Method for forming gate oxide layers with different thicknesses in gate last process
A technology of gate oxide layer and gate-last process, applied in the direction of semiconductor devices, etc., can solve the problems of removal, loss of dielectric layer 13, loss of IO gate oxide layer 11, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
[0060] refer to Figure 8 In the first embodiment, the method for forming gate oxide layers with different thicknesses in the gate-last process includes the following steps:
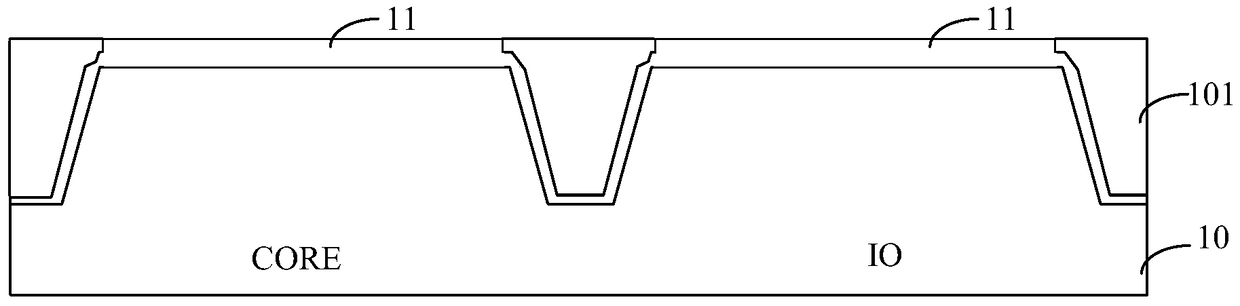
[0061] Step S21, providing a semiconductor substrate, the semiconductor substrate includes a core device region and an IO device region, and the semiconductor substrate of the core device region and the IO device region is covered with an oxide layer;
[0062] Step S22, forming a dielectric layer covering the semiconductor substrate and the oxide layer, the dielectric layer has gate openings in the core device region and the IO device region respectively, and the oxide layer is exposed at the bottom of the gate openings;
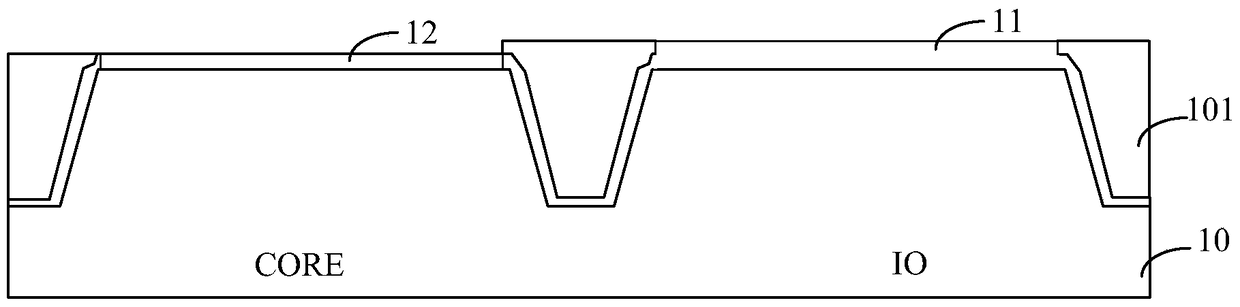
[0063] Step S23, sequentially forming a high-K material layer and a cap layer, the high-K material layer covers the surface of the dielectric layer, the bottom and sidewalls of the gate opening, and the cap layer covers the high-K material layer;
[0064] Step S24, injecting an oxygen...
no. 2 example
[0080] refer to Figure 16 In the second embodiment, the method for forming gate oxide layers with different thicknesses in the gate-last process includes the following steps:
[0081] Step S31, providing a semiconductor substrate, the semiconductor substrate includes a core device region and an IO device region, and the semiconductor substrate of the core device region and the IO device region is covered with an oxide layer;
[0082] Step S32, forming a dielectric layer covering the semiconductor substrate and the oxide layer, the dielectric layer has gate openings in the core device region and the IO device region respectively, and the oxide layer is exposed at the bottom of the gate openings;
[0083] Step S33, sequentially forming a high-K material layer and a cap layer, the high-K material layer covering the surface of the dielectric layer, the bottom and sidewalls of the gate opening, and the cap layer covering the high-K material layer;
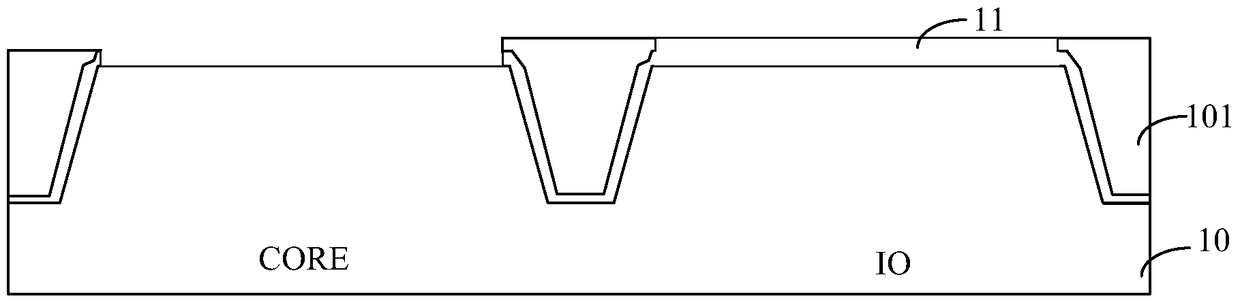
[0084] Step S34, removing the ...
no. 3 example
[0097] In the third embodiment, the step of injecting an oxygen scavenger in the core device region in the first embodiment and the step of removing the cap layer in the IO device region in the second embodiment are combined, and the following still refers to Figure 9 to Figure 15 Describe in detail.
[0098] First, it is possible to provide Figure 13 The structure shown, its formation process can be, for example, Figure 9 to Figure 12 process shown.
[0099] After that, refer to Figure 14 , implant an oxygen scavenger in the core device region, and the oxygen scavenger may be one of Ti ions, Hf ions, Al ions or any combination thereof.
[0100] Afterwards, the photoresist layer 27 is removed, and a new photoresist layer is formed. Patterning the new photoresist layer, removing the photoresist layer in the IO device area; using the patterned photoresist layer as a mask to etch the cap layer 26, removing the cap layer in the IO device area 26; the photoresist layer can...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com