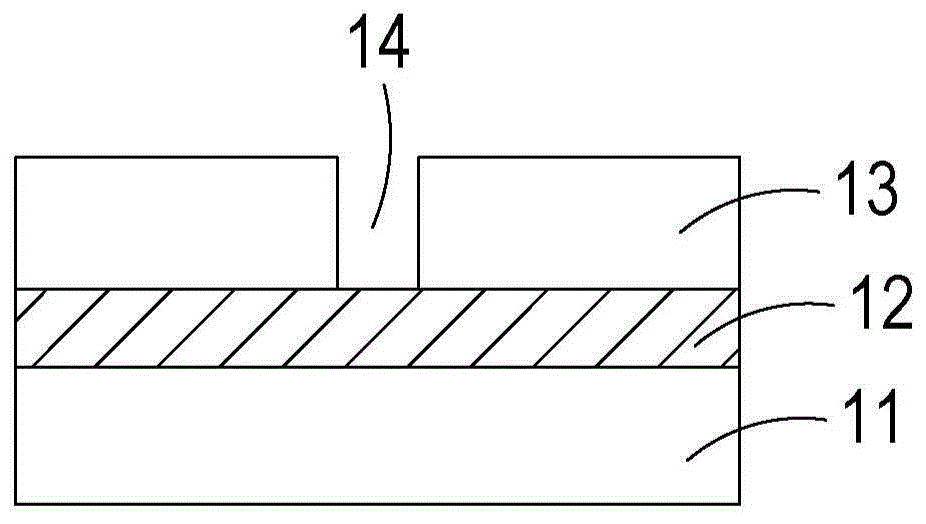
[0045] Figure 1A to Figure 1E A schematic diagram showing the structural flow of the metal circuit microstructure manufacturing method of the first preferred embodiment of the present case; and figure 2 It is a flow chart of the steps of the metal circuit microstructure manufacturing method in the first preferred embodiment of the present application. The metal circuit microstructure method of this case comprises the following steps, at first, as Figure 1A and figure 2 As shown, in step S20 , a substrate 11 is provided, wherein the substrate 11 is a transpare...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com