Method and apparatus for predicate evaluation on compressed variable-length character strings
A predicate evaluation and string technology, which is applied in electrical digital data processing, instruments, calculations, etc., can solve the problems of not making good use of performance advantages, not supporting predicate evaluation, etc., and achieve the effect of enhancing usability and performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
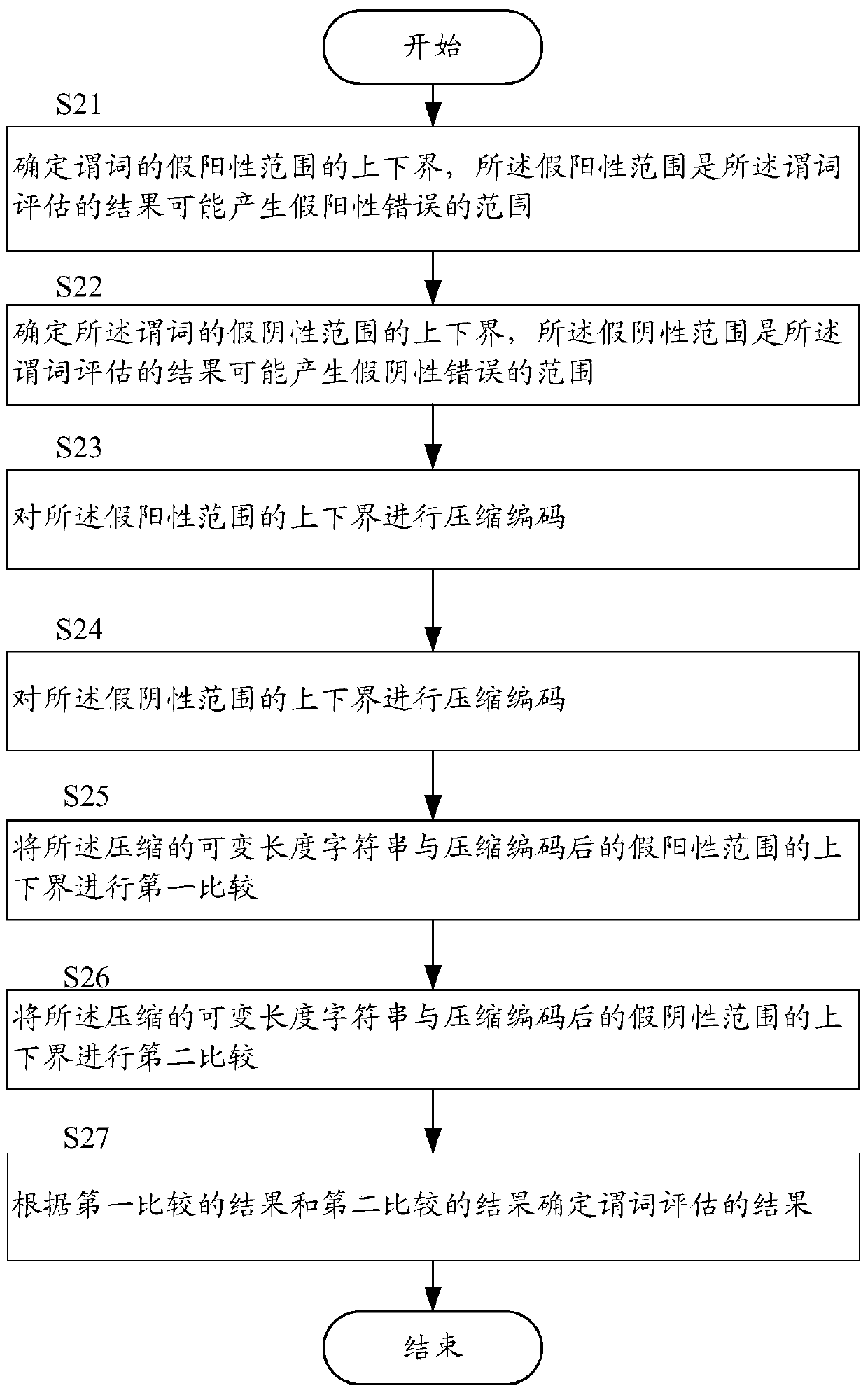
[0025] The following will refer to figure 2 A method of predicate evaluation on compressed variable-length character strings according to a first embodiment of the present invention is described. In this embodiment, the compressed variable-length character string is compressed using a compression encoding method that makes the sequence of the compressed encoded data consistent with the order under the tail space sensitive semantics, and is performed under the tail space insensitive semantics. The predicate evaluation described is illustrated as an example.
[0026] First, the basic idea of this embodiment and the technical terms involved are briefly described.
