Therapeutic agent for ocular disease or prophylactic agent for ocular disease
A technology of therapeutic and preventive agents, applied in the field of therapeutic or preventive agents for eye diseases, which can solve problems such as induced edema and increased vascular permeability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
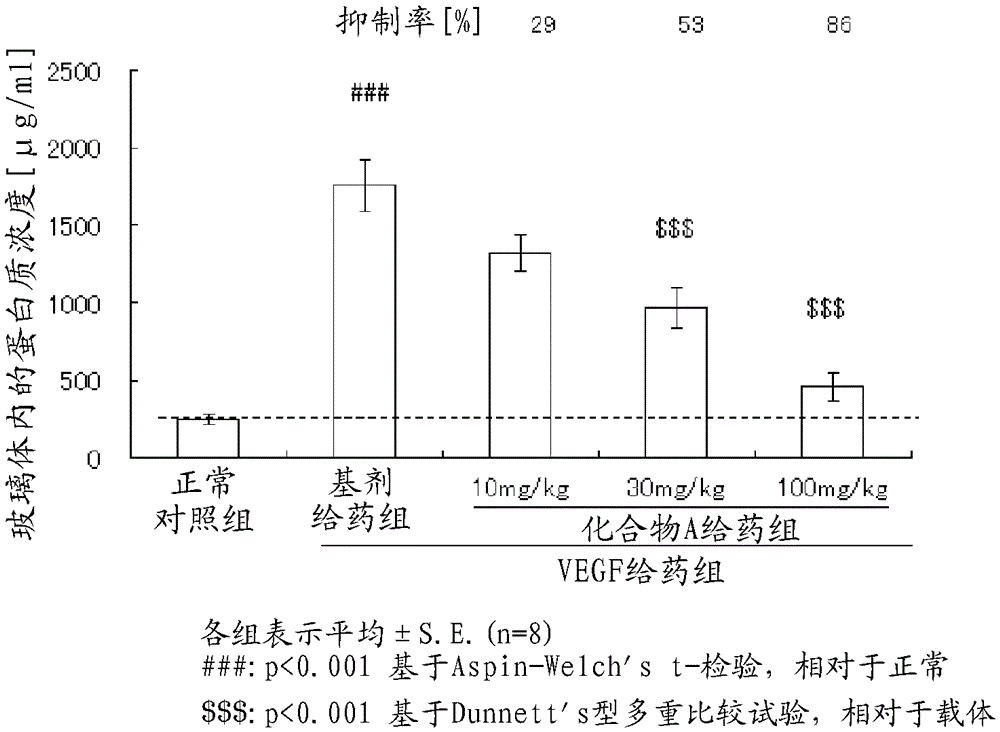
[0095] Experiment 1. Inhibition of retinal vascular permeability by oral administration of Compound A in a rat VEGF-induced retinal vascular permeability increase model
[0096] Using a rat model of increased retinal vascular permeability induced by VEGF, the effect of Compound A on inhibiting increased retinal vascular permeability was evaluated. The animal model was created based on Non-Patent Document 3 and the like with appropriate modifications.
[0097] As the experimental animals, 8-week-old male BrownNorway rats (Charles River Co., Ltd., Japan) were used.
[0098] Intravitreal injection of rat VEGF into both eyes of rats 164 (400ng / eye, R&D Systems Company) (VEGF administration group). D-PBS(-) (Sigma-Aldrich) was intravitreally injected into the vitreous of both eyes of rats in the normal control group. The number of cases in each group was 4 (8 eyes).
[0099] Compound A suspended in 1% (w / v) aqueous methylcellulose was administered at 10 mg / kg, 30 mg / kg or 100 m...
