Method and system for establishing RAID in SSD
A disk and physical page technology, which is applied in the field of RAID formation inside SSD disks, can solve problems such as increased disk write amplification, increased DRAM resources, and reduced efficiency, achieving reduced impact on random performance, reduced DRAM resources, and improved efficiency Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
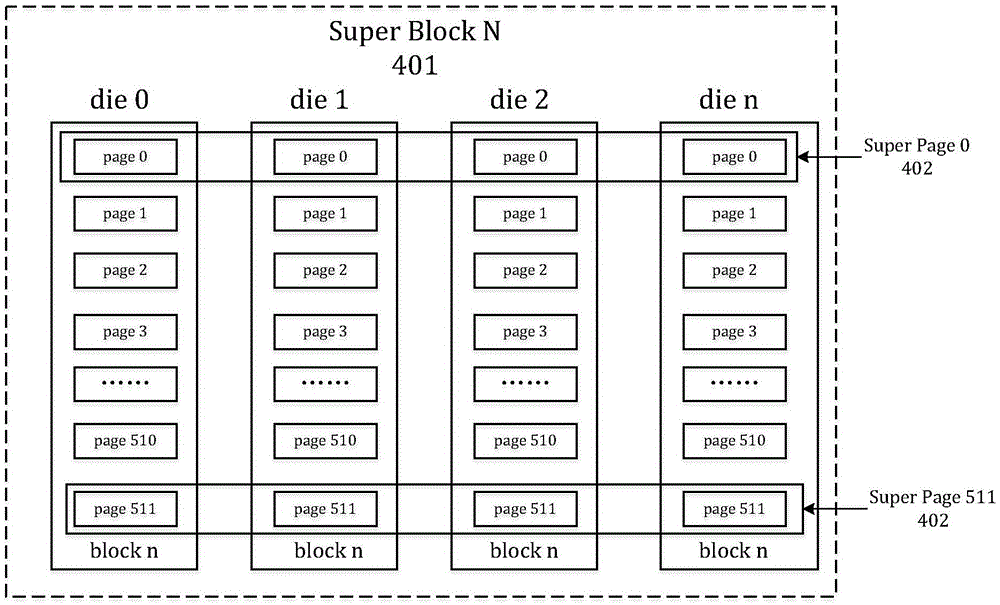
[0044] This embodiment adopts the RAID5 stripe under the situation that there are few physical pages (10 physical pages) and no bad pages in SuperPage, and the specific implementation steps are as follows:
[0045] 1) After obtaining a blank SuperBlock, select a physical block to store the RAID verification data, and record the Die number of the physical block (Die0 in this example) in the block status table of the SuperBlock;
[0046] 2) When the disk executes the write command of the host, the received data is stored in the user data buffer, and the user data buffer is divided according to the NAND Flash physical page size. When the amount of user data received by a buffer reaches the physical page After the maximum amount of user data that can be stored (the physical page size minus the amount of error correction data required for user data), the data in this buffer will be written to Die1 of SuperPage0;
[0047] 3) Add user data buffer buffer0 to the buffer list of the RAI...
Embodiment 2
[0053] This embodiment adopts the RAID5 stripe under the situation that there are few physical pages (10 physical pages) and one bad page in SuperPage, and the specific implementation steps are as follows:
[0054] 1) After obtaining a blank SuperBlock, select a physical block to store the RAID verification data, and record the Die number of the physical block (Die0 in this example) in the block status table of the SuperBlock;
[0055] 2) When the disk executes the host's write command, it stores the received data in the user data buffer divided by the size of the physical page. When the amount of user data received by a buffer reaches the maximum value that can be stored in the physical page After the amount of user data (physical page size minus the amount of error correction data required for user data), the data in the user data buffer will be written to Die1 of SuperPage0;
[0056] 3) Add the user data buffer buffer0 to the buffer list of the RAID calculation task, and judg...
Embodiment 3
[0061] This embodiment adopts the RAID6 stripe adopted in SuperPage in order to improve the reliability of certain data (such as mapping tables), and the specific implementation steps are as follows:
[0062] 1) After obtaining the blank SuperBlock, select two physical blocks to store the RAID verification data, and record the Die numbers of the physical blocks (Die0 and Die1 in this example) in the block status table of the SuperBlock;
[0063] 2) When the disk executes the write command of the host, the received data is stored in the user data buffer, and the user data buffer is divided according to the NAND Flash physical page size. When the amount of user data received by a buffer reaches the physical page After the maximum amount of user data that can be stored (the physical page size minus the amount of error correction data required for user data), the data in the user data buffer will be written to Die2 of SuperPage0;
[0064] 3) Add the user data buffer buffer0 to the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com