[0027] Although as mentioned above, variable-length strings have different orderings under trailing whitespace-insensitive semantics and trailing whitespace-sensitive semantics, so it is difficult to find an appropriate compression encoding that preserves order for both semantics way, but actually most variable-le...
no. 2 example
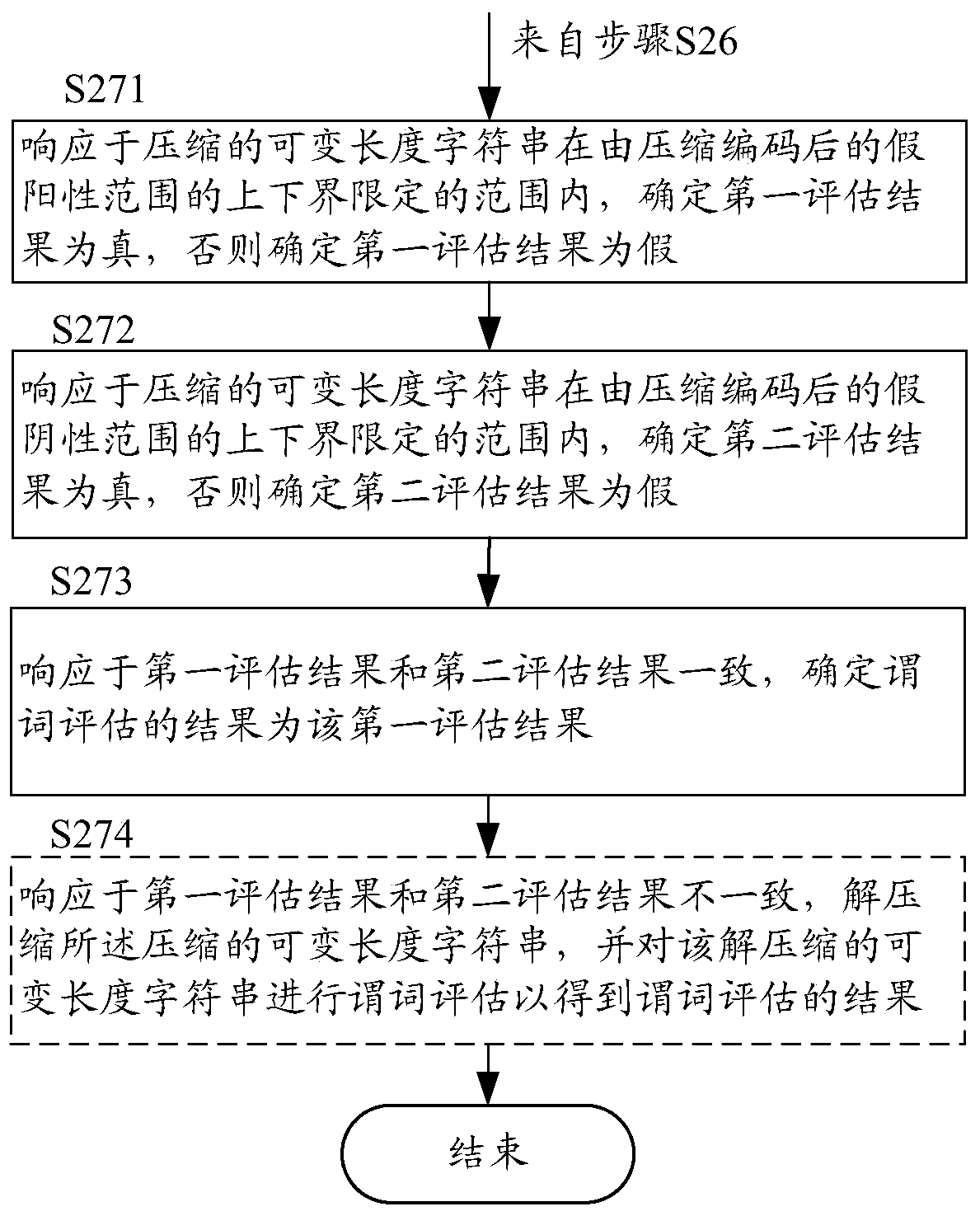
[0076] In the method for predicate evaluation on compressed variable-length strings according to the first embodiment, for a variable-length string predicate, its false positive range and false negative range are respectively determined, and then according to the compressed variable Whether the length string falls within the compressed encoding's false-positive and false-negative ranges determines the result of the predicate evaluation. However, in fact, in many cases, it is not necessary to determine the false negative range and then determine whether the compressed variable-length character string falls within the false negative range of the compression encoding (ie steps S21, S24 and processing in S26). Hereinafter, an example will be described.
[0077] For example, according to the above description, it can be seen that the range of false positives is greater than or equal to the range of false negatives, so if the variable-length string of compressed encoding does not f...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com