Embodiment 2
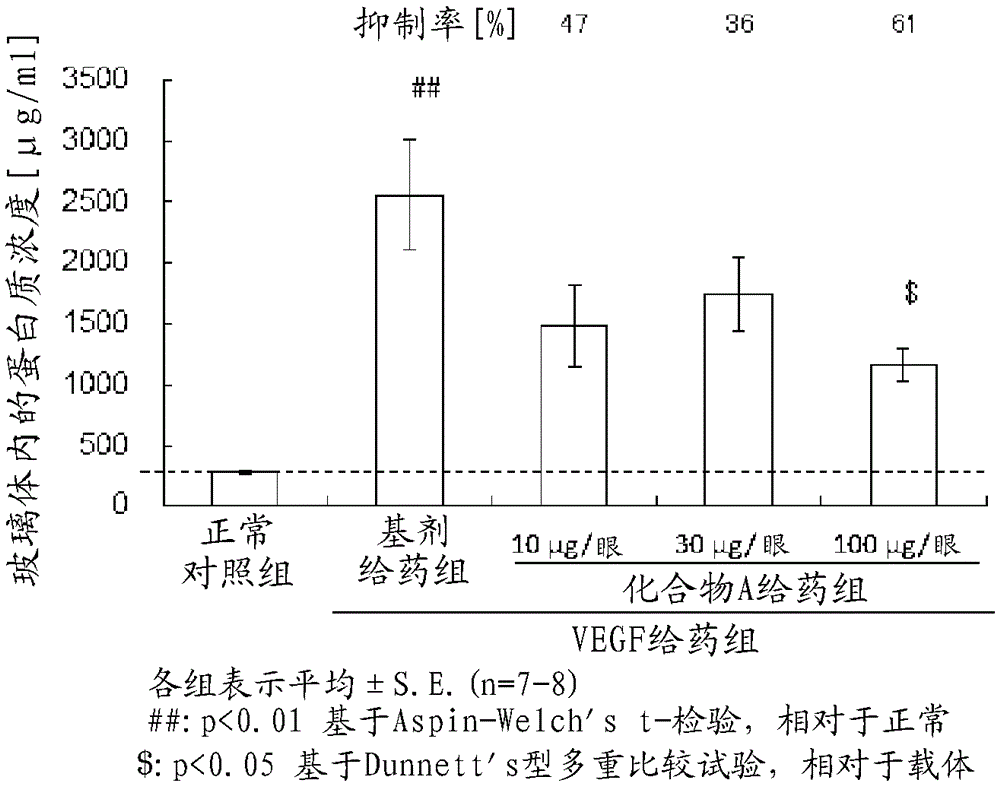
[0109] Experiment 2. Inhibition of retinal vascular permeability by intravitreal injection of Compound A in a rat VEGF-induced increased retinal vascular permeability model
[0110] As the experimental animals, 8-week-old male BrownNorway rats (Charles River Co., Ltd., Japan) were used.
[0111] Intravitreal injection of rat VEGF into both eyes of rats 164 (400ng / eye, R&D Systems Company) and a mixture of compound A (10 μg / eye, 30 μg / eye or 100 μg / eye) dissolved or suspended with a base (compound A administration group). Intravitreal injection of rat VEGF into both eyes of rats in the base-administered group 164 A mixture of bases in the same volume as the above-mentioned Compound A administration group. As the base, an aqueous base was used. D-PBS(-) (SIGMA) was injected into the vitreous body of both eyes of rats in the normal control group. The number of cases in each group was 4 (8 eyes).
[0112] Twenty-four hours after the intravitreal injection of VEGF, the rats we...
Embodiment 3
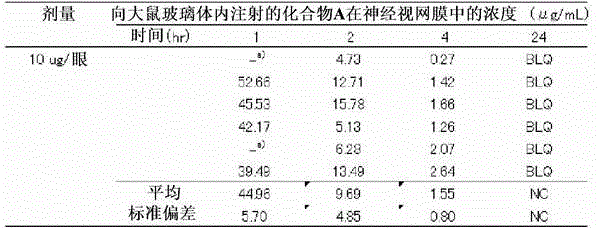
[0120] Experiment 3. Ocular Tissue Distribution and Systemic Exposure of Oral or Intravitreal Compound A
[0121] As the experimental animals, 8-week-old male Crl:CD (SD) rats (Charles River Co., Ltd., Japan) were used.
[0122] Compound A suspended in 1% (w / v) aqueous methylcellulose solution was orally administered to rats at 100 mg / kg. After 0.5, 1, 2, 4, 6 and 24 hours from oral administration, plasma and neural retina were collected, and liquid chromatography mass spectrometry (LC-MS) was used to determine the concentration of Compound A in plasma and neural retina. concentration was quantified.
[0123] Compound A dissolved or suspended in the base for injection at 10 μg / eye, respectively, was injected into the vitreous of both eyes of rats. After 1, 2, 4 and 24 hours from the intravitreal injection, neural retinas were harvested, and the concentration of Compound A in the neural retinas was quantified by LC-MS. The number of cases in each group was 2-3 animals (4-6 e...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com