Robot path planning method and system based on improved artificial potential field method
An artificial potential field method and path planning technology, applied to control/regulation systems, instruments, motor vehicles, etc., can solve problems such as poor versatility, poor environmental adaptability, and inability to solve static potential field problems
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0109] The robot path planning method based on the improved artificial potential field method provided in this embodiment,
[0110] This embodiment provides a robot path planning method based on the improved artificial potential field method, comprising the following steps:
[0111] S1: Obtain the initial state parameters, environmental information and final target point of the robot;
[0112] S2: Obtain the current coordinate position and local target point of the robot;
[0113] S3: Establish the artificial potential field method based on the time virtual driving force to generate the reachable path between the current coordinate position of the robot and the local target point;
[0114] S4: Control the robot to travel along the reachable path;
[0115] S5: Detect whether the current coordinate position of the robot reaches the local target point within the visible range of the laser radar, if not, return to step S4 and continue to control the driving of the robot;
[011...
Embodiment 2
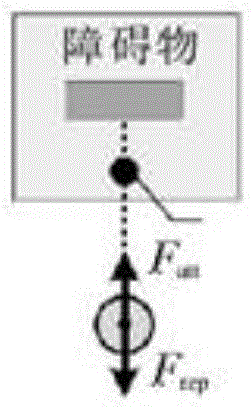
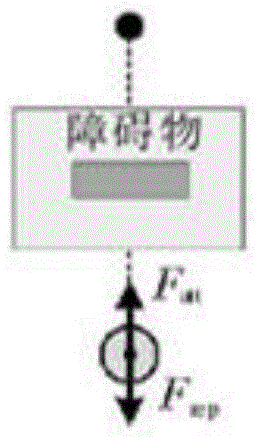
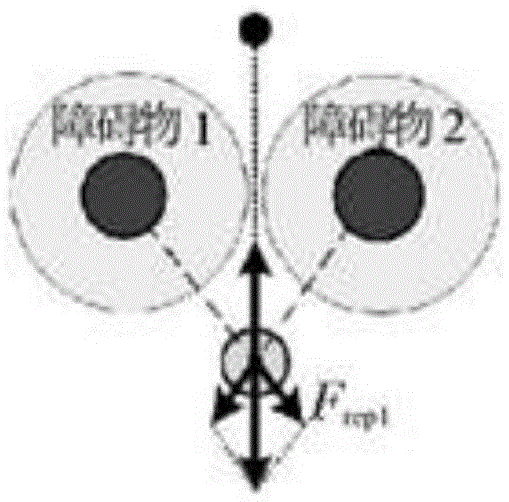
[0194] There are three scenarios in which local minimums will occur in robot path planning based on the artificial potential field method: Figure 1a -c is a schematic diagram of a local minimum scenario in robot path planning based on the artificial potential field method provided in this embodiment; Figure 1a The first common situation in which the robot provided by this embodiment falls into a local minimum (the target is between the obstacle and the robot); the box in the figure indicates the range of influence of the obstacle, the dot in the box indicates the target, and the circle outside the box for the robot; Figure 1b The second common situation in which the robot provided by this embodiment falls into a local minimum (obstacles are between the target and the robot); the box in the figure indicates the range of influence of the obstacle, the dot above the box indicates the target, and the circle outside the box for the robot; Figure 1c The third common situation in...
Embodiment 3
[0251] See flow chart Figure 4 , the technical solution in the embodiment of the present invention will be fully described below in conjunction with the flow chart.
[0252] Step 1: Take the robot's perspective at the starting point as the benchmark for the entire path planning, and establish a plane Cartesian coordinate system (the front of the robot's perspective is the y-axis, and the right-hand side is the x-axis).
[0253] Step 2: Use the inertial navigation system to obtain the initialization state S of the robot at the starting point 0 (including the Cartesian coordinates of the robot position (x 0 ,y 0 )=(0,0), the attitude angle θ of the current robot relative to the initial position 0 = 0° and the current robot speed v 0 =0).
[0254] Step 3: Use the single-line lidar sensor to obtain environmental information, including obstacle information in the environment. And set the Cartesian coordinates of the final target point in the robot control system (x g ,y g ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com