Artificial source tensor electromagnetic exploration method with far references
A remote reference and artificial source technology, applied in the field of electromagnetic detection, can solve problems such as unusable, data information loss, and low signal-to-noise ratio
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0115] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and specific embodiments.
[0116] The prospecting method that the present invention relates to comprises the following steps:
[0117] Step 1. Observation design: Determine the observation target and depth range, determine the observation frequency range according to the actual exploration depth requirements and the background conductivity of the survey area, and determine the observation time length and signal sampling rate of the measurement point according to the required observation frequency; Design survey lines and survey points for targets and survey areas;
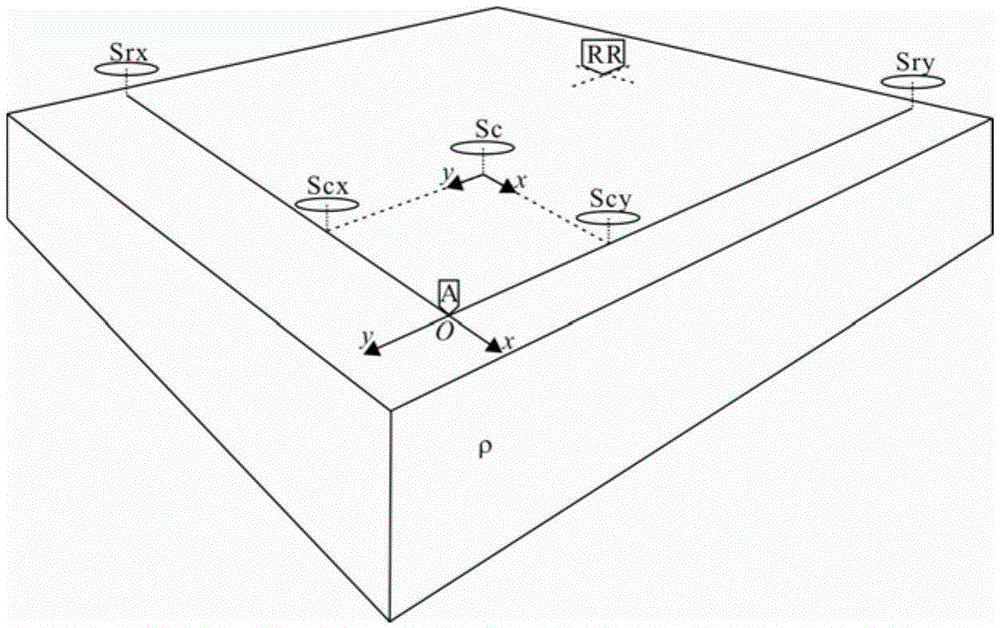
[0118] Step 2, device layout: such as figure 1 As shown, the artificial field source Sc and the measuring point A are arranged in the survey area, and the far reference point RR is arranged in a low-noise area far enough from the survey area; Similarly, with a grounded horizontal electric dipole or an ungr...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com